Lactic acid skin care – Lactic acid skincare is a trending topic for a reason. This gentle chemical exfoliant is revolutionizing skin routines, promising smoother textures, brighter tones, and a more youthful appearance. We’ll delve into the science behind lactic acid, exploring its benefits, how it works, and how to incorporate it safely into your skincare regimen.
From addressing acne scars and hyperpigmentation to improving hydration and reducing the look of wrinkles, lactic acid offers a versatile approach to skincare. We’ll cover everything you need to know to confidently navigate the world of lactic acid treatments, from product types to safe usage practices.
Introduction to Lactic Acid Skincare
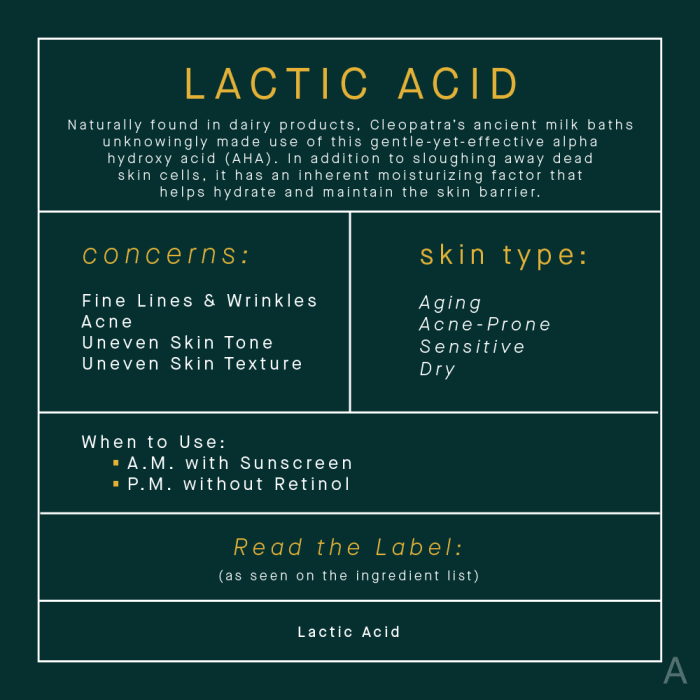
Lactic acid, a naturally occurring alpha-hydroxy acid (AHA), has gained significant traction in the skincare world for its exfoliating and moisturizing properties. Its gentle yet effective action helps improve skin texture, tone, and overall appearance. This detailed exploration will delve into the chemical makeup, historical use, and practical applications of lactic acid in skincare.Lactic acid, chemically known as 2-hydroxypropanoic acid, is a water-soluble carboxylic acid.
Its unique chemical structure allows it to interact with the skin’s surface, dissolving dead skin cells and promoting cell turnover. This process, when carefully managed, leads to a smoother, brighter complexion. Its acidic nature, while crucial for its exfoliating effects, is balanced by its moisturizing properties. This dual functionality is a key reason for its popularity.
Chemical Properties Relevant to Skincare
Lactic acid’s chemical structure allows it to act as a humectant, drawing moisture to the skin’s surface. This is a crucial factor in its ability to hydrate and soften the skin. Its alpha-hydroxy acid (AHA) classification is significant. AHAs work by breaking down the bonds between dead skin cells, facilitating their removal and allowing newer, healthier skin cells to rise to the surface.
This process is crucial for improved skin texture and tone. Its pH level, typically in the range of 1.5 to 3.0, is important in the context of skincare, influencing its effectiveness and potential for skin irritation.
Historical Use in Skincare
Lactic acid’s use in skincare has a long history, originating from its natural presence in fermented milk products. Historically, these products were used to improve skin health and complexion. The understanding of lactic acid’s exfoliating properties has evolved over time, leading to its inclusion in modern skincare formulations. Traditional cultures have recognized the benefits of fermented milk products for their skin-enhancing properties, foreshadowing modern scientific understanding of lactic acid’s role in skin health.
Common Forms and Concentrations
Lactic acid is available in various forms for skincare purposes, including liquids, lotions, and serums. The concentration of lactic acid in these products varies. Common concentrations range from 5% to 20%, with lower concentrations suitable for sensitive skin. Higher concentrations may be used for more significant results but carry a higher risk of irritation. The concentration selection is critical to balancing efficacy and skin tolerance.
| Concentration (%) | Typical Use | Skin Sensitivity |
|---|---|---|
| 5-10 | General exfoliation and hydration | Low |
| 10-15 | Targeted exfoliation for more visible results | Moderate |
| 15-20 | Significant exfoliation, but use cautiously | High |
Skin Concerns Addressed
Lactic acid effectively addresses several skin concerns. It is commonly used to treat acne scars, hyperpigmentation, and fine lines. Its ability to gently exfoliate and hydrate makes it a valuable ingredient for uneven skin tone and texture. Its moisturizing properties also help in maintaining skin hydration. Furthermore, its gentle exfoliating action promotes cell turnover, contributing to a more youthful and radiant complexion.
Benefits of Lactic Acid
Lactic acid, a gentle chemical exfoliant derived from fermented sugars, has gained popularity in skincare routines. Its unique properties offer a range of benefits for skin health and appearance. It works by dissolving the bonds between dead skin cells, promoting cell turnover, and improving the skin’s overall texture.Lactic acid’s multifaceted effects extend beyond simple exfoliation, influencing hydration, tone, and even the appearance of wrinkles.
This comprehensive approach makes it a valuable addition to any skincare regimen, contributing to a healthier and more radiant complexion.
Exfoliating Properties and Skin Texture
Lactic acid’s gentle exfoliation process effectively removes dead skin cells, revealing brighter, smoother skin underneath. This process, when used consistently, can improve skin texture by reducing the appearance of roughness and unevenness. By promoting cell turnover, lactic acid helps to create a more unified and refined skin surface, minimizing the look of pores and fine lines. This improvement in skin texture leads to a more even tone and a healthier overall appearance.
Skin Hydration and Moisture Retention
Lactic acid’s humectant properties draw moisture from the air into the skin, boosting hydration levels. This process helps to retain moisture, which is crucial for maintaining skin elasticity and preventing dryness. The acid’s ability to increase the skin’s hydration is important because a properly hydrated skin is a healthier skin. Maintaining optimal moisture levels with lactic acid helps create a supple and plump complexion, contributing to a more youthful and vibrant appearance.
Improving Skin Tone and Reducing Hyperpigmentation
Lactic acid’s exfoliating action can help to even out skin tone by removing uneven layers of pigmentation. By encouraging cell turnover and removing discoloration from the surface, lactic acid can effectively reduce the appearance of hyperpigmentation. This process can also help to reduce the appearance of dark spots and age spots, making the complexion more unified and luminous.
The result is a more radiant and even-toned complexion.
Reducing Wrinkles and Fine Lines
Lactic acid’s ability to stimulate collagen production and improve skin hydration plays a role in reducing the appearance of wrinkles and fine lines. By plumping the skin and promoting elasticity, lactic acid helps to smooth out the skin, leading to a more youthful and rejuvenated appearance. This improvement in skin texture can help to minimize the visibility of wrinkles and fine lines, giving the skin a smoother and more youthful look.
Comparison to Other Chemical Exfoliants
| Exfoliant | Exfoliation Type | Skin Hydration | Hyperpigmentation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lactic Acid | Gentle | High | Moderate |
| Glycolic Acid | Moderate | Moderate | High |
| Salicylic Acid | Moderate to Strong | Low | Moderate |
This table highlights the different characteristics of various chemical exfoliants. While lactic acid offers a gentle exfoliation with a high degree of hydration, other acids may provide stronger exfoliation but with different effects on hydration and hyperpigmentation. Understanding these differences helps in tailoring a skincare routine to individual needs.
How Lactic Acid Works
Lactic acid, a naturally occurring alpha-hydroxy acid (AHA), gently exfoliates and rejuvenates the skin. Its unique mechanism of action involves several key processes, affecting skin cells and promoting a healthier complexion. Understanding these processes is crucial for harnessing the benefits of lactic acid in skincare routines.
Mechanism of Dead Skin Cell Removal
Lactic acid’s exfoliating properties are attributed to its ability to dissolve the bonds between dead skin cells. Its low pH effectively softens and breaks down the protein structures that bind these cells together. This process is a gentle form of chemical exfoliation, allowing for the natural shedding of dead skin cells. This, in turn, reveals the brighter, healthier skin cells beneath.
Stimulation of Collagen Production
Lactic acid promotes collagen production by encouraging cell turnover and stimulating fibroblasts, the cells responsible for collagen synthesis. This increased collagen production leads to firmer, more elastic skin, reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles. Studies have shown that regular use of lactic acid can enhance skin elasticity and improve overall skin texture.
Impact on Skin Barrier Function
Lactic acid, when used correctly, can actually strengthen the skin barrier. It moisturizes and hydrates the skin, increasing its resilience to environmental stressors. This is crucial because a healthy skin barrier protects against moisture loss and external irritants. By maintaining the skin barrier, lactic acid helps the skin retain its natural moisture, preventing dryness and irritation.
Improvement of Skin Elasticity
The increased collagen production and hydration provided by lactic acid contribute significantly to improved skin elasticity. As collagen is a crucial component of skin structure, its replenishment leads to a noticeable reduction in wrinkles and an overall more youthful appearance. By supporting the skin’s natural structural integrity, lactic acid effectively helps to enhance its elasticity.
Stages of Lactic Acid’s Effect on Skin Cells
Understanding the different stages of lactic acid’s interaction with skin cells provides insight into its overall effect.
| Stage | Process | Effect on Skin |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Application | Lactic acid dissolves the bonds between dead skin cells, causing a softening effect. | The skin feels smoother and more hydrated. Early signs of brighter skin are noticeable. |
| Cell Turnover Acceleration | The skin’s natural cell turnover process is accelerated, with new, healthier skin cells emerging. | The skin appears brighter and more even-toned. The appearance of fine lines and wrinkles may diminish. |
| Collagen Stimulation | Fibroblasts, the cells responsible for collagen production, are stimulated. Collagen production increases. | The skin becomes firmer and more elastic. Wrinkles and fine lines are reduced. |
| Skin Barrier Strengthening | The skin’s moisture barrier is strengthened. The skin retains hydration more effectively. | The skin feels supple and resilient. It is better protected against environmental stressors. |
Types of Lactic Acid Products
Lactic acid, a gentle chemical exfoliant, is available in various skincare product formats. Each format offers unique advantages and caters to different skin concerns and application preferences. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the most effective and suitable lactic acid product for your skin type.Different product formulations influence how lactic acid interacts with the skin. The concentration, delivery method, and accompanying ingredients all play a role in its efficacy and potential irritation.
Product Formats and Their Applications
Different product formats deliver lactic acid to the skin in varying ways, affecting its penetration and efficacy. This section details the common formats and their suitability.
| Product Type | Application | Typical Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Serum | Targeted application, often after cleansing | Improving skin texture, reducing hyperpigmentation, promoting hydration, and evening skin tone. |
| Toner | Used after cleansing, before moisturizing | Balancing skin pH, prepping skin for subsequent products, and providing gentle exfoliation. |
| Moisturizer | Applied as a final step in the skincare routine | Delivering lactic acid while providing hydration and soothing the skin, often suitable for those with sensitive skin. |
| Exfoliating Masks | Localized application for a targeted exfoliation treatment. | Deep exfoliation, improving skin tone and texture. Often used less frequently than other lactic acid products. |
Comparing Product Effectiveness
The effectiveness of lactic acid products depends on factors like concentration, delivery system, and additional ingredients. Serums, typically containing higher concentrations of lactic acid, can offer faster results in terms of exfoliation and skin improvement, but may be more irritating for sensitive skin types. Toners, with lower concentrations, provide gentler exfoliation and are often well-tolerated by sensitive skin.
I’ve been loving incorporating lactic acid into my skincare routine lately. It’s amazing for exfoliation and brightening. While I’m focusing on glowing skin, I’ve also been exploring natural alternatives to ozempic natural alternatives to ozempic for managing my health goals. It’s all about finding holistic solutions, and lactic acid definitely fits the bill for a healthy glow from the inside out, and now I’m on a mission to try out more of these natural solutions for my skin!
Moisturizers, often formulated with lower concentrations and humectants, can effectively hydrate while gently exfoliating, making them a good option for those seeking a more comprehensive skincare solution. Exfoliating masks provide a concentrated dose of lactic acid, suitable for deep exfoliation treatments, but should be used sparingly to avoid skin irritation.
Ideal Products for Different Skin Types
Determining the ideal lactic acid product for a specific skin type requires careful consideration. Sensitive skin may benefit from lower concentrations found in toners or moisturizers, while those with oily or acne-prone skin might find serums more effective. Those with dry or mature skin may prefer moisturizers with lactic acid to maintain hydration.
Product Compatibility and Ingredient Interactions
Compatibility and ingredient interactions are important to consider when incorporating lactic acid into a skincare routine. Some ingredients can enhance or hinder lactic acid’s efficacy or cause irritation. For instance, products containing AHAs (like glycolic acid) or BHAs (like salicylic acid) can be used in conjunction with lactic acid, but the optimal concentration and frequency should be determined based on individual skin responses.
Additionally, products containing retinoids or vitamin C should be carefully incorporated into a routine with lactic acid. Consult a dermatologist or esthetician for personalized advice on combining lactic acid with other active ingredients.
Using Lactic Acid Safely
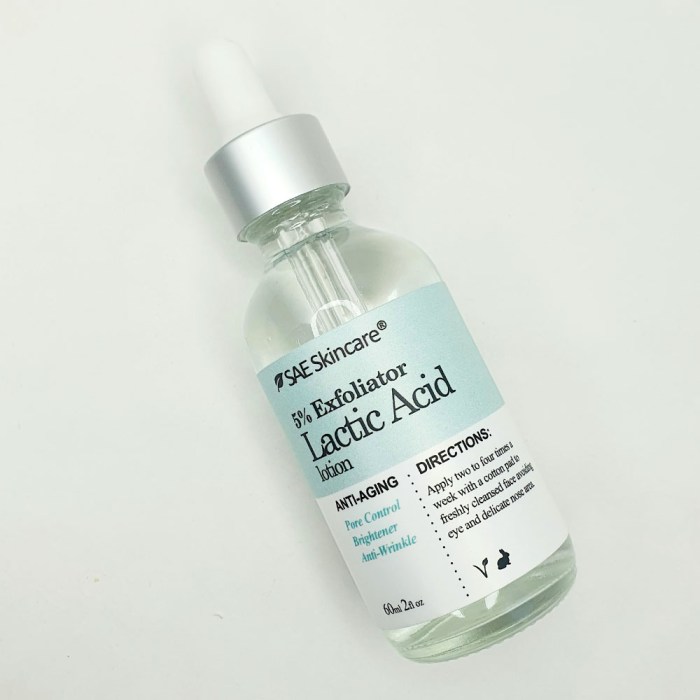

Lactic acid, while a powerful exfoliant, requires careful application to prevent irritation and achieve optimal results. Understanding its safe usage is crucial for experiencing its benefits without setbacks. This section delves into the appropriate application methods, pre-emptive measures to avoid issues, and how to address any potential problems that may arise.
Appropriate Usage
Lactic acid is best used in a gradual and controlled manner. Starting with a low concentration (2-5%) is recommended, especially for those with sensitive skin. Applying lactic acid once or twice a week is a common starting point. Increasing the frequency or concentration should be done gradually, monitoring your skin’s reaction closely. Products containing lactic acid should be applied after cleansing and toning, and ideally, after using a gentle serum.
Avoid using other active ingredients like AHAs or BHAs on the same day. Always follow the product instructions carefully.
Patch Testing
A crucial step before incorporating lactic acid into your routine is patch testing. Applying a small amount of the product to a discreet area, such as the inside of your forearm, allows your skin to react to the substance in a contained environment. Observe the area for any signs of irritation, redness, or other adverse reactions for at least 24-48 hours.
If no negative reaction occurs, you can proceed with using the product on a larger area of your face, starting with a lower frequency and concentration.
Potential Side Effects and Management
Lactic acid, like other exfoliants, can sometimes cause mild side effects, such as redness, dryness, or stinging. These reactions are often temporary and resolve on their own with continued, careful use. If you experience significant redness, burning, or swelling, discontinue use immediately and consult a dermatologist. Moisturizing regularly and using a lower concentration of lactic acid can help manage these side effects.
A gentle, hydrating serum or cream can help soothe any irritation.
Lactic acid skincare is a popular choice for brightening and smoothing skin. Beyond its surface benefits, it might also play a role in boosting your body’s natural defenses, potentially increasing white blood cell activity, which are crucial for fighting infections. Learning more about how to increase white blood cells could lead to a better understanding of the overall health benefits of lactic acid, further supporting its use in skincare routines.
Ultimately, incorporating lactic acid into your regimen could have a multifaceted impact on your skin’s health and well-being.
Incorporating Lactic Acid into Your Routine
Creating a routine that effectively integrates lactic acid requires careful planning. Start by selecting a lactic acid product with a suitable concentration for your skin type and sensitivity level. Apply the product after cleansing and toning, and before moisturizing. If your skin is particularly sensitive, consider layering the product with a hydrating serum. Use a lower concentration and a reduced frequency (e.g., once every other day) to allow your skin to adjust.
Consistency is key, but always listen to your skin’s cues and adjust the routine accordingly.
Frequency and Concentration
The frequency and concentration of lactic acid use should be tailored to individual skin needs and reactions. Start with a low concentration (e.g., 5%) and apply it once or twice a week. Gradually increase the frequency and concentration over time, observing your skin’s response closely. If irritation occurs, reduce the frequency or concentration immediately. Always prioritize your skin’s comfort and well-being.
A dermatologist can provide personalized guidance based on your specific skin type and concerns.
Lactic Acid and Specific Skin Concerns
Lactic acid, a gentle alpha-hydroxy acid (AHA), is increasingly popular for its ability to address a wide range of skin concerns. Beyond its general exfoliating properties, lactic acid’s unique characteristics make it beneficial for various skin types and conditions. Its moisturizing effect and ability to gently dissolve dead skin cells contribute to improved skin tone, texture, and overall health.Lactic acid’s effectiveness stems from its ability to gently exfoliate and hydrate the skin.
It promotes cell turnover, revealing smoother, brighter skin. This gradual resurfacing also helps to fade imperfections and improve the appearance of various skin issues, from acne scars to hyperpigmentation. Importantly, lactic acid’s humectant properties draw moisture into the skin, making it ideal for those with dry or sensitive skin.
Acne Scars
Lactic acid’s exfoliating properties can help to improve the appearance of acne scars by gently removing the damaged skin cells. As new, healthy skin cells rise to the surface, the overall texture of the scar can become less noticeable. The gradual, controlled resurfacing promotes a more even skin tone and minimizes the appearance of pitted scars. This effect is often more pronounced when used in conjunction with a consistent skincare routine and other suitable treatments.
I’ve been exploring lactic acid skincare lately, and it’s fascinating how different ingredients can affect our skin. While I’m finding it effective for my skin concerns, I’ve also learned that some women experience migraine symptoms, and it’s important to understand the potential contributing factors. For instance, checking out the causes of migraine symptoms in females can help identify potential triggers, including some skincare products.
causes of migraine symptoms in females Ultimately, I’m still focused on finding the best lactic acid routine for my skin without causing any unwanted reactions. It’s a balancing act, for sure!
Hyperpigmentation and Sunspots
Lactic acid’s gentle exfoliation can help to lighten hyperpigmentation and sunspots by removing the layers of skin that contain the darkened pigments. The improved cell turnover promotes the production of new, brighter skin cells, leading to a more even skin tone. However, the results can vary depending on the severity and duration of the hyperpigmentation. Consistent use of a lactic acid product, along with sun protection, is key for optimal results.
Dry and Sensitive Skin
Lactic acid, despite its exfoliating properties, is surprisingly gentle on dry and sensitive skin. Its humectant properties attract and retain moisture, effectively hydrating the skin. This moisturizing action helps to soothe dry patches and reduce the appearance of irritation. By gently removing dead skin cells, lactic acid promotes healthier skin cell function, further contributing to the skin’s natural moisture barrier.
Carefully selected lactic acid concentrations are crucial for sensitive skin, with lower concentrations often recommended.
Aging Skin
Lactic acid’s ability to stimulate collagen production and improve skin elasticity contributes to a more youthful appearance. The gentle exfoliation helps to remove dull, damaged skin cells, revealing brighter, healthier skin underneath. This contributes to a reduction in the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, though it’s important to note that significant results might take time and consistent use.
Skin Texture and Uneven Tone
Lactic acid’s gradual exfoliation process effectively reduces the appearance of rough skin textures and uneven skin tone. By promoting cell turnover and encouraging the growth of new, healthy skin cells, lactic acid helps to create a smoother, more uniform complexion. This effect is often visible over time, with consistent application.
Lactic Acid Application for Different Skin Conditions
| Skin Concern | Lactic Acid Application | Expected Results |
|---|---|---|
| Acne Scars | Use a product with a low to medium concentration of lactic acid, incorporated into a consistent skincare routine. | Improved skin texture, reduced appearance of pitted scars, and a more even skin tone. |
| Hyperpigmentation and Sunspots | Use a product with a low to medium concentration of lactic acid, gradually increasing concentration as tolerated. Employing sun protection is crucial. | Lightened hyperpigmentation and sunspots, improved skin tone. |
| Dry and Sensitive Skin | Start with a very low concentration of lactic acid and gradually increase as tolerated. Look for products with moisturizing ingredients. | Improved hydration, reduced dryness, and a smoother skin texture. |
| Aging Skin | Use a product with a moderate concentration of lactic acid, incorporating it into a consistent skincare routine, and use in conjunction with other anti-aging treatments. | Improved skin elasticity, reduced appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, and a more youthful complexion. |
| Skin Texture and Uneven Tone | Use a product with a low to moderate concentration of lactic acid, gradually increasing concentration as tolerated. | Smoother skin texture, reduced appearance of uneven skin tone, and a more even complexion. |
Lactic Acid and Formulation Considerations
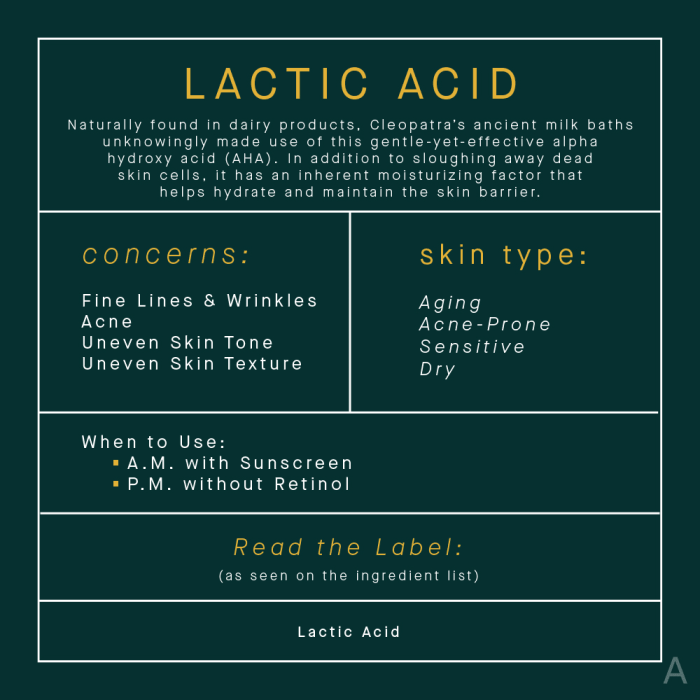
Lactic acid’s effectiveness in skincare isn’t solely determined by its concentration; the interplay with other ingredients and the overall product formulation plays a crucial role. Understanding how lactic acid interacts with various components is key to creating effective and safe products. This section delves into the nuances of lactic acid formulations, from concentration levels to synergistic pairings and potential pitfalls.Formulating skincare products with lactic acid requires careful consideration of concentration, ingredient compatibility, and the desired outcome.
The concentration of lactic acid significantly impacts its exfoliating and moisturizing effects, while the inclusion of other ingredients can either enhance or diminish these effects.
Lactic Acid Concentrations and Effects
Different lactic acid concentrations yield varying results. Lower concentrations (typically 5-10%) are often gentler and suitable for daily use, while higher concentrations (10-20%) can provide more pronounced exfoliation but may be better suited for occasional use or targeted treatments. Concentrations above 20% are generally not recommended for routine use due to the risk of irritation.A 5-10% concentration is ideal for daily use, as it effectively encourages cell turnover without causing significant discomfort.
A 10-20% concentration is often used for more intense exfoliation, perhaps for addressing specific skin concerns like hyperpigmentation or acne scars.
Other Ingredients Paired with Lactic Acid
The effectiveness of lactic acid can be amplified or modified by pairing it with other skincare ingredients. For example, combining lactic acid with hyaluronic acid can enhance hydration and improve skin texture. Similarly, incorporating antioxidants can help protect the skin from environmental damage while lactic acid works.
- Hyaluronic Acid: This humectant draws moisture from the environment into the skin, complementing lactic acid’s hydrating properties. This combination leads to a synergistic effect, improving skin hydration and suppleness.
- Antioxidants: Pairing lactic acid with antioxidants like vitamin C or green tea extract can protect the skin from free radical damage, which is crucial as lactic acid can make the skin more susceptible to environmental stressors. This combination enhances both the efficacy and safety of the treatment.
- Moisturizers: Lactic acid, while exfoliating, can sometimes lead to dryness. Pairing it with moisturizing ingredients like ceramides or glycerin can prevent this and maintain skin’s natural barrier function.
Interaction with Other Skincare Ingredients
Lactic acid can interact with other ingredients in a product. Some ingredients may enhance its effects, while others may diminish its efficacy or even cause incompatibility issues. Careful consideration of these interactions is essential for optimal results.
- AHAs/BHAs: Combining lactic acid with other AHAs or BHAs (like glycolic acid or salicylic acid) can enhance exfoliation, but it’s crucial to monitor the skin’s response to avoid over-exfoliation. A balanced approach is needed, using a gradual increase in the intensity of exfoliation.
- Vitamins: Lactic acid can potentially enhance the absorption of certain vitamins, like vitamin C. However, some vitamins might react negatively or reduce the effectiveness of lactic acid. Careful research into potential interactions is recommended.
- Fragrances and preservatives: Some fragrances and preservatives can irritate the skin, particularly when combined with lactic acid. Choosing fragrance-free or hypoallergenic formulations can mitigate this risk.
Lactic Acid’s Effectiveness and Product Formulation
The effectiveness of lactic acid in a skincare product is heavily influenced by the product formulation. The pH level of the product, the presence of other ingredients, and the stability of the lactic acid itself all play crucial roles.
- pH Level: The ideal pH range for lactic acid products is typically between 3.5 and 4.5. This pH range allows lactic acid to effectively exfoliate without causing irritation. Maintaining the correct pH level is crucial for product efficacy and skin health.
- Product Stability: The stability of lactic acid in a product is critical. Factors such as preservatives, temperature, and the presence of other ingredients can affect its stability. Formulators need to ensure the product remains effective and safe throughout its shelf life.
Examples of Effective Product Formulations
Several effective formulations leverage lactic acid’s properties. A common example is a serum containing lactic acid, hyaluronic acid, and vitamin C. This combination provides exfoliation, hydration, and antioxidant protection. Another example might be a moisturizer incorporating lactic acid with ceramides for enhanced hydration and barrier repair.
- Serum Formulation: A serum containing 10% lactic acid, 2% hyaluronic acid, and 1% vitamin C can offer a balanced approach to exfoliation, hydration, and antioxidant protection.
- Moisturizer Formulation: A moisturizer incorporating 5% lactic acid, ceramides, and glycerin provides gentle exfoliation while maintaining skin hydration and barrier function.
Case Studies and User Experiences: Lactic Acid Skin Care
Lactic acid has gained popularity as a skincare ingredient, and numerous users have reported positive experiences with its ability to improve various skin concerns. Real-world evidence from user testimonials and before-and-after photos provide valuable insights into the efficacy and safety of lactic acid products. This section delves into these experiences, highlighting success stories and providing examples of how lactic acid skincare routines have transformed skin conditions.User experiences with lactic acid skincare products often highlight improvements in skin texture, tone, and overall appearance.
These improvements are frequently observed over time, as lactic acid works gradually to exfoliate the skin and stimulate cell turnover. Many users report noticeable changes within a few weeks of consistent use.
Positive User Experiences
User testimonials and online reviews consistently praise the effectiveness of lactic acid in addressing various skin concerns. Many users report smoother, brighter, and more even-toned skin after incorporating lactic acid into their routine. The positive feedback frequently mentions reduced hyperpigmentation, improved acne scars, and a more youthful complexion.
Improved Skin Conditions, Lactic acid skin care
Lactic acid’s exfoliating properties have been shown to effectively address a range of skin conditions. Users with acne scars, hyperpigmentation, and fine lines have reported noticeable improvements in their skin’s appearance after using lactic acid products. The gradual exfoliation process helps to reveal brighter, smoother skin by removing dead skin cells and promoting collagen production. Many users also report reduced dryness and irritation with consistent use, a testament to the ingredient’s ability to hydrate and balance skin.
Testimonials and Reviews
Numerous online platforms host testimonials and reviews from individuals who have used lactic acid skincare products. These testimonials frequently detail specific skin concerns, such as acne scars or hyperpigmentation, and the positive results they experienced after integrating lactic acid into their routines. For example, many reviews mention noticeable improvements in skin texture and tone after several weeks of regular use.
These reviews often include detailed descriptions of the product used, the skincare routine followed, and the observed improvements.
Before-and-After Photos
Visual evidence significantly supports user experiences with lactic acid skincare. Before-and-after photos often demonstrate the visible improvement in skin texture, tone, and overall appearance. A noticeable reduction in acne scars, hyperpigmentation, and fine lines is often apparent in these photos, showcasing the potential of lactic acid to address various skin concerns. A set of photos, taken over a period of several weeks or months, can provide a clear visual representation of the changes.
The consistency and improvement in the photos illustrate the efficacy of lactic acid.
Success Stories
Several success stories illustrate how lactic acid skincare products have transformed individuals’ skin. For instance, one user, experiencing noticeable hyperpigmentation, reported a significant improvement in their skin tone after consistently using a lactic acid serum twice a week. This routine, combined with a gentle cleanser and moisturizer, helped to reduce the appearance of dark spots and reveal brighter, more even-toned skin.
Another user, dealing with acne scars, noted visible improvements in the appearance of their scars after using a lactic acid toner daily. These examples highlight the efficacy of lactic acid when used consistently as part of a well-rounded skincare routine.
Ultimate Conclusion
In conclusion, lactic acid skincare offers a powerful and effective way to enhance your skin’s natural beauty. By understanding its mechanisms, benefits, and safe application, you can unlock a smoother, brighter, and more youthful complexion. Remember to always patch test and consult with a dermatologist if you have any concerns. Happy glowing!