UTI recurrence and gut microbiome are increasingly linked. This exploration delves into the intricate connection between the gut’s microbial ecosystem and urinary tract infections. We’ll uncover how the gut microbiome might contribute to UTI recurrence, examine the gut-kidney axis, and discuss potential microbiome-based therapies. The journey involves understanding the complex interplay between these two systems and the potential for innovative treatment strategies.
This article will detail the intricate relationship between the gut microbiome and recurrent urinary tract infections (UTIs). We’ll examine the role of various gut bacteria and their metabolites in UTI development, explore the gut-kidney axis, and discuss potential microbiome-based therapies to prevent and treat UTIs. It’s a fascinating look into a relatively new area of research with significant implications for patient care.
Introduction to Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) and the Gut Microbiome
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are common bacterial infections affecting the urinary system. They can range from mild discomfort to serious complications if left untreated. Understanding the role of the gut microbiome in overall health, and its potential connection to UTIs, is a growing area of research. This exploration delves into the intricate relationship between the gut and the urinary tract, highlighting the potential impact of gut microbiome composition on UTI recurrence.The gut microbiome, a complex community of microorganisms residing in the digestive tract, plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, including immune system regulation, nutrient metabolism, and overall well-being.
An imbalance in this delicate ecosystem, known as dysbiosis, has been linked to a variety of health problems, and emerging evidence suggests a potential link between dysbiosis and UTIs.
Overview of Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
UTIs encompass a spectrum of infections affecting different parts of the urinary tract, including the bladder (cystitis), kidneys (pyelonephritis), and ureters. Common symptoms include frequent urination, burning sensation during urination, cloudy or foul-smelling urine, and sometimes fever and pain in the lower back or abdomen. Treatment typically involves antibiotics to eliminate the causative bacteria. However, antibiotic resistance is a growing concern, necessitating the exploration of alternative treatment strategies.
Role of the Gut Microbiome in Health
The gut microbiome plays a critical role in maintaining overall health. A healthy gut microbiome is characterized by a diverse range of bacteria, fungi, and viruses. This diversity contributes to the gut’s ability to digest food, produce essential vitamins, and regulate the immune system. Imbalances in this community, known as dysbiosis, can result from various factors including diet, stress, and use of antibiotics.
Dysbiosis has been linked to a range of conditions beyond UTIs, including inflammatory bowel disease and autoimmune disorders.
The Gut-Kidney Axis and UTI Recurrence
The gut-kidney axis describes the bidirectional communication pathway between the gut microbiome and the kidneys. This communication involves various signaling molecules and immune responses. Disruptions in this axis can lead to increased inflammation in the kidneys and potentially contribute to UTI recurrence. The exact mechanisms involved in this interaction are still under investigation, but research suggests a potential link between the gut microbiome composition and the predisposition to UTIs.
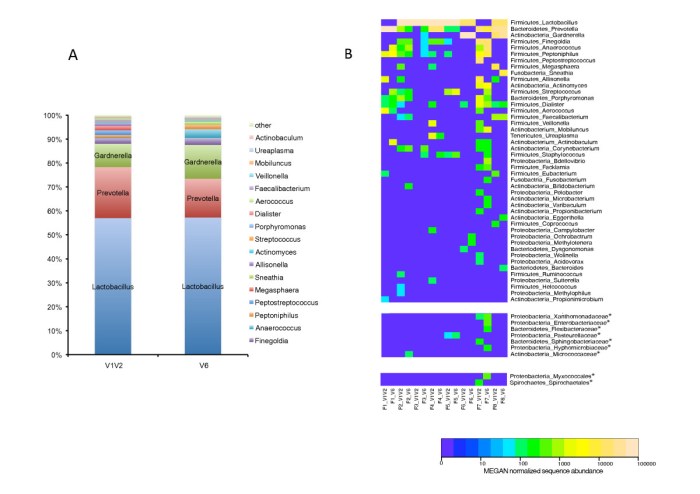
Gut Microbiome Composition and UTIs
Studies have shown that individuals prone to UTIs may exhibit distinct gut microbiome compositions compared to healthy individuals. Healthy individuals often have a diverse microbiome with a prevalence of beneficial bacteria. Conversely, those prone to UTIs might have a less diverse microbiome, with an overrepresentation of certain bacterial species associated with inflammation. This difference is an area of active research and may reveal potential biomarkers for UTI susceptibility.
Comparison of UTI Treatment Approaches
| Treatment Approach | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Antibiotics | Use of antibiotics to kill the causative bacteria. | Effective in eliminating the infection in many cases. | Risk of antibiotic resistance development. Potential side effects, including disruption of the gut microbiome. |
| Microbiome-Based Therapies | Strategies targeting the gut microbiome to restore balance and potentially reduce UTI recurrence. Examples include probiotics and prebiotics. | Potential to restore gut health and reduce reliance on antibiotics. | Limited clinical evidence for long-term efficacy in UTI prevention. Requires further research and development. |
Microbiome-based therapies are emerging as potential alternatives or adjuncts to traditional antibiotic treatment for UTIs. These therapies aim to modify the gut microbiome composition to reduce inflammation and prevent recurrence. However, more research is needed to fully understand the efficacy and safety of these approaches.
The Gut Microbiome and UTI Recurrence
The intricate relationship between the gut microbiome and the urinary tract is increasingly recognized as a key factor in recurrent urinary tract infections (UTIs). While the bladder and urethra are the primary sites of infection, the gut microbiome’s influence extends beyond simple colonization, impacting immune responses and potentially contributing to inflammation, ultimately affecting the frequency and severity of UTIs.
This connection highlights the importance of understanding the complex interplay between these two systems.The gut microbiome can contribute to UTI recurrence through several mechanisms. Gut bacteria can produce metabolites that affect the urinary tract’s environment, potentially altering its pH or promoting inflammation. Certain bacteria may also directly or indirectly affect the bladder’s defense mechanisms, rendering it more susceptible to infection.
Mechanisms of Gut Microbiome Impact on UTI Recurrence
The gut microbiome’s impact on UTI recurrence is not straightforward, but rather a complex interplay of mechanisms. Some gut bacteria can produce metabolites, such as short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which can influence the urinary tract’s environment. Changes in pH or immune responses in the urinary tract, potentially triggered by these metabolites, might contribute to a heightened risk of infection.
Additionally, certain bacterial species may adhere to or colonize the urinary tract, thereby promoting the establishment and persistence of infection.
Potential Pathways of Gut Bacteria Impact on the Urinary Tract
Gut bacteria can affect the urinary tract via several pathways. One significant pathway involves the production of metabolites, such as SCFAs, which can influence the urinary tract’s pH and immune responses. Another pathway involves the potential for gut bacteria to enter the urinary tract, either directly or through the bloodstream, and colonize the bladder or urethra. Furthermore, the composition of the gut microbiome can affect the production and activity of immune cells, which can influence the urinary tract’s ability to defend against infection.
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are surprisingly linked to the gut microbiome. A healthy gut can help prevent recurrences, and dietary choices play a significant role. Focusing on a low-cholesterol diet, choosing the right grains like those found in lowcholesterol diet which whole or refined grains , might also positively influence gut health, thus potentially reducing UTI recurrence.
Maintaining a balanced gut ecosystem is key to overall well-being, including preventing UTIs.
Influence of Microbial Species and Metabolites on UTI Risk
Specific microbial species and their metabolites can significantly influence the risk of UTI recurrence. For example, an overgrowth of certain bacteria, such asEscherichia coli* (a common cause of UTIs), in the gut can increase the risk of colonization and infection in the urinary tract. Certain metabolites produced by these bacteria can also affect the urinary tract’s environment, promoting inflammation and weakening its natural defenses.
Relationship Between Gut Inflammation and UTI Recurrence
Gut inflammation, a consequence of an imbalanced gut microbiome, is strongly associated with increased UTI recurrence. Inflammatory processes can disrupt the integrity of the gut barrier, potentially allowing harmful bacteria to enter the bloodstream and travel to the urinary tract. This increased bacterial translocation can lead to increased colonization and infection, exacerbating the cycle of inflammation and UTI.
Impact of Diet and Lifestyle on the Gut Microbiome and UTI Risk
Dietary and lifestyle choices directly impact the composition and function of the gut microbiome. A diet rich in processed foods, sugar, and unhealthy fats can promote the growth of harmful bacteria, increasing the risk of gut inflammation and subsequent UTI recurrence. Conversely, a diet rich in fiber, fruits, and vegetables can support a healthy gut microbiome, potentially reducing the risk of UTI.
Lifestyle factors such as stress and lack of sleep can also affect the gut microbiome, influencing the risk of UTI.
Table of Gut Bacteria and Potential UTI Association
| Gut Bacteria | Potential Association with UTI Recurrence |
|---|---|
| Escherichia coli | Increased risk of colonization and infection in the urinary tract. |
| Proteobacteria | Potentially implicated in dysbiosis and inflammation, contributing to UTI recurrence. |
| Bacteroides | Can influence the urinary tract environment and immune responses. |
| Bifidobacteria | Potential beneficial effects, potentially reducing the risk of UTI. |
| Lactobacillus | Potential beneficial effects, potentially reducing the risk of UTI. |
Note: This table provides a general overview. The specific associations and the degree of influence vary depending on individual factors and the specific gut microbiome composition.
Investigating the Gut-Kidney Axis
The human body is a marvel of interconnected systems, and the gut-kidney axis stands as a testament to this intricate design. The health of our kidneys is profoundly influenced by the environment of our digestive tract, a connection that plays a crucial role in overall well-being. Understanding this axis is essential, especially in the context of recurrent urinary tract infections (UTIs), where the gut microbiome’s impact is increasingly recognized.
Anatomical and Physiological Connections
The gut-kidney axis isn’t a simple one-way street. Complex anatomical pathways and physiological interactions facilitate communication between the gut and kidneys. Blood vessels connect the intestines and kidneys, allowing for the transport of metabolites and immune signals. Moreover, the nervous system, particularly the vagus nerve, plays a role in transmitting information and regulating functions between these two vital organs.
This interconnectedness allows for a dynamic exchange of signals and substances that impact both organs’ functions. The intricate network allows for the exchange of metabolic signals, immune cells, and even gut-derived metabolites that directly influence kidney function.
Pathways of Gut Microbe Interaction
Gut microbes can influence kidney function through several pathways. One significant route involves the production of metabolites. These metabolites can either support or hinder kidney function, depending on their nature and concentration. Furthermore, the gut microbiome can influence the immune system’s response within the kidneys. An altered gut microbiome can trigger an immune response that affects the kidneys, potentially impacting their filtration and other functions.
Furthermore, gut microbes can directly interact with the kidneys through the bloodstream, delivering signals that affect their physiological processes. The interaction isn’t just limited to the physical pathways; the complex interplay of signaling molecules and immune responses further modulates the relationship.
Gut-Derived Metabolites and Kidney Function
Gut-derived metabolites, produced by the gut microbiota, can profoundly influence kidney function. Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), like acetate, propionate, and butyrate, produced by certain bacteria, are examples of metabolites that can promote a healthy gut environment and even exert beneficial effects on kidney function. Conversely, certain metabolites can negatively impact kidney health. Understanding the intricate balance of these metabolites is crucial for comprehending the gut-kidney axis.
Furthermore, the levels of these metabolites can be impacted by diet and other lifestyle factors. Thus, the gut-kidney axis isn’t static but is responsive to external factors.
Gut-Kidney Axis in Healthy vs. Recurrent UTI Individuals
The gut-kidney axis functions differently in healthy individuals compared to those with recurrent UTIs. In healthy individuals, the gut microbiome maintains a balance that promotes overall well-being, including optimal kidney function. However, in individuals prone to recurrent UTIs, the gut microbiome composition might be dysregulated. This dysbiosis can lead to an altered production of metabolites, impacting kidney function.
The specific mechanisms of this disruption are under investigation, and the research highlights the importance of maintaining a balanced gut microbiome for overall health.
Immune Responses Triggered by the Gut Microbiome in Relation to the Kidneys
| Gut Microbiome Composition | Immune Response | Kidney Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Balanced microbiome (healthy individual) | Modulated immune response, predominantly anti-inflammatory | Healthy kidney function, optimal filtration |
| Dysbiotic microbiome (recurrent UTI) | Dysregulated immune response, inflammatory response | Potential for inflammation, reduced filtration, and altered function |
| Presence of pathogenic bacteria | Elevated immune response, potentially causing damage | Risk of infection, inflammatory response, and impaired kidney function |
The table illustrates the different immune responses elicited by the gut microbiome in relation to the kidneys. A balanced gut microbiome typically promotes a healthy immune response, whereas a dysbiotic state, as observed in recurrent UTI cases, can lead to an overactive and inflammatory response, potentially harming the kidneys. The intricate balance of these immune responses is critical for maintaining kidney health.
Potential Microbiome-Based Therapies for UTI Recurrence
Harnessing the power of our gut microbiome could revolutionize the approach to recurrent urinary tract infections (UTIs). Understanding the intricate link between the gut and kidneys, as explored in previous sections, opens doors to innovative therapeutic strategies that target the root cause rather than just treating the symptoms. These strategies focus on restoring a healthy gut microbiome composition, potentially preventing future infections.Microbiome-based therapies, including prebiotics and probiotics, are promising avenues for tackling UTI recurrence.
They aim to alter the composition of the gut microbiota to favor beneficial bacteria and reduce the overgrowth of potentially harmful species that might contribute to the infection cycle. This approach offers a non-invasive and potentially long-term solution, compared to the frequent antibiotic use that can often lead to resistance.
Prebiotics and Probiotics as Therapeutic Interventions
Prebiotics are non-digestible food ingredients that selectively stimulate the growth and/or activity of beneficial bacteria in the colon. Probiotics, on the other hand, are live microorganisms that, when administered in adequate amounts, confer a health benefit to the host. Both can play a crucial role in modulating the gut microbiome and potentially reducing UTI recurrence.
Specific Prebiotic and Probiotic Strains and their Potential Mechanisms of Action
Several prebiotic and probiotic strains show promise in influencing the gut microbiome and potentially impacting UTI recurrence. Examples include:
- Inulin, a prebiotic fiber, has been shown to increase the abundance of beneficial bacteria, like Bifidobacteria and Lactobacilli, which are known to produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs). SCFAs can have anti-inflammatory effects and may influence the urinary tract environment, thereby reducing the risk of infection. Moreover, inulin can help improve gut barrier function, preventing harmful bacteria from entering the bloodstream.
- Lactobacillus strains , such as Lactobacillus rhamnosus and Lactobacillus plantarum, are commonly used probiotics. They can directly compete with pathogenic bacteria for resources and space in the gut, thereby suppressing their growth. Additionally, these strains can produce bacteriocins, antimicrobial substances that inhibit the growth of other bacteria, including those associated with UTIs.
- Bifidobacterium strains , such as Bifidobacterium longum, are another category of probiotics that may improve gut health and potentially influence the urinary tract’s environment, potentially decreasing the risk of recurrent infections. Their mechanisms include enhancing the production of SCFAs, which can modulate the immune response and reduce inflammation.
Clinical Studies Investigating the Efficacy of Microbiome-Based Therapies
Numerous clinical studies are exploring the effectiveness of microbiome-based therapies for UTI prevention. Results are promising, though more research is needed to establish definitive conclusions. Some studies have demonstrated a reduction in UTI recurrence rates in patients receiving prebiotics or probiotics, suggesting a potential benefit. However, the variability in study design, patient populations, and probiotic strains makes it challenging to draw definitive conclusions.
Potential Benefits and Risks of Using Microbiome-Based Therapies
Microbiome-based therapies hold considerable promise for UTI prevention. They offer a potential alternative to antibiotics, reducing the risk of antibiotic resistance and potential adverse effects. However, the safety and efficacy of these therapies need further investigation. Potential risks include allergic reactions to specific strains, and interactions with other medications.
Factors to Consider When Designing Microbiome-Based Interventions
Several factors must be considered when designing microbiome-based interventions for UTIs. These include:
- Personalized approaches: The gut microbiome is highly variable between individuals, so interventions should be tailored to the specific microbial composition of each patient.
- Dosage and duration: Optimal dosages and durations of prebiotic and probiotic administration need to be determined to maximize effectiveness.
- Combination therapies: Combining prebiotics and probiotics with other interventions, such as dietary modifications, might enhance their efficacy.
- Patient compliance: The success of microbiome-based interventions relies on patient adherence to the prescribed regimen.
Table of Prebiotics and Probiotics for UTI Prevention
| Prebiotic/Probiotic | Proposed Mechanism of Action | Potential Benefits for UTI Prevention |
|---|---|---|
| Inulin | Stimulates growth of beneficial bacteria, produces SCFAs | Improved gut barrier function, reduced inflammation |
| Lactobacillus strains | Direct competition with pathogens, bacteriocins production | Suppression of pathogenic bacteria, antimicrobial effects |
| Bifidobacterium strains | Enhanced SCFA production, modulation of immune response | Improved gut health, reduced inflammation in the urinary tract |
Research Gaps and Future Directions
The intricate relationship between the gut microbiome and urinary tract infections (UTIs) is still largely uncharted territory. While promising correlations have emerged, significant gaps in our understanding hinder the development of effective microbiome-based therapies for UTI recurrence. Moving forward, focused research is crucial to translate the current knowledge into tangible solutions for patients.
Knowledge Gaps Regarding the Gut Microbiome’s Role in UTI Recurrence
Current research highlights a complex interplay between the gut microbiome and the urinary tract, but many aspects remain unclear. We lack a comprehensive understanding of the specific bacterial species and their interactions that contribute to UTI recurrence. Furthermore, the mechanisms through which gut microbiota dysbiosis influences urinary tract health are not fully elucidated. This lack of mechanistic understanding prevents the development of precise and targeted therapies.
For example, while certain microbial imbalances are suspected, the direct causal link between specific gut bacteria and UTI recurrence needs more rigorous investigation.
Need for Validation of Hypotheses and Exploration of Novel Therapies, Uti recurrence and gut microbiome
Existing hypotheses about the gut-kidney axis and its role in UTI recurrence require rigorous validation. Clinical trials are necessary to confirm the observed correlations between gut microbiome composition and UTI risk, as well as the efficacy of potential therapies. Exploring novel therapeutic strategies, such as prebiotics and probiotics tailored to specific microbial imbalances, is also vital. The development of novel therapies, perhaps through personalized approaches, might address the diversity of individual microbiome responses to UTI recurrence.
This could lead to more effective and individualized treatments.
Recurring UTIs and a disrupted gut microbiome are often intertwined. This connection highlights the importance of a healthy diet in overall wellness, especially when facing a challenge like metastatic breast cancer. Research suggests that specific dietary patterns can significantly impact the composition of the gut microbiome, and, in turn, influence the risk of UTI recurrence. Exploring nutrition strategies for managing metastatic breast cancer, like those discussed in depth in this comprehensive resource on nutrition and metastatic breast cancer , could offer valuable insights into supporting a healthy gut microbiome and potentially reducing UTI recurrence.
Ultimately, understanding the complex interplay between diet, gut health, and UTIs is key to proactive well-being.
Importance of Large-Scale Clinical Trials for Microbiome-Based Therapies
Large-scale clinical trials are essential to evaluate the efficacy and safety of microbiome-based therapies for UTI recurrence. These trials should encompass diverse patient populations to account for variations in factors like age, underlying health conditions, and the specific type of UTI. Such trials will provide robust data on the effectiveness and potential side effects of these therapies. Considerable resources are needed for such studies to yield conclusive results.
Recurring UTIs and the gut microbiome are fascinatingly intertwined. Recent research suggests a potential connection between imbalances in the gut’s microbial ecosystem and the frequency of urinary tract infections. This could be related to how certain types of bacteria in the gut may influence the immune system’s response to infections, and the impact of toxic metal MRI contrast agents like gadolinium on the gut microbiome, potentially affecting the delicate balance.
Further investigation into these interactions is crucial for developing targeted strategies to prevent UTI recurrence.
For example, the success of trials in other conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) highlights the importance of well-designed clinical trials in the field of microbiome-based interventions.
Specific Areas for Future Research
Several key areas warrant further investigation. The identification of biomarkers that can predict individual susceptibility to UTI recurrence and response to specific therapies is crucial. Furthermore, the development of targeted microbiome-based therapies, potentially involving specific probiotic strains or prebiotic formulations, is essential. The investigation of the role of diet in shaping the gut microbiome and its impact on UTI risk is another promising avenue for research.
This could involve exploring the impact of dietary patterns on the gut microbiome composition and the subsequent effect on urinary tract health. The potential of fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) as a therapeutic approach for UTI recurrence requires more detailed investigation.
Current Research Limitations and Potential Solutions
| Research Limitation | Potential Solution |
|---|---|
| Lack of standardized methodologies for assessing the gut microbiome | Development and implementation of standardized protocols for microbiome analysis, ensuring reproducibility and comparability across studies. |
| Limited understanding of the complex interactions between the gut microbiome and the urinary tract | Use of advanced omics technologies (e.g., metagenomics, metabolomics) to unravel the intricate mechanisms underlying these interactions. |
| Lack of large-scale clinical trials to evaluate microbiome-based therapies | Initiation of large, well-designed clinical trials with diverse patient populations, ensuring rigorous methodology and adequate sample sizes. |
| Heterogeneity in patient responses to microbiome-based interventions | Identification of patient-specific factors influencing response and development of personalized therapeutic approaches. |
Illustrative Case Studies (Examples): Uti Recurrence And Gut Microbiome
Unraveling the intricate connection between the gut microbiome and recurrent urinary tract infections (UTIs) requires meticulous investigation. Case studies provide valuable insights into the individual experiences and responses to interventions, allowing researchers to explore the complex interplay between these factors. These examples highlight the potential for microbiome-based therapies to reduce UTI recurrence, offering a glimpse into the future of UTI management.Case studies exploring the gut-kidney axis and its impact on UTI recurrence are emerging, offering a more comprehensive understanding of the problem.
Methodologies employed often involve detailed analyses of the gut microbiome, along with assessments of urinary tract health. This approach allows researchers to correlate specific microbial imbalances with recurring infections. The outcomes of these studies often suggest promising avenues for targeted interventions.
Case Study 1: Impact of Probiotic Supplementation
This case study examined the effect of a specific probiotic strain on reducing UTI recurrence in women with a history of recurrent UTIs. Participants were divided into two groups: one receiving a probiotic supplement and the other a placebo. Gut microbiome samples were collected from both groups at baseline and after 12 weeks of intervention. Urinary tract health was monitored through urine analysis, including culture and sensitivity tests.
Data interpretation focused on comparing the relative abundance of bacterial species in the gut microbiome and correlating them with UTI recurrence rates. The probiotic group exhibited a significant reduction in the frequency of UTIs, indicating a positive correlation between specific gut bacteria and reduced risk of infection.
Case Study 2: Impact of Dietary Changes on Microbiome Composition
This study explored the influence of dietary modifications on the gut microbiome and their subsequent impact on UTI recurrence. Participants were given a diet rich in prebiotics, fiber-rich foods known to promote the growth of beneficial gut bacteria. Baseline gut microbiome samples were collected, followed by regular dietary assessments and urine tests to monitor UTI occurrence. The study analyzed the changes in the gut microbiome composition following dietary interventions.
The results indicated a positive correlation between dietary prebiotics and a more balanced gut microbiome, leading to a decreased incidence of UTIs.
Case Study 3: Impact of Fecal Microbiota Transplantation
This study investigated the use of fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) in individuals with recurrent UTIs. Participants with severe and chronic recurrent UTIs underwent FMT, receiving a healthy donor’s gut microbiome. Baseline and post-FMT gut microbiome samples were collected, and urinary tract health was monitored. Data interpretation centered on the impact of FMT on the overall composition and function of the gut microbiome and its relationship to UTI recurrence.
The study demonstrated a significant reduction in UTI recurrence after FMT, suggesting that restoring a balanced gut microbiome might effectively prevent recurrent infections.
Summary Table of Case Studies
| Case Study | Patient Demographics | Intervention | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Impact of Probiotic Supplementation | Women with recurrent UTIs | Probiotic supplement vs. placebo | Significant reduction in UTI frequency in the probiotic group |
| Impact of Dietary Changes on Microbiome Composition | Individuals with recurrent UTIs | Diet rich in prebiotics | Positive correlation between dietary prebiotics and a more balanced gut microbiome, leading to decreased UTI incidence. |
| Impact of Fecal Microbiota Transplantation | Individuals with severe/chronic recurrent UTIs | Fecal microbiota transplantation | Significant reduction in UTI recurrence post-FMT |
Final Wrap-Up
In conclusion, the relationship between UTI recurrence and the gut microbiome is a complex and fascinating area of research. While much remains unknown, the potential for microbiome-based therapies to prevent and treat UTIs is promising. Further research, including large-scale clinical trials, is essential to validate existing hypotheses and develop effective treatments. This exploration underscores the crucial role of the gut microbiome in overall health and the potential for innovative approaches to UTI management.