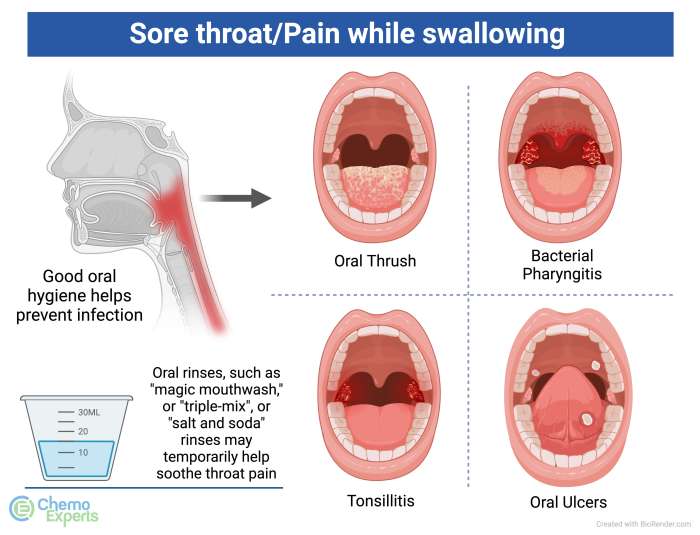
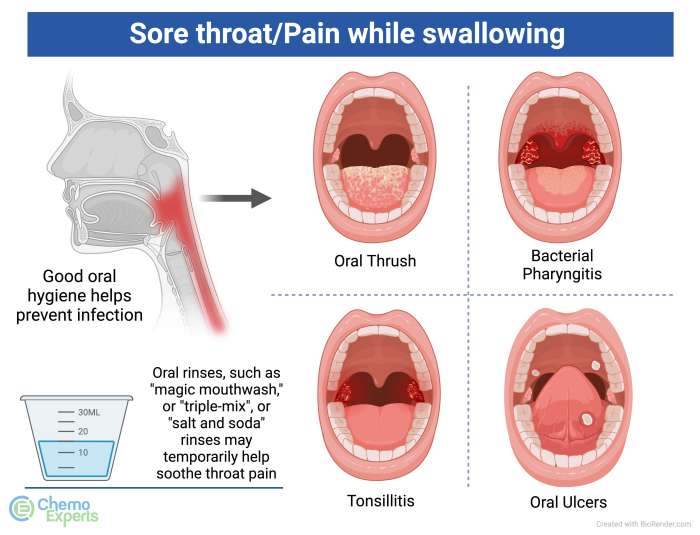
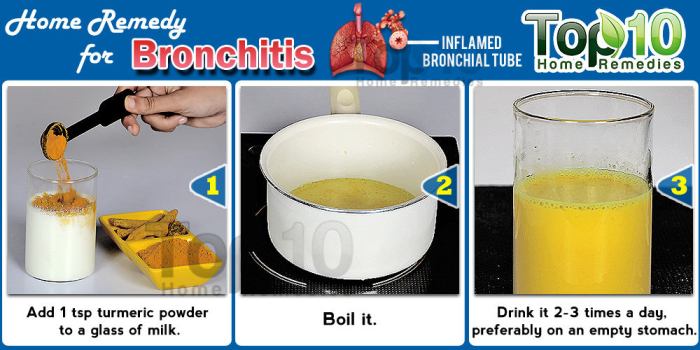
Home remedies for bronchitis offer a natural approach to managing this common respiratory ailment. Whether you’re dealing with the sharp, persistent cough of acute bronchitis or the lingering discomfort of chronic bronchitis, understanding the potential benefits and limitations of various natural remedies can empower you to take a proactive role in your well-being. This guide delves into herbal remedies, dietary suggestions, breathing exercises, and other home care options to help you navigate your bronchitis journey with informed choices.
Bronchitis, characterized by inflammation of the bronchial tubes, can range from a mild, short-term irritation to a more persistent condition. Understanding the nuances of acute and chronic bronchitis, along with their typical symptoms and triggers, is crucial in determining the most appropriate course of action. This comprehensive guide provides a detailed overview of home remedies, their potential benefits, and when seeking professional medical attention is essential.
Introduction to Bronchitis
Bronchitis is a common respiratory infection that inflames the airways, the tubes that carry air to and from your lungs. It’s often accompanied by coughing and difficulty breathing, and while generally not life-threatening, it can significantly impact daily life. Understanding the different types of bronchitis and their triggers is crucial for effective management and prevention.This inflammation can range from a mild, short-term issue to a more persistent, long-term condition.
The key difference lies in the duration and the underlying causes. Let’s delve into the specifics of acute and chronic bronchitis to better grasp their characteristics.
Types of Bronchitis
Bronchitis is categorized into two primary forms: acute and chronic. Acute bronchitis is a short-term inflammation, typically lasting a few weeks, while chronic bronchitis is a more persistent condition, often linked to long-term exposure to irritants. Recognizing the differences in symptoms, duration, and causes helps in proper diagnosis and treatment.
Symptoms of Bronchitis
Common symptoms of bronchitis include a persistent cough, often producing mucus (phlegm), chest discomfort, and shortness of breath. The cough can be dry initially, but often becomes productive, meaning it brings up mucus. Other potential symptoms include fatigue, headaches, and a low-grade fever. The severity of symptoms can vary significantly between individuals.
Triggers for Bronchitis
Several factors can trigger bronchitis. Environmental irritants such as cigarette smoke, air pollution, and dust are common culprits. Exposure to certain chemical fumes or irritants in the workplace can also increase the risk. Lifestyle choices, like a poor diet and lack of exercise, can also weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to respiratory infections, including bronchitis.
So, I’ve been researching home remedies for bronchitis, and it’s fascinating how many natural approaches can ease those pesky coughs and congestion. While I’m not a medical professional, I’ve found some promising ideas, but I’ve also learned that sometimes a small bump on the bottom of your foot, like the ones described in this article on bump on bottom of foot , might require a different approach entirely.
Still, I’m convinced that some home remedies can definitely help soothe bronchitis symptoms.
Comparison of Acute and Chronic Bronchitis
| Feature | Acute Bronchitis | Chronic Bronchitis |
|---|---|---|
| Duration | Usually resolves within a few weeks. | Persistent inflammation lasting for at least three months, recurring annually. |
| Severity | Generally mild to moderate, with symptoms often subsiding naturally. | Can range from moderate to severe, often leading to significant breathing difficulties. |
| Common Causes | Viral infections, like the common cold or flu, are the most frequent triggers. Exposure to irritants, like smoke or dust, can also cause acute bronchitis. | Long-term exposure to irritants like cigarette smoke, air pollution, or occupational dust is the primary cause. |
The table above provides a clear overview of the key differences between acute and chronic bronchitis, emphasizing the duration, severity, and common causes. Understanding these distinctions is vital for appropriate medical intervention and preventive measures.
Understanding Home Remedies
Home remedies for bronchitis, while sometimes helpful, should be approached with caution and a clear understanding of their limitations. They can provide temporary relief from symptoms and potentially support the body’s natural healing process, but they are not a substitute for professional medical care, especially in cases of severe or persistent bronchitis. Understanding the potential benefits and risks of various remedies can empower you to make informed decisions about your health.Many home remedies for bronchitis focus on soothing the symptoms and supporting the body’s natural defenses.
They aim to reduce inflammation, relieve congestion, and ease discomfort, but they typically do not address the underlying cause of the infection. Therefore, it’s essential to be aware that home remedies are often temporary solutions and should be used in conjunction with other treatment strategies recommended by a healthcare professional.
General Principles of Home Remedies
Home remedies for bronchitis are often based on principles of soothing the respiratory system and boosting the immune system. These remedies aim to reduce inflammation, alleviate congestion, and promote expectoration to help clear mucus. For example, warm liquids and humidifiers can thin mucus and make it easier to cough up. Herbal remedies and certain foods are often used to support immune function and reduce inflammation.
Limitations of Home Remedies
It’s crucial to recognize the limitations of home remedies for bronchitis. They may not address the underlying cause of the infection, which is often a viral or bacterial infection. Home remedies can provide temporary relief from symptoms, but they do not cure the condition. In cases of severe bronchitis, persistent symptoms, or if symptoms worsen, professional medical attention is necessary.
Seeking medical advice is crucial to determine the cause of the infection and receive appropriate treatment. This includes getting a diagnosis, exploring potential complications, and understanding the most effective course of action for recovery. Failure to address the underlying cause can lead to complications or prolong the recovery process.
Potential Benefits and Risks of Home Remedies
Home remedies can offer potential benefits in relieving symptoms and supporting the body’s natural healing process. For instance, warm fluids and humidifiers can help thin mucus and make it easier to cough up. However, some home remedies may have potential risks. Certain herbal remedies may interact with medications, and some foods or drinks can irritate the respiratory system or worsen existing conditions.
Carefully considering the potential benefits and risks associated with each remedy is crucial. Consult with a healthcare professional before trying any new home remedy, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking medications.
Home remedies for bronchitis often involve soothing the irritated airways. A key part of managing symptoms is understanding the importance of proper nutrition, like choosing the right carbohydrates. For example, focusing on good complex carbs like whole grains and fruits over simple sugars can significantly improve your overall well-being and support your body’s healing process. Knowing the difference between good vs bad carbs can be a game-changer in your recovery.
This understanding, combined with other home remedies, can make a real difference in managing your bronchitis symptoms effectively. good vs bad carbs are crucial for your overall health.
Categories of Home Remedies for Bronchitis
| Category | Examples | Potential Benefits | Potential Risks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Warm Liquids | Herbal teas, warm water with lemon, broth | Thin mucus, soothe throat, hydrate | May cause mild digestive upset if consumed in excess |
| Humidifiers | Steam inhalation, humidifiers | Moisturize airways, ease congestion | Potential for mold growth if not properly maintained; burns or scalds if not careful |
| Herbal Remedies | Elderberry, licorice root, thyme | Potentially support immune function, reduce inflammation | May interact with medications; allergic reactions possible |
| Dietary Changes | Increased fluids, avoiding irritants like alcohol or smoke | Support body’s healing process, minimize irritation | Potential for individual sensitivities to specific foods |
Herbal Remedies for Bronchitis
Many people turn to natural remedies when dealing with bronchitis, seeking relief from the cough, congestion, and discomfort. Herbal remedies, in particular, have been used for centuries to treat respiratory ailments. This exploration delves into the potential benefits and risks associated with popular herbal choices for bronchitis, providing a balanced perspective on their use.
Popular Herbal Remedies
A variety of herbal remedies are commonly used to alleviate bronchitis symptoms. Honey, ginger, and eucalyptus are among the most popular choices, often incorporated into teas, tinctures, or other preparations. Understanding the potential benefits and safety precautions associated with each is crucial for informed decision-making.
Honey
Honey’s well-established reputation for soothing coughs stems from its viscous nature and antimicrobial properties. Many studies have demonstrated honey’s effectiveness in reducing cough frequency and severity, particularly in children. Its ability to coat the throat and soothe irritated tissues contributes to its popularity. However, honey should be used with caution in young children under one year of age due to the risk of botulism.
Ginger
Ginger’s anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties have made it a popular home remedy for various ailments, including bronchitis. It may help reduce inflammation in the airways and potentially ease congestion. Ginger can be consumed in various forms, including tea, extracts, or as a spice in foods.
Eucalyptus
Eucalyptus, with its aromatic oils, is often used to relieve congestion and promote respiratory function. The volatile oils in eucalyptus are believed to have expectorant properties, assisting in clearing mucus from the airways. It is commonly used in vapor rubs and teas.
Effectiveness Comparison
While anecdotal evidence suggests the effectiveness of these remedies, rigorous scientific studies on the effectiveness of herbal remedies for bronchitis are often limited. Further research is needed to definitively determine the extent of their efficacy in comparison to conventional treatments. The perceived benefits may also vary based on individual responses and the severity of the bronchitis.
Safety Considerations, Home remedies for bronchitis
All herbal remedies, while often considered safe, can potentially pose risks. Individuals with allergies, pre-existing health conditions, or those taking medications should consult with a healthcare professional before using herbal remedies for bronchitis. Interactions with other medications are also a possibility. High doses of certain herbal remedies can cause adverse effects.
Potential Benefits and Side Effects
| Herbal Remedy | Potential Benefits | Possible Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Honey | Reduces cough frequency and severity, soothes throat | Not recommended for infants under 1 year, allergic reactions |
| Ginger | Reduces inflammation, eases congestion | Potential stomach upset, allergic reactions |
| Eucalyptus | Relieves congestion, promotes respiratory function | Potential skin irritation, allergic reactions, avoid in individuals with asthma |
Dietary Recommendations

A balanced diet is crucial during a bronchitis episode. Nutrients support the body’s natural defenses and aid in recovery. Proper nutrition can help reduce inflammation in the airways, easing coughing and shortness of breath. A diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals can bolster the immune system, promoting faster healing.The right foods can significantly impact your bronchitis symptoms.
Certain foods can help thin mucus, promote hydration, and provide the body with the energy it needs to fight infection. Conversely, some foods can irritate the airways, worsen inflammation, and delay recovery. Understanding which foods to include and exclude from your diet is key to managing your symptoms effectively.
Foods to Include
A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins forms the cornerstone of a healthy recovery. These foods are packed with essential nutrients that support respiratory health and overall well-being. They provide the building blocks for repairing damaged tissues and strengthening the immune system.
- Fruits and Vegetables: Berries, citrus fruits (oranges, lemons, grapefruits), leafy greens (spinach, kale), and bell peppers are excellent sources of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. These nutrients help fight inflammation and boost immunity.
- Lean Proteins: Chicken breast, fish (salmon, tuna), and beans are crucial for tissue repair. They provide essential amino acids, promoting healing and supporting the body’s overall recovery.
- Hydrating Beverages: Water, herbal teas, and clear broths are essential for maintaining hydration. Adequate hydration helps thin mucus and aids in expectoration, reducing discomfort.
- Soups: Chicken noodle soup, vegetable broth, and other warm soups can soothe the throat and provide hydration. The warmth can help relieve congestion and reduce coughing.
Foods to Exclude
Certain foods can irritate the airways and worsen bronchitis symptoms. These foods can trigger inflammation and mucus production, hindering your recovery. Avoiding them is crucial for managing your discomfort.
- Spicy Foods: Spicy foods, such as chili peppers, can irritate the throat and worsen coughing. They can increase mucus production and exacerbate inflammation in the airways.
- Dairy Products (in some cases): Dairy products, particularly milk and cheese, can sometimes increase mucus production in some individuals. If you notice a worsening of symptoms after consuming dairy, consider temporarily excluding it from your diet.
- Processed Foods: Processed foods often contain high levels of sodium and unhealthy fats, which can further irritate the airways and hinder recovery. These foods lack essential nutrients, impacting overall health.
- Sugary Drinks: Sugary drinks and processed juices can dehydrate you, potentially worsening bronchitis symptoms. They can also contribute to inflammation and hinder the healing process.
Dietary Recommendations Table
The table below provides a clear overview of foods to include and exclude during a bronchitis episode. This table helps you easily identify foods that can aid your recovery and those that may worsen your symptoms.
| Food Category | Foods to Include | Foods to Exclude | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fruits and Vegetables | Berries, citrus fruits, leafy greens, bell peppers | Spicy peppers, overly acidic fruits | Fruits and vegetables are rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, supporting respiratory health. Spicy or overly acidic foods may irritate the airways. |
| Proteins | Lean chicken, fish, beans | Processed meats, fatty meats | Lean proteins are essential for tissue repair. Fatty or processed meats can hinder recovery. |
| Hydration | Water, herbal teas, clear broths | Sugary drinks, processed juices | Hydration is vital for thinning mucus and expectoration. Sugary drinks and juices can dehydrate you and worsen symptoms. |
| Other | Soups, warm drinks | Fried foods, highly processed foods | Warm drinks and soups can soothe the throat and provide hydration. Fried and processed foods can irritate the airways. |
Breathing Exercises and Techniques
Breathing exercises play a crucial role in managing bronchitis symptoms. By improving lung capacity and reducing inflammation, these techniques can significantly alleviate discomfort and promote better overall respiratory function. Regular practice of appropriate breathing exercises can help to lessen the severity and duration of bronchitis episodes.Effective breathing techniques can help to clear mucus from the airways, making breathing easier and reducing coughing fits.
These methods can also strengthen the respiratory muscles, improving lung function over time. Understanding the different types of exercises and their proper application is essential for optimal results.
Types of Breathing Exercises
Breathing exercises for bronchitis focus on deep, controlled inhalations and exhalations to clear mucus and strengthen respiratory muscles. This process enhances lung capacity and improves overall respiratory function. By improving the efficiency of your breathing, you can reduce inflammation and promote faster recovery.
- Diaphragmatic Breathing: This technique involves using the diaphragm, the primary muscle of respiration, to expand the lungs fully. Place one hand on your chest and the other on your abdomen. Inhale deeply through your nose, feeling your abdomen rise while your chest remains relatively still. Exhale slowly through your mouth, allowing your abdomen to fall. This type of breathing can calm the nervous system, helping to reduce coughing and shortness of breath.
Diaphragmatic breathing is particularly beneficial for individuals experiencing anxiety or stress associated with bronchitis symptoms. This controlled breathing technique can be performed throughout the day to manage symptoms.
- Pursed-Lip Breathing: Inhale slowly and deeply through your nose. Exhale slowly through pursed lips, as if you were blowing out a candle. This technique helps to prolong exhalation, which can help to clear mucus from the airways and reduce coughing. It also helps to stabilize the airways and control the rate of breathing. Practicing pursed-lip breathing can help to relieve shortness of breath and manage anxiety.
- Humming Breathing: This technique involves inhaling deeply and exhaling slowly while making a humming sound. This can help to loosen mucus and promote its removal from the airways. The humming action can also help to calm the respiratory system and reduce coughing. Humming breathing, while often used in yoga, can be a beneficial technique for managing bronchitis.
Breathing Exercise Techniques
Proper execution of breathing exercises is crucial for maximizing their effectiveness. These techniques focus on using controlled and deliberate movements to optimize respiratory function.
- Correct Posture: Sit or lie down in a comfortable position that allows for optimal lung expansion. Good posture promotes the natural functioning of the respiratory system.
- Slow and Controlled Breathing: Avoid rapid or shallow breaths. Concentrate on slow, deep inhalations and controlled exhalations to ensure proper oxygen intake and mucus removal.
- Focus on Exhalation: Exhalation is equally important as inhalation. A longer exhalation phase allows for more efficient mucus removal and lung expansion.
Breathing Exercises Table
| Breathing Exercise | Benefits | Precautions |
|---|---|---|
| Diaphragmatic Breathing | Calms the nervous system, improves lung capacity, reduces coughing. | May not be suitable for individuals with abdominal issues. |
| Pursed-Lip Breathing | Prolongs exhalation, clears mucus, controls coughing, and stabilizes airways. | No significant precautions. |
| Humming Breathing | Loosens mucus, promotes removal, calms respiratory system. | No significant precautions. |
Other Home Remedies
Bronchitis, while often treatable with rest and over-the-counter medications, can sometimes benefit from supportive home remedies. These methods often target easing symptoms, promoting comfort, and potentially aiding the body’s natural healing processes. However, it’s crucial to remember that home remedies are not a substitute for medical advice from a healthcare professional. Always consult your doctor if your bronchitis symptoms worsen or persist.
Steam Inhalation
Steam inhalation involves inhaling warm, moist air to help loosen mucus and clear airways. The heat from the steam can help to soothe irritated tissues in the respiratory tract. This method works by increasing the humidity in the air, making it easier for mucus to drain and reducing the discomfort of coughing. The steam also helps to dilate the airways, making breathing easier.
Warm Drinks
Warm beverages, such as herbal teas, broth, or warm water with lemon, can help soothe a sore throat and potentially thin mucus. The warmth can have a calming effect on the throat and respiratory system, reducing inflammation and irritation. Certain herbal teas, like chamomile or ginger, may have additional benefits due to their potential anti-inflammatory properties. While the scientific evidence for the effectiveness of warm drinks in treating bronchitis is limited, they can certainly contribute to overall comfort.
Other Potential Remedies
Various other remedies are often used to alleviate bronchitis symptoms. These include gargling with salt water to soothe a sore throat, using a humidifier to increase humidity in the air, and getting sufficient rest to aid recovery. However, the evidence supporting the effectiveness of these remedies for bronchitis varies.
Comparison of Home Remedies
| Home Remedy | Method | Potential Benefits | Scientific Basis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Steam Inhalation | Inhaling warm, moist air | Loosens mucus, soothes irritated tissues, reduces coughing, eases breathing | Increased humidity in the air facilitates mucus drainage and airway dilation. |
| Warm Drinks | Drinking warm beverages (e.g., herbal tea, broth) | Soothes sore throat, potentially thins mucus, calms respiratory system | Limited scientific evidence. Possible anti-inflammatory properties in some herbal teas. |
| Saltwater Gargle | Gargling with salt water | Soothes sore throat, reduces inflammation | Saltwater can help reduce inflammation and irritation in the throat. |
| Humidifier | Increasing humidity in the air | Moistens airways, reduces coughing | Increased humidity can help thin mucus and make breathing easier. |
| Rest | Adequate rest and sleep | Allows the body to heal, reduces stress on the respiratory system | Rest is crucial for immune function and overall recovery from illness. |
Safety Precautions and Considerations
Home remedies can be a helpful adjunct to conventional medical treatment for bronchitis, but they are not a substitute for professional medical care. It’s crucial to understand the limitations and potential risks associated with these remedies to ensure their safe and effective use. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new treatment, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking other medications.Using home remedies without understanding their potential interactions with existing medications can lead to adverse effects.
It’s important to approach these remedies with caution and a thorough understanding of your individual health needs. This section highlights vital safety precautions and considerations for using home remedies for bronchitis.
Importance of Professional Consultation
Seeking guidance from a healthcare professional is paramount before implementing any home remedy. A doctor can assess your specific condition, rule out any underlying complications, and determine if home remedies are appropriate for your situation. They can also provide personalized recommendations tailored to your individual needs and medical history. This proactive approach prevents potential harm and ensures that any treatment plan complements, rather than conflicts with, your overall health.
Potential Drug Interactions
Many home remedies contain active ingredients that may interact with prescribed medications. These interactions can either diminish the effectiveness of your medication or cause adverse reactions. For example, some herbal remedies can interfere with blood thinners, increasing the risk of bleeding. Always inform your doctor about all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you are taking to avoid potential complications.
This comprehensive approach to medication management minimizes the risk of unexpected and potentially harmful drug interactions.
Recognizing Ineffectiveness and Seeking Medical Attention
Home remedies can be helpful in alleviating some symptoms of bronchitis, but they are not always effective. If your symptoms worsen, persist, or do not improve after a reasonable period of time, it’s essential to seek medical attention. Symptoms like high fever, difficulty breathing, or persistent chest pain should never be ignored. Prompt medical intervention is critical for severe or worsening conditions.
Trying to soothe a nagging cough? Home remedies for bronchitis can be surprisingly effective. While some swear by honey and lemon, others find relief in steaming, and plenty of rest. Interestingly, the role of vitamin C in fighting off respiratory illnesses is often debated, and research into does vitamin c help with colds is ongoing.
Regardless, staying hydrated and prioritizing a healthy lifestyle are key components of any bronchitis treatment plan.
Potential Side Effects and Contraindications
Certain home remedies may cause side effects or be contraindicated for specific individuals. For instance, honey, while often recommended for coughs, can be harmful to infants under one year old. Similarly, some herbal remedies may interact negatively with pre-existing medical conditions. Always check with your doctor about potential side effects and contraindications specific to your situation.
List of Potential Side Effects and Contraindications
- Allergic reactions: Some individuals may experience allergic reactions to certain herbal ingredients, leading to skin rashes, itching, or swelling. This is a significant concern, and immediate medical attention is necessary if such a reaction occurs.
- Drug interactions: Many herbal remedies can interact with prescribed medications, potentially reducing their effectiveness or causing adverse reactions. For instance, some herbal remedies can interfere with blood thinners, increasing the risk of bleeding.
- Exacerbation of underlying conditions: Home remedies may exacerbate pre-existing medical conditions in susceptible individuals. For example, certain herbal remedies can trigger asthma attacks in people with asthma.
- Specific contraindications for certain age groups: Some home remedies are not suitable for specific age groups. For example, honey should not be given to infants under one year old, as it can pose a choking hazard.
- Individual sensitivities: Individual sensitivities to certain ingredients in home remedies can lead to adverse reactions. Always consult with a healthcare professional to determine if a specific remedy is safe for you.
Illustrative Examples: Home Remedies For Bronchitis
Home remedies can be powerful allies in managing bronchitis symptoms. Understanding how to properly prepare and utilize these remedies is crucial for effective symptom relief and overall well-being. This section will delve into specific examples, providing detailed instructions and safety considerations for each.
Honey and Lemon Drink
This simple remedy is well-known for its soothing properties. Honey’s antibacterial qualities and lemon’s vitamin C content can help alleviate coughs and soothe irritated throats.
Ingredients:
- 1 tablespoon of honey
- 1/2 teaspoon lemon juice
- 1/2 cup warm water
Instructions:
- Combine honey and lemon juice in a small mug.
- Gradually add warm water, stirring until the honey dissolves completely.
- Drink the mixture slowly, allowing it to coat the throat and soothe any irritation.
Important Note: Honey should be used with caution in children under one year of age due to the risk of botulism. If you have any concerns, consult with a healthcare professional.
Steam Inhalation with Essential Oils
Steam inhalation can provide significant relief from congestion and respiratory discomfort. However, safety is paramount when using essential oils.
Safety First: Essential oils should never be directly inhaled. Always dilute them with a carrier oil, like water, and never use undiluted oils on the skin or in the eyes. Use caution with children and individuals with underlying health conditions. Always consult with a doctor before using essential oils, especially if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
Ingredients:
- 2 cups of hot water
- 2-3 drops of diluted essential oil (e.g., eucalyptus, peppermint, tea tree)
- A towel
Instructions:
- Pour hot water into a bowl.
- Add the diluted essential oil drops to the water.
- Cover your head with a towel, ensuring the bowl is at a safe distance to avoid burns.
- Inhale the steam for 5-10 minutes. Avoid inhaling for extended periods or if discomfort arises.
Ginger Tea for Respiratory Issues
Ginger is known for its anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant properties, which can be beneficial for easing respiratory symptoms.
Ingredients:
- 1 inch piece of fresh ginger, peeled and sliced
- 1 cup of boiling water
- Optional: honey or lemon to taste
Instructions:
- Place the sliced ginger in a mug.
- Pour boiling water over the ginger.
- Cover and steep for 5-10 minutes.
- Strain the tea and add honey or lemon, if desired.
- Drink the tea while warm. The ginger will warm and soothe your throat.
Healthy Diet for Bronchitis
A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can support the body’s natural healing processes during bronchitis. Nutrients play a crucial role in maintaining immune function.
Visual Representation:
Imagine a colorful plate divided into four sections. One section displays a variety of brightly colored fruits like berries, oranges, and bananas. Another section highlights a mix of colorful vegetables, including leafy greens, carrots, and bell peppers. A third section shows whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, and oats. The final section includes lean protein sources like fish, poultry, or beans.
This visual representation emphasizes the importance of consuming a wide range of nutrients for optimal health during bronchitis.
Outcome Summary
This exploration of home remedies for bronchitis highlights the potential of natural approaches to alleviate symptoms and promote healing. While home remedies can provide some relief, it’s essential to remember their limitations. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new treatment, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking other medications. Ultimately, a holistic approach combining home remedies with professional medical guidance is often the most effective strategy for managing bronchitis effectively and safely.