Hidradenitis suppurative and covid 19 – Hidradenitis suppurative and COVID-19: a complex relationship is emerging as researchers explore potential links between these conditions. HS, a chronic inflammatory skin disorder, can significantly impact a person’s quality of life, and now, the COVID-19 pandemic presents another layer of potential complications. This exploration delves into the potential connections, examining inflammatory responses, potential treatment implications, and management considerations during a pandemic.
Understanding the interplay between these two conditions is crucial for developing better treatment strategies and patient care.
The intricate interplay between HS and COVID-19 is a fascinating area of research. While the exact nature of this connection remains unclear, early indications suggest potential shared inflammatory pathways. Understanding how COVID-19 might influence HS severity, and conversely, how HS might affect a COVID-19 patient’s response, is crucial. This overview aims to summarize the current understanding of this evolving area.
Introduction to Hidradenitis Suppurativa (HS)
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that primarily affects apocrine sweat glands. Characterized by painful, pus-filled lesions, HS can significantly impact a person’s quality of life due to its recurring nature and often debilitating symptoms. Understanding the various aspects of this condition, including its locations, symptoms, and potential severity, is crucial for effective management and support.
Common Locations of HS Lesions
The locations of HS lesions are often influenced by the distribution of apocrine sweat glands. These glands are found primarily in areas with high friction or skin-to-skin contact. Common affected areas include the armpits, groin, buttocks, inner thighs, and under the breasts. Lesions can also develop in less common locations, such as the back, neck, and perineum.
These locations often lead to discomfort and difficulty with daily activities due to the pain and inflammation.
Typical Symptoms Associated with HS
The symptoms of HS can vary in severity and presentation from person to person. Common symptoms include painful, swollen lumps or boils, which can eventually drain pus or form discharging sinuses. These lesions can be accompanied by redness, warmth, and tenderness in the affected areas. In some cases, fever and fatigue may accompany the skin manifestations. The persistent nature of these symptoms often leads to psychological distress and social limitations.
Potential Impact of HS on Quality of Life
Hidradenitis suppurativa can have a substantial impact on a person’s quality of life. The persistent pain, discomfort, and frequent flare-ups can lead to limitations in daily activities, work, and social interactions. The physical appearance of the lesions can cause significant emotional distress and body image issues. These effects highlight the importance of early diagnosis and effective treatment strategies to mitigate the negative impact of HS.
Stages of HS Severity
Understanding the different stages of HS severity is essential for appropriate treatment planning. The table below Artikels the different stages, symptoms, and potential treatment options.
| Stage | Symptoms | Treatment Options | Additional Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mild | Occasional, localized inflammatory lesions. Minimal pain and discomfort. | Topical treatments (e.g., antibiotics, retinoids), lifestyle modifications (e.g., weight management). | Usually responds well to conservative measures. |
| Moderate | More frequent, deeper lesions with increased pain and swelling. Potential for sinus tracts and drainage. | Oral antibiotics, topical steroids, or a combination of treatments. Potentially surgical intervention (e.g., incision and drainage). | Requires more intensive management strategies. |
| Severe | Extensive, deep-seated lesions affecting multiple sites. Significant pain, discomfort, and potential for significant scarring. | Combination of systemic medications (e.g., immunosuppressants), biologics, or surgery. Possible referral to a specialist (e.g., dermatologist, surgeon). | May require long-term management and ongoing monitoring. |
| Recurrent | Lesions recur despite treatment. Significant impact on quality of life due to prolonged discomfort and disability. | Specialized treatments like biologics, advanced surgical procedures, and lifestyle adjustments. Ongoing support and education crucial. | Represents a significant challenge in management, requiring a tailored approach. |
Overview of COVID-19
COVID-19, caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus, has profoundly impacted global health and society. Understanding its characteristics, immune response, potential long-term effects, and common symptoms is crucial for informed discussions and preventative measures. This section provides a comprehensive overview of the virus and its impact.
Ever wondered how things like hidradenitis suppurative and COVID-19 might be connected? While seemingly unrelated, understanding how contagious diseases spread, like bird flu, is crucial. For example, the transmission of bird flu to humans often involves close contact with infected birds, highlighting the importance of hygiene and safety precautions. Knowing how these diseases spread, such as how does bird flu spread to humans , helps us better understand the potential interplay between various infectious agents, including those related to hidradenitis suppurative and COVID-19.
Primary Characteristics of COVID-19 Infection
The SARS-CoV-2 virus primarily infects the respiratory system, causing a wide range of symptoms. Key characteristics include its ability to rapidly spread through respiratory droplets and its capacity to mutate, leading to new variants with varying transmissibility and severity. Different variants exhibit distinct features, impacting the disease’s progression and response to treatments. The virus’s tropism for the ACE2 receptor on human cells allows for efficient entry into host cells, initiating the infection cascade.
Immune System’s Response to COVID-19
The human immune system mounts a complex response to COVID-19 infection. Initial responses involve innate immune cells, such as macrophages and neutrophils, attempting to contain the viral spread. Subsequently, adaptive immune responses, including B cells producing antibodies and T cells targeting infected cells, become activated. The effectiveness and duration of these responses vary among individuals, influencing the severity and outcome of the infection.
Some individuals develop long-lasting immunity, while others experience recurrent infections. The magnitude and nature of the immune response contribute significantly to the clinical presentation and long-term consequences of the infection.
Potential Long-Term Health Effects of COVID-19 (Long COVID)
Long COVID, or post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection (PASC), encompasses a range of persistent symptoms that can persist for weeks, months, or even years after the initial infection. These symptoms can affect various organ systems, including the cardiovascular, neurological, respiratory, and gastrointestinal systems. For instance, some individuals experience chronic fatigue, cognitive impairment, or breathing difficulties long after the acute phase.
Factors such as the severity of the initial infection, pre-existing health conditions, and individual genetic predisposition may influence the likelihood and severity of long COVID.
Common Symptoms Experienced During and After COVID-19 Infection
A wide array of symptoms can manifest during and after COVID-19 infection. Common symptoms during the acute phase include fever, cough, fatigue, loss of taste or smell, and shortness of breath. Post-infection, individuals may experience lingering symptoms such as muscle aches, joint pain, or persistent fatigue. The severity and duration of these symptoms can vary significantly, highlighting the diverse impact of the infection on individuals.
Stages of COVID-19 Infection
| Stage | Symptoms | Duration | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Infection (Incubation Period) | Typically asymptomatic or mild symptoms like fatigue, headache, muscle aches, and mild respiratory symptoms. | 2-14 days | Supportive care, rest, and hydration. Early intervention with antiviral medications in severe cases may be considered. |
| Acute Phase | Symptoms escalate, including fever, cough, shortness of breath, and potentially pneumonia. | Several days to a few weeks | Hospitalization, oxygen therapy, antiviral medications, and supportive care, depending on severity. |
| Recovery | Symptoms gradually subside, and patients experience improvement in respiratory function and overall health. | Several weeks to months | Rest, rehabilitation, and monitoring for lingering symptoms. |
| Long COVID (PASC) | Persistence of symptoms beyond the acute phase, impacting various organ systems. Examples include fatigue, brain fog, shortness of breath, and digestive issues. | Weeks, months, or years | Management of specific symptoms, rehabilitation, and long-term follow-up care. |
Potential Links Between HS and COVID-19
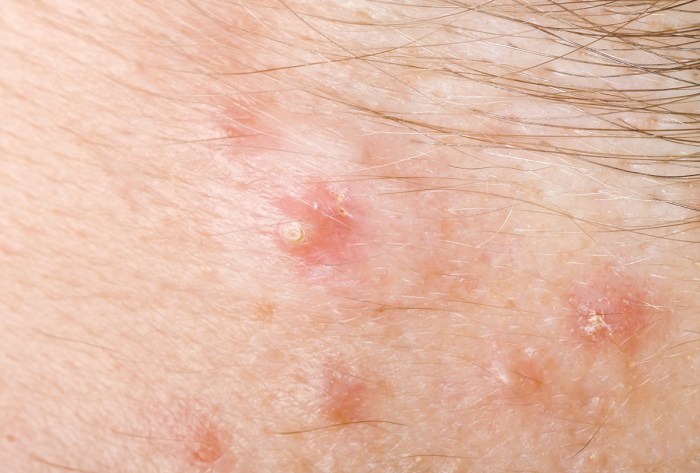
The relationship between Hidradenitis Suppurativa (HS) and COVID-19 is an area of emerging interest, although still under investigation. Both conditions are characterized by inflammatory responses, and there’s a growing body of anecdotal and preliminary research suggesting potential connections. This exploration delves into the possible correlations between these two conditions, focusing on shared inflammatory pathways and potential influences on disease severity.
Potential Correlations Between HS and COVID-19 Infection
Preliminary data suggests a potential correlation between COVID-19 infection and flares of HS in some individuals. While a direct causal link isn’t definitively established, observations suggest that certain inflammatory mechanisms might overlap and exacerbate existing HS conditions. This warrants further investigation into the specific ways these conditions may interact.
Comparison of Inflammatory Responses in HS and COVID-19
Both HS and COVID-19 involve significant inflammatory responses. HS is characterized by chronic inflammation in apocrine glands, often leading to recurrent skin abscesses and fistulas. COVID-19 triggers a systemic inflammatory response, ranging from mild to severe, often involving the lungs and other organs. While the specific inflammatory pathways differ in their targets, some overlap exists in the activation of immune cells and the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines.
Further research is needed to fully understand the extent of this overlap.
Potential Mechanisms by Which COVID-19 Might Influence HS
Several potential mechanisms exist through which COVID-19 could influence HS. One possibility is that the systemic inflammatory response triggered by COVID-19 could exacerbate the existing inflammatory processes in HS. The immune dysregulation associated with COVID-19 might also lead to increased production of inflammatory mediators, potentially impacting the progression of HS. Another possibility is that the stress response associated with COVID-19 infection, including emotional and physical stress, could contribute to HS flares in susceptible individuals.
I’ve been researching hidradenitis suppurative (HS) and its potential connection to COVID-19, and one area that’s piqued my interest is diet. Switching to healthier alternatives to full-fat dairy products, like those outlined in this helpful guide healthy alternatives to full fat dairy products , might be a beneficial strategy for managing inflammation, which could potentially be relevant to HS and how the body reacts to COVID-19.
Further research into this connection between diet and HS/COVID-19 is needed, but I’m hopeful about these potential avenues.
Potential Factors Influencing HS Severity in Individuals with COVID-19
Several factors could influence the severity of HS in individuals with COVID-19. Pre-existing HS severity, the severity of COVID-19 infection, and individual immune responses are all likely to play a role. Nutritional status, stress levels, and concomitant medications are additional variables that may impact the interaction between the two conditions. More research is needed to pinpoint these contributing factors.
Shared Inflammatory Pathways Between HS and COVID-19
Identifying potential shared pathways between the inflammatory responses of HS and COVID-19 is crucial for understanding their potential interaction. This table illustrates potential overlapping mechanisms, highlighting the similarities in the underlying biological processes.
Recent research has explored potential links between hidradenitis suppurative (HS) and COVID-19, but the exact nature of their relationship remains unclear. While some studies suggest a possible connection, more research is needed. Interestingly, similar inflammatory conditions like rheumatoid arthritis are often treated with disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), for example, DMARDs for rheumatoid arthritis , and understanding these treatments might offer clues for managing HS flare-ups during or after a COVID-19 infection.
This further emphasizes the need for continued investigation into HS and COVID-19’s complex interplay.
| Pathway | HS Mechanism | COVID-19 Mechanism | Potential Interaction |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cytokine Storm | Increased production of pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α and IL-1β | Dysregulated immune response leading to excessive cytokine production | COVID-19 may exacerbate pre-existing cytokine imbalance in HS, leading to more severe flares. |
| Oxidative Stress | Chronic inflammation in HS leads to increased production of reactive oxygen species | COVID-19 infection may induce oxidative stress | Combined oxidative stress could potentially worsen tissue damage and inflammation in both conditions. |
| Immune Cell Activation | Activation of neutrophils, macrophages, and T cells | Systemic activation of immune cells, including T cells and macrophages | Overactivation of immune cells in COVID-19 could potentially amplify inflammation in HS. |
| Vascular Dysfunction | Inflammation can cause microvascular changes in the skin | COVID-19 can lead to vascular damage and inflammation in various organs | Potential interaction in skin tissue with inflammation contributing to the characteristic lesions of HS. |
Existing Research and Studies
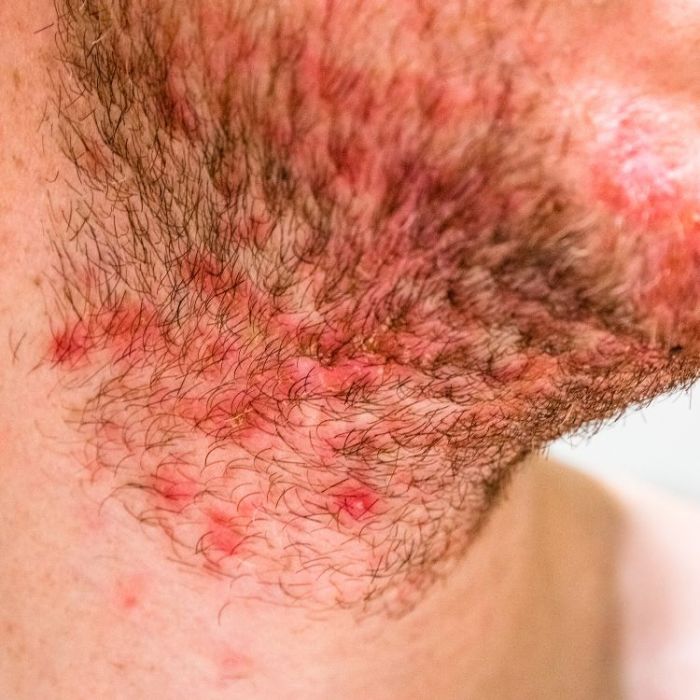
Currently, research exploring the link between hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) and COVID-19 is limited. While anecdotal reports and preliminary observations suggest potential connections, robust, controlled studies are still needed to establish a definitive relationship. This scarcity of evidence highlights the urgent need for further investigation into this complex interplay.
Summary of Existing Research
The existing research on the interplay between HS and COVID-19 is largely observational and descriptive, lacking the rigorous design of controlled clinical trials. Many studies focus on correlational analysis, examining potential associations between the two conditions without definitively proving a causal link. The small sample sizes and diverse methodologies employed in these studies often make it challenging to draw firm conclusions.
Clinical Studies and Methodology
A significant gap in the current research lies in the limited number of well-designed clinical trials specifically investigating the relationship between HS and COVID-19. The methodologies employed in existing studies often vary, hindering the ability to compare findings and draw consistent conclusions. For example, some studies may have assessed HS severity using questionnaires, while others may have used clinical assessments, potentially leading to inconsistencies in the data.
Future studies should employ standardized methodologies to ensure comparability and reproducibility of results.
Reported Changes in HS Presentation
Anecdotal reports and some preliminary observational studies suggest potential changes in HS presentation during or after COVID-19 infection. These changes may include fluctuations in disease activity, either an increase or decrease in the frequency or severity of lesions, or alterations in the location of HS lesions. However, these observations require further validation through larger, more rigorously designed clinical trials.
The reasons for these potential changes remain unclear, and further investigation is necessary to understand the underlying mechanisms.
Gaps in Current Knowledge
A key gap in the current knowledge base is the lack of understanding regarding the potential mechanisms linking HS and COVID-19. Specific questions regarding the influence of COVID-19-related inflammation, immune dysregulation, or other factors on HS activity need to be addressed. Further research is crucial to explore the potential role of the immune system and the interplay of inflammatory pathways in both conditions.
Longitudinal studies are needed to track changes in HS activity over time in patients with COVID-19. Moreover, studies examining the impact of COVID-19 vaccination on HS are needed.
Examples of Existing Research Approaches
Many existing studies employ retrospective analyses of patient data. For instance, researchers might analyze medical records of patients diagnosed with both HS and COVID-19 to identify potential correlations. Another approach involves comparing the clinical characteristics of patients with HS and COVID-19 to those with HS alone or COVID-19 alone. A more sophisticated approach involves controlled clinical trials where researchers randomly assign participants to different groups, such as a group receiving a specific treatment and a control group receiving a placebo.
This approach helps minimize bias and increase the reliability of the results.
Potential Impact on Treatment Strategies
The COVID-19 pandemic has profoundly impacted various aspects of healthcare, and hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) treatment is no exception. Understanding the potential interplay between these conditions is crucial for optimizing patient care and tailoring treatment approaches. The pandemic’s influence on access to care, healthcare resource allocation, and patient adherence to treatment plans must be considered.The potential effects of COVID-19 on HS treatment approaches are multifaceted.
The pandemic has disrupted routine healthcare, potentially affecting the timely diagnosis and management of HS. Changes in access to specialist care, delays in appointments, and concerns about clinic visits might have influenced treatment decisions and outcomes.
Potential Implications of COVID-19 on Existing HS Treatments
The pandemic’s impact on the effectiveness of existing HS treatments is a significant concern. Reduced access to dermatologists, delays in appointments, and fear of exposure to the virus could potentially affect patients’ adherence to prescribed treatments. This might lead to a worsening of symptoms and a delayed response to therapies. For example, patients might delay seeking care or stop treatments altogether due to fear of contracting COVID-19 in a healthcare setting.
The need for remote monitoring and telehealth visits has also introduced new considerations for treatment management.
Comparison of Treatment Approaches for HS in Patients with and without COVID-19 History
Tailoring treatment strategies for HS patients with and without a COVID-19 history is crucial. While general treatment approaches remain similar, the potential for increased inflammation and altered immune responses in post-COVID patients necessitates careful consideration. A patient with a recent history of COVID-19 might require adjustments in treatment intensity or frequency to mitigate any potential adverse interactions or exacerbation of existing conditions.
Modifications to Current HS Management Guidelines
Current HS management guidelines may need modifications in light of the COVID-19 pandemic. These modifications should address the unique challenges posed by the pandemic, such as reduced access to care, fear of exposure, and potential treatment interactions. The adaptation of treatment protocols should consider the potential for individual variations in response to COVID-19 and its aftermath.
Table: Potential Modifications to Existing HS Treatment Protocols
| Treatment Protocol | Potential Modification for Patients with COVID-19 History | Rationale | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intralesional corticosteroids | Reduced frequency or dosage for the first 4-6 weeks post-COVID-19 infection. | To minimize potential exacerbation of inflammation. | Monitor for adverse effects, and consider alternative treatments. |
| Oral antibiotics | Close monitoring for potential interactions with COVID-19 medications. | To avoid adverse reactions. | Consider alternatives or adjust dosage if necessary. |
| Biologic therapies | Evaluate the need for adjustments in dosage or frequency based on the severity of COVID-19 infection and recovery status. | To mitigate any potential adverse effects. | Monitor closely for signs of infection and inflammation. |
| Surgical interventions | Delay surgical procedures if possible. If absolutely necessary, prioritize patients with well-controlled HS and minimize exposure risk. | To minimize risk of complications in post-COVID patients. | Strict adherence to pre- and post-operative protocols. |
Patient Management Considerations
Navigating a COVID-19 outbreak requires a nuanced approach to managing Hidradenitis Suppurativa (HS) patients. The unique challenges of HS, coupled with the potential for COVID-19 complications, necessitate a proactive and supportive strategy to optimize patient well-being and minimize exacerbations. This section focuses on crucial considerations for patient care during a pandemic, emphasizing preventative measures, prioritized needs, and the vital role of patient education.
Prioritizing Patient Needs During a Pandemic, Hidradenitis suppurative and covid 19
HS patients often experience significant emotional and physical distress. A pandemic further complicates their situation, potentially increasing anxiety and impacting access to necessary medical care. Recognizing the compounded burden is crucial. Prioritizing access to healthcare, ensuring timely and appropriate medical interventions, and addressing emotional needs are paramount. Telemedicine, when applicable, can play a critical role in maintaining consistent care while minimizing exposure.
This proactive approach ensures patients feel supported and maintain their well-being, crucial for both their physical and mental health during a challenging time.
Strategies for Minimizing HS Exacerbation During COVID-19 Infection
Managing HS exacerbations during a COVID-19 infection requires a multi-faceted approach. Maintaining good hygiene practices, including frequent handwashing and mask-wearing, is vital. Maintaining a consistent skincare routine, as recommended by healthcare providers, is critical. Additionally, stress management techniques, such as meditation or mindfulness exercises, can play a significant role in mitigating flare-ups. A patient’s understanding of these strategies, combined with appropriate medical intervention, can reduce the risk of complications and improve the patient experience.
Importance of Patient Education and Support
Providing comprehensive education to HS patients about COVID-19 precautions and HS management is essential. Clear, accessible information about preventative measures, potential symptom overlap, and available resources can empower patients to actively participate in their care. Patient support groups, either virtual or in-person (when feasible), offer invaluable avenues for shared experiences, coping strategies, and encouragement. These resources provide a platform for mutual support and a sense of community, which can be particularly beneficial during times of stress and uncertainty.
Preemptive Measures and Preventative Strategies
Effective strategies require proactive measures to minimize both COVID-19 infection and HS exacerbation. Understanding the potential overlap of symptoms and the importance of maintaining consistent HS care is vital.
| Preemptive Measures | Preventative Strategies | Potential Impact | Implementation Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Frequent handwashing with soap and water for at least 20 seconds. | Maintaining a consistent skincare routine, including gentle cleansing and moisturization. | Reduces the risk of infection and minimizes skin irritation. | Ensure readily available soap and water in frequently used areas. Provide clear instructions and support for proper technique. |
| Regular use of face masks in public spaces. | Avoiding close contact with individuals who may be infected or showing symptoms. | Minimizes exposure to respiratory droplets. | Emphasize the importance of proper mask use and disposal. Offer guidance on alternative social interactions. |
| Vaccination against COVID-19 (if eligible). | Stress management techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing exercises. | Reduces the severity of COVID-19 infection and associated complications. | Educate patients about vaccine safety and benefits. Facilitate access to vaccination opportunities. |
| Regular communication with healthcare providers, including telehealth options. | Adherence to prescribed medications for HS and other conditions. | Ensures prompt intervention for any concerning symptoms. | Promote proactive communication and provide guidance on available telehealth platforms. Encourage adherence to prescribed treatment plans. |
Future Directions and Research
Unraveling the intricate relationship between hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) and COVID-19 requires a proactive and multifaceted approach. The potential links, while intriguing, remain largely unexplored, necessitating a concerted effort in future research to understand this complex interaction. This section Artikels promising avenues for investigation and the importance of collaborative research to address this critical gap in knowledge.
Potential Research Areas
Further research into the underlying mechanisms linking HS and COVID-19 is crucial. Identifying specific immune responses and inflammatory pathways affected by both conditions is vital for developing targeted therapies. Examining the role of genetic predisposition, environmental factors, and lifestyle choices in exacerbating or mitigating the interaction is also essential.
Large-Scale Longitudinal Studies
Large-scale, longitudinal studies are needed to comprehensively assess the impact of COVID-19 on the course and severity of HS. These studies should meticulously track HS patients’ disease activity before, during, and after COVID-19 infection. Such studies can provide valuable data on the long-term effects of the virus on HS, allowing for more precise risk stratification and potentially identifying specific subgroups at higher risk.
For instance, a study might follow 1000 HS patients over a five-year period, tracking their disease activity and COVID-19 infection status, to identify any correlation between infection severity and HS flare-ups.
Multidisciplinary Collaboration
A collaborative approach involving dermatologists, immunologists, infectious disease specialists, and other relevant experts is paramount. Such interdisciplinary collaboration will foster a comprehensive understanding of the complex interplay between HS and COVID-19. The combined expertise of various specialists can contribute to the development of more effective diagnostic and treatment strategies. For example, a research team could include dermatologists to assess HS disease activity, immunologists to study immune responses, and infectious disease specialists to study the impact of COVID-19 on HS.
Investigation of Specific Immune Responses
Further investigation into the specific immune responses implicated in both HS and COVID-19 is crucial. Researchers should investigate whether certain immune cells or pathways are more significantly affected in individuals with both conditions. Understanding the impact of these immune dysregulations on the progression of HS is a vital step towards developing tailored therapies. This investigation might involve examining the levels of specific cytokines, chemokines, or immune cell populations in HS patients who have had COVID-19 compared to those who have not.
Impact of COVID-19 Vaccines on HS
The impact of COVID-19 vaccines on HS activity deserves attention. Studies should investigate whether vaccination is associated with any changes in HS severity or disease course. This information could have implications for vaccination strategies and potentially guide the timing of vaccinations for individuals with HS. For instance, a study could compare HS disease activity in vaccinated and unvaccinated HS patients over a specific time period.
Final Review: Hidradenitis Suppurative And Covid 19
In conclusion, the relationship between hidradenitis suppurativa and COVID-19 is a complex area needing further investigation. While early research hints at potential correlations and shared inflammatory pathways, more robust studies are needed to fully understand the impact of COVID-19 on HS and vice versa. Ultimately, this knowledge will be critical in developing more tailored treatment strategies and patient management guidelines, especially during future outbreaks.

Leave a Reply