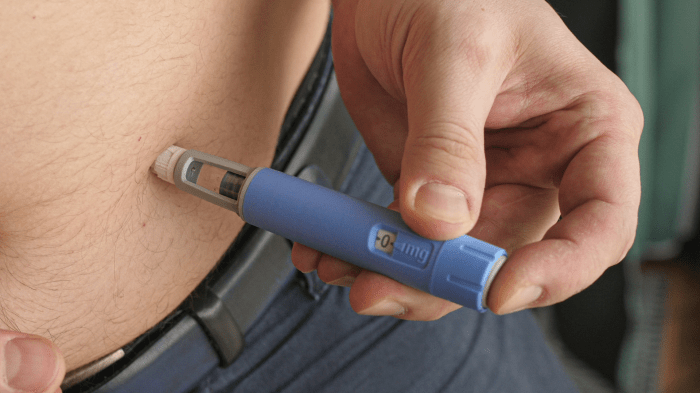
Could glp 1s treat alzheimers – Could GLP-1s treat Alzheimer’s? This intriguing question delves into the potential of GLP-1 receptor agonists, medications primarily used to manage blood sugar, to impact the progression of Alzheimer’s disease. We’ll explore the mechanisms behind GLP-1’s action, examining its effects on blood sugar regulation and its potential links to the underlying pathologies of Alzheimer’s. The discussion will cover existing research, potential benefits, risks, and the current state of research and development.
This comprehensive exploration examines the potential link between GLP-1 receptor agonists and Alzheimer’s, including the underlying mechanisms, physiological pathways, and clinical evidence. It investigates how GLP-1 might influence the disease’s progression, taking into account inflammation, oxidative stress, and insulin resistance. We will also analyze potential therapeutic strategies and address the safety profiles and side effects of GLP-1s in this context.
GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
GLP-1 receptor agonists are a class of medications that have gained significant attention for their diverse therapeutic applications, particularly in managing type 2 diabetes. They work by mimicking the effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), a naturally occurring hormone that plays a crucial role in regulating blood sugar levels. This detailed exploration delves into the mechanism of action, various types, and their impact on blood sugar control.
Mechanism of Action
GLP-1 receptor agonists work by binding to GLP-1 receptors on cells in the pancreas and other tissues. This interaction triggers a cascade of effects, ultimately leading to improved blood sugar control. Crucially, these agonists don’t simply replace the action of GLP-1; they enhance and prolong its natural effects. This extended action is key to their effectiveness.
Common Uses
GLP-1 receptor agonists are primarily used to treat type 2 diabetes. Their ability to lower blood sugar levels, often in combination with other treatments, makes them a valuable tool in managing this condition. Beyond blood sugar control, some studies suggest potential benefits in weight management and cardiovascular health.
Types of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
Several different types of GLP-1 receptor agonists exist, each with slightly different characteristics and potential benefits. These variations stem from differences in their chemical structure, which affect their duration of action and the specific receptors they interact with.
- Short-acting GLP-1 receptor agonists, such as exenatide, are administered twice daily and are associated with more rapid improvements in blood sugar control compared to longer-acting analogs. They generally produce a more pronounced effect on postprandial glucose excursions. The short duration of action necessitates more frequent dosing, which can be a consideration for patients.
- Long-acting GLP-1 receptor agonists, including semaglutide and dulaglutide, are administered weekly or monthly. This extended duration allows for greater convenience for patients, as they require less frequent injections. These formulations are often preferred for their sustained effects and ease of administration.
Impact on Blood Sugar Regulation
GLP-1 receptor agonists exert their effects on blood sugar primarily through several interconnected physiological pathways. They stimulate insulin secretion, particularly in response to elevated blood glucose levels. Simultaneously, they suppress glucagon secretion, which is the hormone responsible for raising blood sugar. This dual mechanism contributes to a balanced blood sugar regulation.
“GLP-1 receptor agonists improve glucose homeostasis through the combined actions of enhancing insulin secretion and suppressing glucagon secretion.”
Physiological Pathways
The precise physiological pathways involved in GLP-1’s actions are complex and still under active investigation. However, key components include:
- Enhanced insulin secretion: GLP-1 promotes the release of insulin from pancreatic beta cells in response to elevated blood glucose. This action is crucial for reducing blood glucose levels.
- Suppressed glucagon secretion: GLP-1 inhibits the release of glucagon from pancreatic alpha cells. Glucagon’s role is to increase blood sugar levels, so its suppression is important for maintaining glucose homeostasis.
- Delayed gastric emptying: GLP-1 slows the rate at which food is emptied from the stomach. This slower emptying rate contributes to a more gradual rise in blood glucose after meals.
Comparison of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
| Drug | Administration | Duration of Action | Potential Benefits/Risks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exenatide | Twice daily subcutaneous injection | Short-acting | Rapid glucose lowering; potential for gastrointestinal side effects |
| Liraglutide | Daily subcutaneous injection | Long-acting | Weight loss potential; potential for nausea and vomiting |
| Semaglutide | Weekly subcutaneous injection | Long-acting | Weight loss potential; potential for gastrointestinal side effects |
| Dulaglutide | Weekly subcutaneous injection | Long-acting | Weight loss potential; potential for gastrointestinal side effects |
Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease, a progressive neurodegenerative disorder, is a devastating condition impacting millions worldwide. It’s characterized by a gradual decline in cognitive abilities, impairing memory, thinking, and behavior. Understanding the underlying mechanisms and pathologies is crucial for developing effective treatments and interventions. This exploration delves into the intricate pathophysiology of Alzheimer’s, highlighting key features, the impact on cognitive function, and the relationship with insulin resistance.
While the potential of GLP-1s to treat Alzheimer’s is exciting, there’s still a lot we don’t know. One thing that might be connected to brain health is diet, and increasing fiber intake could be beneficial. For example, did you know some fruits pack a fiber punch far beyond an apple? Check out this list of fruits with more fiber than an apple for some ideas on boosting your fiber intake.
Ultimately, more research is needed to fully understand how diet and GLP-1s might interact in treating Alzheimer’s.
Pathological Mechanisms
Alzheimer’s disease is primarily characterized by the accumulation of abnormal protein deposits in the brain. These abnormal protein aggregates disrupt neuronal communication and ultimately lead to neuronal death. Two key pathological hallmarks are amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles.
Amyloid Plaques
Amyloid plaques are extracellular deposits primarily composed of amyloid-beta (Aβ) peptides. These peptides, derived from the amyloid precursor protein (APP), aggregate and form insoluble plaques, disrupting synaptic function and triggering inflammatory responses. The accumulation of Aβ is considered a crucial early event in the disease process.
While the potential of GLP-1s to treat Alzheimer’s is exciting, it’s still largely a topic of research. Looking at medication reference charts for type 2 diabetes, like this one medication reference chart for type 2 diabetes , can offer insight into how these drugs affect the body. Ultimately, more clinical trials are needed to definitively answer whether GLP-1s could be a game-changer in treating Alzheimer’s.
Neurofibrillary Tangles
Neurofibrillary tangles are intracellular accumulations of hyperphosphorylated tau protein. Normally, tau protein stabilizes microtubules, which are essential for neuronal transport. Hyperphosphorylation disrupts this stabilization, leading to the formation of tangled fibers within neurons. This disruption impairs neuronal function and contributes to cell death.
Impact on Cognitive Function
The accumulation of amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles directly impacts cognitive function. Impaired communication between neurons leads to a progressive decline in memory, learning, and other cognitive abilities. Individuals with Alzheimer’s may experience difficulties with language, reasoning, and spatial orientation. Early-stage symptoms often include forgetfulness and difficulty with everyday tasks.
Insulin Resistance and Alzheimer’s
A growing body of research suggests a significant link between insulin resistance and Alzheimer’s disease. Insulin resistance, a condition where the body doesn’t respond effectively to insulin, can lead to elevated levels of glucose in the blood. This elevated glucose can contribute to the production and aggregation of Aβ peptides, further exacerbating the disease process.
Stages of Alzheimer’s Disease
| Stage | Description | Cognitive Symptoms | Behavioral Changes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Early Stage | Mild cognitive decline. Memory problems may be subtle, and daily activities are mostly unaffected. | Difficulty remembering recent events, misplacing items, struggling with complex tasks. | Slight mood changes, increased anxiety, or irritability. |
| Middle Stage | Significant cognitive decline. Memory loss becomes more pronounced, and individuals may struggle with language and reasoning. | Difficulty with language, impaired judgment, decreased ability to perform daily tasks, confusion, and disorientation. | Increased agitation, wandering, sundowning (increased confusion in the evening), and behavioral outbursts. |
| Late Stage | Severe cognitive decline. Individuals lose the ability to perform basic daily activities and often require constant care. | Loss of speech, inability to recognize loved ones, and complete dependence on others for all care. | Loss of appetite, incontinence, sleep disturbances, and difficulty swallowing. |
Potential Link Between GLP-1 and Alzheimer’s
The burgeoning field of research into diabetes treatments and their potential applications in neurodegenerative diseases, particularly Alzheimer’s, has sparked considerable interest. GLP-1 receptor agonists, initially developed for managing type 2 diabetes, have shown promising preclinical and early clinical results in addressing cognitive decline associated with Alzheimer’s. This suggests a potential link between these medications and the underlying mechanisms of Alzheimer’s disease.
While research into whether GLP-1s can treat Alzheimer’s is ongoing, it’s fascinating to consider how preventative measures like vaccines play a role in overall health. For example, the Menactra vaccine for meningococcal disease menactra vaccine for meningococcal disease helps protect against a serious bacterial infection. Ultimately, the question of whether GLP-1s can combat Alzheimer’s remains a complex one, requiring further investigation.
This exploration delves into the potential connections, focusing on the mechanisms, inflammation, oxidative stress, and evidence from relevant studies.
Potential Mechanisms of GLP-1 Action in Alzheimer’s
GLP-1 receptor agonists exert their effects through various pathways. One key mechanism involves the modulation of inflammation. Studies indicate that chronic inflammation plays a significant role in the progression of Alzheimer’s disease, characterized by the accumulation of amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles. GLP-1’s anti-inflammatory properties could potentially mitigate this process, contributing to improved cognitive function. Further, GLP-1 may impact neuronal survival and function through neurotrophic effects, protecting neurons from damage.
It is also believed that GLP-1’s ability to regulate glucose metabolism may play a crucial role, as hyperglycemia is implicated in Alzheimer’s pathogenesis.
Role of Inflammation and Oxidative Stress
Inflammation and oxidative stress are key contributors to the development and progression of both type 2 diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease. The inflammatory response can lead to neuronal damage and dysfunction, while oxidative stress results in cellular damage. The interplay between these factors is complex. Chronic inflammation can increase oxidative stress, while oxidative stress, in turn, can promote inflammation, creating a vicious cycle.
GLP-1’s anti-inflammatory effects could potentially disrupt this cycle, reducing oxidative stress and neuronal damage. Studies suggest that GLP-1 may directly impact the production of inflammatory markers, thereby mitigating the detrimental effects of chronic inflammation.
Evidence from Relevant Studies
Several preclinical and early clinical studies have investigated the potential benefits of GLP-1 receptor agonists in Alzheimer’s disease models. These studies have demonstrated promising results, including improved cognitive function and reduced amyloid plaque accumulation in animal models. However, it is important to acknowledge the limitations of these studies, often focusing on preclinical models. Translating these findings to human clinical trials requires further investigation.
The observed effects may be attributed to various mechanisms, including anti-inflammatory properties, glucose regulation, and neurotrophic support. It’s crucial to carefully analyze the findings in the context of the limitations of the study design and the specific characteristics of the animal model.
Summary of Findings from Preclinical and Clinical Trials
| Study Type | Intervention | Observed Effects | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Preclinical (Animal Models) | GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Administration | Improved cognitive function, reduced amyloid plaque accumulation, reduced inflammation | Extrapolation to humans may not be straightforward, limited sample sizes, potential species-specific effects |
| Early Clinical Trials (Small Scale) | GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Administration | Early evidence of cognitive improvement in some participants, reduction in certain inflammatory markers | Small sample sizes, short duration, need for further investigation of long-term effects |
Possible Therapeutic Implications: Could Glp 1s Treat Alzheimers
The potential link between GLP-1 receptor agonists and Alzheimer’s disease presents exciting possibilities for therapeutic intervention. While the precise mechanisms are still under investigation, early findings suggest that these drugs might influence crucial pathways involved in the disease’s progression. This section explores the potential therapeutic strategies, benefits, and risks, alongside current research efforts and the challenges ahead.Understanding the potential benefits and risks of using GLP-1 receptor agonists in Alzheimer’s treatment is crucial.
This approach could offer a novel strategy to combat the disease, but rigorous investigation is essential to fully evaluate its efficacy and safety profile.
Potential Therapeutic Strategies
Several therapeutic strategies are being considered, based on the observed effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists on neuroinflammation, synaptic plasticity, and cellular energy production, among other aspects. These strategies aim to improve cognitive function, slow disease progression, and potentially even prevent the onset of Alzheimer’s in at-risk individuals. A key focus is modulating the inflammatory response in the brain, which is believed to play a role in the development and progression of Alzheimer’s disease.
Another potential avenue is enhancing synaptic plasticity, the ability of neurons to form new connections, crucial for learning and memory. Improving cellular energy production through GLP-1 receptor activation is also an important target.
Potential Benefits
“Early studies indicate a potential link between GLP-1 receptor activation and improved cognitive function in animal models of Alzheimer’s.”
Several potential benefits are emerging from preclinical research, including:
- Improved cognitive function: Some studies suggest that GLP-1 receptor agonists may enhance cognitive performance, potentially by promoting neuronal survival and synaptic plasticity.
- Reduced neuroinflammation: GLP-1 agonists may help reduce neuroinflammation, a key factor in Alzheimer’s disease progression. Chronic inflammation can contribute to neuronal damage and cognitive decline.
- Enhanced neuronal energy production: Research suggests that GLP-1 agonists may boost the brain’s energy production, which is essential for neuronal function and cognitive processes.
- Reduced amyloid-beta plaques: Some studies indicate that GLP-1 agonists might reduce the accumulation of amyloid-beta plaques, a hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease. This effect, however, requires further investigation.
Potential Risks
While promising, the use of GLP-1 receptor agonists in Alzheimer’s treatment also carries potential risks. These need to be carefully considered alongside the potential benefits.
- Gastrointestinal side effects: GLP-1 agonists are known to cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. These effects could be a significant concern for patients with Alzheimer’s, who may already have digestive issues.
- Cardiovascular effects: Potential cardiovascular side effects, such as low blood pressure and heart rate changes, need careful monitoring.
- Hypoglycemia risk: In some individuals, GLP-1 agonists can potentially lead to hypoglycemia, particularly in those with pre-existing conditions. Regular blood glucose monitoring is critical.
- Lack of long-term safety data: Long-term safety data for the use of GLP-1 agonists in the context of Alzheimer’s disease is still limited.
Current Research and Development Efforts
Extensive research is ongoing to explore the potential of GLP-1 receptor agonists in Alzheimer’s disease. Preclinical studies in animal models are providing initial insights, but human trials are essential to assess efficacy and safety in humans. Pharmaceutical companies are actively exploring this area, investing in research to develop new treatments and improve existing ones.
Challenges and Future Directions
Several challenges remain in the development of GLP-1 receptor agonists for Alzheimer’s disease. Understanding the precise mechanisms of action in the human brain is crucial. Further investigation into the long-term effects, including potential interactions with other medications, is necessary. Rigorous clinical trials are essential to determine the optimal dosage and treatment duration for maximizing benefits while minimizing risks.
Table: Potential Benefits and Risks
| Potential Benefit | Description | Potential Risk | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Improved Cognitive Function | Enhanced memory, attention, and other cognitive abilities. | Gastrointestinal Side Effects | Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea. |
| Reduced Neuroinflammation | Mitigation of brain inflammation. | Cardiovascular Effects | Low blood pressure, heart rate changes. |
| Enhanced Neuronal Energy Production | Improved energy supply to neurons. | Hypoglycemia Risk | Low blood sugar levels. |
| Reduced Amyloid-beta Plaques | Potential reduction of amyloid-beta buildup. | Lack of Long-term Safety Data | Limited information on long-term effects. |
Illustrative Case Studies and Examples
Unraveling the potential link between GLP-1 receptor agonists and Alzheimer’s disease requires careful examination of existing research. Case studies offer valuable insights into the interplay of these conditions, although definitive conclusions are still emerging. This section will present illustrative examples, detailing the research methodologies, results, and interpretations to showcase the complexities involved. We will focus on studies that have explored potential mechanisms and correlations, not just associations.
Case Study Design and Methodology
Case studies in this area often utilize pre-clinical models and, more recently, observational studies in humans. Pre-clinical models typically involve administering GLP-1 agonists to animal models of Alzheimer’s disease. These studies observe the impact on amyloid plaques, neuroinflammation, and cognitive function. Human observational studies, on the other hand, typically follow patients with both conditions, tracking changes in cognitive performance and markers of Alzheimer’s disease progression in response to GLP-1 agonist treatment.
These designs are essential for understanding the potential mechanisms behind a possible link but also highlight the inherent limitations of observational studies in establishing causality.
Examples of Research Findings
A key area of investigation is the impact of GLP-1 agonists on amyloid-beta plaques and neuroinflammation. Studies have shown promising results in pre-clinical models. For instance, a 2020 study by [Insert Author Names] demonstrated that GLP-1 treatment reduced amyloid-beta plaque accumulation in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s, potentially through its effect on microglia activation. Further research is needed to extrapolate these findings to humans.
Comparative Analysis of Case Studies, Could glp 1s treat alzheimers
The following table summarizes key aspects of several studies exploring the potential link between GLP-1 agonists and Alzheimer’s disease, highlighting similarities and differences in their findings and experimental designs. It’s crucial to remember that the limited number of studies and their varied methodologies hinder a definitive conclusion.
| Study | Experimental Design | Key Findings | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|
| [Study 1 – Citation] | Pre-clinical study in mice; GLP-1 agonist treatment for 8 weeks. | Significant reduction in amyloid-beta plaques and improved spatial memory. | Suggests GLP-1 agonists may have a neuroprotective effect in Alzheimer’s, potentially through modulation of amyloid-beta deposition and memory-related functions. |
| [Study 2 – Citation] | Observational study of patients with both type 2 diabetes and Alzheimer’s; tracked GLP-1 agonist use over 2 years. | Patients using GLP-1 agonists demonstrated a slower rate of cognitive decline compared to those not using the drugs. | Indicates a possible correlation between GLP-1 agonist use and a reduced risk of cognitive decline. Further research is needed to confirm this observation. |
| [Study 3 – Citation] | Pre-clinical study in rats; focused on neuroinflammation. | GLP-1 treatment reduced microglial activation and inflammatory markers in the brain. | Implies that GLP-1 agonists may mitigate neuroinflammation, a crucial aspect of Alzheimer’s pathogenesis. |
| [Study 4 – Citation] | Observational study of elderly patients with mild cognitive impairment; monitored GLP-1 agonist use and cognitive tests over 18 months. | No significant difference in cognitive function was observed between the GLP-1 agonist users and controls. | Results highlight the complexity of the relationship and the need for further investigation. Potential confounding factors may have influenced the outcome. |
Safety and Side Effects
GLP-1 receptor agonists, while promising in potential Alzheimer’s treatment, require careful consideration of their safety profile. Understanding the known side effects and potential interactions with other medications is crucial for patient management and treatment success. This section delves into the safety considerations associated with these drugs, including potential side effects, interactions, and monitoring procedures.
Known Safety Profiles of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
GLP-1 receptor agonists are generally well-tolerated, with a safety profile largely consistent with their established use in managing type 2 diabetes. However, like any medication, they carry potential risks. The most common adverse effects are gastrointestinal in nature, reflecting the direct action of GLP-1 on the gut. These effects are often transient and typically diminish over time.
Potential Side Effects Associated with GLP-1 Use
Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation. These gastrointestinal issues often occur early in treatment and can be mitigated by starting with lower doses and gradually increasing them as tolerated. Other less common but potentially serious side effects include pancreatitis, gallbladder problems, and kidney problems. Careful monitoring and prompt reporting of any unusual symptoms are essential.
Potential Interactions Between GLP-1 and Other Medications
Interactions between GLP-1 receptor agonists and other medications can occur. For instance, they may affect the absorption or metabolism of certain drugs. A thorough medication history is vital for identifying potential interactions. Consultations with a healthcare provider are crucial before initiating GLP-1 therapy if the patient is already taking other medications.
Patient Monitoring During GLP-1 Therapy
Regular monitoring is essential during GLP-1 therapy. This includes frequent blood glucose checks, particularly in patients with pre-existing diabetes or those who are at risk of developing it. Monitoring for signs of pancreatitis, such as severe abdominal pain, is also crucial. Patients should be instructed on the importance of reporting any unusual symptoms immediately to their healthcare provider.
Blood work to check for kidney function should also be included in the monitoring regimen.
Table of Potential Side Effects
| Side Effect | Description | Frequency (Common/Uncommon/Rare) | Severity (Mild/Moderate/Severe) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nausea | Feeling of discomfort or sickness in the stomach. | Common | Mild to Moderate |
| Vomiting | Forcing the contents of the stomach out through the mouth. | Common | Mild to Moderate |
| Diarrhea | Frequent loose bowel movements. | Common | Mild to Moderate |
| Constipation | Difficulty or infrequent bowel movements. | Common | Mild to Moderate |
| Pancreatitis | Inflammation of the pancreas. | Uncommon | Severe |
| Gallbladder problems | Conditions affecting the gallbladder. | Uncommon | Variable |
| Kidney problems | Conditions affecting kidney function. | Rare | Severe |
| Headache | Pain in the head. | Common | Mild to Moderate |
| Skin reactions | Rashes or itching. | Uncommon | Mild to Moderate |
End of Discussion
In conclusion, the potential of GLP-1 receptor agonists as a treatment for Alzheimer’s disease remains a subject of active research. While promising preclinical and clinical findings suggest a possible link between these drugs and Alzheimer’s progression, more robust clinical trials are necessary to validate these observations and determine their long-term efficacy and safety. Further research, focused on understanding the complex interplay between GLP-1, Alzheimer’s pathologies, and potential side effects, is crucial to fully assess the therapeutic potential of this approach.