How to prevent dry socket is crucial for a smooth recovery after a tooth extraction. This guide dives deep into understanding this painful complication and provides practical strategies to minimize your risk. We’ll explore the causes, symptoms, and preventative measures you can take to ensure a healthy healing process.
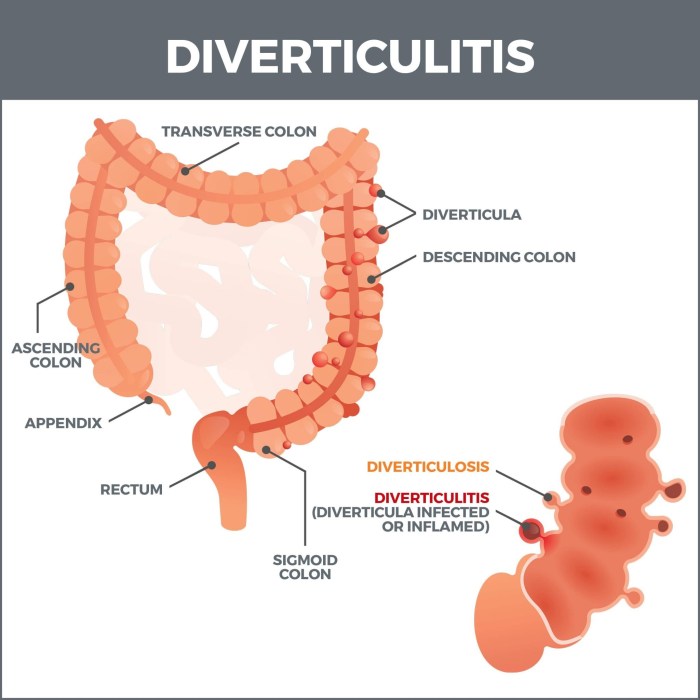
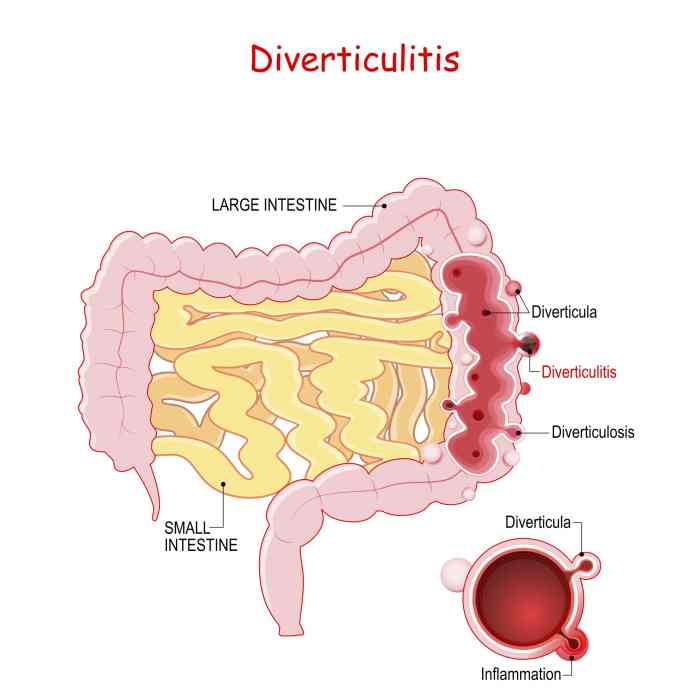
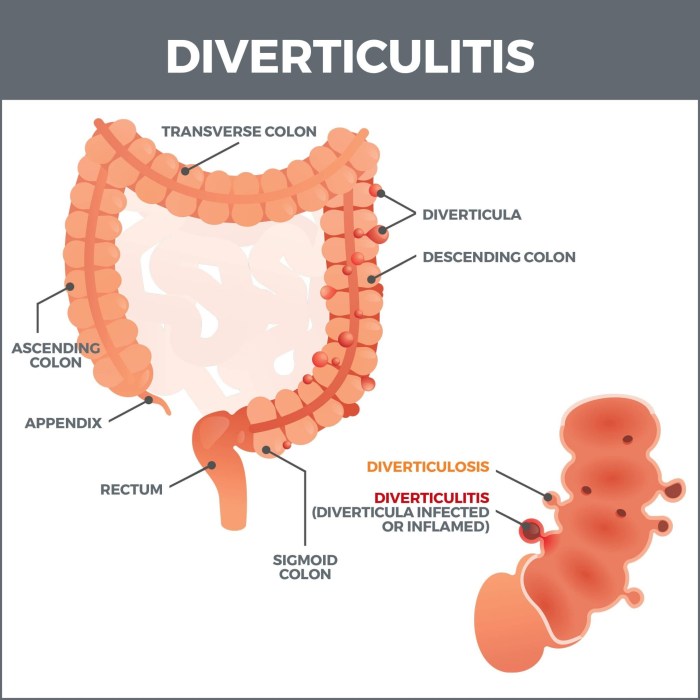
Dry socket, also known as alveolar osteitis, is a painful condition that can occur after a tooth extraction. It’s characterized by the loss of the blood clot that forms in the extraction socket, exposing the underlying bone. This often leads to intense pain, and can significantly impact your comfort and daily life. Learning how to prevent dry socket can make all the difference in your recovery.
Understanding Dry Socket
Dry socket, a painful oral complication, is a significant concern for patients undergoing tooth extractions. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and typical progression is crucial for both patients and dentists to manage the condition effectively. This detailed look at dry socket aims to equip readers with the knowledge needed to recognize and address this issue.Dry socket, medically known as alveolar osteitis, is a condition that occurs after a tooth extraction when the blood clot that forms in the socket is lost or dislodged prematurely.
This exposes the underlying bone, leading to severe pain and discomfort. The absence of this protective clot allows the bone to become inflamed and vulnerable to infection.
Causes of Dry Socket
Various factors can contribute to the development of dry socket. Surgical procedures, particularly tooth extractions, increase the risk. Factors that can contribute to a higher risk include:
- Surgical Procedures: Certain surgical procedures increase the risk of dry socket. Complex extractions, extractions involving multiple teeth, and extractions in areas with poor blood supply are examples of procedures that may increase the risk.
- Smoking and Tobacco Use: Smoking interferes with the body’s natural healing processes. Nicotine and other chemicals in tobacco products can impair blood clotting, increasing the risk of dry socket.
- Medications: Certain medications, including blood thinners, can also affect blood clotting and increase the risk of dry socket.
- Patient-Specific Factors: Individual patient factors, such as pre-existing medical conditions, hormonal fluctuations, and poor oral hygiene, can also play a role in the development of dry socket.
Symptoms of Dry Socket
The hallmark symptom of dry socket is intense, throbbing pain that typically begins 2-4 days after the extraction. The pain is often described as sharp, excruciating, and localized to the extraction site. It may radiate to the surrounding areas, including the jaw and temple.
- Pain Intensity: The pain associated with dry socket is often described as severe, often escalating to a level that interferes with daily activities.
- Pain Location: The pain is localized to the extraction site and its surrounding areas. Patients may experience pain when they chew or touch the affected area.
Timeline of Dry Socket Development
Dry socket typically develops a few days after the extraction procedure. The initial blood clot, which helps protect the underlying bone, forms immediately after the procedure. However, if the clot is lost or dislodged, pain and inflammation typically start 2-4 days after the extraction.
Symptoms, Severity, Duration, and Possible Causes
| Symptoms | Severity | Duration | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intense throbbing pain | Severe | 2-7 days (often resolves within 7 days) | Loss of blood clot, poor blood supply, smoking, certain medications |
| Tenderness or sensitivity to touch | Moderate | 2-7 days | Inflammation of the extraction site |
| Bad taste or odor | Mild to moderate | 2-7 days | Infection at the extraction site |
| Swelling | Mild to moderate | 2-7 days | Inflammation, infection |
Risk Factors and Prevention Strategies: How To Prevent Dry Socket

Preventing dry socket, a painful post-extraction complication, hinges on understanding the factors that contribute to its development. By identifying and mitigating these risks, both dentists and patients can significantly reduce the likelihood of this unfortunate outcome. A proactive approach, combining meticulous surgical techniques with patient education, is key to optimal post-extraction healing.Surgical techniques play a critical role in minimizing dry socket risk.
Proper handling of the extraction site during surgery, coupled with appropriate patient management, significantly reduces the risk. This includes meticulous tissue handling, careful removal of the tooth, and ensuring a stable blood clot formation. Patient factors, such as smoking and oral hygiene habits, also influence the healing process.
Taking care of your mouth after oral surgery is key to preventing dry socket. Things like avoiding straws, smoking, and using a harsh mouthwash are important. Interestingly, managing anxiety can also indirectly help with healing. A supplement like the lemme chill for anxiety kardashian supplement might help with reducing stress, which could, in turn, aid the healing process and potentially lower your risk of dry socket.
Following your dentist’s post-op instructions is still the best way to prevent dry socket, though.
Surgical Techniques for Dry Socket Prevention
Careful surgical techniques during tooth extraction are essential for establishing favorable conditions for healing. This includes minimizing trauma to the surrounding tissues and promoting clot formation. Maintaining a sterile field and employing appropriate instruments are crucial for preventing infection. Using meticulous surgical techniques can significantly reduce the likelihood of dry socket.
- Precise extraction: Avoiding excessive force or unnecessary tissue damage during extraction minimizes the risk of disrupting the blood clot formation.
- Gentle tissue handling: Careful management of the soft tissues around the extraction site reduces the potential for trauma and promotes blood clot stability.
- Appropriate instrumentation: Using appropriate instruments for extraction reduces the risk of damage to the underlying tissues, thereby enhancing the chances of a stable blood clot.
- Clot formation promotion: Employing techniques that promote clot formation, such as using a suitable dressing or packing material, can increase the likelihood of a stable healing environment.
Patient Factors Affecting Dry Socket Risk
Patient-related factors can significantly influence the risk of developing dry socket. Understanding these factors allows for personalized prevention strategies. Factors like smoking, oral hygiene practices, and underlying systemic conditions all contribute to the risk. Understanding the patient’s habits and medical history is vital in tailoring preventive measures.
- Smoking: Smoking significantly impairs blood clot formation and increases the risk of dry socket. Nicotine interferes with the healing process by constricting blood vessels, hindering the body’s ability to deliver nutrients to the extraction site. Patients who smoke should be counselled on the detrimental effects of smoking on wound healing and offered smoking cessation support.
- Oral Hygiene: Poor oral hygiene can contribute to infection, which can disrupt the healing process and increase the risk of dry socket. Maintaining proper oral hygiene practices, including brushing and flossing, is vital for overall oral health and to minimize the risk of infection following extractions.
- Systemic Conditions: Certain systemic conditions, such as blood clotting disorders, can affect the body’s ability to form and maintain a stable blood clot at the extraction site. Patients with pre-existing conditions should be evaluated by their dentist to determine the appropriate preventative measures. Dentists should be aware of and take into account these conditions when planning extractions and provide necessary precautions.
The Role of Blood Clots in Healing
A stable blood clot is crucial for the healing process after tooth extraction. It acts as a protective barrier, preventing infection and providing a foundation for new tissue growth. The clot’s integrity is essential for proper healing, as it prevents the exposed bone and nerve endings from being exposed and vulnerable to infection. A disruption in the blood clot can lead to dry socket.
Preventing dry socket after a tooth extraction is crucial, just like proper care for a calf strain muscle spasm of the leg. Proper oral hygiene, avoiding straws and spitting, and following your dentist’s instructions are key. While a calf strain muscle spasm of the leg might seem unrelated , the underlying principle of gentle care and avoiding strenuous activity applies to both.
A calm approach to healing is important for both, ensuring a swift and smooth recovery.
- Formation and Function: The blood clot provides a protective barrier against infection and a scaffold for new tissue growth. It’s essential to maintain the integrity of this clot to promote optimal healing.
- Disruption and Risk: Any disruption of the blood clot can lead to exposure of the underlying bone and nerve endings, increasing the risk of dry socket. This is particularly vulnerable in the initial days post-extraction.
Prevention Strategies Table
| Risk Factor | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|
| Smoking | Counsel patients about the detrimental effects of smoking on healing and offer smoking cessation support. |
| Poor Oral Hygiene | Emphasize the importance of maintaining good oral hygiene, including brushing and flossing, before and after extractions. |
| Systemic Conditions | Assess patients for any systemic conditions that might affect blood clotting or healing and consult with specialists if necessary. |
| Surgical Technique | Employ meticulous surgical techniques, minimizing trauma to surrounding tissues, to ensure proper clot formation. |
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing dry socket requires a careful approach, combining clinical evaluation with patient history. Prompt and accurate diagnosis is crucial for initiating appropriate treatment and minimizing discomfort. The process often involves a combination of observation, palpation, and patient communication to differentiate dry socket from other potential oral health issues.
Preventing dry socket after a tooth extraction is crucial. Good oral hygiene, like gentle rinsing and avoiding smoking, are key. Interestingly, some research suggests that natural remedies like honey might play a role in wound healing, as seen in studies on can honey help heal wounds. But ultimately, following your dentist’s post-extraction instructions is the best way to ensure a speedy and healthy recovery from dry socket.
Diagnostic Procedures
Accurate diagnosis of dry socket hinges on a thorough understanding of the patient’s symptoms and a meticulous physical examination. The dentist or oral surgeon must carefully assess the affected area, looking for signs of inflammation, pain intensity, and the presence of any blood clots. A detailed patient history, including the date of extraction, any pain medication taken, and any relevant medical conditions, is essential.
This information helps to distinguish dry socket from other painful conditions. Careful palpation of the extraction site is vital; the absence of a healthy blood clot, along with severe pain, can point towards dry socket.
Treatment Options
Several treatment options are available for managing dry socket, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The primary goal is to alleviate pain, promote healing, and prevent further complications. Treatment options often involve a combination of approaches, tailored to the individual patient’s needs.
- Medication: Pain management is a key component of dry socket treatment. Analgesics, such as over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen and acetaminophen, can help control pain. In some cases, stronger opioid analgesics may be necessary to manage severe pain. Antibiotics might be prescribed to address any secondary infections. The specific medications and dosages will be determined by the healthcare provider based on the patient’s condition and response to treatment.
- Debridement: Gentle debridement, or cleaning of the extraction site, is often performed to remove any debris or blood clots that might be contributing to the pain. This procedure involves carefully removing necrotic tissue or any foreign material. Debridement is a crucial part of the treatment process, as it promotes healing and reduces pain.
- Irrigation: Irrigation of the extraction site with saline solution or other antiseptic solutions can help to flush out debris and promote a cleaner environment for healing. Irrigation is often used in conjunction with other treatment modalities to enhance the effectiveness of the treatment plan.
- Local Anesthesia: Local anesthetic injections can provide temporary relief from pain, enabling the patient to better tolerate other procedures. This is often used in conjunction with other treatments.
- Packing: In some cases, a medicated dressing or packing material may be placed over the extraction site to help protect the area, control bleeding, and promote healing. The specific type of packing material will depend on the individual needs of the patient.
Pain Management Strategies
Effective pain management is crucial for the comfort and well-being of patients experiencing dry socket. Various strategies are employed to manage pain, from over-the-counter analgesics to more intensive interventions. A multi-faceted approach is often required to achieve optimal pain relief.
- Analgesics: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen and acetaminophen, can help control mild to moderate pain. Prescription-strength analgesics, such as opioids, might be necessary for severe cases. The choice of analgesic depends on the severity of the pain and the patient’s response to treatment.
- Other Techniques: In addition to analgesics, other techniques, such as cold compresses and relaxation exercises, may be recommended to manage pain and promote comfort. Applying ice packs to the affected area can help reduce swelling and inflammation, providing temporary relief. Relaxation techniques can also help manage the anxiety and stress associated with pain.
Role of Debridement
Debridement plays a vital role in treating dry socket. It involves carefully removing the necrotic tissue, blood clots, and debris that accumulate at the extraction site, thus creating a clean environment for healing. This procedure is often performed under local anesthesia and is aimed at promoting tissue regeneration and reducing pain. The specific debridement technique will depend on the extent of the damage and the individual needs of the patient.
Comparison of Treatment Options
| Treatment Option | Effectiveness | Side Effects | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Analgesics (over-the-counter) | Generally effective for mild to moderate pain | Potential for stomach upset, allergic reactions | Low |
| Analgesics (prescription) | Highly effective for severe pain | Potential for addiction, nausea, constipation | Moderate to high |
| Debridement | Effective in removing debris and promoting healing | Potential for bleeding, discomfort | Moderate |
| Irrigation | Helps clean the extraction site | Minimal side effects | Low |
| Packing | Provides protection and promotes healing | Potential for discomfort, allergic reactions | Moderate |
Home Care and Aftercare s
Taking care of yourself after a tooth extraction is crucial for a smooth healing process and preventing complications like dry socket. Proper home care involves managing pain, maintaining oral hygiene, and avoiding certain foods and activities. This section will provide detailed instructions for each aspect, ensuring a comfortable and healthy recovery.
Managing Pain and Discomfort
Effective pain management after a tooth extraction is essential. Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help alleviate discomfort. Follow the dosage instructions carefully and consult your dentist if you experience severe or persistent pain. Applying ice packs to the outside of the cheek, wrapped in a thin cloth, can also help reduce swelling and pain.
Remember to maintain a consistent schedule for taking pain medication. Applying gentle pressure with a gauze pad to the extraction site can help reduce bleeding.
Oral Hygiene Practices
Maintaining good oral hygiene is paramount during the healing process. Gentle brushing and flossing are crucial, but avoid the extraction site directly. Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and a gentle, circular motion around the affected area. Floss gently around the extraction site without inserting anything directly into the socket. Rinsing with a prescribed mouthwash (if provided) is recommended.
Avoid vigorous rinsing, as this could dislodge the blood clot. If you experience excessive bleeding, follow the instructions provided by your dentist.
Avoiding Foods and Activities
Certain foods and activities can disrupt the healing process and increase the risk of complications. Avoid using a straw for a few days as it could dislodge the blood clot. Refrain from strenuous activities that may increase blood pressure or cause excessive stress on the jaw area. Avoid smoking, as it can hinder healing and increase the risk of dry socket.
Correct Mouth Rinsing Method
After extraction, gently rinse your mouth with warm salt water. Do not rinse forcefully. Gently swish the solution around your mouth for about 30 seconds, then spit it out. Avoid rinsing excessively or aggressively, as this can disrupt the forming blood clot. Rinse only when needed to remove food particles.
Foods to Avoid and Suitable Foods
| Foods to Avoid | Suitable Foods |
|---|---|
| Extremely hot or cold foods | Soft, lukewarm foods like yogurt, mashed potatoes, or applesauce |
| Hard, crunchy foods (chips, nuts, pretzels) | Soups, smoothies, or easily chewed foods like cooked vegetables |
| Sticky foods (caramels, taffy) | Soft, mashed, or blended foods |
| Spicy foods | Mild-flavored foods |
| Foods that require extensive chewing | Foods that can be easily swallowed or require minimal chewing |
Remember to follow your dentist’s specific instructions for your particular situation. This information is for general guidance only.
Complications and Long-Term Effects
Dry socket, while often temporary, can sometimes lead to more serious complications if not properly managed. Understanding these potential issues is crucial for effective prevention and treatment. Ignoring the symptoms or delaying care can increase the risk of complications. Prompt intervention and adherence to aftercare instructions are essential to minimizing the negative impact of dry socket.The potential complications of dry socket extend beyond the immediate discomfort.
They can affect the healing process, potentially causing long-term issues within the oral cavity and surrounding tissues. A thorough understanding of these potential outcomes empowers patients and dental professionals to take proactive measures for optimal recovery.
Potential Complications of Dry Socket
Dry socket can lead to a cascade of complications, ranging from localized infection to more extensive issues. The severity of these complications depends on various factors, including the individual’s overall health, the extent of the initial injury, and the promptness of treatment.
Infection
Infections are a serious concern following any oral surgery or dental procedure. A dry socket can create a wound environment conducive to bacterial growth, leading to localized infections. Symptoms of infection include increased pain, swelling, fever, and bad breath. Prompt medical attention is crucial to manage any infection and prevent its spread. Prompt and appropriate antibiotic therapy is a vital part of treating an infection associated with dry socket.
Delayed Healing
A dry socket can significantly hinder the natural healing process of the extraction site. Without a blood clot, the underlying bone and tissues are exposed, potentially delaying healing and increasing the risk of further complications. The delay in healing can result in prolonged discomfort, increased susceptibility to infection, and potential scarring. This can lead to a prolonged recovery period, impacting the individual’s overall well-being.
Long-Term Effects on Oral Tissues
The immediate and long-term effects of dry socket can affect the oral cavity and surrounding tissues. While usually resolving with proper care, persistent issues could manifest. Persistent pain, lingering discomfort, and difficulty chewing or speaking can occur. In extreme cases, chronic inflammation or scarring could potentially affect the surrounding tissues. A thorough evaluation by a dentist is necessary to address these potential issues.
Table of Potential Complications
| Potential Complication | Cause | Prevention Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Infection | Exposure of the bone and tissues to bacteria in the absence of a blood clot. | Prompt diagnosis and treatment, proper oral hygiene, and adherence to aftercare instructions. |
| Delayed Healing | Absence of a blood clot, exposing the underlying bone and tissues. | Following post-operative instructions carefully, maintaining good oral hygiene, and promptly reporting any signs of pain or discomfort. |
| Chronic Inflammation | Persistent irritation and exposure of the tissues. | Diligent adherence to prescribed medications, regular dental checkups, and early intervention in case of discomfort. |
| Scarring | Prolonged exposure of tissues and delayed healing. | Prompt treatment of dry socket, maintaining oral hygiene, and following prescribed care instructions. |
Case Studies and Illustrations
Understanding dry socket requires more than just theoretical knowledge; it’s crucial to see how it manifests in real-life cases and how the healing process differs from a healthy socket. This section delves into case studies, illustrating the symptoms, treatment, and outcomes, as well as the anatomical structures involved. Visual representations of healthy and affected sockets will help solidify your comprehension.
Detailed Case Study of a Dry Socket Patient
A 28-year-old female patient presented with severe pain and halitosis following an extraction of a lower molar. Symptoms began 48 hours post-extraction, characterized by sharp, throbbing pain radiating to the ear and temple. The pain was exacerbated by chewing and talking. The patient reported a dry, painful area in the extraction site. Upon examination, the extraction site lacked a blood clot, exposing the underlying bone.
The diagnosis was confirmed as dry socket.The treatment involved irrigation of the extraction site with saline solution, followed by application of a medicated dressing. Pain medication, including over-the-counter analgesics and prescription-strength opioids, was prescribed to manage the intense pain. The patient was instructed to avoid smoking, hard foods, and excessive rinsing. Regular follow-up appointments ensured the healing process was progressing as expected.
Within a week, the pain subsided significantly, and a blood clot began to form. The patient reported complete resolution of symptoms within two weeks, and the socket healed completely without complications.
Healing Process of a Dry Socket
The healing process of a dry socket follows a distinct timeline and can be visualized in stages.
- Initial Stage (24-48 hours): The socket typically forms a blood clot that acts as a protective layer. In dry socket, this clot fails to form or dislodges prematurely, exposing the underlying bone. This exposes the sensitive bone and nerves, leading to the characteristic severe pain. The exposed bone is highly sensitive, leading to pain that is difficult to manage.
- Intermediate Stage (48-72 hours): The body’s natural healing mechanisms attempt to reestablish the protective blood clot in a dry socket. However, due to the absence of a protective blood clot, the pain remains intense and localized, with the throbbing pain often intensified by oral stimulation or chewing. The healing process is delayed and potentially hampered by the persistent pain.
- Final Stage (7-14 days): With proper treatment and patient compliance, the socket begins to regenerate a blood clot. The inflammatory response subsides, and the pain significantly reduces. The socket gradually heals, and the patient experiences a return to normalcy, including the cessation of pain and improved oral function.
Anatomical Structures Affected by Dry Socket, How to prevent dry socket
Dry socket directly impacts the anatomical structures surrounding the extraction site.
- Bone (alveolar bone): The exposed bone is the most sensitive area affected. This bone provides structural support to the teeth and surrounding tissues. The absence of the blood clot exposes this sensitive area to bacteria and irritants.
- Nerves (trigeminal nerve): The trigeminal nerve is responsible for sensation in the face, including the mouth and jaw. The exposed nerve endings experience direct stimulation from the surrounding environment, leading to the severe pain associated with dry socket.
- Soft tissues (mucosa, periosteum): The exposed bone can cause inflammation and irritation in the surrounding soft tissues. The lack of a protective clot can disrupt the natural healing process in these areas.
Comparison of Healthy and Dry Socket Healing
| Feature | Healthy Socket | Dry Socket |
|---|---|---|
| Clot Formation | Rapid formation of a stable blood clot, covering the extraction site. | Absence or premature dislodgement of the blood clot, exposing the underlying bone. |
| Pain | Minimal to moderate pain, typically manageable with over-the-counter pain relievers. | Severe, throbbing pain, often requiring stronger pain medications. |
| Inflammation | Mild and localized inflammation, resolving rapidly. | Significant inflammation, persisting for an extended period. |
| Healing Time | Typically 7-10 days. | Prolonged healing time, often requiring 10-14 days or more. |
Illustrations of Healthy and Dry Socket
A healthy extraction socket is characterized by a firm blood clot covering the extraction site. The surrounding tissues are intact and exhibit minimal inflammation. The clot acts as a protective barrier against infection. A dry socket, conversely, shows a lack of a blood clot, exposing the underlying bone. The surrounding tissues exhibit inflammation, and the exposed bone appears red and sensitive.
Last Recap

Preventing dry socket involves a multi-faceted approach, encompassing both patient and dentist responsibilities. By understanding the risk factors and implementing the preventative strategies Artikeld in this guide, you can significantly reduce your chances of experiencing this painful complication. A healthy recovery after any dental procedure is possible with proper care and knowledge. Remember, proactive measures are key to a comfortable and successful healing process.