How to prevent osteoporosis? This comprehensive guide delves into the crucial aspects of maintaining strong bones throughout life. We’ll explore dietary choices, lifestyle habits, and medical considerations, equipping you with the knowledge to build and preserve bone density.
From the vital roles of calcium and vitamin D to the impact of exercise and lifestyle factors like stress and smoking, this guide covers it all. We’ll also examine the importance of bone health across different life stages, from childhood to old age. This isn’t just about avoiding osteoporosis; it’s about living a healthier, more active life with strong, resilient bones.
Dietary Considerations for Preventing Osteoporosis: How To Prevent Osteoporosis

A strong and healthy skeletal system is crucial for overall well-being, especially as we age. Osteoporosis, a condition characterized by weakened bones, can lead to fractures and decreased mobility. Adopting a diet rich in essential nutrients plays a pivotal role in preventing and managing this condition. Proper dietary choices, including adequate calcium and vitamin D intake, along with other important nutrients, contribute to maintaining bone density and overall bone health.
The Role of Calcium and Vitamin D in Bone Health
Calcium is the primary mineral component of bones and teeth. It provides structural support and strength, enabling bones to withstand stress and pressure. Vitamin D is essential for the absorption and utilization of calcium. Without sufficient vitamin D, the body cannot effectively absorb calcium from the diet, hindering bone growth and maintenance. Adequate levels of both calcium and vitamin D throughout life are crucial for preventing osteoporosis.
Importance of Protein Intake for Bone Density
Protein plays a significant role in bone health, acting as a building block for bone tissue. Studies have shown a correlation between adequate protein intake and increased bone density. Protein contributes to bone strength and structure, alongside calcium and vitamin D. The maintenance of bone protein is important in preventing bone loss.
Impact of Dietary Factors on Bone Health
Certain dietary factors can negatively impact bone health. High sodium intake can lead to increased calcium excretion in urine, potentially decreasing bone density. Excessive caffeine consumption may also contribute to calcium loss. Alcohol consumption can interfere with calcium absorption and bone metabolism, negatively affecting bone health.
Recommended Daily Intake Amounts
The recommended daily intake of calcium, vitamin D, and protein varies depending on age and gender. Children and adolescents require higher amounts for growth and development, while adults need sufficient amounts to maintain bone health. Older adults, particularly women, may require even higher amounts to counteract age-related bone loss. Consulting with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian can help determine personalized recommendations.
Recommended Daily Intake of Calcium, Vitamin D, and Protein for Different Age Groups
| Age Group | Calcium (mg) | Vitamin D (IU) | Protein (g) ||———————-|————–|—————-|————-|| Infants (0-6 months) | 200-260 | 400 | 9-12 || Infants (7-12 months) | 260-700 | 400 | 11-13 || Children (1-8 years) | 700-1000 | 600 | 19-34 || Adolescents (9-18 years)| 1300 | 600 | 46-52 || Adults (19-50 years) | 1000 | 600 | 56-63 || Adults (51+ years) | 1200 | 800 | 56-70 |
Preventing osteoporosis often involves a healthy diet and lifestyle. Prioritizing calcium-rich foods is key, but did you know that olive oil, often touted for its various health benefits, might also play a role in managing skin conditions like eczema? For more on how olive oil can help with eczema, check out this informative article on olive oil for eczema.
Ultimately, a balanced approach to diet and exercise is crucial for building strong bones and overall health to fight against osteoporosis.
Calcium-Rich Food Sources
A diverse range of foods provide calcium. A balanced diet including dairy products, leafy green vegetables, and fortified foods can contribute to adequate calcium intake. It is important to consume a variety of calcium-rich foods to ensure adequate intake and to benefit from other essential nutrients.
| Food Source | Calcium Content (mg) |
|---|---|
| Milk (1 cup) | 300 |
| Yogurt (1 cup) | 400 |
| Cheese (1 oz) | 200 |
| Sardines (3 oz) | 350 |
| Spinach (1 cup) | 250 |
| Almonds (1/4 cup) | 75 |
Lifestyle Choices and Exercise for Strong Bones
Building strong bones isn’t just about diet; a proactive lifestyle plays a crucial role. Regular exercise, especially weight-bearing and resistance training, is essential for maintaining bone density throughout life. This crucial process helps prevent osteoporosis and promotes overall skeletal health. Bone health isn’t static; it’s a dynamic process of constant remodeling.
Types of Beneficial Exercises
Physical activity is vital for maintaining bone density and preventing bone loss. Different types of exercises stimulate bone growth and remodeling in unique ways. Weight-bearing exercises, in particular, are crucial for bone health, as they force the bones to work harder against gravity.
Weight-Bearing Exercises
Weight-bearing exercises are those that require your body to work against gravity. These activities are particularly effective at stimulating bone growth and maintaining bone density. They’re crucial for preventing osteoporosis, especially as we age. Examples include walking, jogging, dancing, stair climbing, and jumping rope. The intensity and duration of these exercises can be adjusted to suit individual fitness levels.
- Walking: A low-impact, accessible exercise suitable for most fitness levels. Increasing the speed, incline, or adding hills can elevate the intensity. A brisk 30-minute walk most days of the week is a great starting point.
- Jogging/Running: A higher-impact exercise that puts more stress on the bones, leading to greater bone density gains. Starting slowly and gradually increasing intensity is important to prevent injuries. Listen to your body and adjust the duration and intensity as needed.
- Dancing: A fun and engaging activity that combines weight-bearing with coordination. Different styles of dance offer varying levels of impact and intensity.
- Stair Climbing: A simple but effective weight-bearing exercise that strengthens leg bones and improves cardiovascular health. Using stairs instead of elevators whenever possible is a great way to incorporate this into daily life.
- Jumping Rope: A high-impact exercise that significantly increases bone density. Beginners should start with short bursts and gradually increase the duration and intensity.
Resistance Exercises
Resistance exercises, also known as strength training, involve using weights or resistance bands to build muscle mass. This muscle strengthening is important for overall health and also enhances bone density. Muscle strength can help prevent falls and fractures.
- Lifting Weights: Using dumbbells, barbells, or weight machines to perform exercises like squats, lunges, bench presses, and rows. Appropriate weights and proper form are essential to avoid injuries.
- Bodyweight Exercises: Exercises like push-ups, pull-ups, squats, and lunges that utilize your own body weight for resistance. These exercises can be modified to suit various fitness levels.
- Resistance Bands: These elastic bands provide variable resistance for a wide range of exercises, targeting different muscle groups and offering a convenient way to incorporate resistance training into routines.
Importance of Regular Physical Activity
Regular physical activity, encompassing both weight-bearing and resistance exercises, is essential for maintaining bone density throughout life. It’s not just about building bone mass in youth; it’s also about slowing bone loss in adulthood and preventing osteoporosis. The process of bone remodeling, a constant cycle of bone breakdown and rebuilding, is directly influenced by physical activity.
Physical Activity and Bone Remodeling
Bone remodeling is a continuous process where old bone tissue is broken down and replaced with new bone tissue. Physical activity, particularly weight-bearing exercises, stimulates bone formation, leading to increased bone density. The stresses placed on bones during exercise trigger signals for bone rebuilding. This is a crucial process for maintaining bone strength and preventing fractures.
Bone remodeling is a continuous process where old bone tissue is broken down and replaced with new bone tissue. Physical activity is a significant factor in stimulating this process, leading to increased bone density and strength.
Taking steps to prevent osteoporosis, like getting enough calcium and vitamin D, is crucial for strong bones. It’s also important to be vigilant about reviewing your Explanation of Benefits (EOB) statements to avoid costly mistakes. Knowing how to avoid errors on your EOB, like double-checking for coding discrepancies, can save you headaches down the road. This way, you can focus on keeping your bones healthy.
how to avoid errors on your eob Ultimately, staying proactive about your health, both in terms of bone health and reviewing your billing statements, will set you up for a healthier future.
Sample Weekly Exercise Plan
This sample plan provides a starting point for incorporating weight-bearing and resistance exercises into your weekly routine. Adjust the exercises and intensity based on your fitness level and preferences.
- Monday: Weight-bearing exercise (e.g., brisk walking, stair climbing). Resistance training (e.g., bodyweight squats, push-ups).
- Tuesday: Rest or low-impact activity (e.g., yoga, stretching).
- Wednesday: Weight-bearing exercise (e.g., jogging, dancing). Resistance training (e.g., dumbbell rows, bicep curls).
- Thursday: Rest or low-impact activity.
- Friday: Weight-bearing exercise (e.g., jumping jacks, hiking). Resistance training (e.g., squats, lunges).
- Saturday: Active recovery (e.g., cycling, swimming). Resistance training (e.g., lat pulldowns, shoulder press).
- Sunday: Rest or light activity (e.g., stretching, walking).
Benefits of Different Exercises on Bone Health
| Exercise Type | Benefits for Bone Health |
|---|---|
| Weight-bearing exercises (e.g., walking, jogging) | Stimulates bone formation, increases bone density, reduces risk of fractures. |
| Resistance exercises (e.g., weightlifting, bodyweight exercises) | Strengthens muscles, improves balance, reduces risk of falls, supports bone health indirectly. |
| Low-impact exercises (e.g., swimming, cycling) | Lowers stress on joints, promotes cardiovascular health. May not be as effective for direct bone density gains as weight-bearing exercises. |
Lifestyle Factors Impacting Bone Health
Maintaining strong bones isn’t just about diet and exercise; your lifestyle choices play a crucial role in bone density and overall skeletal health. Factors like smoking, alcohol consumption, stress levels, sleep, and even sun exposure can significantly influence bone health. Understanding these connections is key to building and maintaining a robust skeletal framework.Lifestyle factors beyond diet and exercise profoundly affect bone health.
These influences, ranging from the seemingly minor to the more significant aspects of daily life, contribute to the overall strength and resilience of your bones. A holistic approach to well-being, including healthy lifestyle choices, becomes essential in preventing osteoporosis.
Smoking and Alcohol Consumption’s Impact on Bone Health
Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption are detrimental to bone health. Nicotine in cigarettes interferes with calcium absorption, reducing bone density. Alcohol inhibits calcium absorption and increases bone resorption, leading to weaker bones. Individuals who smoke and/or consume excessive amounts of alcohol are at a higher risk of fractures and osteoporosis compared to those who abstain. For example, smokers often have lower bone mineral density than non-smokers.
Chronic Stress and Sleep Quality’s Role in Bone Health
Chronic stress and inadequate sleep disrupt the delicate balance in the body, impacting bone health. High levels of stress hormones, such as cortisol, can lead to increased bone breakdown. Insufficient sleep negatively affects bone remodeling processes, hindering the body’s ability to build and repair bone tissue. This can lead to a reduced bone mineral density, making bones more susceptible to fractures.
For instance, individuals experiencing chronic stress due to job-related pressures or personal problems might show a decline in bone density. Poor sleep patterns often observed in individuals experiencing insomnia or sleep disorders might also have a similar impact.
Sun Exposure and Vitamin D Synthesis
Sunlight is crucial for vitamin D synthesis in the body. Vitamin D is essential for calcium absorption, a critical component for strong bones. When exposed to sunlight, the body converts a precursor molecule into active vitamin D, which then plays a key role in regulating calcium levels. This process is vital for maintaining optimal bone density.
Sun Exposure and Vitamin D Production
Different levels of sun exposure lead to varying degrees of vitamin D production. Moderate sun exposure, often achievable through daily outdoor activities, is sufficient for many individuals to produce adequate vitamin D. However, prolonged exposure to intense sunlight can increase the risk of skin damage. Conversely, limited sun exposure can result in insufficient vitamin D production, potentially leading to deficiencies.
The intensity and duration of sunlight exposure directly influence the rate of vitamin D synthesis. For instance, individuals living in areas with less sunlight might need to supplement their vitamin D intake.
Lifestyle Changes for Better Bone Health
Adopting healthy lifestyle choices can significantly improve bone health. Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol consumption can help reduce bone loss. Managing stress through relaxation techniques, such as yoga or meditation, can positively impact bone health. Prioritizing sufficient and quality sleep is equally important.
Table: Lifestyle Factors and Bone Health Risks
| Lifestyle Factor | Impact on Bone Health | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Smoking | Interferes with calcium absorption, reducing bone density. | A smoker has a higher risk of osteoporosis than a non-smoker. |
| Excessive Alcohol Consumption | Inhibits calcium absorption and increases bone resorption. | Heavy drinkers often experience reduced bone density. |
| Chronic Stress | Increases bone breakdown due to elevated stress hormones. | Individuals under constant work pressure might experience bone loss. |
| Poor Sleep Quality | Affects bone remodeling processes, hindering bone repair. | People with insomnia might have reduced bone density. |
| Insufficient Sun Exposure | Reduces vitamin D production, impacting calcium absorption. | Individuals living in northern latitudes might need vitamin D supplements. |
Medical Considerations and Supplements
Osteoporosis, a condition characterized by weakened bones, can significantly impact quality of life. While lifestyle choices and dietary considerations play crucial roles in prevention and management, medical interventions can also be vital. Understanding the role of hormone replacement therapy, regular screenings, medications, and supplements is essential for effective osteoporosis prevention and treatment.Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) and other medical interventions are sometimes necessary to combat bone loss.
However, the decision to utilize these approaches should always be made in consultation with a healthcare professional. This involves a careful evaluation of individual risk factors, potential benefits, and potential side effects. Factors such as age, overall health, and specific medical conditions are all critical components of this evaluation.
Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT)
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is a treatment option for postmenopausal women, which can sometimes help to prevent bone loss. HRT works by replenishing the estrogen levels that often decrease after menopause, which is a significant factor in bone density loss. However, it’s important to note that HRT has potential side effects, including an increased risk of certain cancers and blood clots.
The potential benefits and risks of HRT must be carefully weighed against individual needs and circumstances.
Bone Density Screenings
Regular bone density screenings are crucial for early detection of osteoporosis and monitoring its progression. These screenings, often utilizing a dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) scan, measure bone mineral density (BMD). The results of these scans help determine the risk of fracture and guide treatment decisions. The frequency of screenings is dependent on individual risk factors, such as age, family history, and prior fractures.
Women over 65 and those with specific risk factors often benefit from more frequent screenings.
Medications for Osteoporosis Prevention and Treatment
Various medications are available to prevent and treat osteoporosis. These medications work through different mechanisms to either slow bone loss or increase bone formation. Choosing the right medication depends on several factors, including the severity of osteoporosis, the individual’s overall health, and potential side effects.
Summary of Osteoporosis Medications, How to prevent osteoporosis
- Bisphosphonates: These medications, such as alendronate and risedronate, primarily work by inhibiting bone resorption. They are commonly prescribed for both prevention and treatment. Potential side effects include gastrointestinal issues like heartburn and esophageal irritation. Proper administration, such as taking the medication with a full glass of water and remaining upright for at least 30 minutes afterward, can mitigate these risks.
- Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators (SERMs): Drugs like raloxifene act like estrogen in some parts of the body, promoting bone health while potentially reducing the risk of certain cancers. However, SERMs might increase the risk of blood clots and should be used with caution.
- Denosumab: This medication is a monoclonal antibody that targets a protein involved in bone resorption. It is often prescribed for postmenopausal women with severe osteoporosis. Potential side effects include an increased risk of certain infections and dental problems.
- Teriparatide and Abaloparatide: These are parathyroid hormone analogs that stimulate new bone formation. These medications are generally used for more severe osteoporosis cases where other therapies haven’t been effective. Potential side effects include leg cramps and nausea.
Calcium and Vitamin D Supplements
Calcium and vitamin D are essential nutrients for bone health. They work together to support bone formation and strength. Adequate calcium intake through diet or supplements is crucial, especially in individuals with low dietary calcium. Vitamin D is critical for calcium absorption, and sufficient levels are essential for optimal bone health. In some cases, supplements are necessary to meet the recommended daily intake, especially in individuals with limited sun exposure or absorption issues.
Comparison Table of Osteoporosis Medications
| Medication Type | Mechanism of Action | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Bisphosphonates | Inhibit bone resorption | Gastrointestinal issues, atypical femur fractures (rare) |
| SERMs | Mimic estrogen effects on bone | Increased risk of blood clots, possible uterine issues |
| Denosumab | Targets a protein involved in bone resorption | Increased risk of certain infections, dental problems |
| Parathyroid Hormone Analogs | Stimulate new bone formation | Leg cramps, nausea |
Bone Health Throughout the Lifespan
Our bones are living tissues that constantly remodel themselves throughout our lives. Understanding how bone development and density change across different life stages is crucial for optimizing bone health and preventing osteoporosis. From childhood growth spurts to the challenges of aging, each phase presents unique opportunities and risks.Bone health is not just about preventing fractures; it’s about maintaining mobility, independence, and overall well-being throughout our entire lives.
Strategies for promoting strong bones in children, teenagers, and adults will ultimately benefit our senior years.
Bone Development and Growth in Children and Adolescents
Bone development begins in childhood and continues into adolescence. During these years, bone density increases rapidly, laying the foundation for lifelong bone health. Proper nutrition and regular physical activity are essential during this period. Growth spurts, particularly during adolescence, are critical times for bone density development.
Importance of Healthy Habits During Teenage Years and Young Adulthood
Healthy habits established during the teenage years and young adulthood have a profound impact on bone density for the future. A balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D, coupled with weight-bearing exercise, is paramount. Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption is also critical. These habits not only support bone health but also influence overall health and well-being.
Maintaining a healthy weight is important for bone density, as obesity can increase the risk of fractures.
Boosting bone health is crucial for preventing osteoporosis, and a healthy diet rich in calcium and vitamin D is key. Understanding what causes post nasal drip, like allergies or infections, can also indirectly affect your overall health, and thus your bone density. For more information on the causes of post nasal drip, check out this helpful resource: what causes post nasal drip.
Ultimately, a holistic approach to well-being, including a balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle, is your best defense against osteoporosis.
Effects of Aging on Bone Density and Osteoporosis Risk in Older Adults
As we age, bone density naturally decreases. This decline, coupled with hormonal changes, particularly in women after menopause, increases the risk of osteoporosis. The rate of bone loss varies between individuals, influenced by genetic predisposition, lifestyle choices, and medical conditions. A decrease in bone density can lead to fractures with minimal trauma, a significant concern for older adults.
Strategies for Preventing Osteoporosis During Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
Pregnancy and breastfeeding can place extra demands on calcium stores. Ensuring adequate calcium and vitamin D intake during these periods is crucial for the mother’s bone health and the developing baby’s skeletal development. Adequate calcium intake in pregnant women is essential to maintain bone density and to meet the needs of the growing fetus.
Importance of Bone Health for Maintaining Mobility and Independence in Older Adults
Strong bones are essential for maintaining mobility and independence in older adults. Bone health directly impacts the ability to perform daily activities and participate in social and recreational activities. Preventing fractures through healthy lifestyle choices is vital for preserving independence and quality of life.
Summary of Key Factors Impacting Bone Health at Different Life Stages
| Life Stage | Key Factors |
|---|---|
| Childhood/Adolescence | Adequate calcium and vitamin D intake, regular weight-bearing exercise, and avoidance of smoking. |
| Teenage Years/Young Adulthood | Balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D, weight-bearing exercise, avoidance of smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, maintaining a healthy weight. |
| Older Adults | Maintaining a healthy diet, regular weight-bearing exercise, sufficient calcium and vitamin D intake, managing any underlying medical conditions, and addressing hormonal changes (especially in women). |
| Pregnancy/Breastfeeding | Adequate calcium and vitamin D intake, maintaining a healthy diet, and monitoring bone density. |
Risk Factors and Prevention Strategies
Osteoporosis, a condition characterized by weakened bones, significantly increases the risk of fractures, particularly in older adults. Understanding the risk factors and adopting proactive prevention strategies is crucial for maintaining bone health throughout life. By addressing modifiable risk factors, individuals can significantly reduce their likelihood of developing osteoporosis and its associated complications.
Major Risk Factors
Several factors contribute to the development of osteoporosis. Genetics play a substantial role, with family history of the condition being a significant predictor. Ethnicity also influences risk; individuals of Caucasian and Asian descent, for example, have a higher predisposition. Body size also contributes; smaller body frames tend to have lower bone density, increasing vulnerability. Other factors, like smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and certain medications, also elevate the risk.
Recognizing these factors allows for targeted interventions and preventative measures.
Importance of Early Prevention
Early intervention is key to mitigating the impact of osteoporosis. Implementing preventive measures early in life, through proper nutrition and exercise, strengthens bones and builds a foundation for lifelong bone health. This early investment in bone health is crucial in reducing the risk of fractures and other complications later in life. It’s not just about preventing future problems; it’s about ensuring a higher quality of life as we age.
Strategies for Reducing Falls in Older Adults
Falls are a major concern for older adults, often leading to fractures. Implementing strategies to reduce the risk of falls is critical for maintaining independence and preventing complications. These strategies include regular exercise to improve balance and coordination, home modifications to reduce tripping hazards, and appropriate footwear choices. By addressing the risk of falls, we can help maintain a higher quality of life for older adults.
Risk Factors and Preventive Measures
| Risk Factor | Preventive Measure |
|---|---|
| Genetics (family history) | Maintain a healthy lifestyle, including diet and exercise, even if family history exists. |
| Ethnicity (Caucasian, Asian) | Focus on calcium and vitamin D intake, along with weight-bearing exercises. |
| Small body frame | Prioritize calcium-rich foods, vitamin D supplementation, and resistance exercises. |
| Smoking | Quit smoking to improve bone density and overall health. |
| Excessive alcohol consumption | Moderate alcohol intake to minimize negative impacts on bone health. |
| Certain medications | Discuss medication options with a healthcare professional to understand potential bone health impacts. |
Regular Checkups for Bone Health
Regular checkups with a healthcare professional are essential for bone health. These checkups can include bone density scans (DEXA scans), especially for individuals at high risk. These scans provide valuable insights into bone health, enabling proactive interventions and personalized strategies. They can detect bone loss early, allowing for timely adjustments to lifestyle and treatment options. Early detection is vital for preventing more severe bone loss.
Resources for Further Information
- National Osteoporosis Foundation (NOF): The NOF offers comprehensive information, resources, and support for individuals concerned about osteoporosis.
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): The CDC provides information on various health issues, including fall prevention and osteoporosis risk factors.
- Your healthcare provider: Consult your doctor for personalized advice and recommendations based on your specific health situation and risk factors.
Closing Summary
In conclusion, preventing osteoporosis is a multifaceted approach that requires attention to diet, lifestyle, and medical advice. By understanding the critical role of calcium, vitamin D, and regular exercise, combined with healthy habits and proactive medical care, you can significantly reduce your risk of osteoporosis. This comprehensive guide provides a roadmap to achieving and maintaining optimal bone health, empowering you to live a fulfilling life with strong bones throughout the years.





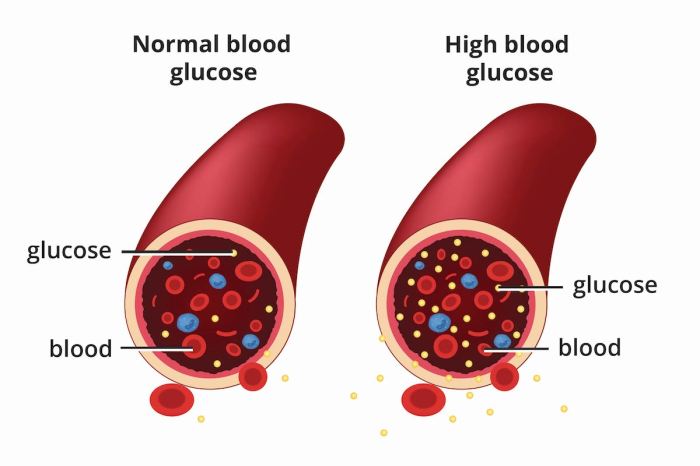
 The figure illustrates the potential progression of both diabetes and colon cancer in a single patient. The x-axis represents time, and the y-axis represents the severity of each disease. The figure demonstrates how poorly controlled diabetes, represented by the upward trend in blood glucose levels, can correlate with the development and progression of precancerous polyps and ultimately, colon cancer. The figure highlights the importance of early detection and consistent management of both conditions to mitigate the risk and improve outcomes.
The figure illustrates the potential progression of both diabetes and colon cancer in a single patient. The x-axis represents time, and the y-axis represents the severity of each disease. The figure demonstrates how poorly controlled diabetes, represented by the upward trend in blood glucose levels, can correlate with the development and progression of precancerous polyps and ultimately, colon cancer. The figure highlights the importance of early detection and consistent management of both conditions to mitigate the risk and improve outcomes.