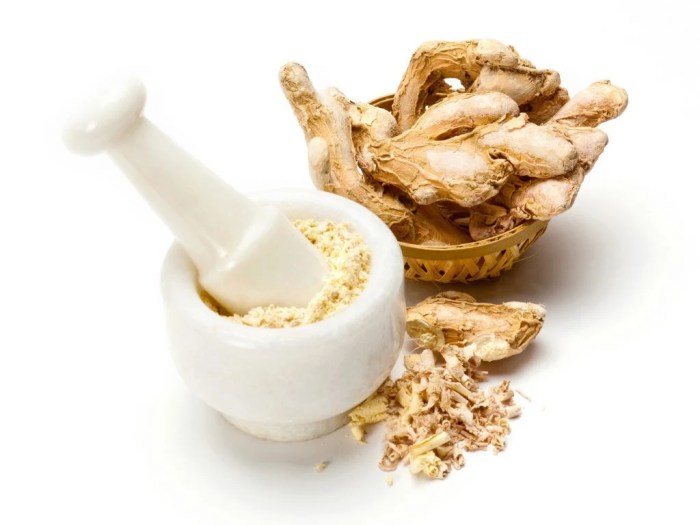
Everything you need to know about grapefruit seed extract dives deep into this potent natural remedy. From its origins and uses to potential benefits and risks, we’ll explore the science behind this popular supplement. We’ll also examine dosage guidelines, interactions with other substances, safety precautions, and even its traditional uses.
Grapefruit seed extract (GSE) has gained attention for its purported health benefits. This comprehensive guide explores its chemical composition, available forms, and the evidence behind its various claims. We’ll look at potential benefits for immune support, digestion, and skin health, alongside potential risks and side effects.
Introduction to Grapefruit Seed Extract
Grapefruit seed extract (GSE) is a natural product derived from the seeds of grapefruit. It’s gained popularity for its purported antimicrobial and antioxidant properties, leading to various uses in health and personal care products. While promising, scientific evidence supporting many of these claims remains inconclusive. Understanding the composition and forms of GSE is crucial to evaluating its potential benefits and limitations.Grapefruit seed extract’s purported benefits are often linked to its rich chemical composition.
So, you’re diving into the world of grapefruit seed extract? Great choice! Understanding its potential benefits often hinges on the significance of pH balance in your body. A good understanding of how pH balance affects your overall health is key to getting the most out of this supplement. Check out this article on pH balance significance function associated conditions for a deeper dive into the science behind it.
Ultimately, knowing about pH balance helps you understand how grapefruit seed extract might support your well-being. This knowledge is crucial for making informed decisions about your health and wellness journey.
Key active compounds, such as limonoids, flavonoids, and phenolic acids, are believed to contribute to its potential effects. However, more rigorous research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms and effectiveness of these compounds in various applications.
Chemical Composition of GSE
The chemical makeup of GSE is complex, containing various bioactive compounds. Limonoids, a class of compounds found in citrus fruits, are thought to possess antimicrobial properties. Flavonoids, another significant component, contribute to antioxidant activity, potentially protecting cells from damage. Phenolic acids, often associated with potent antioxidant properties, are also present in GSE. Understanding the interactions and concentrations of these components is vital for assessing the potential therapeutic effects.
Forms of Grapefruit Seed Extract
GSE is available in various forms, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The most common forms include capsules, tablets, and liquid extracts. Choosing the right form depends on individual preferences and desired applications.
Comparison of GSE Forms
| Form | Benefits | Drawbacks | Recommended Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capsules | Convenient to take, standardized dosage, often available in bulk. | May not dissolve well in the stomach, some individuals experience digestive discomfort. | One to three capsules daily, with meals, as directed by a healthcare professional. |
| Tablets | Easy to swallow, often less expensive than capsules, solid form is convenient to transport. | May have similar digestive issues as capsules, potential for variability in the active compound concentration. | One to two tablets daily, with water, as directed by a healthcare professional. |
| Liquids | Potentially higher bioavailability due to direct absorption, some prefer the taste. | Requires careful measurement, may be less stable than capsules/tablets. | A few drops to a tablespoon, as directed by a healthcare professional. |
Note: The recommended usage varies depending on the specific product and individual needs. Always consult with a healthcare professional before using GSE, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking other medications.
Potential Benefits of GSE
Grapefruit seed extract (GSE) has garnered attention for its purported health benefits, largely attributed to its bioactive compounds. While promising, scientific evidence supporting these claims is often limited and needs further rigorous investigation. This section explores potential benefits of GSE, focusing on immune support, digestive health, skin health, and potential antibacterial/antiviral effects. Caveats about the lack of conclusive evidence are included where appropriate.The purported health benefits of GSE stem from its claimed antimicrobial properties.
These properties are often attributed to the presence of certain compounds, such as limonoids and other phytochemicals. However, more rigorous studies are needed to fully understand the mechanisms and effectiveness of these purported benefits.
Immune Support
The purported immune-boosting properties of GSE are often linked to its antioxidant and antimicrobial effects. Some studies suggest that GSE may enhance the activity of immune cells, potentially supporting the body’s natural defenses against infection. However, these findings are often preliminary or based on in vitro studies, which do not always translate to human outcomes.
Digestive Health
Some studies propose that GSE might have a positive impact on digestive health. This potential benefit is often attributed to its antimicrobial properties, which may help reduce the presence of harmful bacteria in the gut. However, the specific mechanisms and clinical relevance of GSE for digestive issues remain largely unexplored.
Skin Health
GSE’s potential impact on skin health is another area of interest. Its antimicrobial properties might be beneficial in treating certain skin conditions, but more research is needed to understand its efficacy and safety in dermatological applications.
Antibacterial and Antiviral Properties
Research suggests that GSE may possess antibacterial and antiviral properties. Some studies have shown its effectiveness against specific bacteria and viruses in laboratory settings. However, further investigation is required to determine the extent to which these properties translate to practical applications and human health benefits.
Summary of Potential Benefits
| Area of Health | Potential Benefits | Supporting Evidence |
|---|---|---|
| Immune Support | May enhance immune cell activity, potentially supporting natural defenses against infection. | Limited, often preliminary, and based on in vitro studies. |
| Digestive Health | May reduce harmful bacteria in the gut, potentially aiding digestion. | Limited research, mechanisms not fully understood. |
| Skin Health | Potential benefit in treating certain skin conditions due to antimicrobial properties. | Further research needed for efficacy and safety. |
| Antibacterial/Antiviral | May have activity against specific bacteria and viruses in laboratory settings. | More research needed for clinical application. |
Potential Risks and Side Effects of GSE: Everything You Need To Know About Grapefruit Seed Extract
Grapefruit seed extract (GSE), while touted for various health benefits, isn’t without potential risks. Understanding these potential downsides is crucial for responsible use. Before incorporating GSE into your routine, it’s vital to weigh the possible benefits against the potential drawbacks and consult with a healthcare professional.Consuming GSE, like any supplement, can have unintended consequences. Factors such as individual sensitivity, dosage, and underlying health conditions can influence the outcome.
Careful monitoring and awareness of potential interactions with other medications are essential for safe GSE use.
Potential Interactions with Medications
Many individuals take multiple medications, and GSE can interact with these, potentially altering their effectiveness or causing adverse reactions. The most significant concern involves blood thinners, as GSE may affect their efficacy and increase the risk of bleeding.
- GSE may interfere with the metabolism of certain medications, altering their blood levels and potential side effects. For example, it could increase the blood levels of some medications, potentially leading to overdose-like symptoms.
- Some studies suggest potential interactions with medications used to treat heart conditions, mental health issues, and certain types of cancer. The exact nature and severity of these interactions are not always clear and require further investigation.
- It’s crucial to consult with a doctor or pharmacist before using GSE if you’re taking any prescription medications. They can assess your specific situation and determine if GSE poses a risk of interaction.
Potential Allergic Reactions and Other Adverse Effects
While not as prevalent as interactions with medications, allergic reactions to GSE can occur. These reactions can manifest in various ways, from mild skin rashes to more severe symptoms like difficulty breathing or swelling.
- Allergic reactions to GSE can range from mild skin rashes and itching to more serious symptoms like anaphylaxis. Individuals with known allergies to citrus fruits or similar compounds should exercise caution.
- Gastrointestinal issues, such as nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea, have been reported in some individuals consuming GSE. These symptoms often subside with discontinuation of use.
- Some users have reported headaches, dizziness, or fatigue. These side effects are typically mild and transient, but monitoring is recommended.
Summary Table of Potential Side Effects, Precautions, and Contraindications
This table provides a concise overview of potential side effects, precautions, and contraindications associated with GSE use. It’s important to remember that this is not an exhaustive list and individual experiences may vary. Always consult a healthcare professional before using GSE.
| Potential Side Effect | Precautions | Contraindications |
|---|---|---|
| Gastrointestinal upset (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea) | Start with a low dose and gradually increase. Take with food. | Severe digestive disorders. |
| Allergic reactions (skin rash, itching, anaphylaxis) | Monitor for any unusual reactions. Stop use if symptoms appear. | Known allergies to citrus fruits or similar compounds. |
| Interactions with medications (particularly blood thinners) | Consult with a doctor or pharmacist before use. Avoid use with medications requiring close monitoring of blood levels. | Concurrent use of blood thinners or other medications requiring close monitoring without medical supervision. |
| Headaches, dizziness, fatigue | Monitor for symptoms. Adjust dosage if necessary. | Pre-existing conditions affecting the central nervous system. |
Scientific Evidence and Research on GSE
Grapefruit seed extract (GSE) has garnered attention for its purported health benefits, but the scientific evidence supporting these claims is often mixed and incomplete. Evaluating the existing research is crucial to understanding the potential effectiveness and safety of GSE. This section delves into the available scientific literature, examining the methodologies, findings, and limitations of studies investigating GSE’s effects on various health conditions.A significant challenge in assessing GSE’s effectiveness lies in the variability of study designs, sample sizes, and the specific formulations of GSE used.
This makes it difficult to draw definitive conclusions about its efficacy. The lack of standardized protocols and consistent measurement methods across studies also contributes to the inconsistencies in the reported results.
Summary of Research Findings
The existing research on GSE’s effectiveness for various health conditions is diverse and often inconclusive. Some studies suggest potential benefits, while others show little or no effect. The reported effects vary considerably, highlighting the need for more rigorous and well-controlled studies.
Methodologies Used in GSE Research, Everything you need to know about grapefruit seed extract
Studies investigating GSE have employed a range of methodologies, leading to varied results. Different research designs, such as randomized controlled trials (RCTs), observational studies, and in vitro (test-tube) experiments, have been utilized. These different approaches provide valuable insights but require careful consideration of their limitations. For example, in vitro studies, while helpful for initial screening, often do not translate directly to human effectiveness.
- Sample Sizes: Many studies have relatively small sample sizes, which can limit the statistical power to detect significant effects. This is a critical limitation because small sample sizes can lead to misleading conclusions. Larger, more robust studies with more participants are needed to strengthen the evidence base.
- Study Designs: The methodological approach employed significantly impacts the reliability of the results. For example, RCTs, which randomly assign participants to treatment and control groups, are generally considered the gold standard for evaluating the effectiveness of interventions. Observational studies, while providing valuable insights, are more susceptible to confounding factors and cannot establish causality.
- Dosage and Formulation: Variations in the dosage and formulation of GSE used across studies make it difficult to compare results directly. Standardized protocols for GSE extraction, concentration, and administration are crucial for conducting meaningful comparisons.
Comparison of Findings Across Studies
Different studies on GSE have yielded varying results, creating inconsistencies and hindering definitive conclusions. This variability is often attributed to the methodological differences mentioned above. For instance, some studies report antimicrobial effects of GSE, while others do not observe significant effects. These inconsistencies emphasize the need for more standardized protocols and larger-scale trials.
Ever wondered about grapefruit seed extract? It’s a natural remedy gaining popularity for various health benefits. However, when it comes to hip, knee, and joint pain, especially in people with multiple sclerosis, more research is needed. For a deeper dive into how MS impacts these areas, check out this informative article on hip knee and joint pain in ms.
Ultimately, while promising for many, grapefruit seed extract’s effectiveness in joint pain remains a subject of ongoing study.
| Study Focus | Key Findings | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Antimicrobial Activity | Some studies suggest GSE possesses antimicrobial properties against certain bacteria and fungi. | Results are inconsistent, and often lack rigorous validation using standardized methodologies. |
| Immune System Modulation | Limited evidence suggests GSE may influence immune responses, but the effects are not consistent across studies. | Studies are often small-scale and lack long-term follow-up. |
| Cardiovascular Effects | Some studies show potential effects on blood pressure and cholesterol levels, but the evidence is weak and inconclusive. | Longitudinal studies with larger sample sizes are needed. |
Dosage and Usage Guidelines for GSE
Grapefruit seed extract (GSE) has gained popularity for its potential health benefits, but its safe and effective use hinges on proper dosage and usage guidelines. Understanding the recommended amounts and appropriate application methods is crucial for maximizing potential benefits and minimizing potential risks. This section provides a detailed overview of dosage and usage, considering different forms of GSE, age groups, and underlying health conditions.The recommended dosage for GSE varies significantly depending on the form of the extract (e.g., capsules, liquid, or topical), the intended use, and individual needs.
Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any GSE regimen. They can assess your specific health situation and recommend a safe and appropriate dosage plan.
Recommended Dosage Guidelines for Different Forms
Different forms of GSE, like capsules, liquids, and topical applications, require varying dosage guidelines. Consistency and adherence to the recommended intake are key to experiencing potential benefits.
- Capsules: The typical dosage for GSE in capsule form ranges from 250 to 1000 mg per day, often taken in divided doses (e.g., 250 mg twice daily). However, this is just a general guideline and should be personalized based on individual needs and health conditions. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions on the label for specific dosage recommendations.
- Liquid Extracts: Liquid GSE is typically measured in drops or milliliters. The recommended dosage for liquid extracts can vary significantly, from a few drops to several milliliters per day. It’s crucial to precisely measure the liquid extract and strictly adhere to the prescribed dosage, as the concentration can vary greatly between products. Always refer to the product label for specific instructions.
- Topical Applications: Topical GSE products, like creams or lotions, are generally applied topically to the affected area. The concentration and frequency of topical application may vary depending on the specific product and the intended use. Consult the product label for appropriate application instructions.
Frequency and Duration of Use
The frequency and duration of GSE use are critical considerations. Consistent use is essential for potential benefits, but exceeding recommended durations can lead to adverse effects.
- Frequency: The frequency of GSE use typically depends on the form and the specific intended use. For example, oral capsules might be taken once or twice daily, whereas topical applications might be used more frequently. Refer to the product instructions for specific guidance on how often to use the product.
- Duration: The duration of GSE use should be determined in consultation with a healthcare professional. While some people might experience benefits after a few weeks, the long-term effects of GSE are still being researched. Avoid using GSE for extended periods without professional guidance. Consult with a healthcare provider to determine the appropriate duration for your specific needs.
Dosage Considerations for Different Age Groups and Health Conditions
The appropriate dosage of GSE can differ based on age and pre-existing health conditions. Children, pregnant women, and individuals with specific medical conditions may require different dosage guidelines.
- Children: GSE is generally not recommended for children due to the lack of extensive research on its safety and efficacy in this population. Always consult a pediatrician before administering GSE to children.
- Pregnant and Breastfeeding Women: The use of GSE during pregnancy and breastfeeding is not recommended without consulting a healthcare provider. Potential risks to the developing fetus or infant are unknown.
- Individuals with Specific Medical Conditions: People with certain medical conditions, such as kidney or liver problems, should exercise caution when using GSE. Consult a healthcare provider before using GSE if you have any underlying health concerns.
Dosage Recommendations Table
| Intended Use | Form of GSE | Typical Dosage Range (mg/day) | Important Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| General Health Support | Capsules | 250-1000 | Consult a healthcare professional for personalized recommendations |
| Immune Support | Liquid Extract | Few drops – Several milliliters | Follow product instructions carefully |
| Topical Antiseptic | Cream/Lotion | As directed by product label | Apply topically to affected area |
| Wound Healing | Topical | As directed by product label | Consult a healthcare professional for wound care |
GSE and Interactions with Other Substances
Grapefruit seed extract (GSE) is a potent compound with various potential benefits, but like any supplement or medication, it can interact with other substances. Understanding these interactions is crucial for safe and effective use. This section explores the potential interactions between GSE and other supplements, medications, and foods, highlighting the importance of consulting a healthcare professional before incorporating GSE into your routine.GSE, with its bioactive compounds, can influence the metabolism and absorption of other substances.
This can lead to either increased or decreased effectiveness of those substances, potentially resulting in undesirable side effects or diminished therapeutic benefits. The variability in individual responses to GSE, coupled with the complexity of the human body’s interactions with diverse substances, makes it critical to approach GSE use with caution and professional guidance.
Potential Interactions with Medications
A variety of medications can interact with GSE. These interactions can affect the efficacy of the medication or potentially increase the risk of adverse side effects. It’s essential to consult a healthcare professional before using GSE if you are taking any medications.
- Blood thinners: GSE may potentially interact with blood thinners like warfarin, increasing the risk of bleeding. The interaction is based on the theoretical effect of GSE on liver enzymes and their role in regulating blood clotting. If you are taking blood thinners, consult your doctor before adding GSE to your regimen.
- Immunosuppressants: GSE’s potential to affect the immune system raises concerns about its possible interaction with immunosuppressants. This interaction is still under research, and more studies are needed to establish a clear picture of the potential risks.
- Anti-diabetic medications: GSE could potentially influence blood sugar levels. This could be relevant for individuals taking anti-diabetic medications, and careful monitoring is advised.
Potential Interactions with Supplements
Certain supplements can also interact with GSE. These interactions may not always be immediately apparent, emphasizing the importance of discussing all supplements with a healthcare professional before adding GSE.
So, you’re diving into grapefruit seed extract? Great choice! It’s touted for its potential immune-boosting properties, but wondering how it stacks up against other options like Airborne or Emergen-C? Comparing it to those popular brands like airborne vs emergen c can help you decide what’s best for your needs. Ultimately, more research is always a good idea to fully understand the potential benefits and risks of grapefruit seed extract for your overall health.
- Vitamins and minerals: Some vitamins and minerals may interact with GSE, potentially altering their absorption or effectiveness. For example, GSE may interfere with the absorption of certain fat-soluble vitamins.
- Herbal remedies: Many herbal remedies have known or potential interactions with other supplements or medications. GSE, being a plant-derived extract, may interact with herbal remedies, potentially affecting their efficacy or increasing side effects. A thorough discussion with a healthcare provider is vital.
Potential Interactions with Foods
Certain foods may interact with GSE. This is a complex area, and further research is needed to establish definitive guidelines.
- Foods high in vitamin K: GSE may potentially affect the metabolism of vitamin K, a nutrient crucial for blood clotting. Foods rich in vitamin K, such as leafy green vegetables, might need careful consideration in conjunction with GSE use.
Importance of Professional Consultation
Given the potential for interactions, consulting a healthcare professional before using GSE is strongly recommended. Your doctor or pharmacist can assess your individual health status and medication regimen to determine if GSE is appropriate for you. They can also help you understand any potential risks and recommend appropriate dosage guidelines.
Potential Interactions Table
| Substance | Potential Interaction | Consequences |
|---|---|---|
| Blood thinners (e.g., warfarin) | Increased risk of bleeding | Possible serious complications |
| Immunosuppressants | Possible alteration of immune response | Increased risk of infection or decreased effectiveness of treatment |
| Anti-diabetic medications | Potential influence on blood sugar levels | Possible need for dosage adjustments |
| Fat-soluble vitamins | Potential interference with absorption | Possible vitamin deficiencies |
| Herbal remedies | Possible interactions, affecting efficacy or side effects | Varied, depending on specific herbal remedy and GSE |
| Foods high in vitamin K | Potential effect on vitamin K metabolism | Possible need for monitoring and adjustments |
GSE and Safety Precautions

Grapefruit seed extract (GSE) has shown promise for various health benefits, but like any supplement, it’s crucial to approach its use with caution. Understanding the safety precautions and responsible use of GSE is vital to maximizing potential benefits while minimizing risks. This section delves into important considerations for safe GSE consumption.Proper use and storage are paramount for ensuring GSE’s efficacy and preventing potential adverse effects.
Knowing the safe limits of consumption and understanding potential interactions with other substances is equally important for responsible use.
Important Safety Considerations
GSE, while generally considered safe, can have side effects in some individuals. Sensitivity to GSE can vary significantly, making individual reactions unpredictable. Some users may experience allergic reactions, digestive issues, or other adverse effects. Therefore, it’s critical to be mindful of potential sensitivities and discontinue use if any adverse reaction occurs. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting GSE supplementation, especially if you have pre-existing medical conditions or are taking other medications.
Storage Guidelines for Maintaining Quality and Safety
Proper storage is crucial for preserving the quality and safety of GSE. Store GSE in a cool, dark, and dry place, away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. The ideal storage environment helps maintain the potency and purity of the extract. Use airtight containers to prevent moisture absorption and oxidation, which can affect its effectiveness. Ensure the container is properly labeled with the product name, batch number, and expiration date.
Discard GSE if the product has been exposed to excessive heat or moisture or if the container is damaged.
Avoiding Excessive Consumption
Excessive consumption of GSE can lead to adverse effects. The recommended dosage should always be adhered to. Do not exceed the suggested daily intake, as this may increase the likelihood of side effects. Individual tolerances vary, so starting with a lower dose and gradually increasing it as tolerated is often recommended. Always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized dosage advice.
Safety Tips for GSE Users
| Category | Safety Tip |
|---|---|
| Storage | Store GSE in a cool, dark, and dry place, away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. Use airtight containers. |
| Handling | Always follow the recommended dosage guidelines and consult with a healthcare professional before starting GSE supplementation, especially if you have pre-existing medical conditions or are taking other medications. |
| Consumption | Do not exceed the suggested daily intake of GSE. Start with a lower dose and gradually increase as tolerated. |
| Adverse Reactions | Discontinue use immediately if you experience any adverse reactions such as allergic reactions, digestive issues, or other uncomfortable symptoms. |
| Interaction | Inform your healthcare provider about all medications and supplements you are taking, including GSE, to avoid potential interactions. |
GSE and Traditional Uses
Grapefruit seed extract (GSE) has a fascinating history, woven into various traditional healing practices across different cultures. While modern science is constantly refining our understanding of GSE’s potential, exploring its traditional uses provides valuable insights into its perceived benefits and applications. Understanding these historical contexts can help us appreciate the evolution of GSE’s role in health and wellness.Traditional uses of GSE, often passed down through generations, offer a glimpse into the diverse ways in which cultures have harnessed its potential.
The underlying rationale for these uses frequently revolves around the perceived antimicrobial and antiseptic properties of the extract, which have been used in various traditional remedies.
Traditional Remedies Involving GSE
Traditional applications of grapefruit seed extract often involve its use as a natural antiseptic and preservative. These applications are rooted in the belief that GSE can combat bacteria, fungi, and viruses, making it useful for treating various ailments. Examples include using it as a mouthwash for sore throats or as a topical treatment for minor wounds and skin infections.
Some cultures also incorporate GSE into household cleaning products, reflecting its perceived ability to disinfect and sanitize.
Cultural Contexts of Traditional Uses
The use of grapefruit seed extract varies significantly across cultures. In some traditional medical systems, it might be employed as a general remedy for a wide range of ailments, while in others, its application is more focused on specific conditions. Cultural contexts significantly shape the understanding and application of GSE. For instance, some cultures might emphasize its use as a dietary supplement for overall health and wellness, whereas others might prioritize its use in specific remedies for digestive or skin issues.
This demonstrates the rich diversity in the application of GSE across different cultural practices.
Comparison with Modern Scientific Research
Modern scientific research provides a framework for evaluating the efficacy and safety of GSE, while traditional uses offer insights into the historical applications and perceptions of the extract. Modern research focuses on specific mechanisms of action, dosage, and potential side effects, often contrasting with the often more general and holistic approaches of traditional medicine. Traditional uses, while valuable in understanding historical contexts, lack the rigorous scientific validation of modern studies.
Modern research is essential for confirming or refuting the claims made about GSE’s effects in specific applications.
Summary Table: Traditional Uses vs. Modern Interpretations
| Traditional Use | Modern Interpretation (Potential Benefits/Limitations) |
|---|---|
| Mouthwash for sore throats | May have some antiseptic effect, but further research needed to confirm effectiveness. |
| Topical treatment for minor wounds | May have some antiseptic properties, but rigorous studies on efficacy and safety are required. |
| Household cleaning product | Possible antimicrobial properties, but potential environmental impact and toxicity need assessment. |
| General health supplement | Limited scientific evidence to support general health benefits. |
Grapefruit Seed Extract: A Balanced Perspective
Grapefruit seed extract (GSE) has garnered attention for its purported health benefits, but like any supplement, it’s crucial to approach it with a balanced understanding of its potential benefits, risks, and limitations. This comprehensive exploration delves into the scientific evidence and practical considerations surrounding GSE use, providing a clearer picture of its role in holistic wellness.
A Summary of Key Considerations
Understanding the multifaceted nature of GSE necessitates a holistic approach. It’s not a magic bullet for all ailments, but its potential for certain applications warrants careful consideration. This section provides a concise overview of the key considerations for GSE usage.
- Potential Benefits: GSE is often touted for its antimicrobial properties, and some studies suggest potential benefits in supporting immune function and digestive health. However, more robust, well-designed research is needed to definitively confirm these claims.
- Potential Risks and Side Effects: Like any supplement, GSE can cause adverse reactions in some individuals. These can include allergic reactions, digestive issues, and interactions with medications. Consult a healthcare professional before incorporating GSE into your routine.
- Scientific Evidence: While some studies show promising results, further research is needed to establish conclusive evidence for many purported benefits. Quality and consistency in research methodology are crucial to drawing valid conclusions.
- Dosage and Usage Guidelines: The recommended dosage of GSE varies depending on the intended use and the individual’s health condition. Adherence to recommended dosages and guidelines is vital for safety and effectiveness.
- Interactions with Other Substances: GSE may interact with certain medications, particularly blood thinners and other supplements. It’s essential to discuss any potential interactions with your healthcare provider.
- Safety Precautions: Prioritize safety by consulting a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking other medications.
- Traditional Uses: GSE has been used traditionally for various purposes, but its effectiveness in these applications needs further validation through rigorous scientific research.
Important Considerations Regarding GSE
Thorough investigation and cautious consideration are essential for anyone contemplating using GSE. This section highlights crucial factors to weigh before introducing GSE into your wellness routine.
- Individual Variation: Individual responses to GSE can differ significantly. What works for one person might not work for another. Consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriateness of GSE for your specific needs.
- Quality Control: The quality of GSE products varies significantly. Look for reputable brands and manufacturers with established quality control measures to ensure you are receiving a consistent and safe product.
- Long-Term Effects: Limited long-term studies exist on the effects of GSE use. More research is needed to fully understand the long-term implications of regular GSE consumption.
Conclusion
Grapefruit seed extract presents a complex picture with potential benefits and associated risks. Carefully evaluating the scientific evidence, potential interactions, and individual needs is paramount. Ultimately, informed decision-making and open communication with healthcare professionals are key to integrating GSE into a holistic wellness strategy.
Final Summary
In conclusion, grapefruit seed extract offers a fascinating blend of traditional uses and modern scientific scrutiny. While promising potential benefits exist, careful consideration of dosage, potential interactions, and individual sensitivities is crucial. Always consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating GSE into your routine. Remember that this information is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice.