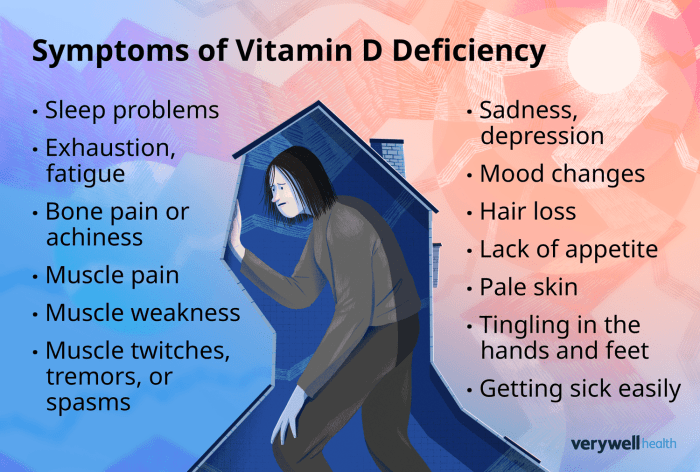
Risks and complications of seizures can significantly impact a person’s life, ranging from immediate dangers to long-term consequences. This comprehensive exploration delves into the various types of seizures, their potential triggers, and the wide-ranging risks associated with them. Understanding these risks is crucial for both individuals experiencing seizures and those who care for them.
From the immediate threat of injury during a seizure to the potential for long-term cognitive and emotional challenges, the consequences can be substantial. This article will discuss the different types of risks, ranging from the most immediate dangers to more chronic effects. It will also examine how these risks vary depending on the type of seizure.
Introduction to Seizures
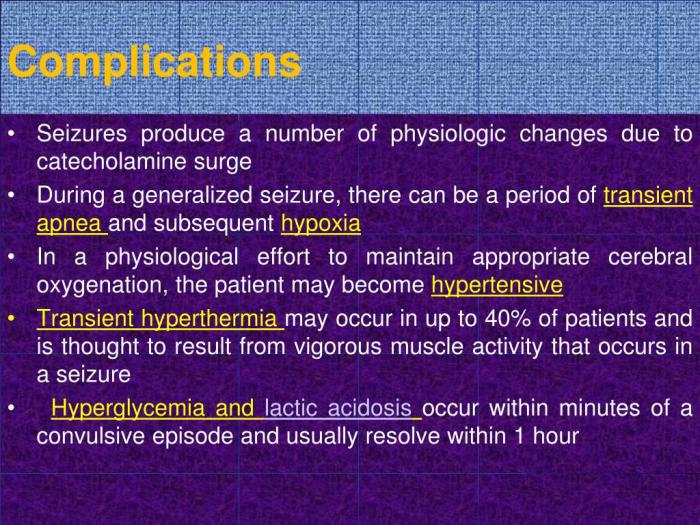
Seizures are sudden, temporary disturbances in brain activity that can cause a variety of physical and behavioral changes. They result from abnormal electrical activity in the brain, disrupting normal brain function. Different types of seizures can manifest in various ways, impacting individuals differently. Understanding the underlying mechanisms and triggers is crucial for appropriate diagnosis and management.Seizures are characterized by abnormal, excessive electrical discharges in groups of nerve cells in the brain.
These abnormal discharges disrupt normal brain communication, leading to the various symptoms associated with seizures. The underlying cause of these abnormal discharges can range from genetic predisposition to acquired brain injuries. Triggers can vary significantly and play a crucial role in the onset of seizures.
Types of Seizures
Different types of seizures are categorized based on where in the brain the abnormal electrical activity originates and the extent of its spread. This classification helps in diagnosis and treatment planning.
Focal Seizures
Focal seizures originate in a specific area of the brain. They can manifest with subtle symptoms, such as altered sensations or brief periods of confusion, or more pronounced symptoms, like involuntary movements of a limb or face. Some focal seizures may not involve noticeable outward signs, while others can be visually noticeable. Focal seizures can be further classified based on whether they remain localized or spread to other brain regions.
Generalized Seizures
Generalized seizures involve both hemispheres of the brain, exhibiting more widespread electrical activity. They can cause a range of symptoms, including loss of consciousness, convulsions, and altered awareness. Generalized seizures are typically more pronounced than focal seizures. Examples include tonic-clonic (grand mal) seizures, characterized by muscle stiffening and jerking movements, and absence seizures (petit mal), characterized by brief lapses in attention and awareness.
Table Comparing Focal and Generalized Seizures
| Feature | Focal Seizures | Generalized Seizures |
|---|---|---|
| Brain Region Affected | Specific area | Both hemispheres |
| Symptoms | Variable, may include sensory changes, motor movements, or altered awareness | Often involve loss of consciousness, convulsions, or altered awareness |
| Awareness | May or may not involve loss of awareness | Often involve loss of awareness |
| Progression | May remain localized or spread | Typically involve widespread brain activity |
Triggers of Seizures
Several factors can trigger seizures. These triggers can be environmental, medical, or psychological. Identifying and avoiding triggers is often crucial in seizure management.
- Stress: High levels of stress can sometimes trigger seizures in susceptible individuals. Emotional distress can sometimes precipitate seizures.
- Sleep Deprivation: Lack of adequate sleep can increase the risk of seizures. A consistent sleep schedule can help regulate brain activity and reduce seizure frequency.
- Medication Changes: Changes in medications, including the introduction of new drugs or alterations in dosages, can affect seizure control.
- Flickering Lights: Some individuals are sensitive to flashing lights, which can trigger seizures. Avoiding such visual stimuli can help prevent seizures.
- Certain Foods: Specific foods or dietary deficiencies can occasionally trigger seizures. Maintaining a balanced diet can be helpful.
Types of Risks and Complications: Risks And Complications Of Seizures
Seizures, while often temporary, can carry a range of immediate and long-term risks and complications. Understanding these potential consequences is crucial for both patients and caregivers to proactively manage the condition and seek appropriate support. This section delves into the various dangers associated with seizures, emphasizing the importance of vigilance and appropriate medical intervention.
Immediate Risks Associated with Seizures
The immediate aftermath of a seizure can pose significant threats. These risks demand prompt attention and appropriate medical response. Unforeseen complications can occur during and immediately following a seizure.
- Loss of Consciousness: A seizure can temporarily interrupt normal brain function, resulting in a loss of awareness and responsiveness. This loss of consciousness can vary in duration and severity, potentially leading to further complications if not promptly addressed.
- Injury: Falling during a seizure can lead to various injuries, including head trauma, fractures, and soft tissue damage. The severity of these injuries depends on the duration of the seizure, the individual’s environment, and their ability to protect themselves. Protective measures, such as ensuring a safe environment, are essential.
- Aspiration: If a seizure occurs while an individual is consuming food or liquid, there’s a risk of aspiration. Aspiration involves the entry of food or liquid into the lungs, which can lead to pneumonia and other respiratory complications. Careful monitoring and preventative measures, such as ensuring the individual is in a safe position to avoid choking, are crucial.
Long-Term Risks of Recurrent Seizures
Recurrent seizures can significantly impact a person’s quality of life, leading to a variety of long-term risks. These consequences highlight the importance of ongoing management and treatment to mitigate these challenges.
- Cognitive Impairment: Repeated seizures can potentially damage brain tissue, leading to cognitive impairments, such as difficulties with memory, learning, and concentration. The degree of impairment varies depending on the seizure type, frequency, and individual factors. Educational and therapeutic support can help manage these challenges.
- Mental Health Issues: Individuals experiencing frequent seizures may experience increased stress, anxiety, and depression. The emotional toll of living with a chronic condition like epilepsy can be substantial. Mental health support is often crucial to maintaining emotional well-being.
- Physical Disabilities: In some cases, recurrent seizures can lead to long-term physical disabilities. The impact on physical function varies depending on the seizure type and frequency, and can impact daily activities. Physical therapy and rehabilitation can be beneficial in addressing these limitations.
Comparison of Risks Across Seizure Types
Different types of seizures are associated with varying degrees of risk. Understanding the specific risks linked to different seizure types is vital for appropriate management and preventative strategies.
- Generalized Seizures: Generalized seizures often involve both hemispheres of the brain, leading to more widespread effects. The risks associated with generalized seizures can include loss of consciousness, prolonged periods of unresponsiveness, and increased risk of injury due to falls. Specific examples include tonic-clonic seizures and absence seizures.
- Focal Seizures: Focal seizures, originating in a specific part of the brain, can manifest in various ways, and their impact depends on the affected brain region. Focal seizures may involve motor symptoms, sensory experiences, or changes in awareness. Risks associated with focal seizures include injury from involuntary movements and potential cognitive effects specific to the location of the affected brain region.
Summary Table of Risks and Complications
This table summarizes the potential risks and complications associated with different seizure types, categorized by severity. This table provides a concise overview for better understanding and comparison.
| Seizure Type | Immediate Risks | Long-Term Risks | Severity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Absence Seizures | Brief loss of awareness, possible minor injury | Potential for learning difficulties, subtle cognitive impairments | Low |
| Tonic-Clonic Seizures | Loss of consciousness, falls, injuries, aspiration | Significant cognitive impairment, increased risk of mental health issues, physical disabilities | High |
| Focal Seizures (Simple Partial) | Sensory or motor symptoms, possible brief loss of awareness | Potential for cognitive difficulties, depending on the brain region affected | Moderate |
| Focal Seizures (Complex Partial) | Loss of awareness, altered behavior, possible injuries | Increased risk of cognitive and behavioral changes, mental health issues | Moderate to High |
Diagnosis and Management

Unraveling the mysteries of seizures requires a meticulous approach, encompassing a comprehensive diagnostic process and tailored management strategies. Accurate identification of the specific seizure type and underlying cause is crucial for effective treatment and seizure control. This often involves a multi-faceted evaluation, encompassing various diagnostic tests and ongoing monitoring.The management of seizures involves a combination of strategies aimed at minimizing seizure frequency and severity, and improving the quality of life for those affected.
These strategies may include medications, lifestyle modifications, and alternative therapies, each with its own set of benefits and potential drawbacks. A collaborative approach between the patient, healthcare provider, and support network is essential for successful management.
Seizures, while often temporary, can bring a range of risks and complications. Understanding these potential issues is crucial for managing them effectively. One important factor to consider is how these complications can sometimes interact with other conditions like, for example, what is hemophilia disease. Ultimately, recognizing these potential issues is key to ensuring the best possible outcomes for those experiencing seizures.
Diagnostic Process for Identifying Seizure Disorders
Accurate diagnosis of seizure disorders hinges on a careful evaluation of the patient’s medical history, a thorough neurological examination, and a range of diagnostic tests. The history includes details about the patient’s past medical conditions, family history of seizures, and specific characteristics of the seizures themselves, such as their duration, frequency, and associated symptoms. A neurological examination assesses the patient’s neurological function, including motor skills, sensory perception, and cognitive abilities.
Methods for Monitoring Seizure Activity
Monitoring seizure activity is essential for evaluating the effectiveness of treatment and identifying patterns or triggers. Various methods are employed to capture and analyze seizure events, allowing healthcare professionals to tailor management strategies effectively. These methods include:
- Electroencephalography (EEG): This technique records the electrical activity of the brain, providing valuable insights into the timing and patterns of seizure activity. An EEG can identify abnormal electrical discharges that characterize seizures, helping to pinpoint the location of the seizure focus in the brain.
- Video-EEG Monitoring: This sophisticated method combines video recording with EEG to provide a comprehensive record of seizure events. The video component captures the patient’s behavior during the seizures, offering crucial information about the type of seizure and any associated symptoms.
- Ambulatory EEG: This allows continuous monitoring of brainwave activity over an extended period, often days or weeks, enabling detection of infrequent or subtle seizures that may not be captured during a routine EEG. This is particularly useful in cases where seizures occur intermittently or in response to specific triggers.
Treatment Options for Managing Seizures
Managing seizures involves a combination of approaches, ranging from medications to lifestyle modifications and alternative therapies. The chosen treatment strategy depends on several factors, including the type of seizure, its frequency, and the patient’s overall health.
Anti-Seizure Medications
Pharmacological interventions are a cornerstone of seizure management. Numerous anti-seizure medications (ASMs) are available, each with varying mechanisms of action and side effect profiles. Selection of the appropriate medication is often a complex process requiring careful consideration of individual patient needs.
| Medication | Mechanism of Action | Common Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Levetiracetam | Inhibits neuronal excitability | Fatigue, dizziness, decreased appetite, irritability |
| Lamotrigine | Modulates voltage-gated sodium channels | Rash, nausea, headache, dizziness |
| Phenytoin | Inhibits voltage-gated sodium channels | Gingival hyperplasia, hirsutism, ataxia, nausea |
Note: This table provides a brief overview. A healthcare professional should provide specific advice on medication selection. Detailed information on the potential side effects, dosage, and interactions should be discussed with a medical expert.
Alternative Therapies
While not a replacement for conventional medical treatments, alternative therapies may offer complementary support in managing seizures. These approaches may include dietary interventions, stress reduction techniques, and specific types of therapies like acupuncture or yoga. However, it is crucial to discuss these options with a healthcare provider to ensure they do not interfere with standard medical care.
Impact on Quality of Life
Living with seizures can significantly impact a person’s quality of life, affecting daily routines, social interactions, and emotional well-being. The frequency, severity, and type of seizures, along with the individual’s coping mechanisms and support system, all play a role in the degree of this impact. Understanding these challenges is crucial for developing effective management strategies.
Impact on Daily Life Activities
Seizures can disrupt various daily activities, impacting productivity and independence. Simple tasks like showering, dressing, or eating can become challenging, particularly during or immediately after a seizure. The unpredictability of seizures can lead to anxiety and avoidance of certain situations, further limiting independence. For example, a person experiencing frequent seizures might avoid social gatherings or certain activities that they once enjoyed.
Impact on Social Interactions
Social interactions can be significantly affected by seizures. Fear of embarrassment, judgment, or misunderstanding can lead to social isolation. The stigma surrounding seizures can make it difficult for individuals to form and maintain relationships. Open communication and education about seizures are essential for fostering understanding and acceptance from friends, family, and colleagues.
Emotional and Psychological Effects
Living with seizures can have profound emotional and psychological consequences. Anxiety, depression, and feelings of frustration are common responses to the unpredictable nature of seizures. The fear of future seizures can create significant stress and impact overall well-being. Seeking support from mental health professionals and support groups can be vital for managing these emotional challenges.
Coping Strategies
Developing effective coping strategies is essential for managing the impact of seizures on daily life. These strategies can range from relaxation techniques to time management strategies. For instance, incorporating regular exercise, mindfulness practices, and maintaining a healthy diet can contribute to stress management and overall well-being.
Table: Impact of Seizures on Daily Life Aspects
| Aspect of Daily Life | Potential Impact | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Work | Missed workdays, reduced productivity, difficulty concentrating, potential job loss | An employee with frequent seizures might miss important meetings or deadlines. They might be perceived as unreliable, potentially leading to job loss. |
| Education | Missed school days, difficulty concentrating, potential academic setbacks | A student experiencing seizures might miss crucial class time, making it challenging to keep up with the curriculum. |
| Social Life | Limited social interactions, fear of judgment, social isolation | A person with seizures might avoid social events or activities due to anxiety about potential reactions from others. |
| Personal Care | Difficulty performing self-care tasks, reduced independence | Tasks like bathing, dressing, and eating might become more challenging due to seizure frequency or post-seizure fatigue. |
Prevention and Prognosis
Seizures, while often unpredictable, can sometimes be managed through proactive strategies and a comprehensive understanding of influencing factors. This section delves into preventative measures, prognostic considerations, and the crucial role of lifestyle modifications in seizure management. A proactive approach can significantly impact the long-term well-being of individuals experiencing seizures.Understanding the potential triggers and adopting preventative measures can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of seizures.
Prognosis, or the expected course of a condition, is influenced by a complex interplay of factors. This section will highlight the factors affecting prognosis and the importance of lifestyle choices in optimizing seizure management.
Preventative Measures
Strategies to minimize seizure risk often involve identifying and mitigating potential triggers. A careful approach to managing potential triggers and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce the likelihood of future seizures. Consistent medication adherence, as prescribed by a medical professional, plays a critical role in preventing seizures.
- Medication Adherence: Strictly following the prescribed medication regimen is essential. Missed doses or inconsistent intake can lead to increased seizure risk. Regular communication with the neurologist is vital for adjusting medication as needed.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Regular sleep patterns, stress management techniques, and a balanced diet contribute to overall well-being and can potentially reduce seizure activity. Maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, and managing stress through exercise and relaxation techniques are crucial components of this approach.
- Environmental Control: Identifying and avoiding potential triggers in the environment is another key preventative measure. This might involve avoiding known environmental stressors or modifying the home environment to minimize risk factors.
Factors Influencing Seizure Prognosis
The success in managing seizures and the long-term outlook are influenced by various factors. The prognosis for seizures varies significantly depending on the underlying cause, the type of seizure, and the individual’s response to treatment.
Navigating the complexities of seizures can be tough, from understanding the risks and potential complications to communicating with others about the condition. It’s similar to explaining a skin condition like vitiligo to someone who doesn’t understand it – you need to be clear, patient, and informative, like when referencing explaining vitiligo to others. Ultimately, though, managing seizures effectively requires a thorough understanding of potential complications and how to best approach any challenges that arise.
- Type and Severity of Seizures: The type of seizure and its frequency and severity directly influence the prognosis. Simple partial seizures may have a better prognosis compared to complex partial or generalized tonic-clonic seizures.
- Underlying Medical Conditions: Conditions like brain tumors, infections, or metabolic disorders can impact seizure prognosis. Early diagnosis and effective management of the underlying condition can significantly improve the outcome.
- Individual Response to Treatment: Individual responses to medication vary. Some individuals may experience significant seizure reduction, while others may require adjustments in medication or therapies to achieve satisfactory control.
Lifestyle Modifications in Seizure Management
Lifestyle modifications are integral to seizure management and can positively impact seizure frequency and severity.
- Diet: A balanced diet can contribute to overall health and may influence seizure frequency. Some studies suggest a link between specific dietary patterns and seizure activity. A dietitian can help create a personalized plan.
- Sleep Hygiene: Adequate sleep is crucial for maintaining overall health. Regular sleep patterns and a consistent sleep schedule can contribute to reduced seizure risk.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can trigger seizures in some individuals. Stress management techniques, such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises, can be helpful.
Preventative Strategies and Effectiveness
The effectiveness of preventative strategies varies depending on the individual and the specific circumstances. The following table provides a general overview of common preventative strategies and their potential impact.
Seizures can have some serious risks and complications, like long-term brain damage or even death. It’s crucial to understand the potential side effects of any treatment, and this includes considering alternative treatments like watchful waiting. While antibiotics for sinus infection antibiotics for sinus infection are sometimes necessary, it’s equally important to weigh the potential benefits against the possible side effects.
Proper management of seizures, with a focus on prevention and early intervention, can significantly minimize these risks.
| Preventative Strategy | Effectiveness | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Medication Adherence | High | Consistent medication intake is crucial for preventing seizures. |
| Lifestyle Modifications (Diet, Sleep, Stress Management) | Moderate | These strategies can contribute to overall well-being and potentially reduce seizure frequency. |
| Environmental Control | Variable | Effectiveness depends on the specific triggers and the ability to control them. |
Medical Emergencies During Seizures
Seizures, while often a frightening experience, can be managed effectively with prompt and appropriate first aid. Understanding the different types of seizures and the steps to take during an episode is crucial for ensuring the safety and well-being of the individual experiencing it, and those around them. This section provides vital information on first aid measures, safety precautions, and procedures in public settings.
First Aid Measures During a Seizure
Immediate action during a seizure can significantly impact the individual’s safety and recovery. A calm and informed approach is essential. The following steps Artikel the recommended first aid measures.
- Protecting the Individual from Injury: The primary concern during a seizure is preventing injury. Ensure the person is on a soft surface, if possible, to cushion any falls. Clear the immediate area of any hard objects that could cause harm. Never restrain the individual, as this can cause further distress and potential injury.
- Positioning and Monitoring: Turn the person on their side to facilitate drainage of saliva or vomit. This prevents choking and ensures a clear airway. Monitor the individual closely, noting the duration of the seizure and any unusual characteristics. If the seizure lasts longer than five minutes, or if the person doesn’t regain consciousness, call emergency services immediately.
- Recording the Event: If possible, note the start time and duration of the seizure. This information can be helpful for medical professionals when they arrive. Keep track of any unusual or noteworthy aspects of the seizure, such as unusual movements, sounds, or loss of consciousness.
Ensuring the Safety of the Individual
Safeguarding the individual experiencing a seizure is paramount. The goal is to minimize potential harm while the seizure is occurring.
- Preventing Falls: Remove any obstacles that could cause the person to trip or fall. If possible, gently guide them to a safe, soft area, like the floor or a padded surface. Do not attempt to pick them up unless absolutely necessary to move them to a safer location. Do not put anything in their mouth.
- Protecting the Head and Extremities: Ensure the individual is not hitting their head or limbs on hard surfaces. Gently guiding the head to prevent impacts can reduce the risk of injury. If possible, move any objects from the immediate surroundings that may cause harm.
- Managing the Environment: The surrounding environment can affect the person’s safety. Try to ensure the area is free from potential hazards, such as loose rugs, furniture, or electrical cords.
Actions in Public Places
Responding to a seizure in a public place requires careful consideration for the individual’s safety and the safety of others.
- Ensuring Accessibility: If the seizure occurs in a public area, try to create a safe space for the individual. This might involve moving them away from traffic, crowds, or other hazards.
- Informing Others: Alert others in the area about what is happening, and ask if anyone has witnessed the seizure or has any relevant information. This can assist emergency responders with details of the event. Avoid unnecessary alarm or panic.
- Calling Emergency Services: If the seizure lasts longer than five minutes, or if the person doesn’t regain consciousness, immediately call emergency services. Provide the location of the incident and any relevant information to the dispatcher.
Preventing Injury During a Seizure
Minimizing injury during a seizure is a priority. Taking precautions beforehand can significantly reduce the risk.
- Identifying Potential Hazards: In the individual’s home, assess and eliminate potential hazards. Secure loose rugs, cords, and other items that could cause tripping or falls. Ensure that the environment is free of potential injury sources.
- Using Protective Equipment: In some cases, medical professionals may recommend protective devices, such as helmets, to minimize the risk of head injury during a seizure. Discuss this with the person’s healthcare provider to determine if this is appropriate.
- Following Medical Advice: Regularly review and follow the medical advice provided by the healthcare team. This can include adjustments to medications, environmental considerations, or other recommendations that can enhance safety.
Impact on Family and Caregivers
Caring for someone with seizures can be incredibly challenging, impacting not only the individual experiencing the seizures but also the entire family unit. The emotional and psychological toll on caregivers can be significant, demanding considerable adjustments to daily routines, finances, and personal well-being. This section will explore the multifaceted effects on families and caregivers, highlighting available support systems and practical strategies for managing stress.The constant worry, uncertainty, and potential for unpredictable events surrounding seizures can take a heavy emotional toll on family members and caregivers.
This can manifest in a range of feelings, including anxiety, fear, frustration, and even guilt. Managing the physical demands of caregiving, such as administering medications, monitoring symptoms, and providing transportation, can add further stress and strain.
Emotional and Psychological Effects
Caregivers often experience a spectrum of emotional and psychological reactions to the demands of caring for a loved one with seizures. These reactions are a normal response to the challenging circumstances. Grief over the impact of the condition on the person’s life, alongside the emotional burden of dealing with potential crises, is common. Frustration over unpredictable events, and the difficulty in navigating healthcare systems, can also contribute to stress.
Support Systems Available
Recognizing and utilizing available support systems is crucial for mitigating the impact on families and caregivers. Support groups provide a safe space to connect with others facing similar challenges. These groups offer emotional support, practical advice, and a sense of shared understanding. Professionals such as social workers and therapists can offer counseling and guidance to navigate the emotional and psychological effects of caregiving.
Furthermore, financial assistance programs may be available to ease the burden of medical expenses.
Strategies for Managing Stress and Maintaining Well-being
Maintaining well-being amidst the demands of caregiving is essential. Prioritizing self-care is paramount. This includes setting realistic expectations, scheduling regular breaks, and engaging in activities that promote relaxation and enjoyment. Seeking support from friends, family, and support groups can provide much-needed emotional relief. Communicating openly with the person experiencing seizures and other family members is also vital.
This open communication helps in addressing concerns and anxieties effectively.
Available Support Resources
| Resource Type | Description | Contact Information/Example |
|---|---|---|
| Support Groups | Offer emotional support, practical advice, and shared experiences for caregivers. | Local Epilepsy organizations, online forums. |
| Mental Health Professionals | Provide counseling and therapy to address the emotional and psychological challenges of caregiving. | Social workers, therapists, psychologists. |
| Financial Assistance Programs | Provide financial aid to offset medical expenses and related costs. | Government programs, non-profit organizations. |
| Healthcare Providers | Essential for ongoing medical management and support for the person with seizures and their family. | Neurologists, epilepsy specialists, primary care physicians. |
| Educational Resources | Provide information and guidance about seizure management, caregiving, and support services. | Epilepsy Foundation, medical websites. |
Illustrative Cases
Understanding the diverse spectrum of seizures requires exploring real-life examples. Case studies provide valuable insights into the diagnostic process, treatment approaches, and long-term impacts on individuals and their families. These narratives help us connect abstract concepts with tangible experiences, highlighting the complexity and variability of this neurological condition.
Case Study 1: Focal Onset Seizures
This case focuses on a 32-year-old woman, Sarah, who presented with focal onset seizures characterized by brief, staring spells followed by repetitive movements of the right arm and hand. Initial investigations revealed no structural brain abnormalities, but an EEG showed intermittent spike-and-wave discharges localized to the temporal lobe. The diagnosis of focal onset seizures with secondary generalization was confirmed.Sarah was prescribed levetiracetam, a medication effective in reducing seizure frequency.
She experienced a significant reduction in seizure episodes within a few months of treatment. However, she also experienced mild side effects, including fatigue and occasional dizziness. This underscores the importance of careful monitoring and potential adjustments to treatment regimens to optimize efficacy and minimize adverse effects.The long-term prognosis for Sarah is generally positive, given the successful response to treatment.
The impact on her quality of life was initially substantial due to the unpredictable nature of her seizures. However, with consistent management and lifestyle adjustments, she was able to resume her daily activities, including work and social engagements. While occasional adjustments and adaptations to her daily schedule were necessary, Sarah demonstrated remarkable resilience and adaptation.
Case Study 2: Absence Seizures in Childhood
This case study examines a 9-year-old boy, Ethan, diagnosed with absence seizures. Ethan’s seizures were characterized by brief lapses in awareness, often accompanied by a blank stare and cessation of activity. The episodes were typically short, lasting only a few seconds. An EEG showed characteristic 3 Hz spike-and-wave discharges.Ethan’s treatment involved the use of ethosuximide, which effectively controlled the frequency of absence seizures.
This medication allowed him to maintain a more stable and predictable state of awareness and activity. Ethan’s overall development and cognitive function remained unaffected.The prognosis for Ethan is excellent. The impact on his quality of life was primarily related to the unpredictable nature of his seizures and the potential for disruption in school and social activities. However, with prompt diagnosis and effective medication management, Ethan was able to participate fully in school and extracurricular activities, experiencing minimal limitations in his overall development.
Summary Table
| Characteristic | Case Study 1 (Sarah) | Case Study 2 (Ethan) |
|---|---|---|
| Age | 32 | 9 |
| Seizure Type | Focal onset, secondary generalization | Absence |
| Symptoms | Brief staring spells, repetitive arm/hand movements | Brief lapses in awareness, blank stare, cessation of activity |
| Diagnosis Confirmation | EEG, no structural abnormalities | EEG, characteristic 3 Hz spike-and-wave discharges |
| Treatment | Levetiracetam | Ethosuximide |
| Impact on Quality of Life | Initially substantial, improved with treatment | Minimal impact, fully participated in school and activities |
| Prognosis | Generally positive | Excellent |
Long-Term Management
Living with seizures requires a proactive and ongoing approach to management. This phase extends beyond initial diagnosis and treatment, focusing on sustained well-being and minimizing potential complications. Long-term strategies are crucial for maintaining a good quality of life and preventing future crises.
Importance of Ongoing Monitoring and Follow-up Care
Regular check-ups and monitoring are essential for optimizing seizure management. These appointments allow healthcare providers to track treatment effectiveness, detect any emerging issues, and make necessary adjustments to the treatment plan. Proactive monitoring can prevent complications from escalating and ensure the best possible outcomes. The frequency of these appointments depends on the individual’s specific needs and seizure characteristics.
Role of Regular Check-ups and Medication Adjustments, Risks and complications of seizures
Regular check-ups are vital for assessing treatment efficacy and adjusting medication as needed. Blood tests and other diagnostic procedures might be conducted to monitor medication levels and identify potential side effects. Adjustments to medication dosages or types are often necessary to maintain optimal seizure control and minimize adverse effects. These adjustments are tailored to each individual’s response to treatment and seizure patterns.
Strategies for Managing Potential Complications
Managing potential complications requires a multi-faceted approach. Strategies may include lifestyle modifications, such as stress reduction techniques, dietary changes, or regular exercise, to support overall health and potentially mitigate triggers. Recognizing and addressing any emotional or psychological challenges is equally important, as stress and anxiety can sometimes influence seizure frequency. Early intervention for any emerging symptoms is crucial.
Routine Check-up and Medication Adjustment Schedule
This table Artikels a sample schedule for routine check-ups and medication adjustments. Individual needs may vary.
| Visit Type | Frequency | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Evaluation | Within 1-2 weeks of diagnosis | Establish baseline, discuss treatment plan, initial medication prescription |
| Follow-up Check-up | Every 1-3 months (depending on severity and treatment response) | Monitor seizure frequency, medication effectiveness, assess for side effects, adjust medication if needed |
| Comprehensive Evaluation | Every 6-12 months | Thorough review of medical history, neurological exam, comprehensive blood work, EEG, and other tests as needed to assess overall health and treatment effectiveness. |
| Emergency Visits/Urgent Appointments | As needed | Address immediate concerns regarding seizures, side effects, or any changes in health status. |
Wrap-Up
In conclusion, seizures can pose a multifaceted challenge, impacting not only the individual experiencing them but also their families and caregivers. Navigating the risks and complications requires a multifaceted approach, encompassing medical management, emotional support, and proactive strategies to enhance quality of life. By understanding the diverse aspects of seizures, from diagnosis and treatment to long-term management and support, individuals can better prepare for and manage this condition.