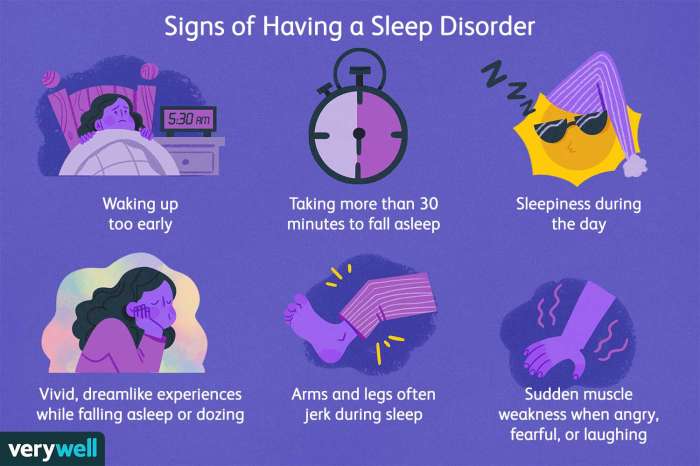
What is a hypnagogic jerk and what causes sleep starts? This intriguing phenomenon, often experienced as a sudden, involuntary body jolt as you’re drifting off to sleep, is more common than you might think. We’ll delve into the science behind these sleep starts, exploring their causes, frequency, and impact on your overall well-being.
From the neurological mechanisms at play to the role of stress and sleep deprivation, we’ll uncover the secrets behind these fascinating involuntary movements. We’ll also look at how to manage these sleep starts and improve your sleep quality.
Defining Hypnagogic Jerks: What Is A Hypnagogic Jerk And What Causes Sleep Starts
Hypnagogic jerks, often referred to as sleep starts, are a common experience for many people. These brief, involuntary muscle contractions typically occur just as a person is drifting off to sleep or waking up. They are usually accompanied by a sudden jolt or feeling of falling. Understanding the physiology behind these seemingly minor occurrences can shed light on the complex interplay between the brain and body during the transition between wakefulness and sleep.Hypnagogic jerks are characterized by a sudden, brief, and often powerful muscular contraction that can involve the entire body or specific muscle groups.
The sensation is usually described as a jolt or a feeling of falling. These involuntary movements are often accompanied by a brief gasp or cry. The sensations are usually not painful, though the surprise element can sometimes lead to a startle response.
Physiological Aspects of Hypnagogic Jerks
The precise physiological mechanisms underlying hypnagogic jerks are not fully understood, but research suggests a complex interplay of neural processes. As the brain transitions from wakefulness to sleep, there are fluctuations in brainwave activity. These fluctuations can sometimes trigger unexpected muscle contractions. A possible explanation is the desynchronization of signals between the brain regions controlling movement and those involved in sleep regulation.
This temporary disruption in communication may lead to the involuntary muscle spasms characteristic of sleep starts. Additionally, changes in neurotransmitter levels, particularly those involved in muscle control and relaxation, may play a role.
Comparison with Other Sleep Phenomena
| Sleep Phenomenon | Description | Key Differences from Hypnagogic Jerks |
|---|---|---|
| Hypnagogic Jerks | Sudden, involuntary muscle contractions, often associated with the feeling of falling. | Occur during the transition between wakefulness and sleep. Generally brief and not associated with significant distress or sleep disruption. |
| Sleep Paralysis | Inability to move or speak while falling asleep or waking up, often accompanied by hallucinations. | Characterized by the inability to move, not just a brief muscle twitch. Usually involves fear and anxiety, whereas hypnagogic jerks are typically not distressing. |
| Night Terrors | Episodes of intense fear and panic during sleep, often accompanied by screaming and thrashing. | Significantly more disruptive and distressing than hypnagogic jerks. Typically occur during deep sleep stages, unlike hypnagogic jerks. |
| REM Sleep Behavior Disorder | Acting out dreams during REM sleep, with potentially dangerous physical movements. | Involves complex actions during REM sleep, not just isolated muscle contractions. Often requires medical attention, unlike hypnagogic jerks. |
The table above provides a concise overview of hypnagogic jerks and their distinction from other sleep phenomena. These differences highlight the specific characteristics of hypnagogic jerks and their relative mildness compared to other sleep disorders. Important to note is that while these are distinct, the exact boundary lines may sometimes overlap in experience, depending on the individual.
Common Terminology for Sleep Starts
The term “hypnagogic jerk” is the most widely accepted and scientific term for sleep starts. However, the term “sleep start” is commonly used in everyday language to describe the experience. These terms are interchangeable and used interchangeably by the public. The experience is universal, as everyone will have these occurrences to some degree.
Ever experienced a sudden jolt as you’re drifting off to sleep? That’s a hypnagogic jerk, a common sleep phenomenon. It’s often caused by your brain’s temporary confusion between wakefulness and sleep. While some find relief from stress and anxiety with activities like are cold showers good for you , the exact reasons for these sleep starts are still being researched.
Regardless of the cause, these involuntary twitches are usually harmless and a normal part of the sleep cycle.
Prevalence and Demographics
Hypnagogic jerks, those sudden, involuntary muscle contractions that often jolt us awake, are a common experience for many people. Understanding who experiences them most frequently, and at what ages, provides valuable insight into their potential causes and implications. This section delves into the demographics associated with sleep starts.
Age Ranges of Prevalence
Hypnagogic jerks are most prevalent during childhood and adolescence. The peak incidence often occurs during the preteen and teenage years, likely due to the rapid physiological changes and hormonal fluctuations associated with these developmental stages. As individuals age, the frequency of these experiences generally decreases. This observation is consistent with the changing sleep patterns and neurological functions that accompany aging.
While some adults may still experience them occasionally, the overall prevalence tends to decline.
Gender Differences
Studies on hypnagogic jerks have not consistently demonstrated significant differences in prevalence between males and females. While some research suggests a slight tendency for one gender to experience them more frequently, the differences are usually not substantial enough to establish a definitive gender-based pattern. The lack of definitive conclusions suggests that factors other than gender likely play a more significant role in determining the frequency of sleep starts.
Summary Table
| Demographic Category | Prevalence Observation |
|---|---|
| Children (ages 5-12) | High prevalence, potentially linked to rapid growth and sleep development. |
| Adolescents (ages 13-19) | High prevalence, possibly due to hormonal changes and sleep patterns. |
| Adults (ages 20-64) | Prevalence generally decreases, though some individuals may still experience them occasionally. |
| Elderly (ages 65+) | Prevalence tends to be lower than in younger age groups. |
| Gender | No significant difference in prevalence between males and females has been consistently observed. |
Causes of Sleep Starts

Sleep starts, those sudden, jarring muscle contractions that jolt us awake, are more common than you might think. They often leave us feeling disoriented and sometimes even frightened. Understanding the underlying mechanisms can help alleviate anxiety and promote a more peaceful night’s sleep. While often harmless, they can sometimes signal an underlying health issue.The neurological pathways involved in the transition between wakefulness and sleep are complex and not entirely understood.
The brain’s electrical activity fluctuates dramatically during this transition, often resulting in unexpected muscle twitches. This interplay between the brain’s activity and our physical response is a key factor in understanding hypnagogic jerks.
Neurological Mechanisms of Sleep Starts
The brain’s activity patterns shift significantly as we drift off to sleep. The brain waves, from the high-frequency, alert beta waves to the slower theta and delta waves associated with deep sleep, transition through various stages. During this transition, there’s often a brief period of heightened neuronal activity, which can lead to involuntary muscle contractions. This burst of activity is believed to be the trigger for the hypnagogic jerk.
Imagine the brain as a conductor orchestrating a complex symphony; sometimes, a discordant note can disrupt the smooth transition.
Ever experienced a sudden, involuntary muscle spasm as you’re drifting off to sleep? That’s a hypnagogic jerk, or sleep start, often caused by a mix of factors like stress, sleep deprivation, or even caffeine. Unfortunately, sometimes understanding these occurrences is complicated by difficulties accessing medical records, which can impact diagnosis and treatment options. For more insight on the challenges of denied access to medical records , and how this can affect your health journey, check out this article.
Ultimately, understanding these sleep starts can help you get a better night’s sleep.
Role of Brain Activity Patterns During Wakefulness-Sleep Transition
The brain’s shift from wakefulness to sleep involves a complex interplay of neurotransmitters and electrical signals. As the brain begins to slow down, the signals responsible for muscle control can sometimes become erratic, leading to involuntary movements. This temporary imbalance is thought to be the culprit behind the sudden muscle contractions that we experience as sleep starts. These transitions are natural and usually harmless, like a minor hiccup in the body’s natural sleep cycle.
Ever experienced a sudden jolt as you’re drifting off to sleep? That’s a hypnagogic jerk, a common sleep phenomenon often caused by the brain’s sudden shift from wakefulness to sleep. While some people swear by the idea that consuming a healthy snack like beef jerky helps regulate sleep patterns, a quick search into the benefits of is beef jerky healthy will show that its nutritional value is often questionable.
Ultimately, understanding the causes of hypnagogic jerks is more about focusing on sleep hygiene and relaxation techniques than snack choices.
Impact of Sleep Deprivation on Sleep Starts, What is a hypnagogic jerk and what causes sleep starts
Sleep deprivation can significantly increase the likelihood and intensity of hypnagogic jerks. When we consistently don’t get enough sleep, our brain’s ability to regulate the transition between wakefulness and sleep is compromised. This disruption in the natural sleep cycle can lead to more frequent and pronounced muscle contractions. Think of sleep deprivation as a conductor missing several crucial rehearsals; the performance (the sleep cycle) will be less smooth and more prone to errors.
Connection Between Sleep Starts and Underlying Medical Conditions
While most sleep starts are benign, in some cases, they can be a symptom of an underlying medical condition. Certain neurological disorders, such as multiple sclerosis or Parkinson’s disease, can manifest with unusual sleep patterns, including increased frequency of sleep starts. Medical professionals should be consulted if sleep starts become excessively frequent or are accompanied by other concerning symptoms.
It’s crucial to remember that this is not a definitive diagnosis; consulting a healthcare professional is essential.
Possible Causes of Sleep Starts
| Cause | Description | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Stress and Anxiety | Increased stress levels can disrupt the sleep cycle, leading to more frequent sleep starts. | Common |
| Sleep Deprivation | Insufficient sleep disrupts the natural sleep cycle, increasing the likelihood of sleep starts. | Common |
| Caffeine and Nicotine Intake | Stimulants can interfere with the sleep transition process, potentially triggering sleep starts. | Common |
| Underlying Neurological Conditions | Certain neurological disorders can be associated with more frequent or intense sleep starts. | Less Common |
| Medications | Certain medications can have side effects that disrupt sleep patterns, increasing the risk of sleep starts. | Variable |
Associated Factors and Triggers
Sleep starts, those sudden, jarring muscle contractions that wake you from a seemingly peaceful slumber, are more than just an occasional annoyance. Understanding the factors that contribute to their occurrence can help you manage and potentially reduce their frequency. While often harmless, they can sometimes be a sign of an underlying sleep disorder or other medical condition.The experience of a hypnagogic jerk isn’t entirely random.
Various factors, both internal and external, can influence the likelihood of experiencing these involuntary movements. These triggers can range from simple environmental elements to more complex issues like stress and medication interactions. By identifying these triggers, you can potentially gain control over these fleeting awakenings.
Common Factors Triggering Sleep Starts
A number of factors can contribute to the occurrence of hypnagogic jerks. These can be categorized broadly as psychological, physiological, and environmental. Recognizing these elements is key to understanding why these sudden muscle twitches happen.
- Stress and Anxiety: Chronic stress and anxiety can significantly impact sleep quality. High levels of stress hormones like cortisol can disrupt the delicate balance of neurochemicals involved in sleep regulation, potentially increasing the likelihood of sleep starts. For example, someone experiencing a stressful work deadline or a significant personal issue may find their sleep is more easily interrupted by hypnagogic jerks.
- Certain Medications: Some medications, particularly those affecting the central nervous system, can interfere with sleep patterns. This can lead to more frequent sleep starts. Examples include some antidepressants, antihistamines, and certain blood pressure medications. It’s crucial to discuss potential sleep-related side effects with your physician if you’re taking medication and experiencing increased sleep start frequency.
- Environmental Factors: Environmental factors can also play a role in triggering hypnagogic jerks. A noisy or uncomfortable sleeping environment can lead to sleep disruptions, making the body more susceptible to these muscle spasms. For instance, a bedroom with bright lights or excessive noise can prevent a person from achieving deep, restful sleep, making sleep starts more likely.
- Dietary Factors: Poor dietary habits, such as consuming caffeine or alcohol close to bedtime, can also contribute to sleep disturbances. Caffeine is a stimulant that can disrupt the natural sleep-wake cycle. Similarly, alcohol, while it might initially induce sleepiness, can interfere with the later stages of sleep, increasing the potential for sleep starts. A balanced diet and mindful consumption of stimulants and depressants before bed can make a difference.
Impact of Stress and Anxiety
Chronic stress and anxiety are significant factors in sleep quality and the occurrence of sleep starts. Elevated levels of stress hormones, like cortisol, disrupt the delicate balance of neurochemicals that regulate sleep. These hormonal imbalances can lead to fragmented sleep, making individuals more prone to these involuntary muscle twitches. Furthermore, the mental strain associated with stress can affect the body’s ability to transition smoothly between sleep stages, increasing the chance of sleep starts.
Influence of Medications and Substances
Certain medications and substances can influence sleep start frequency. Medications that affect the central nervous system, including some antidepressants, antihistamines, and blood pressure medications, can disrupt sleep patterns. Furthermore, substances like caffeine and alcohol can also interfere with sleep quality. Caffeine, a stimulant, disrupts the natural sleep-wake cycle, while alcohol, despite inducing initial sleepiness, can lead to fragmented sleep later in the night.
Consulting a doctor about potential sleep-related side effects of any medication is essential.
Environmental Factors Affecting Sleep Starts
Environmental factors can significantly impact sleep quality, increasing the likelihood of hypnagogic jerks. A noisy or uncomfortable sleeping environment can lead to sleep disruptions. Bright lights, excessive noise, or uncomfortable temperatures can all hinder deep, restful sleep. A well-maintained sleep environment, characterized by darkness, quiet, and comfortable temperature, is crucial for minimizing sleep disruptions and potentially reducing sleep starts.
Correlation Between Factors and Sleep Starts
| Factor | Potential Impact on Sleep Starts |
|---|---|
| Stress/Anxiety | Disrupts sleep, increases likelihood of sleep starts |
| Medications (e.g., antidepressants, antihistamines) | Disrupts sleep patterns, increases sleep start frequency |
| Caffeine/Alcohol | Interferes with sleep quality, potentially increasing sleep starts |
| Environmental Factors (noise, light, temperature) | Disrupts sleep, increases susceptibility to sleep starts |
| Dietary Habits | Disrupts sleep, may increase sleep start frequency |
Impact on Sleep and Well-being
Sleep starts, those jarring awakenings that often leave you feeling disoriented, can significantly impact your overall sleep quality and well-being. While often dismissed as a minor inconvenience, frequent hypnagogic jerks can disrupt your sleep cycle, leading to a cascade of effects on your daily life. Understanding these impacts can help you address this common sleep phenomenon effectively.The impact of hypnagogic jerks extends beyond simple discomfort.
These involuntary muscle contractions, often accompanied by a feeling of falling or floating, can interrupt the delicate transition between wakefulness and sleep. This disruption can lead to a less restful and restorative sleep experience, ultimately affecting your ability to function optimally during the day.
Potential Impact on Overall Sleep Quality
Hypnagogic jerks frequently occur during the transition phase of non-REM sleep, specifically the stage just before entering deeper sleep. This disruption of the sleep cycle can prevent individuals from reaching the restorative stages of sleep, impacting their ability to consolidate memories and recover from the day’s activities. This lack of quality sleep can lead to feelings of fatigue, difficulty concentrating, and reduced cognitive function.
Chronic sleep deprivation can be detrimental to various aspects of health, including physical and mental well-being.
Effect on Daytime Alertness and Performance
Frequent sleep starts can significantly impair daytime alertness and performance. The fragmented sleep associated with these interruptions can leave individuals feeling tired, sluggish, and unable to focus effectively. This diminished alertness can negatively affect work performance, academic outcomes, and even safety in situations requiring concentration and quick reaction times. For example, a truck driver experiencing frequent sleep starts could have impaired judgment and reaction time, leading to potential safety risks on the road.
Contribution to Sleep Disorders or Worsening Existing Conditions
While hypnagogic jerks are usually benign, their frequent occurrence can contribute to or worsen existing sleep disorders. The consistent disruption of sleep patterns can lead to insomnia, sleep apnea, or other sleep-related issues. For instance, someone with pre-existing anxiety might find that sleep starts exacerbate their anxiety, leading to a vicious cycle of poor sleep and increased anxiety. This disruption can also make it harder for individuals to manage other chronic health conditions, as sleep plays a crucial role in overall health and recovery.
Emotional Impact of Frequent Sleep Starts
The emotional impact of frequent sleep starts can be significant, leading to feelings of frustration, anxiety, and even irritability. The unpredictability and discomfort associated with these sudden awakenings can create a sense of unease and disrupt a person’s sense of well-being. Individuals experiencing these frequent jerks may find themselves feeling more stressed and anxious about their sleep, which can have a negative impact on their overall mood and emotional state.
Relationship Between Sleep Starts and Sleep Disturbances
| Sleep Disturbance | Potential Relationship with Sleep Starts |
|---|---|
| Insomnia | Frequent sleep starts can disrupt the sleep cycle, making it harder to fall asleep and stay asleep. |
| Sleep Apnea | Sleep starts may exacerbate existing sleep apnea by disrupting the sleep cycle, which can be linked to the breathing difficulties associated with sleep apnea. |
| Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS) | Sleep starts might be associated with RLS, as both conditions can stem from underlying neurological factors. |
| Anxiety and Depression | The chronic disruption of sleep by frequent sleep starts can worsen symptoms of anxiety and depression by increasing stress levels and impairing emotional regulation. |
Management and Treatment Strategies
Hypnagogic jerks, while often harmless, can disrupt sleep and lead to feelings of frustration or even anxiety for some individuals. Fortunately, various strategies can help manage these involuntary muscle contractions and improve sleep quality. Addressing underlying causes, adopting healthy sleep habits, and exploring relaxation techniques are key components of effective management.Understanding the factors contributing to sleep starts is crucial for developing personalized strategies for managing them.
Lifestyle adjustments, including relaxation techniques and consistent sleep hygiene, often prove effective in reducing the frequency and intensity of these episodes.
Relaxation Techniques for Minimizing Sleep Starts
Relaxation techniques can be incredibly helpful in reducing the occurrence of hypnagogic jerks. These techniques aim to calm the mind and body, easing the transition into sleep and minimizing the likelihood of muscle spasms.
- Progressive Muscle Relaxation: This technique involves systematically tensing and relaxing different muscle groups in the body. By consciously relaxing each muscle group, you can promote a sense of calm and reduce muscle tension that might contribute to sleep starts. Practicing this technique before bed can help prepare the body for a more relaxed sleep.
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Slow, deep breaths can help calm the nervous system and promote relaxation. Focusing on the breath can redirect your attention away from racing thoughts and physical tension, leading to a more peaceful transition into sleep. Incorporating deep breathing exercises into your bedtime routine can significantly aid in reducing sleep starts.
- Mindfulness Meditation: Mindfulness meditation encourages present-moment awareness without judgment. By focusing on your breath, bodily sensations, and thoughts, you can observe them without getting carried away. This practice can help to quiet the mind and reduce stress, which are often contributing factors to sleep starts.
Sleep Hygiene Practices for Reducing Sleep Starts
Consistent sleep hygiene practices are essential for improving sleep quality and reducing the frequency of sleep starts. Creating a regular sleep schedule, optimizing your sleep environment, and avoiding certain activities before bed can significantly impact the likelihood of experiencing these episodes.
- Establish a Regular Sleep Schedule: Going to bed and waking up around the same time each day, even on weekends, regulates your body’s natural sleep-wake cycle. This consistency can minimize the disruptions that can trigger sleep starts.
- Optimize Your Sleep Environment: Create a dark, quiet, and cool bedroom conducive to sleep. Use blackout curtains, earplugs, or a white noise machine to block out distractions. A comfortable mattress and pillows also play a significant role in promoting relaxation and reducing muscle tension.
- Avoid Stimulants Before Bed: Caffeine, nicotine, and alcohol can interfere with sleep quality and increase the likelihood of sleep starts. Avoid consuming these substances several hours before bedtime.
The Role of Medical Intervention
In some cases, medical intervention may be necessary to address underlying medical conditions that contribute to sleep starts. However, for the majority of individuals, lifestyle changes and relaxation techniques are sufficient.
- Underlying Medical Conditions: Conditions like restless legs syndrome, anxiety disorders, or sleep apnea can exacerbate sleep starts. Addressing these conditions through appropriate medical treatment can help reduce the frequency of sleep starts.
Treatment Options and Effectiveness
| Treatment Option | Description | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Relaxation Techniques | Progressive muscle relaxation, deep breathing, mindfulness | Generally effective in reducing sleep starts for many individuals, especially when combined with other strategies. |
| Sleep Hygiene Practices | Regular sleep schedule, optimized sleep environment, avoiding stimulants before bed | Highly effective in improving sleep quality and reducing sleep starts by creating a conducive sleep environment. |
| Medical Intervention (for underlying conditions) | Addressing conditions like restless legs syndrome, sleep apnea, or anxiety disorders | Highly effective in reducing sleep starts when the underlying condition is treated. |
Misconceptions and Myths Surrounding Sleep Starts
Sleep starts, those sudden, jarring muscle contractions that wake you from sleep, are often shrouded in misconceptions and myths. These beliefs, while harmless in most cases, can sometimes lead to unnecessary worry or even misdiagnosis. Understanding the scientific reality behind sleep starts is crucial for managing any associated anxieties and promoting better sleep hygiene.Common misconceptions often center around the perceived severity or cause of these brief awakenings.
Many people attribute sleep starts to external factors, emotional distress, or even supernatural influences. However, a deeper understanding reveals that sleep starts are largely a normal physiological phenomenon, often stemming from the transition between sleep stages.
Common Misconceptions
Sleep starts are often misinterpreted as signs of underlying medical conditions or emotional distress. This can lead to unnecessary anxiety and potentially even misdirected medical attention. It’s important to remember that the majority of sleep starts are perfectly normal occurrences.
- Sleep starts are a sign of a serious medical condition.
- Sleep starts indicate emotional or psychological issues.
- Sleep starts are caused by external factors, such as cold temperatures or drafts.
- Sleep starts are a sign of poor sleep quality, always requiring intervention.
Scientific Basis for Dispelling Misconceptions
Sleep starts, also known as hypnic jerks, are typically harmless and involuntary muscle contractions that occur during the transition between wakefulness and sleep. They are characterized by a sudden, brief, and often startling sensation. Neurological activity during this transition can trigger the muscle contractions, but the precise mechanism is not fully understood.
- Normal physiological phenomenon: Sleep starts are generally a normal part of the transition between wakefulness and sleep, often occurring during stage 1 of non-REM sleep, where the brain is shifting between states of alertness and rest. These brief contractions are not indicative of a serious medical condition.
- Not associated with psychological issues: While stress and anxiety can sometimes impact sleep quality, sleep starts themselves are not typically directly linked to emotional or psychological problems.
- No causal link to external factors: While factors like temperature fluctuations can influence sleep, there’s no direct correlation between external stimuli and sleep starts. These occurrences are predominantly a result of neurological processes within the body.
- Not always indicative of poor sleep quality: While poor sleep quality can exacerbate sleep issues, sleep starts are not necessarily a marker of poor sleep hygiene. Many healthy individuals experience them occasionally.
Common Myths About Causes
Several myths surround the causes of sleep starts, often attributing them to external forces or emotional factors. These myths are not supported by scientific evidence.
- Sleep starts are caused by an external disturbance: This myth suggests that cold air, drafts, or other environmental factors directly trigger these muscle spasms. However, research does not support this claim. While environmental factors can influence sleep, the primary cause of sleep starts is physiological, not external.
- Sleep starts are a sign of evil spirits or supernatural forces: This myth often stems from cultural beliefs or historical misunderstanding. Sleep starts are purely physiological phenomena with a neurological basis.
- Sleep starts are a symptom of a serious disease: This myth can be alarming and lead to unnecessary medical concerns. Sleep starts are typically benign and do not signal a significant health issue.
Negative Impact of Perpetuating Myths
The perpetuation of myths surrounding sleep starts can have a negative impact on individuals’ well-being. It can lead to unnecessary stress, anxiety, and misdiagnosis. Understanding the true nature of sleep starts promotes informed decision-making and better management of sleep-related concerns.
- Increased anxiety and stress: Misinterpreting sleep starts as a symptom of a serious problem can lead to unnecessary stress and anxiety.
- Misdirected medical attention: Individuals may seek medical help for sleep starts, leading to unnecessary tests and procedures.
- Disruption of sleep hygiene: Fear or misunderstanding of sleep starts may lead to avoidance of sleep, further impacting sleep quality.
Myth vs. Reality Table
| Myth | Scientific Reality |
|---|---|
| Sleep starts are caused by external factors like cold air. | Sleep starts are primarily a physiological response, not linked to external stimuli. |
| Sleep starts indicate a serious medical condition. | Sleep starts are usually benign and not indicative of a significant health issue. |
| Sleep starts are a sign of emotional distress. | While stress can impact sleep, sleep starts are not directly linked to emotional problems. |
| Sleep starts are a supernatural phenomenon. | Sleep starts have a neurological basis and are a normal part of the sleep-wake cycle. |
Closing Summary
In conclusion, hypnagogic jerks, or sleep starts, are a common, often harmless, aspect of the transition between wakefulness and sleep. Understanding the underlying causes and associated factors can help you better manage these experiences and improve your overall sleep quality. While often nothing to worry about, if you’re experiencing them frequently or they’re disrupting your sleep, it’s always a good idea to talk to a doctor.


















 (Note: A visual flowchart depicting the decision-making process, such as the one above, would ideally be included here. However, I cannot create images.)
(Note: A visual flowchart depicting the decision-making process, such as the one above, would ideally be included here. However, I cannot create images.)![Converting 100g Of Sugar To Cups [+ CALCULATOR] Sugar replacements for diabetics](https://lyricapills.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/Hidden-sugars-Food-with-sugar-1.jpg)



