Psychotropic medications uses types side effects administration are crucial in managing mental health conditions. These medications, encompassing a range of types from anti-anxiety drugs to mood stabilizers, play a significant role in treating various disorders. Understanding their diverse applications, potential side effects, and proper administration is essential for both patients and healthcare providers.
This comprehensive overview explores the different classes of psychotropic medications, their mechanisms of action, and their indications for use. We’ll also delve into the potential side effects, necessary administration protocols, and the importance of patient counseling. Ultimately, this exploration aims to provide a deeper understanding of these powerful tools in mental healthcare.
Overview of Psychotropic Medications
Psychotropic medications are a crucial component of modern mental health care, playing a vital role in managing and treating a wide range of conditions. These medications act on the brain and nervous system to alter chemical processes, influencing mood, behavior, and thought patterns. Understanding their diverse categories, mechanisms of action, and historical context is essential for comprehending their significance in mental health.These medications work by affecting neurotransmitters, the chemical messengers that transmit signals between nerve cells.
By modulating neurotransmitter levels or receptor activity, psychotropic medications can help alleviate symptoms and improve the quality of life for individuals struggling with mental health disorders.
Categories of Psychotropic Medications
Psychotropic medications are broadly categorized based on their primary targets and mechanisms of action. These categories encompass a range of medications, each with its own specific uses and potential side effects.
- Antidepressants: These medications are used to treat mood disorders, primarily depression, but can also be effective for anxiety and other conditions. Examples include selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) like fluoxetine (Prozac) and sertraline (Zoloft), serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) like venlafaxine (Effexor), and tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs).
- Antipsychotics: These medications are primarily used to treat psychosis, a condition characterized by distorted thinking and perception, often seen in schizophrenia and other severe mental illnesses. Typical antipsychotics, such as haloperidol, act on dopamine receptors, while atypical antipsychotics, like risperidone and olanzapine, target multiple neurotransmitter systems.
- Mood Stabilizers: These medications are designed to regulate mood swings and prevent episodes of mania and depression, particularly in bipolar disorder. Lithium and valproate are examples of mood stabilizers.
- Anxiolytics/Anti-anxiety Medications: These medications are used to reduce anxiety and related symptoms. Benzodiazepines, such as diazepam (Valium) and alprazolam (Xanax), are commonly prescribed for their rapid-acting effects. However, their use is often limited due to potential dependence.
- Stimulants: These medications increase activity in the central nervous system. They are often used to treat attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy. Examples include methylphenidate (Ritalin) and amphetamine-based medications.
Historical Context
The development of psychotropic medications has been a significant advancement in mental health care. Early attempts involved the use of natural substances, but the discovery of neurotransmitters and their role in brain function paved the way for the creation of targeted medications. The 1950s saw the introduction of chlorpromazine, a groundbreaking antipsychotic that revolutionized the treatment of psychosis. Subsequent decades witnessed the development of newer, more specific medications, leading to a greater understanding of the complexities of mental illness.
Mechanism of Action
Psychotropic medications influence the brain by modulating neurotransmitter activity. This involves either increasing or decreasing the availability of neurotransmitters in the synaptic cleft. This table provides a concise overview:
| Medication Type | Primary Use | Brief Mechanism of Action |
|---|---|---|
| Antidepressants (SSRIs) | Major Depressive Disorder | Block the reuptake of serotonin, increasing its availability in the synapse. |
| Antipsychotics (Typical) | Psychosis | Block dopamine receptors, reducing dopamine activity. |
| Mood Stabilizers (Lithium) | Bipolar Disorder | Alters ion transport and neurotransmitter release, reducing mood swings. |
| Anxiolytics (Benzodiazepines) | Anxiety | Enhance the effects of GABA, an inhibitory neurotransmitter, leading to increased neuronal inhibition. |
| Stimulants (Methylphenidate) | ADHD | Increase the release of dopamine and norepinephrine in the synapse. |
Specific Types of Psychotropic Medications
Psychotropic medications are a diverse group of drugs that affect the brain and nervous system, impacting mood, behavior, and thoughts. Understanding the various classes and their specific actions is crucial for effective use and management of mental health conditions. These medications target different neurochemical pathways, leading to varying effects on the brain’s function.This exploration delves into the key classes of psychotropic medications, highlighting common examples, intended uses, and contrasting their mechanisms of action.
Each class addresses different aspects of mental health conditions, and understanding these nuances is essential for responsible use and effective treatment.
Anti-Anxiety Medications, Psychotropic medications uses types side effects administration
Anti-anxiety medications, also known as anxiolytics, are primarily used to relieve anxiety and its associated symptoms. These medications act on neurotransmitter systems in the brain, often by enhancing the effects of GABA, an inhibitory neurotransmitter. This leads to a calming effect and a reduction in anxiety-related responses.
- Benzodiazepines, such as diazepam (Valium) and alprazolam (Xanax), are commonly prescribed for short-term relief of anxiety symptoms. Their mechanism of action involves enhancing GABAergic neurotransmission, which promotes relaxation and reduces anxiety. Benzodiazepines are known for their rapid onset of action, but long-term use can lead to dependence. Chemical structures of benzodiazepines often feature a fused benzene and diazepine ring.
They are primarily used for acute anxiety, panic attacks, and insomnia.
- Buspirone (Buspar) is a non-benzodiazepine anxiolytic. It differs from benzodiazepines in its mechanism of action, as it primarily affects serotonin and dopamine neurotransmitter systems. Buspirone’s onset of action is slower than benzodiazepines, requiring several weeks for full effectiveness. It is often used for generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). Buspirone is not associated with the same degree of dependence as benzodiazepines.
Psychotropic medications, used to treat various mental health conditions, come in different types, each with specific uses and potential side effects. Understanding the administration process is crucial for managing these medications effectively. While exploring alternative approaches, some people consider the potential benefits of omega 3 fatty acids omega 3 fatty acids as a complementary treatment. However, it’s important to remember that these should not replace prescribed psychotropic medications, and always consult a healthcare professional before making any changes to your treatment plan.
Antidepressants
Antidepressants are a diverse group of medications used to treat various mood disorders, including depression, anxiety disorders, and some eating disorders. They work by influencing neurotransmitter systems, primarily serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine.
- Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs), such as fluoxetine (Prozac) and sertraline (Zoloft), are commonly prescribed for depression and anxiety. SSRIs selectively inhibit the reuptake of serotonin in the brain, increasing its availability and potentially improving mood. Chemical structures of SSRIs often involve a substituted tricyclic structure.
- Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs), such as venlafaxine (Effexor) and duloxetine (Cymbalta), are another class of antidepressants that affect both serotonin and norepinephrine. Their effects are similar to SSRIs, but they may be more effective for individuals who do not respond well to SSRIs alone.
- Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs), such as amitriptyline (Elavil) and imipramine (Tofranil), are older antidepressants that affect multiple neurotransmitters. They are generally less selective than SSRIs or SNRIs, potentially leading to more side effects.
Antipsychotics
Antipsychotics are used to treat psychosis, a condition characterized by distorted thoughts, perceptions, and behaviors. These medications often target dopamine receptors in the brain.
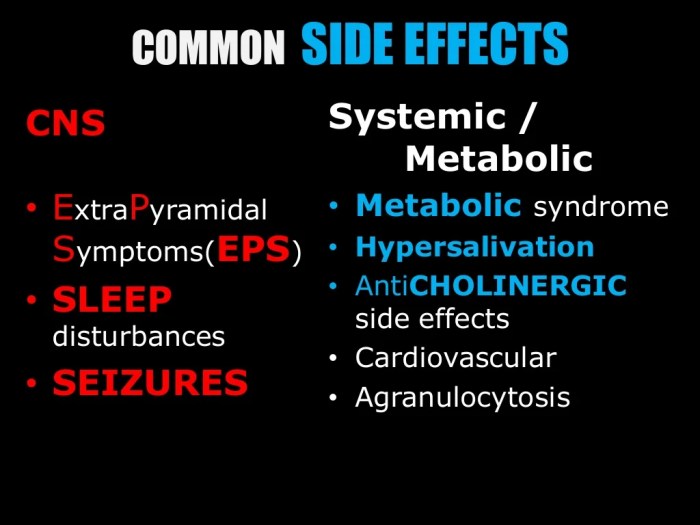
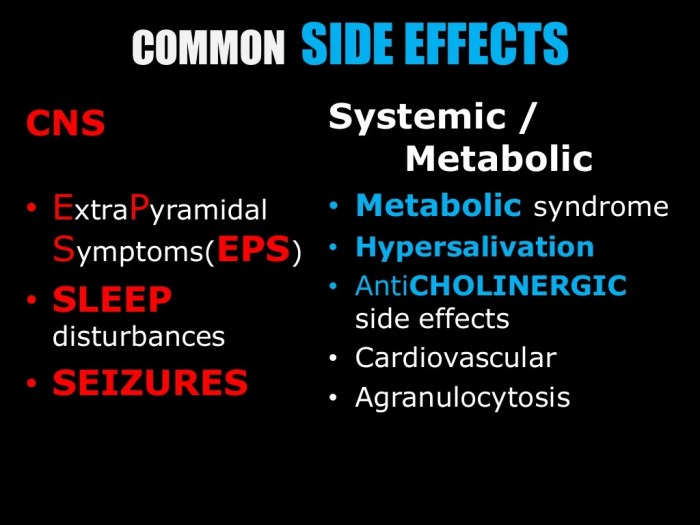
- Typical antipsychotics, such as haloperidol (Haldol), primarily block dopamine D2 receptors. These medications are often effective in reducing positive symptoms of psychosis, but they can also cause significant extrapyramidal side effects (EPS), such as tardive dyskinesia.
- Atypical antipsychotics, such as risperidone (Risperdal) and olanzapine (Zyprexa), are newer medications that target multiple neurotransmitter systems, including dopamine, serotonin, and others. They are often preferred over typical antipsychotics due to a lower risk of EPS, but they may still cause other side effects, such as weight gain and metabolic syndrome.
Mood Stabilizers
Mood stabilizers are used to treat bipolar disorder, a condition characterized by extreme mood swings. These medications aim to regulate mood fluctuations and prevent manic and depressive episodes.
- Lithium is a naturally occurring element that is often used as a mood stabilizer. Its mechanism of action is not fully understood, but it appears to affect multiple neurotransmitter systems. It’s crucial to monitor lithium levels closely due to its narrow therapeutic window.
- Anticonvulsants, such as valproate (Depakote) and lamotrigine (Lamictal), are also used as mood stabilizers. They are typically used to prevent seizures, but they also have mood-stabilizing effects in bipolar disorder.
| Medication Class | Mechanism of Action | Intended Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Anti-anxiety | Enhance GABAergic neurotransmission | Reduce anxiety, promote relaxation |
| Antidepressants | Affect serotonin, norepinephrine, and/or dopamine | Improve mood, reduce depressive symptoms |
| Antipsychotics | Block dopamine receptors (typical) or multiple receptors (atypical) | Reduce psychotic symptoms |
| Mood Stabilizers | Regulate mood fluctuations (various mechanisms) | Prevent manic and depressive episodes |
Mechanisms of Action
Psychotropic medications work by influencing the complex interplay of neurotransmitters in the brain. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for selecting the appropriate medication and managing potential side effects. These medications affect the brain’s chemical messengers, which ultimately impact mood, thoughts, and behaviors. They can alter the balance of neurotransmitters in the brain, leading to changes in the way neurons communicate.These medications exert their effects through various mechanisms, primarily targeting specific neurotransmitter systems and their receptors.
They may increase or decrease the availability of neurotransmitters, or modify how neurotransmitters interact with their receptors. This intricate interplay of neurotransmitters and receptors underlies the effectiveness of these medications in treating a wide range of mental health conditions.
Neurotransmitter Systems Targeted
Psychotropic medications often act on specific neurotransmitter systems, such as dopamine, serotonin, norepinephrine, GABA, and glutamate. These neurotransmitters play critical roles in regulating mood, cognition, and behavior. Understanding the specific neurotransmitter systems targeted by a medication is essential to predicting its potential effects.
- Dopamine: Dopamine is involved in motivation, reward, and movement. Antipsychotic medications, for example, often work by blocking dopamine receptors, reducing the overactivity of dopamine systems that may contribute to symptoms like hallucinations and delusions. Conversely, medications for Parkinson’s disease aim to increase dopamine levels or enhance its effects. This illustrates the delicate balance required in managing neurotransmitter systems.
- Serotonin: Serotonin plays a crucial role in mood regulation, sleep, and appetite. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are a common class of antidepressants that increase serotonin levels in the synaptic cleft, thereby alleviating depressive symptoms. This happens by preventing the reabsorption of serotonin into the neuron that released it.
- Norepinephrine: Norepinephrine is involved in alertness, focus, and stress response. Norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitors (NDRIs) are used to treat some depressive disorders, increasing the availability of norepinephrine and dopamine in the synapse. This can help improve mood and concentration.
- GABA: Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is an inhibitory neurotransmitter, meaning it reduces neuronal activity. Benzodiazepines, for instance, enhance the effects of GABA, leading to a calming effect and reducing anxiety. This increased inhibition of neuronal firing can lead to sedation and other side effects, which vary by individual and the specific medication.
- Glutamate: Glutamate is an excitatory neurotransmitter, involved in learning and memory. Certain medications for cognitive impairment may target glutamate receptors to modulate its excitatory effects. However, excessive glutamate activity can contribute to neurodegenerative processes, emphasizing the delicate balance needed in these systems.
Receptor Interactions
Psychotropic medications interact with specific receptors in the brain. These receptors are protein molecules embedded in the cell membrane of neurons. The binding of a neurotransmitter to its receptor triggers a cascade of intracellular events that ultimately influence neuronal activity.
- Specific Receptor Binding: Many psychotropic medications bind to specific receptors, either enhancing or blocking the neurotransmitter’s effect. For example, an SSRI (Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor) blocks the reuptake of serotonin, leaving more serotonin available in the synapse to bind to its receptors, potentially improving mood. This targeted action helps explain the diverse effects of these medications.
- Agonists and Antagonists: Some medications act as agonists, mimicking the effects of a neurotransmitter by binding to its receptor and triggering a response. Others act as antagonists, blocking the neurotransmitter from binding to its receptor and preventing the typical response. Understanding whether a medication is an agonist or antagonist is crucial for predicting its effects.
Neurotransmitters Targeted by Medication Classes
| Medication Class | Primary Neurotransmitter(s) Targeted | Mechanism of Action |
|---|---|---|
| Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) | Serotonin | Block serotonin reuptake, increasing serotonin levels in the synapse. |
| Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs) | Serotonin and Norepinephrine | Block the reuptake of both serotonin and norepinephrine, increasing levels of both neurotransmitters. |
| Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs) | Serotonin and Norepinephrine | Block the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine, similar to SNRIs, but with broader effects on other neurotransmitter systems. |
| Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs) | Dopamine, Norepinephrine, Serotonin | Inhibit the enzyme monoamine oxidase, preventing the breakdown of dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin, thereby increasing their levels. |
| Antipsychotics | Dopamine | Block dopamine receptors, reducing dopamine activity in the brain. |
Indications for Use: Psychotropic Medications Uses Types Side Effects Administration
Psychotropic medications are powerful tools in the mental health arsenal, carefully prescribed to address a wide range of conditions. Understanding the specific indications for each type is crucial for both clinicians and patients. This section delves into the conditions for which various psychotropic medications are commonly used, providing examples and rationale.
Common Mental Health Conditions and Corresponding Medications
Different psychotropic medications target distinct neurochemical pathways in the brain, leading to varying effects. This targeted approach allows clinicians to tailor treatment to the specific needs of each patient. The table below Artikels common mental health conditions and the corresponding medication types often prescribed.
| Mental Health Condition | Medication Type | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) | Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) | SSRIs increase serotonin levels in the brain, which can alleviate symptoms of depression. The rationale behind this approach is that low serotonin levels are implicated in depressive symptoms. Examples of diagnostic criteria include persistent feelings of sadness, loss of interest in activities, and changes in appetite or sleep patterns. |
| Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) | Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) | SSRIs can be effective in managing GAD, though other medications like benzodiazepines are sometimes preferred for acute anxiety relief. This is often because SSRIs take time to build up an effect. Diagnostic criteria for GAD include excessive worry and anxiety about a range of events or activities, impacting daily functioning. |
| Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) | Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs), Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs) | SSRIs and SNRIs can help manage the emotional and behavioral symptoms of PTSD. They can improve mood and reduce anxiety, crucial components of managing the condition. Diagnostic criteria for PTSD include exposure to a traumatic event, resulting in intrusive thoughts, avoidance, and hyperarousal. |
| Bipolar Disorder | Mood stabilizers (e.g., Lithium, Valproate) | Mood stabilizers help regulate mood swings and prevent manic and depressive episodes in bipolar disorder. This is because these medications can help balance the brain’s chemical imbalances, stabilizing mood. Diagnostic criteria include distinct periods of elevated mood (mania) and depressed mood (depression). |
| Schizophrenia | Antipsychotics | Antipsychotics target the positive symptoms of schizophrenia, such as hallucinations and delusions, and can also help with negative symptoms. This is done by reducing the effects of neurotransmitters implicated in these symptoms. Diagnostic criteria for schizophrenia include significant disturbances in thinking, perception, and behavior. |
Specific Examples and Diagnostic Criteria
The table above provides a general overview. It’s essential to understand that specific diagnostic criteria for each condition exist, and the selection of a medication depends on the individual’s specific presentation.
- Major Depressive Disorder (MDD): The DSM-5 criteria for MDD include a persistent depressed mood, loss of interest in activities, significant weight loss or gain, insomnia or hypersomnia, feelings of worthlessness, and recurrent thoughts of death or suicide. A diagnosis requires that these symptoms be present for at least two weeks and significantly impair daily functioning.
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD): Excessive worry and anxiety about a number of events or activities, occurring more days than not for at least six months, are key symptoms. The worry must be difficult to control and associated with physical symptoms such as restlessness, fatigue, difficulty concentrating, irritability, muscle tension, and sleep disturbance.
Rationale Behind Medication Selection
The choice of psychotropic medication is a complex process, involving careful consideration of the patient’s individual needs, medical history, and potential side effects. Factors such as the severity of symptoms, the presence of other medical conditions, and the patient’s response to previous treatments are crucial. A comprehensive evaluation by a mental health professional is essential.
Side Effects and Adverse Reactions
Psychotropic medications, while vital for treating mental health conditions, can unfortunately come with a range of side effects. Understanding these potential side effects is crucial for both patients and healthcare professionals. Proper monitoring and management of these side effects are key to ensuring optimal treatment outcomes and minimizing harm.
Common Side Effects Across Medication Classes
A variety of side effects are possible, stemming from the medications’ impact on the central nervous system. These can manifest in different ways, depending on the specific drug and the individual patient. Common side effects can include changes in mood, sleep disturbances, and gastrointestinal issues.
- Antidepressants: Common side effects of antidepressants include nausea, vomiting, constipation, and sexual dysfunction. Dry mouth, dizziness, and weight changes are also potential side effects. The severity and frequency of these side effects vary greatly depending on the specific antidepressant and the individual patient. For example, some selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are known to cause more gastrointestinal distress than others.
- Antipsychotics: Common side effects of antipsychotics include extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS), such as tremors, rigidity, and akathisia (restlessness). Metabolic side effects, including weight gain, elevated blood sugar, and dyslipidemia, are also frequently observed. The severity of EPS can vary widely, with some patients experiencing only mild symptoms, while others may experience more severe and debilitating side effects.
- Mood Stabilizers: Mood stabilizers, like lithium, can cause gastrointestinal distress, tremors, and kidney problems. Monitoring kidney function is crucial when prescribing lithium due to its potential toxicity. Other side effects may include weight gain and changes in thyroid function.
Mechanisms of Side Effect Occurrence
The mechanisms behind psychotropic medication side effects are complex and often not fully understood. However, some general principles apply. These side effects often arise from the drug’s interaction with neurotransmitter systems in the brain, potentially leading to imbalances in neurotransmission. For example, blocking dopamine receptors can result in EPS, while disrupting serotonin pathways can lead to gastrointestinal distress.
Importance of Monitoring
Careful monitoring of patients taking psychotropic medications is essential. Regular check-ups allow healthcare professionals to assess the effectiveness of the treatment and identify any emerging side effects. Prompt recognition and management of side effects can prevent them from escalating into serious problems.
Table Categorizing Side Effects
The table below provides a categorized overview of potential side effects, grouped by medication class and severity. This is not an exhaustive list, and the specific side effects experienced by a patient can vary significantly.
| Medication Class | Common Side Effects | Severity (Mild/Moderate/Severe) |
|---|---|---|
| Antidepressants | Nausea, insomnia, sexual dysfunction | Mild to Moderate |
| Antidepressants | Suicidal ideation (rare but serious) | Severe |
| Antipsychotics | EPS (tremors, rigidity), weight gain | Mild to Moderate |
| Antipsychotics | Neuroleptic malignant syndrome (rare, life-threatening) | Severe |
| Mood Stabilizers | Tremors, gastrointestinal upset | Mild to Moderate |
| Mood Stabilizers | Kidney problems (with lithium) | Moderate to Severe |
Administration and Dosage
Psychotropic medications, while crucial for managing mental health conditions, require careful administration and dosage adjustments to ensure efficacy and minimize potential side effects. Understanding the different routes of administration, typical dosages, and factors influencing those dosages is vital for both patients and healthcare professionals. Precise adherence to the prescribed regimen is paramount for optimal treatment outcomes.
Standard Routes of Administration
Various routes exist for administering psychotropic medications, each with its own advantages and considerations. Oral administration is the most common route, typically involving swallowing pills or liquids. Intravenous (IV) administration delivers medication directly into the bloodstream, providing rapid onset but requiring specialized equipment and trained personnel. Intramuscular (IM) injection is another parenteral route, offering a slower but sustained release compared to IV.
The chosen route depends on factors such as the medication’s properties, the patient’s condition, and the desired therapeutic effect.
Typical Dosages and Patient Populations
Dosage guidelines for psychotropic medications vary considerably based on the specific medication, the patient’s age, weight, and overall health. Factors like kidney function, liver function, and the presence of other medical conditions can also influence dosage. For instance, a lower initial dose might be necessary for elderly patients due to potential decreased metabolism. Dosage adjustments may also be required during pregnancy or lactation.
It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized dosage recommendations.
Importance of Adherence
Adherence to the prescribed dosage and schedule is essential for the effectiveness of psychotropic medications. Consistent medication intake helps maintain therapeutic blood levels, maximizing the medication’s benefits while minimizing potential side effects. Missed doses or inconsistent schedules can lead to fluctuations in blood levels, potentially hindering treatment efficacy or increasing the risk of relapse. Open communication with healthcare providers is key to addressing any challenges in adhering to the prescribed regimen.
Factors Influencing Dosage Adjustments
Several factors can necessitate dosage adjustments. Age-related changes in metabolism and organ function often require dosage modifications. Weight plays a role in determining the appropriate dose, as higher weights may necessitate higher dosages to achieve the desired therapeutic effect. Kidney and liver function can also influence medication clearance, potentially affecting dosage. Co-existing medical conditions or other medications the patient is taking may also necessitate dosage adjustments.
Safe Medication Administration
Safe medication administration is paramount. Healthcare professionals must carefully follow established protocols, including verifying patient identity, checking allergies, and documenting the administration of the medication. Accurate calculations and precise measurement are crucial to avoid errors. Proper storage and handling of medications are equally important. Strict adherence to the medication label is paramount to prevent any accidental errors.
Administration Routes, Typical Dosages, and Potential Interactions
| Administration Route | Typical Dosages (Example) | Potential Interactions |
|---|---|---|
| Oral | SSRIs: 10-20mg daily; Antipsychotics: 2.5-10mg daily (depending on medication and patient factors) | May interact with other medications, such as MAOIs, increasing the risk of serotonin syndrome. |
| Intravenous | Emergency situations, rapid onset of action. Specific dosages vary greatly depending on the medication and the clinical need. | Requires close monitoring for adverse reactions. Potential for incompatibility with other IV fluids. |
| Intramuscular | Depot antipsychotics, for sustained release. Specific dosages vary greatly depending on the medication and the clinical need. | Potential for pain, swelling, or infection at the injection site. May cause local tissue damage if administered incorrectly. |
Patient Counseling and Education
Educating patients about their psychotropic medications is crucial for successful treatment. This involves more than just dispensing a prescription; it necessitates clear communication, addressing potential concerns, and empowering patients to actively participate in their recovery. Effective patient education fosters medication adherence, reduces adverse effects, and ultimately improves overall treatment outcomes.
Key Information for Patient Education Materials
Comprehensive patient education materials should cover various aspects of psychotropic medication use. These materials should be tailored to the specific medication and the individual patient’s needs, ensuring clear and concise information.
Understanding psychotropic medications – their various uses, different types, potential side effects, and proper administration – is crucial. Sometimes, unrelated issues like vaginal itching can arise, and exploring natural remedies, like those discussed in this helpful guide on natural remedies for vaginal itching , might be beneficial. Ultimately, though, it’s vital to remember that proper medical guidance from a healthcare professional is always essential when considering any medication, whether psychotropic or otherwise.
- Medication Name and Purpose: Clearly state the medication’s name, its intended use in treating the patient’s condition, and the expected benefits. For example, if the medication is an antidepressant, explain how it is thought to work in the brain to improve mood and reduce symptoms of depression. This explanation should be tailored to the patient’s understanding and avoid overly technical jargon.
- Dosage and Administration Instructions: Provide detailed instructions on the prescribed dosage, frequency, and route of administration. Include clear examples, like “Take one tablet by mouth with a glass of water twice daily.” Visual aids, such as diagrams, can be extremely helpful in illustrating the process.
- Potential Side Effects: Artikel potential side effects, including common and less common reactions. Explain the likelihood of each side effect occurring and how to recognize them. It is important to emphasize that not all patients will experience all side effects, and many side effects are temporary. For instance, insomnia is a potential side effect of some antidepressants, but it may resolve within a few weeks as the body adjusts to the medication.
Encourage patients to report any unusual or concerning side effects immediately.
- Important Warnings and Precautions: Clearly state any specific warnings or precautions associated with the medication. This includes potential interactions with other medications, alcohol, or specific foods. For example, certain medications should not be taken with grapefruit juice due to potential drug interactions. Also, highlight any potential risks, such as suicidal thoughts or behaviors, especially in younger adults or adolescents, when appropriate.
- Missed Dose Instructions: Clearly Artikel what patients should do if they miss a dose. This should include whether they should take the missed dose if it is close to the next scheduled dose, or if they should skip the missed dose and proceed with the next scheduled dose.
- Storage Instructions: Provide specific instructions on how to store the medication to maintain its efficacy and safety. This includes recommendations about temperature, light, and humidity.
- Contact Information: Include contact information for the prescribing physician, pharmacist, or other relevant healthcare professionals, such as a mental health specialist, in case of questions or concerns.
Strategies for Communicating with Patients
Effective communication with patients about their medications is vital. This includes active listening, addressing concerns, and ensuring that the patient understands the information provided.
- Active Listening: Pay close attention to the patient’s questions and concerns. Create a safe space for them to ask questions without feeling judged. Active listening helps to understand their perspectives and tailor the information to their needs.
- Addressing Concerns: Be prepared to address any anxieties or concerns the patient may have regarding the medication. Emphasize the importance of open communication and encourage them to discuss any questions or concerns promptly.
- Promoting Adherence: Work with the patient to develop strategies to improve medication adherence. This might involve creating a medication schedule, using reminders, or connecting the medication to a daily routine.
- Building Trust: Establish a trusting relationship with the patient. This fosters open communication and promotes adherence to the treatment plan.
Role of the Healthcare Provider in Monitoring Patient Response
Regular monitoring of patients’ responses to psychotropic medication is essential.
- Regular Follow-up Appointments: Schedule regular follow-up appointments to assess the patient’s progress, monitor for side effects, and adjust the treatment plan as needed.
- Tracking Symptoms: Encourage patients to track their symptoms and report any changes to the healthcare provider. This can be accomplished through symptom diaries or other tracking methods.
- Adjusting Treatment: Be prepared to adjust the medication dosage or type if the patient isn’t responding adequately or if side effects become problematic.
Interactions with Other Medications
Psychotropic medications, while vital for managing mental health conditions, can interact with other drugs, potentially altering their effectiveness or introducing adverse effects. Understanding these interactions is crucial for prescribing and managing patients on multiple medications. These interactions can be complex and vary based on individual factors, so a thorough review of all medications is essential.Interactions between psychotropic medications and other drugs can lead to unpredictable outcomes.
For instance, combining a particular antidepressant with a specific pain medication could lead to a significant increase in the blood levels of either drug, potentially causing side effects that range from mild discomfort to serious complications. This underscores the importance of thorough medication reconciliation and careful monitoring when a patient is taking multiple medications.
Potential Drug Interactions
A variety of factors can influence the interactions between psychotropic medications and other drugs. These include the specific psychotropic medication, the other medication being taken, the dosage of each drug, and the patient’s individual characteristics such as age, health conditions, and other medications being taken.
Understanding psychotropic medications – their various uses, different types, potential side effects, and proper administration – is crucial. For instance, managing mental health conditions effectively often involves these medications. Knowing about the specific drugs used in treating HIV, like those listed on list of approved hiv antiretroviral drugs , can be valuable, but it’s important to remember that those drugs are completely separate from psychotropic medications.
Ultimately, proper knowledge of psychotropic medications remains essential for responsible and effective healthcare.
Examples of Common Interactions
Many psychotropic medications can interact with other drugs, leading to altered efficacy or increased side effects. For example, some psychotropics, like certain antipsychotics, can interact with medications used to treat high blood pressure or heart conditions, potentially affecting blood pressure regulation. Similarly, antidepressants can interact with medications for other conditions, like diabetes or ulcers.
Table of Potential Interactions
| Psychotropic Medication | Interacting Medication | Potential Consequences | Precautions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) | MAOIs (Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors) | Serotonin Syndrome (potentially life-threatening) | Significant time gap between switching medications is crucial. Consult with a physician. |
| Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs) | Certain Anticholinergics | Increased risk of anticholinergic side effects (e.g., dry mouth, constipation, urinary retention) | Monitor for signs of anticholinergic toxicity. Consider alternative medications if possible. |
| Benzodiazepines | Alcohol | Increased sedation and respiratory depression | Caution is advised. Avoid alcohol consumption while taking benzodiazepines. |
| Lithium | Diuretics | Increased lithium levels, potentially leading to toxicity | Monitor lithium levels closely. Adjust dosage as needed. |
| Antipsychotics | Certain Antihypertensives | Significant blood pressure changes | Monitor blood pressure frequently. Adjust antihypertensive medication dosage as needed. |
Important Considerations
“Medication interactions are complex and should be evaluated on a case-by-case basis.”
Patients taking multiple medications, including psychotropics, should inform all healthcare providers about all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies they are using. This includes over-the-counter medications and supplements. Regular monitoring of blood levels for certain medications is crucial to prevent adverse effects. A detailed medication list, including dosages, should be kept and shared with all healthcare providers involved in a patient’s care.
This proactive approach ensures the safest and most effective treatment plan.
Illustrative Cases

Understanding how psychotropic medications work in real-world scenarios is crucial for effective treatment. This section provides illustrative cases to demonstrate the application of these medications across diverse patient populations, highlighting the rationale behind specific choices and the importance of considering various factors during prescription. Each case study emphasizes the complexity of mental health conditions and the need for personalized approaches.Illustrative case studies below showcase how psychotropic medications are used in different situations.
Factors like age, pre-existing conditions, and the specific symptoms presented influence the choice of medication and dosage. The expected outcomes are not always guaranteed, and adjustments to treatment plans are often necessary based on patient response.
Case Study 1: Major Depressive Disorder in a Young Adult
“A 22-year-old female presents with symptoms of persistent sadness, loss of interest in activities, and difficulty concentrating. She has no significant past medical history, and her family history includes a history of depression. A diagnosis of Major Depressive Disorder is made. Given her age and lack of significant medical issues, a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) such as sertraline is initiated at a low dose. The rationale for this choice is that SSRIs are generally well-tolerated, have a lower risk of serious side effects compared to other antidepressants in younger patients, and are considered first-line treatment for major depressive disorder. The expected outcome is a reduction in depressive symptoms and an improvement in overall functioning within a few weeks. Regular monitoring of the patient’s mood, potential side effects, and adherence to the treatment plan is essential.”
Case Study 2: Bipolar Disorder in an Adolescent
“A 15-year-old male presents with episodes of elevated mood, racing thoughts, impulsivity, and decreased need for sleep. He also experiences periods of low mood and apathy. A diagnosis of Bipolar Disorder is suspected. Given the patient’s age and the potential for mood swings, a combination of mood stabilizers and an antipsychotic is likely. For example, a mood stabilizer like lithium or valproate may be prescribed in conjunction with an antipsychotic, such as aripiprazole, to manage both manic and depressive episodes. The rationale is to stabilize mood swings, reduce the severity of manic episodes, and improve overall stability. Expected outcomes include reduced manic episodes, improved sleep patterns, and increased stability in mood and behavior. Close monitoring for side effects, particularly concerning weight gain, is crucial, along with a focus on supporting the patient and family through this complex process.”
Case Study 3: Generalized Anxiety Disorder in an Older Adult
“An 80-year-old female presents with excessive worry, anxiety, and difficulty sleeping. She also has a history of hypertension and osteoarthritis. A diagnosis of Generalized Anxiety Disorder is made. Given her age and pre-existing conditions, a low-dose benzodiazepine, such as lorazepam, might be considered, but this would be carefully monitored and prescribed cautiously. The rationale is to address anxiety symptoms quickly while minimizing potential interactions with other medications. Alternatively, a non-benzodiazepine anxiolytic such as buspirone may be a suitable option. The expected outcome is a reduction in anxiety and improvement in sleep quality. Important factors to consider include the potential for cognitive impairment, the risk of falls, and the need for close monitoring of the patient’s overall health.”
Ultimate Conclusion
In conclusion, psychotropic medications are vital tools in the management of mental health. Their varied uses, types, and potential side effects necessitate careful consideration during prescription and administration. Proper patient education and adherence to prescribed dosages are key to successful treatment outcomes. This detailed exploration provides a foundation for a better understanding of these medications and their crucial role in supporting mental well-being.