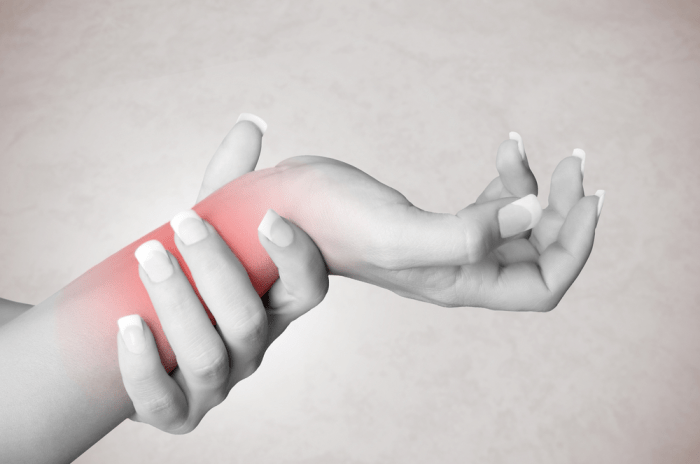
Numbness on one side of the body can be a concerning symptom, potentially signaling an underlying medical condition. This comprehensive guide explores the various causes, symptoms, diagnostic processes, and treatment options for this often perplexing issue. We’ll delve into the neurological pathways, anatomical locations, and potential complications to provide a thorough understanding of this medical concern.
Understanding the different types of numbness, ranging from mild tingling to profound loss of sensation, is crucial. We’ll also examine how associated symptoms like pain, weakness, and changes in sensation can help pinpoint the potential cause. This exploration aims to equip readers with knowledge to navigate this potentially serious health issue.
Causes of Numbness
Numbness on one side of the body can be a concerning symptom, potentially indicating an underlying medical issue. While often a temporary condition, persistent or worsening numbness warrants immediate medical attention to determine the root cause and initiate appropriate treatment. This exploration delves into the various medical conditions that can lead to this symptom, highlighting the neurological pathways and anatomical structures involved.Understanding the potential causes of unilateral numbness is crucial for timely diagnosis and effective management.
It’s important to remember that this information is for educational purposes only and should not be considered a substitute for professional medical advice.
Potential Medical Conditions
A range of medical conditions can cause numbness on one side of the body. These conditions can affect different neurological pathways and structures, leading to localized symptoms. The specific symptoms and their severity can vary significantly depending on the underlying cause.
- Stroke: Ischemic stroke, caused by a blocked artery, or hemorrhagic stroke, resulting from a ruptured blood vessel, can disrupt blood flow to specific brain regions. This interruption of blood supply can lead to the loss of function in areas controlled by those regions, including the sensation of numbness. For example, a stroke affecting the right side of the brain can cause numbness on the left side of the body.
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS): This chronic autoimmune disease affects the myelin sheath, the protective covering around nerve fibers. Degradation of this sheath can disrupt nerve signals, potentially causing numbness and other neurological symptoms, like muscle weakness or vision problems. MS symptoms can vary widely in their manifestation and intensity.
- Brain Tumors: The growth of a tumor within the brain can compress or damage surrounding tissues and nerves. This compression can lead to numbness in the area served by the affected nerves. The location of the tumor, its size, and growth rate significantly influence the resulting symptoms.
- Cervical Spondylosis: This condition involves degenerative changes in the cervical spine, often causing the formation of bone spurs or herniated discs. These changes can compress nerves in the neck, leading to numbness in the arms, hands, and even parts of the face. The extent of compression determines the extent of the numbness.
- Trauma to the Head or Neck: Physical injuries to the head or neck, like concussions or fractures, can damage or compress nerves, resulting in numbness. The severity of the injury correlates with the severity of the resulting symptoms.
Neurological Pathways and Structures, Numbness on one side of the body
Numbness on one side of the body often arises from damage or dysfunction in the brain, spinal cord, or peripheral nerves. The specific pathways affected determine the precise location of the numbness.
- Spinal Cord: The spinal cord is a vital pathway for transmitting sensory information from the body to the brain. Damage to the spinal cord, such as from a spinal cord injury, can interrupt these signals, leading to numbness below the level of injury. For example, damage to the thoracic spinal cord can lead to numbness in the lower extremities.
- Peripheral Nerves: Peripheral nerves transmit sensory information from the extremities to the spinal cord. Conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome or nerve entrapment can compress peripheral nerves, causing numbness and pain in the affected area. For instance, carpal tunnel syndrome, which compresses the median nerve, can lead to numbness in the thumb, index, middle, and ring fingers.
- Brain Regions: Specific regions in the brain are responsible for processing sensory information from different parts of the body. Damage to these areas can cause numbness on the opposite side of the body. For example, damage to the right parietal lobe can cause numbness on the left side of the body.
Anatomical Locations
The precise location of numbness can provide clues about the potential source of the problem.
- Brain Stem: Damage to the brainstem, a vital region connecting the brain to the spinal cord, can disrupt sensory signals, causing numbness. This often manifests as a widespread or global numbness rather than being localized to one side.
- Cervical Spine: Issues in the cervical spine can affect nerves exiting from the spinal cord in the neck region, causing numbness in the shoulder, arm, and hand. This is common in conditions like cervical spondylosis.
- Brachial Plexus: This network of nerves in the shoulder can be injured by trauma, leading to numbness and weakness in the arm. This is commonly seen in sports injuries or accidents.
Detailed Table of Conditions
| Condition | Symptoms (besides numbness) | Possible Risk Factors | Treatment Options |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stroke | Weakness, speech difficulties, vision problems | High blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking | Medication to dissolve blood clots, rehabilitation |
| Multiple Sclerosis | Muscle weakness, fatigue, vision problems | Genetics, environmental factors | Disease-modifying therapies, symptom management |
| Brain Tumors | Headaches, seizures, personality changes | Genetics, exposure to certain chemicals | Surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy |
| Cervical Spondylosis | Neck pain, stiffness, headaches | Age, repetitive neck movements | Physical therapy, medication, surgery (in severe cases) |
Symptoms and Associated Factors
Numbness on one side of the body can manifest in a variety of ways, and understanding these nuances is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. This section delves into the different presentations of this symptom, including intensity, duration, and accompanying sensations, to highlight the importance of detailed symptom reporting. Recognizing patterns and associated factors can significantly aid in identifying the potential underlying causes.The experience of numbness is highly subjective, but a detailed description of the symptoms, including their location, extent, and duration, can provide vital information to healthcare professionals.
This detailed description is important to pinpoint the potential causes and guide the diagnostic process. Factors such as the presence of other symptoms, such as pain, tingling, or weakness, can also provide valuable insights.
Experiencing numbness on one side of your body can be a concerning symptom. It’s crucial to understand that this isn’t something to ignore, and consulting a doctor is always the best first step. While exploring potential causes, it’s interesting to consider dietary supplements like fish oil and how long they remain in your system. For example, knowing how long does fish oil stay in your system might offer some insight, but remember that this is just one potential factor.
Ultimately, proper medical evaluation is essential for determining the underlying cause of the numbness.
Varied Presentations of Numbness
Different individuals experience numbness with varying intensities, durations, and patterns. Some might feel a mild, fleeting sensation, while others experience a profound, persistent loss of feeling. The duration can range from momentary to lasting for days or even weeks. Furthermore, the pattern of the numbness might be constant, intermittent, or follow a specific sequence, such as spreading from a central point.
Recognizing these variations is critical in assessing the potential causes. For example, a sudden, intense numbness, often associated with a stroke, is markedly different from the gradual onset of numbness that might accompany a nerve compression.
Accompanying Symptoms
Numbness is often accompanied by other sensations. Tingling, often described as “pins and needles,” is frequently reported alongside numbness. Pain, ranging from mild discomfort to severe throbbing, can also be present. Weakness or a loss of muscle strength on the affected side of the body is another possible associated symptom. Changes in sensation, such as a loss of temperature or touch perception, can also occur.
Experiencing numbness on one side of your body can be a concerning symptom. It’s important to understand that this could stem from various factors, and it’s always best to consult a doctor. One potential dietary element that might play a role is magnesium intake, and knowing how long magnesium citrate stays in your system might be relevant to your overall health and well-being.
For more information on how long magnesium citrate stays in your system , consider this helpful resource. Ultimately, if the numbness persists or worsens, don’t hesitate to seek professional medical advice.
These additional symptoms, when considered in conjunction with the numbness, provide a more complete picture of the condition. For example, numbness accompanied by severe pain and weakness might suggest a spinal cord injury, whereas numbness with tingling and intermittent pain could point to a nerve compression.
Location and Extent of Numbness
The specific location and extent of the numbness can be highly suggestive of the underlying cause. For instance, numbness confined to the hand might indicate carpal tunnel syndrome, while numbness extending down the arm and into the hand might point to a more widespread nerve issue. Numbness in the face, combined with drooping on one side, could suggest a stroke.
The extent of the numbness, whether it affects a small area or a larger region, can also help in differentiating potential causes. A carefully mapped area of numbness can provide vital information for the diagnosis. For instance, a precise area of numbness in the leg, combined with pain, might indicate a herniated disc.
Comparison of Numbness Types
| Type of Numbness | Potential Origins | Associated Symptoms | Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sudden, severe numbness (e.g., stroke) | Vascular issues, stroke, trauma | Weakness, slurred speech, facial droop, vision changes | Often widespread, may affect one side of the body |
| Gradual numbness (e.g., nerve compression) | Nerve entrapment, pinched nerves, tumors | Tingling, pain, weakness, altered sensation | May start in a localized area and spread |
| Numbness related to diabetes | Peripheral neuropathy | Tingling, pain, loss of sensation, foot ulcers | Often affects the extremities (feet, hands) |
This table provides a simplified comparison of different types of numbness. It is important to remember that this is not an exhaustive list, and many other factors can contribute to the development of numbness. Furthermore, the presence of multiple symptoms and the interplay of various factors often lead to a more complex picture. Always consult with a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Diagnostic Considerations
Pinpointing the exact cause of one-sided numbness requires a methodical approach that combines a thorough patient history with a series of diagnostic tests. This process aims to differentiate between various potential neurological and systemic conditions. A comprehensive understanding of the patient’s symptoms, medical history, and lifestyle factors is crucial in directing the diagnostic pathway and ultimately leading to an accurate diagnosis.The diagnostic process for one-sided numbness involves a systematic evaluation, beginning with a detailed history and physical examination.
This initial assessment helps narrow down the possibilities and prioritize further investigations. Imaging studies, neurological examinations, and blood tests play vital roles in identifying the underlying cause. The choice of specific tests is tailored to the suspected etiology, reflecting the clinician’s judgment based on the gathered information.
Medical History
The patient’s medical history provides valuable context for understanding the potential cause of the numbness. Factors such as prior neurological conditions, recent illnesses, medications, and family history of neurological disorders can significantly influence the diagnostic process. For example, a patient with a history of stroke is more likely to have a cerebrovascular cause for their numbness than a patient with no such history.
Similarly, recent infections or exposure to toxins might suggest an infectious or environmental etiology. Allergies and other pre-existing conditions also play a role in determining the potential causes.
Neurological Examination
A neurological examination assesses the function of the nervous system. This involves evaluating reflexes, muscle strength, sensation, coordination, and balance on both sides of the body. Specific neurological deficits, such as weakness or altered reflexes on the affected side, can point to the involvement of specific nerve pathways. For instance, a diminished or absent corneal reflex on the affected side could indicate a lesion in the trigeminal nerve.
The results of the neurological examination guide the choice of further investigations.
Imaging Studies
Imaging techniques, such as MRI and CT scans, provide detailed images of the brain and spinal cord. MRI scans are often preferred for visualizing soft tissues like the brain and spinal cord due to their high resolution. CT scans, on the other hand, are useful for detecting bony structures and identifying possible fractures or abnormalities in the skull.
The choice between MRI and CT depends on the suspected pathology and the clinical context. For example, if a patient presents with sudden onset numbness and suspected stroke, a CT scan is often prioritized to rule out bleeding in the brain. In contrast, if the numbness is associated with chronic pain, an MRI might be more informative.
Blood Tests
Blood tests help evaluate various bodily functions and detect underlying systemic conditions that might be contributing to the numbness. These tests may include complete blood counts, metabolic panels, and specific markers for infections or autoimmune diseases. For example, elevated levels of certain inflammatory markers could suggest an autoimmune process, while abnormal blood cell counts might indicate an underlying hematological disorder.
The results of blood tests can provide clues about systemic causes of numbness.
Diagnostic Tests Summary
| Diagnostic Test | Purpose | Information Provided |
|---|---|---|
| MRI Scan | Visualizes soft tissues (brain, spinal cord) | Structures, lesions, inflammation |
| CT Scan | Detects bony structures and possible fractures | Bone abnormalities, hemorrhages |
| Neurological Examination | Evaluates nervous system function | Reflexes, muscle strength, sensation, coordination |
| Blood Tests | Assesses various bodily functions | Infections, autoimmune disorders, metabolic abnormalities |
Potential Treatments and Management
One-sided numbness can stem from a variety of underlying conditions, necessitating tailored treatment strategies. Effective management hinges on accurate diagnosis and prompt intervention, addressing the root cause rather than just the symptom. This section explores potential treatments for different causes of this discomfort, emphasizing the importance of a personalized approach.
Treatment Approaches Based on Underlying Conditions
Various treatment options are available, ranging from lifestyle modifications to medical interventions. The most suitable approach depends critically on the specific cause of the numbness. For example, if the numbness is due to a nerve compression, physical therapy and medications might be prescribed, whereas a vascular issue could require more intensive treatments, such as angioplasty or medication to improve blood flow.
Pharmacological Treatments
Medications play a significant role in managing the symptoms and underlying causes of one-sided numbness. These can include pain relievers, anti-inflammatory drugs, and medications to address specific conditions, such as nerve damage or vascular problems. The selection of medications and their dosages is crucial and should be determined by a healthcare professional after a thorough assessment. For instance, anti-seizure medications might be beneficial in cases of nerve compression or certain neurological disorders.
Non-Pharmacological Treatments
Non-pharmacological interventions are often a key component of a comprehensive treatment plan. These can include lifestyle adjustments, physical therapy, and occupational therapy. For instance, gentle stretching exercises and posture correction can alleviate pressure on nerves, while ergonomic adjustments in the workplace can reduce the risk of repetitive strain injuries.
Surgical Interventions
In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to address the underlying cause of the numbness. This is particularly true for conditions like nerve entrapment or vascular blockages. The decision to pursue surgery is made on a case-by-case basis, considering the patient’s overall health, the severity of the condition, and the potential benefits and risks of the procedure.
For example, surgical decompression of a compressed nerve might restore sensation and function in a patient experiencing numbness due to a herniated disc.
Complementary and Alternative Therapies
Complementary and alternative therapies, such as acupuncture, massage therapy, and mindfulness exercises, may also be considered as adjunctive treatments. While these therapies may not be a primary treatment for the underlying condition, they can be helpful in managing pain, reducing stress, and improving overall well-being. These therapies can be beneficial in conjunction with other treatments.
Importance of Timely Intervention and Proper Management
Early diagnosis and prompt treatment are critical in mitigating the long-term effects of one-sided numbness. Delaying treatment can lead to permanent nerve damage, muscle atrophy, or other complications. The patient’s commitment to the treatment plan is also vital for successful outcomes. This includes regular follow-up appointments, adherence to medication regimens, and lifestyle adjustments as recommended by the healthcare professional.
Treatment Options Table
| Treatment Option | Effectiveness | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Pain relievers | Generally effective for managing mild to moderate pain | Potential for gastrointestinal upset, allergic reactions |
| Anti-inflammatory drugs | Can reduce inflammation associated with some conditions | Potential for stomach ulcers, kidney problems |
| Physical therapy | Effective in improving nerve function and reducing pain in some cases | Muscle soreness, temporary discomfort |
| Surgical interventions | Potentially curative for specific conditions | Surgical risks (infection, bleeding, etc.) |
| Complementary therapies | May provide adjunctive support | Generally low, but potential interactions with medications |
Lifestyle and Preventive Measures
One-sided numbness can stem from various underlying causes, some linked to lifestyle choices. Understanding these connections is crucial for preventative measures and managing potential risks. Modifying certain habits can significantly reduce the likelihood of developing conditions that lead to this discomfort. This section delves into actionable strategies to mitigate risk.
Dietary Considerations
A balanced diet plays a vital role in overall health and can influence the risk of conditions associated with numbness. Consuming a diet rich in essential nutrients supports healthy nerve function and vascular health, both critical for preventing numbness.
- Nutrient-Rich Foods: Incorporating foods rich in vitamins (like B vitamins, vitamin D, and E) and minerals (like magnesium and potassium) is crucial. These nutrients support nerve function and blood circulation, reducing the risk of nerve damage and blood vessel issues. Examples include leafy greens, fruits, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Hydration: Adequate hydration is essential for optimal bodily functions, including nerve function. Dehydration can lead to nerve dysfunction and exacerbate existing conditions. Maintaining a regular intake of water throughout the day is crucial.
- Reducing Processed Foods: Diets high in processed foods, sugar, and saturated fats can contribute to inflammation and vascular problems, potentially increasing the risk of nerve damage. Limiting these types of foods can have a positive impact on overall health and reduce the risk of developing conditions associated with numbness.
Physical Activity and Posture
Regular physical activity promotes healthy blood circulation and strengthens the body’s supporting structures. Poor posture and prolonged periods of inactivity can contribute to nerve compression and exacerbate numbness.
- Exercise Routine: Engaging in regular exercise, including both cardiovascular and strength training, can significantly improve blood circulation and reduce the risk of nerve compression. Finding activities you enjoy, like brisk walking, swimming, or cycling, makes it easier to maintain a consistent routine.
- Postural Awareness: Maintaining good posture, whether sitting, standing, or sleeping, is vital. Proper posture reduces stress on nerves and blood vessels, minimizing the risk of compression and associated discomfort. Ergonomic adjustments at work or while using electronic devices can be very helpful.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can negatively impact the nervous system, potentially contributing to nerve damage and numbness. Implementing stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises, can be beneficial.
Stress Management Techniques
Chronic stress can significantly impact the nervous system, potentially exacerbating or triggering numbness. Implementing stress management strategies is crucial for reducing risk.
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Practicing mindfulness and meditation techniques can help regulate the nervous system, reduce stress hormones, and improve overall well-being. These practices can positively impact nerve function and reduce the likelihood of numbness.
- Relaxation Techniques: Employing relaxation techniques like progressive muscle relaxation, deep breathing exercises, or guided imagery can help manage stress and anxiety, thereby minimizing potential negative impacts on nerve function.
- Prioritizing Sleep: Adequate sleep is essential for the body to repair and restore itself. Getting sufficient sleep allows the nervous system to function optimally, reducing the risk of numbness or exacerbating existing conditions.
Environmental Factors
Certain environmental factors can contribute to or exacerbate one-sided numbness.
Experiencing numbness on one side of your body can be a concerning symptom. It’s important to remember that maintaining a healthy lifestyle in your 30s, like those outlined in 30s lifestyle changes for longevity , can contribute to overall well-being and potentially reduce the risk of various health issues. So, if you’re noticing this, scheduling a check-up with your doctor is crucial for a proper diagnosis and personalized care plan.
- Exposure to Toxins: Exposure to certain toxins or chemicals in the environment can negatively impact nerve function. Reducing exposure to these toxins can help minimize risk. This includes minimizing exposure to heavy metals, pesticides, and other harmful substances.
- Temperature Extremes: Exposure to extreme temperatures can constrict blood vessels, potentially affecting nerve function and leading to numbness. Taking precautions to avoid extreme heat or cold, particularly in prolonged periods, can be helpful.
Illustrative Case Studies
One-sided numbness can be a perplexing symptom, demanding a careful diagnostic approach. Understanding the diverse causes and the nuances of each patient’s experience is crucial for effective treatment. These case studies illustrate the complexity of these situations and highlight the importance of individualized care.The following case studies depict patients with varying presentations of one-sided numbness. Each case emphasizes the need for a comprehensive evaluation, considering both the patient’s medical history and the specific neurological examination findings.
The diagnostic process, including imaging and other tests, and the ultimate treatment strategies, are described. This approach underscores the critical role of personalized care in managing such conditions.
Case Study 1: Cervical Spondylosis
This patient, a 65-year-old woman, presented with progressive numbness in her left arm and hand. The numbness started subtly, gradually worsening over several months. She also reported neck pain and stiffness. The patient’s medical history included osteoarthritis and hypertension. A neurological examination revealed decreased sensation in the left arm, along with some weakness.
Imaging studies, including X-rays and MRI of the cervical spine, showed signs of cervical spondylosis, specifically narrowing of the spinal canal at the C5-C6 level. Treatment focused on pain management with anti-inflammatory medications and physical therapy exercises to improve posture and neck mobility. The patient experienced significant symptom improvement after several months of treatment. This case demonstrates how age-related degenerative changes in the spine can cause neurological symptoms.
Case Study 2: Stroke
A 58-year-old man presented with sudden onset of numbness on his right side, including the face, arm, and leg. He also experienced slurred speech and difficulty with balance. His medical history included hypertension, diabetes, and a family history of stroke. A rapid neurological assessment confirmed the presence of hemiparesis (weakness on one side of the body) and sensory deficits.
An immediate CT scan ruled out intracranial hemorrhage and showed evidence of an ischemic stroke. The patient received intravenous thrombolysis, a clot-busting treatment, within the critical timeframe. Rehabilitation therapy was crucial in restoring his functional abilities. The patient showed marked improvement in motor and sensory functions. This case highlights the critical importance of recognizing stroke symptoms and the urgent need for prompt medical intervention.
Case Study 3: Multiple Sclerosis
A 30-year-old woman experienced intermittent episodes of numbness and tingling in her right leg, followed by similar symptoms in her left arm. The symptoms waxed and waned over several months. Her medical history was unremarkable. A neurological examination revealed fluctuating sensory deficits, and the patient reported visual disturbances. An MRI of the brain and spinal cord showed characteristic demyelinating lesions, supporting a diagnosis of multiple sclerosis.
Treatment involved disease-modifying therapies (DMTs) to reduce the frequency and severity of relapses. Regular follow-up visits and adjustments to treatment strategies were essential to manage the patient’s condition effectively. This case illustrates the diagnostic challenge of fluctuating neurological symptoms and the importance of considering less common conditions.
Illustrative Anatomical Diagrams: Numbness On One Side Of The Body
Understanding the sensory pathways and potential sites of damage is crucial for comprehending numbness on one side of the body. This section will delve into the intricate anatomical structures involved, focusing on the affected side and illustrating the pathways transmitting sensory information to the brain. Visualizing these structures and their relationships is key to understanding the underlying causes of the numbness.
Sensory Pathways: A Detailed Overview
The sensory system is a complex network that relays information from the body to the brain. Sensory neurons, specialized cells, detect stimuli like touch, temperature, and pain. These signals are then transmitted along specific pathways to the brain for processing and interpretation. These pathways are composed of various anatomical structures, and damage or dysfunction in any part of this complex network can result in numbness.
Peripheral Nerves and their Branches
Peripheral nerves are bundles of axons that extend from the central nervous system (spinal cord and brain) to the rest of the body. These nerves carry sensory information from the skin, muscles, and other tissues to the spinal cord. These nerves branch extensively to reach every part of the body. Damage to a specific nerve or its branches can lead to numbness in the corresponding area.
For instance, damage to the ulnar nerve in the arm can result in numbness and tingling in the ring and little fingers. Illustrative diagrams should show the intricate branching pattern of peripheral nerves in the affected area, highlighting the potential locations for injury or compression.
Spinal Cord and Sensory Tracts
Once sensory information reaches the spinal cord, it travels along specific sensory tracts. These tracts relay the information to higher centers in the brain. The dorsal columns, for example, carry information about touch and proprioception (body position). Damage to these tracts within the spinal cord can lead to numbness, affecting the areas innervated by the damaged nerves. The diagrams should depict the spinal cord’s cross-section, emphasizing the locations of the sensory tracts and their connections to the peripheral nerves.
Consider highlighting potential compression sites within the spinal canal.
Brain Stem and Sensory Relay Centers
The brainstem acts as a crucial relay station for sensory information. Various nuclei within the brainstem process and further transmit the sensory signals to the thalamus. The thalamus acts as a central processing hub, directing sensory input to the appropriate cortical areas in the brain. Diagrams should showcase the location and structure of the relevant brainstem nuclei and their connections to the thalamus.
Highlight potential sites of damage within the brainstem that might cause numbness on one side of the body.
Cerebral Cortex: Processing Sensory Information
Finally, the sensory information reaches the cerebral cortex, where it is processed and interpreted. The somatosensory cortex, located in the parietal lobe, is responsible for processing tactile information. Illustrative diagrams should show the location of the somatosensory cortex and its relationship to other cortical areas involved in sensory perception. The diagrams should visually represent how the sensory input from the affected side of the body is processed in the cortex.
Importance of Immediate Medical Attention
One-sided numbness can be a worrisome symptom, and delaying medical attention can have serious consequences. Understanding the potential complications and the urgency of prompt diagnosis is critical for effective management and preventing long-term issues. Ignoring this symptom can lead to irreversible damage, especially if the underlying cause involves the nervous system.Prompt medical intervention is crucial because the longer you wait, the more difficult it becomes to pinpoint the exact cause and implement the most effective treatment strategy.
This delay can also allow the condition to worsen, potentially causing more significant problems and impacting your quality of life.
Potential Consequences of Delayed Treatment
Delaying treatment for one-sided numbness can allow underlying conditions to progress, potentially leading to irreversible damage. The specific consequences vary depending on the underlying cause, but some common outcomes include further nerve damage, loss of function, and long-term disability. Prompt diagnosis and intervention are essential to prevent these detrimental outcomes.
Potential Complications of Delayed Diagnosis and Treatment
| Potential Complication | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Further Nerve Damage | Prolonged pressure or injury to nerves can lead to further deterioration of nerve function, potentially resulting in permanent loss of sensation, movement, or both. | Progressive loss of function, pain, and disability. |
| Stroke | If the numbness is caused by a stroke, delaying treatment can limit the effectiveness of clot-busting medications, potentially increasing the extent of brain damage and resulting in long-term disabilities, such as speech impairment, paralysis, or cognitive deficits. | Severe disability, potentially life-threatening. |
| Spinal Cord Injury | Delayed diagnosis of a spinal cord injury can lead to irreversible paralysis and loss of function in the affected areas, significantly impacting mobility and daily activities. | Permanent paralysis, loss of bladder and bowel control, and other severe complications. |
| Multiple Sclerosis Progression | In cases where numbness is a symptom of Multiple Sclerosis, delayed treatment can allow the disease to progress further, potentially worsening neurological symptoms and leading to a more severe and debilitating condition. | Progressive worsening of neurological symptoms, including muscle weakness, vision problems, and cognitive impairment. |
| Peripheral Neuropathy | Delayed diagnosis of peripheral neuropathy can lead to further nerve damage and more widespread symptoms. This can lead to chronic pain, muscle weakness, and decreased mobility. | Chronic pain, loss of function, and potentially difficulty with daily tasks. |
It’s important to emphasize that these are potential complications, and not every case will result in all of these consequences. However, the risk of complications significantly increases with delay.
Wrap-Up
In conclusion, numbness on one side of the body warrants immediate medical attention. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are paramount to preventing potential complications and restoring function. Remember, this guide provides valuable information but does not substitute professional medical advice. Always consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plans.