Macular degeneration coping support and living well is a comprehensive guide to navigating the challenges and embracing the possibilities of life with this condition. It delves into understanding the different types, symptoms, and progression of macular degeneration, equipping you with practical coping strategies, support systems, and lifestyle choices. This journey will help you learn how to maintain independence, build a supportive community, and ultimately live a fulfilling life despite the challenges.
This guide will explore the diverse aspects of managing macular degeneration, from the initial diagnosis to adapting to a life with reduced vision. We’ll cover practical techniques for maintaining daily tasks, assistive technologies, and important support systems, including family, friends, and healthcare professionals. We’ll also discuss the crucial role of maintaining a healthy lifestyle, emotional well-being, and connecting with a supportive community.
Understanding Macular Degeneration
Macular degeneration is a progressive eye disease that affects the macula, the central part of the retina responsible for sharp, detailed vision. This crucial area of the eye is essential for tasks like reading, driving, and recognizing faces. Understanding the different types of macular degeneration, their symptoms, and how they progress is vital for early detection and effective management.
This knowledge empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their eye health and overall well-being.Macular degeneration, a significant cause of vision loss, is characterized by the gradual deterioration of the macula. This leads to a decline in central vision, impacting daily activities that rely on sharp, detailed sight. The disease progresses at different rates, and its impact on vision varies depending on the type and stage of the condition.
Types of Macular Degeneration
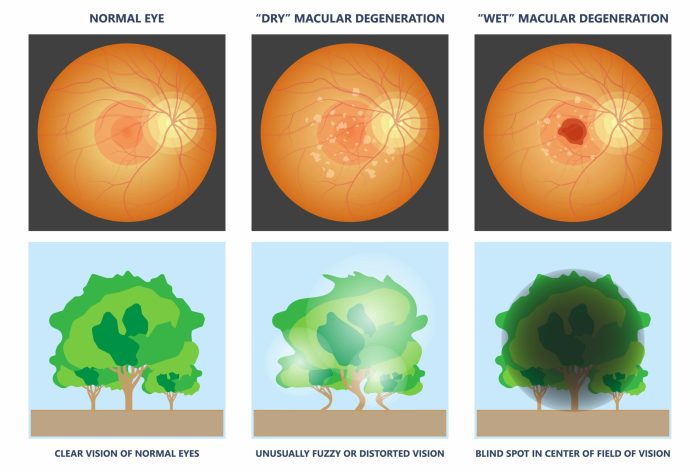
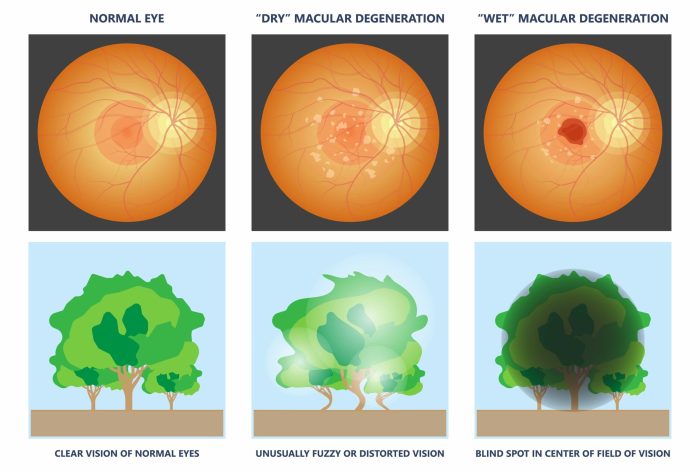
Macular degeneration manifests in two primary forms: dry and wet. Understanding the distinctions between these forms is crucial for appropriate management and treatment.
Dry Macular Degeneration
Dry macular degeneration, the more common type, typically begins with the gradual thinning and deterioration of the light-sensitive cells in the macula. This process can be slow and often asymptomatic in the early stages. The loss of vision is usually gradual and subtle. In many cases, dry macular degeneration progresses slowly over many years, and the impact on vision can be mild, but in some cases, it can lead to significant vision loss.
This form is often associated with age-related changes in the eye.
Wet Macular Degeneration
Wet macular degeneration is a more aggressive form of the disease. In this type, abnormal blood vessels grow under the macula, leaking fluid and blood. This leakage damages the light-sensitive cells and leads to rapid vision loss. The vision loss associated with wet macular degeneration is often more significant and occurs more quickly than in dry macular degeneration.
The abnormal blood vessels are responsible for the rapid progression of vision loss in wet macular degeneration.
Symptoms and Signs of Macular Degeneration
The symptoms of macular degeneration can vary, depending on the type and stage of the disease. Common signs and symptoms include:
- Blurred central vision: Objects directly in front of the eyes may appear blurry or distorted.
- Straight lines appearing wavy or distorted: This is a common early symptom of macular degeneration.
- Difficulty reading or recognizing faces: Tasks requiring sharp central vision may become challenging.
- Dark or empty spots in the center of vision: These are sometimes described as “blind spots.”
Progression of Macular Degeneration
The progression of macular degeneration varies significantly. In dry macular degeneration, the vision loss is often slow and gradual, with some individuals experiencing little to no impact on their daily activities. In contrast, wet macular degeneration can lead to a rapid decline in vision, potentially causing significant impairment within a short period. It’s important to note that the progression of macular degeneration is not uniform, and the rate of vision loss can differ from person to person.
Comparison of Wet and Dry Macular Degeneration
| Feature | Dry Macular Degeneration | Wet Macular Degeneration |
|---|---|---|
| Cause | Thinning and breakdown of the light-sensitive cells in the macula. | Abnormal blood vessel growth under the macula, causing leakage of fluid and blood. |
| Progression | Slow and gradual. | Rapid and significant. |
| Symptoms | Often subtle, including blurred central vision and straight lines appearing wavy. | Can include rapid central vision loss, distorted vision, and dark spots. |
| Treatment | Often supportive care, including eye exams and vitamin supplements. | May involve treatments like injections or laser therapy. |
Coping Strategies for Vision Loss
Navigating daily life with macular degeneration requires adapting to changes in vision. This involves not just adjusting to reduced sight, but also embracing strategies for maintaining independence, connection, and overall well-being. Understanding effective coping mechanisms and assistive technologies can empower individuals to live fulfilling lives despite the challenges posed by vision loss.Effective coping strategies are crucial for managing daily tasks with reduced vision.
They encompass a wide range of approaches, from simple adjustments to utilizing advanced assistive technologies. Finding the right balance between adaptation and preservation of independence is key to maintaining a positive outlook.
Practical Coping Mechanisms for Daily Tasks
Managing daily tasks requires thoughtful adjustments. Simple modifications can significantly enhance daily life. For example, using larger print, strategically placed lighting, and organizing items in a predictable manner can ease navigation and reduce frustration. Utilizing a magnifying glass or a digital magnifier can greatly assist in tasks like reading, writing, or inspecting small objects. Creating a well-organized space with accessible items, reducing clutter, and maintaining clear pathways are crucial for minimizing obstacles and enhancing safety.
Assistive Technologies for Daily Living
Assistive technologies play a vital role in facilitating daily tasks and maintaining independence. These technologies range from simple tools to sophisticated computer programs. For example, screen readers, such as JAWS or NVDA, convert text on a computer screen into audible speech, enabling individuals with vision loss to access digital information and communications. Voice-activated devices and software are beneficial for controlling household appliances, managing calendars, and performing tasks that require minimal visual input.
Adaptive switches and controls can be customized to accommodate various needs, enabling individuals to operate electronics and appliances with ease.
Maintaining Independence and Social Engagement
Maintaining independence is a key aspect of coping with vision loss. Strategies include relying on a support network of family and friends, utilizing public transportation systems with accessible features, and arranging transportation with care. Using adaptive devices such as talking clocks and calendars can help maintain daily routines and enhance time management. Learning to adapt and rely on technology for daily tasks will enable independent living.
For social engagement, joining support groups and organizations focused on vision loss can provide a valuable network of peers and professionals who understand the challenges and offer encouragement.
Resources for Support Groups and Organizations
Numerous support groups and organizations offer invaluable assistance to individuals dealing with vision loss. These resources provide a platform for sharing experiences, gaining practical advice, and connecting with others who understand the unique challenges of living with macular degeneration. The National Federation of the Blind (NFB) and the American Foundation for the Blind (AFB) are prominent examples. Local chapters of these organizations and similar groups provide in-person support, resources, and advocacy opportunities.
Many hospitals and community centers also offer support groups for vision loss. Connecting with these resources allows for building a strong support network, enabling individuals to share experiences and receive guidance.
Navigating macular degeneration can be tough, but finding ways to cope and live well is key. Managing the day-to-day discomfort, like when a toothache strikes, can be surprisingly helpful. For instance, exploring over-the-counter dental pain relief options like otc dental pain relief can really ease some of that pain. Ultimately, prioritizing self-care and support groups remains crucial for a positive outlook and maintaining a good quality of life.
| Organization | Description |
|---|---|
| National Federation of the Blind (NFB) | A prominent national organization advocating for the rights and needs of blind and visually impaired individuals. |
| American Foundation for the Blind (AFB) | Provides extensive resources, services, and advocacy for individuals with vision loss. |
Support Systems and Resources
Navigating macular degeneration requires a multifaceted approach, encompassing medical care, emotional support, and practical assistance. This section highlights the vital roles of various support systems in helping individuals cope with the challenges and maintain a high quality of life. Understanding the available resources can significantly ease the burden and empower those affected by this condition.
Family and Friends
Family and friends play a crucial role in providing emotional support and practical assistance. They can offer companionship, encouragement, and a listening ear during difficult times. Their understanding and willingness to help with daily tasks, like transportation or household chores, can significantly improve the quality of life for someone with macular degeneration. Family members can also act as advocates, helping navigate medical appointments and understand treatment options.
Building a strong support network among loved ones is invaluable in managing the emotional and practical aspects of the condition.
Healthcare Professionals
Healthcare professionals, including ophthalmologists, optometrists, and other specialists, are essential for managing macular degeneration. They provide crucial medical care, monitor disease progression, and recommend appropriate treatments. Beyond the medical aspect, they can offer valuable information about resources, support groups, and coping strategies. Regular communication with healthcare professionals is vital to stay informed and make informed decisions. This allows for prompt interventions and helps individuals maintain their independence.
Government Assistance Programs and Financial Resources
Numerous government assistance programs and financial resources are available to support individuals with macular degeneration. These programs can provide financial aid for medical expenses, assistive devices, and modifications to the home. Examples include Medicare, Medicaid, and state-specific programs for low-income individuals. Detailed information about eligibility criteria and application procedures can be obtained from local social service agencies and government websites.
Exploring these options can alleviate financial burdens associated with the condition.
Support Groups and Online Communities
Support groups and online communities offer invaluable opportunities for connection and shared experiences. These platforms provide a safe space for individuals to connect with others who understand the challenges of macular degeneration. They can share practical tips, coping strategies, and emotional support. Participating in these groups can reduce feelings of isolation and foster a sense of community.
Online forums and in-person support groups provide a valuable network of people who are navigating similar journeys.
Navigating macular degeneration can be tough, but finding support groups and resources for living well is key. While dealing with a sudden injury like a gunshot wound requires immediate action, like knowing how to treat a gunshot wound, how to treat a gunshot wound is a different kind of challenge entirely. Focusing on practical strategies for coping with macular degeneration, like adapting daily routines and embracing assistive technology, is vital for maintaining a positive outlook and quality of life.
Therapists and Counselors
Therapists and counselors play a vital role in managing the emotional well-being of individuals with macular degeneration. They can provide guidance and support for dealing with the emotional challenges of vision loss, including feelings of frustration, anxiety, and depression. Counseling can help individuals develop coping mechanisms, adjust to lifestyle changes, and maintain a positive outlook. Therapy can empower individuals to manage the emotional impact of macular degeneration and navigate the changes in their lives.
Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle
Living well with macular degeneration involves more than just managing vision loss. A holistic approach that prioritizes overall health plays a crucial role in maintaining quality of life. This includes making informed choices about diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and actively managing stress. These factors directly influence your physical and emotional well-being, allowing you to better cope with the challenges of the condition.A healthy lifestyle is fundamental in managing macular degeneration.
By adopting positive habits, you can support your body’s natural ability to function optimally, thereby potentially slowing the progression of the disease and improving your overall quality of life. It’s not about a quick fix, but rather a sustained commitment to well-being that will yield long-term benefits.
Dietary Recommendations for Eye Health
A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients is vital for maintaining good eye health. Many nutrients contribute to the overall health and function of the eyes.
- Antioxidants: Antioxidants, such as vitamins C and E, lutein, and zeaxanthin, play a crucial role in protecting the eyes from damage caused by free radicals. These nutrients are found in colorful fruits and vegetables like berries, leafy greens, and carrots. A diet rich in these foods can help maintain healthy eye tissues and potentially slow the progression of macular degeneration.
For example, incorporating spinach, kale, and blueberries into your diet provides valuable antioxidants.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Omega-3 fatty acids are essential for eye health, contributing to the structural integrity of the retina. These are commonly found in fatty fish like salmon, tuna, and mackerel. Consider incorporating fish oil supplements as a way to obtain these essential nutrients.
- Zinc: Zinc is an important mineral for eye health, and it is involved in the transport of vitamin A to the retina. Foods high in zinc include oysters, beef, and pumpkin seeds. A sufficient intake of zinc is vital for optimal retinal function.
- Vitamin A: Vitamin A is essential for maintaining healthy eye tissue. Foods like sweet potatoes, carrots, and leafy greens are excellent sources of vitamin A. A balanced diet that includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can provide sufficient amounts of vitamin A.
Importance of Regular Exercise
Regular physical activity is crucial for overall health and well-being, and it plays a significant role in managing macular degeneration.
- Cardiovascular Health: Regular exercise improves cardiovascular health, which is beneficial for blood flow to all parts of the body, including the eyes. This can help maintain healthy retinal blood vessels, which are vital for vision. For instance, brisk walking, swimming, or cycling can be beneficial for eye health.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for overall health and can potentially slow the progression of macular degeneration. Exercise plays a vital role in weight management, helping you achieve and maintain a healthy body weight. For example, consistent exercise routines help control weight and improve overall health.
- Stress Reduction: Exercise is an effective stress management technique, reducing stress hormones and promoting relaxation. This contributes to improved mental and emotional well-being. Physical activity, like yoga or meditation, can reduce stress levels.
Stress Management Techniques
Stress can have a significant impact on overall health, including eye health. Effective stress management techniques are essential for maintaining emotional well-being and coping with the challenges of macular degeneration.
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Mindfulness and meditation practices help to cultivate awareness of the present moment, reducing stress and promoting relaxation. Regular mindfulness exercises can be beneficial for emotional regulation.
- Yoga and Tai Chi: These practices combine physical postures, breathing techniques, and meditation, promoting relaxation, flexibility, and stress reduction. Yoga and Tai Chi are excellent stress reduction techniques.
- Social Support: Maintaining strong social connections and seeking support from family and friends can provide emotional comfort and reduce stress levels. Connecting with others can be a crucial coping mechanism for stress.
Living Well with Macular Degeneration
Adjusting to macular degeneration requires proactive strategies to maintain independence and quality of life. This involves understanding how the condition affects daily routines and implementing modifications to the home, transportation, and social environment. Embracing new approaches to activities and social connections can be empowering and allow individuals to continue thriving despite vision loss.
Sample Daily Routine for Reduced Vision
A tailored daily routine can significantly improve the experience of living with macular degeneration. This structured approach can help individuals feel more in control and organized.
- Morning Routine: Begin with a well-lit environment. Use large-button clothing and clocks with large numbers. Prepare a visual schedule of tasks with clear instructions. Ensure sufficient time for morning activities, allowing for potential delays due to reduced visual acuity.
- Meal Preparation: Prepare meals in advance, using clear labels on containers and organized storage systems. Utilize kitchen aids with large handles and well-lit areas for food preparation. Consider pre-portioned meals or simple recipes that are easy to prepare.
- Afternoon Activities: Schedule activities with ample time between tasks, allowing for adjustments and breaks. Prioritize tasks that require minimal visual effort in the afternoon. Utilize audio books, podcasts, or other auditory resources during downtime.
- Evening Routine: Dim the lights gradually to prepare for sleep. Use a night light and a well-defined path to the bathroom or bedroom. Keep frequently used items within easy reach.
Modifying Home Environments for Independent Living
Adapting the home environment is crucial for maintaining independence. Careful modifications can significantly improve daily living.
- Lighting: Maximize natural light. Use task lighting with adjustable brightness, and consider using bright, contrasting colors for rooms. Install strategically placed lamps and light fixtures to enhance visibility.
- Furniture and Flooring: Ensure clear pathways, avoiding clutter. Choose contrasting colors for rugs and floors to delineate spaces. Utilize furniture with large, easily accessible features.
- Kitchen and Bathroom: Install grab bars, non-slip mats, and adjustable counters for improved accessibility. Use contrasting colors for kitchen cabinets and appliances to enhance visibility. Organize frequently used items within easy reach.
- Technology: Explore assistive technology like screen readers, magnifiers, and voice-activated devices. Ensure technology is user-friendly and easy to operate.
Accessible Transportation Options
Transportation options should be accessible and reliable, allowing for easy navigation and independence.
- Public Transportation: Utilize public transportation systems with clear signage and well-marked routes. Learn the specific routes and schedules in advance. Communicate with transportation officials about specific needs.
- Ride-Sharing Services: Research ride-sharing services and evaluate their accessibility features. Communicate specific needs to the drivers. Ensure clear communication and instructions.
- Accessible Vehicles: Consider accessible vehicles with ramps and modifications for easier entry and exit. Consult with specialists for tailored vehicle recommendations.
Maintaining Social Connections and Engagement
Maintaining social connections and engagement in activities is vital for overall well-being. Adapting to vision loss should not limit participation in activities.
- Social Activities: Engage in social activities that are accessible and adaptable to vision loss. Explore activities like group discussions, book clubs, or online communities. Seek out organizations and clubs with supportive environments.
- Support Groups: Join support groups to connect with others facing similar challenges. Support groups provide a valuable platform for sharing experiences and gaining practical advice.
- Adaptive Activities: Engage in activities that can be modified to accommodate vision loss. For example, consider group activities with auditory components or visual aids. Research modified options for hobbies and recreational pursuits.
Accessible Communication and Information
Navigating life with macular degeneration often involves adapting communication and information access methods. This section details various strategies to ensure you remain connected and informed despite vision loss. Understanding the options available allows you to maintain independence and build strong support networks.Effective communication and access to information are vital for maintaining a fulfilling life with macular degeneration. This includes adapting to different communication methods and learning to effectively communicate visual challenges to others.
Access to accessible formats for information and media is also crucial for continuing to engage with the world around you.
Methods for Receiving Accessible Information
Different methods for receiving accessible information cater to various needs and preferences. These methods include audio descriptions, large print materials, braille, and electronic formats like screen readers. Choosing the best method often depends on your individual needs and learning styles.
- Audio descriptions: Provide auditory descriptions of visual elements in movies, television shows, and other media. This allows viewers to understand the content despite not seeing it. Many streaming services offer audio description options. This is particularly useful for enjoying entertainment and staying informed about current events.
- Large print materials: Enlarge text and images to make them easier to read. Many organizations and libraries offer materials in large print. This approach helps those with decreased visual acuity read documents and books more comfortably.
- Braille: A tactile writing system that uses raised dots. Many books, magazines, and documents are available in braille. Braille offers an alternative for those with significant vision loss.
- Electronic formats: Accessible documents, websites, and software with screen readers and other assistive technology help individuals with vision loss access digital content. Screen readers are software programs that convert text into speech. This approach allows those with impaired vision to navigate digital environments effectively.
Assistive Devices for Communication
Assistive devices are tools that aid in communication and information access. Many devices are designed to increase independence and help maintain social connections. Consider using them in combination with other methods to create a personalized approach.
- Screen readers: Software that converts text on a computer screen into audio, allowing users to navigate and interact with digital content without relying on visual input. Many screen readers can be customized to suit individual needs.
- Magnifying glasses: Optical aids that enlarge text and images, making them easier to read. Various types of magnifying glasses are available, ranging from handheld devices to tabletop models. These can significantly improve reading and viewing experiences.
- Closed-captioning: Displaying text on a screen that synchronizes with audio content, enabling viewers to follow along with the dialogue and other spoken words. This is extremely helpful for understanding conversations and following along with lectures or presentations.
- Text-to-speech software: Software that converts text into speech. This tool is particularly helpful for reading articles, emails, or documents. Text-to-speech can be used in conjunction with screen readers to improve accessibility.
Communicating Effectively with Others
Clear and open communication is crucial when discussing visual impairment. Understanding the specific challenges you face will help others offer appropriate support. Emphasize the need for adjustments and reasonable accommodations.
Navigating macular degeneration can be tough, but finding support and ways to live well is key. Understanding your options for financial support is also crucial, and that includes exploring gold plan health insurance, like gold plan health insurance what is it. Knowing what’s covered can significantly ease the burden, which is essential for overall well-being in managing this condition.
- Open communication: Explain your specific needs and challenges clearly and openly. Sharing your experience will help others understand your perspective and provide effective support.
- Active listening: Pay attention to the other person’s responses. Ask clarifying questions to ensure you understand their perspectives and concerns. This will help foster a more collaborative and supportive environment.
- Seeking accommodations: Explain the need for accommodations in various situations, such as at work or in social settings. Explain how certain changes will make interactions more inclusive.
- Using appropriate language: Avoid using phrases that imply judgment or pity. Focus on practical solutions and strategies for support. Using respectful and considerate language enhances communication.
Accessing Accessible Information and Media
Finding accessible information and media requires awareness and exploration. Many organizations and websites offer accessible content. It’s important to actively seek these resources.
- Online resources: Many websites provide accessible information, including audio descriptions and transcripts. Look for websites with accessibility features and use assistive technologies.
- Libraries and community centers: Local libraries and community centers often have accessible materials and resources. Utilize these resources to acquire books, magazines, and other media in accessible formats.
- Government agencies: Government agencies offer a wealth of accessible information on a variety of topics. Use these resources to find relevant information in accessible formats.
- Organizations specializing in vision loss: Many organizations specifically cater to individuals with vision loss. These organizations provide accessible information, support groups, and other resources.
Professional Guidance and Treatment
Navigating macular degeneration requires a multi-faceted approach, including understanding the disease, adopting coping strategies, and seeking appropriate professional guidance. Expert advice and tailored treatment plans are crucial for managing the condition and maintaining quality of life. This section delves into the roles of ophthalmologists and optometrists, available therapies, and the importance of regular eye check-ups.Effective management of macular degeneration hinges on accurate diagnosis, personalized treatment strategies, and ongoing monitoring.
This involves a collaboration between patients and their healthcare providers to ensure optimal outcomes and address the evolving needs of the individual.
Roles of Ophthalmologists and Optometrists
Ophthalmologists are medical doctors specializing in eye care, including the diagnosis and treatment of macular degeneration. They are trained to perform comprehensive eye exams, diagnose various eye conditions, and prescribe medications or conduct surgical procedures. Optometrists, on the other hand, are primary eye care providers who conduct routine eye exams, diagnose refractive errors (like nearsightedness or farsightedness), and prescribe corrective lenses.
They play a vital role in early detection and monitoring of macular degeneration, often referring patients to ophthalmologists when necessary.
Types of Therapies and Treatments
Various therapies and treatments are available for managing macular degeneration, although there is no cure. These therapies aim to slow the progression of the disease, manage symptoms, and improve quality of life. Treatments include:
- Anti-VEGF injections: These injections target and inhibit the growth of blood vessels that contribute to macular damage, thereby slowing the progression of the disease. They are often administered by ophthalmologists. For example, a patient with neovascular age-related macular degeneration might receive regular anti-VEGF injections to control the growth of new blood vessels.
- Laser therapy: In some cases, laser treatment can help to reduce abnormal blood vessel growth. This is often a supplementary or complementary therapy used in conjunction with other treatments, such as anti-VEGF injections.
- Low vision aids: These tools, such as magnifying glasses, large-print materials, and specialized computer software, help individuals with vision loss perform daily tasks and maintain independence. They are often recommended by optometrists and low vision specialists.
- Lifestyle modifications: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management techniques, can contribute to overall well-being and potentially slow the progression of the disease. This may include dietary adjustments rich in antioxidants and vitamins.
Importance of Regular Eye Check-ups and Monitoring
Regular eye check-ups are essential for early detection and management of macular degeneration. Early diagnosis allows for prompt intervention and potential slowing of the disease’s progression. Monitoring helps track the progression of the condition and adjust treatment strategies as needed. A patient’s baseline vision and specific characteristics are considered to provide accurate monitoring.
Comparison of Eye Care Professionals
| Professional | Focus | Role in Macular Degeneration Management |
|---|---|---|
| Ophthalmologist | Medical eye care, including surgery | Diagnoses, treats, and monitors the disease, often prescribing medication and performing procedures like anti-VEGF injections. |
| Optometrist | Primary eye care, vision correction | Conducts routine eye exams, detects early signs, and provides low vision aids and support. Refers patients to ophthalmologists when necessary. |
| Low Vision Specialist | Specialized care for vision loss | Prescribes and fits assistive devices and techniques to maximize remaining vision. Provides support for adaptive strategies. |
Visual Aids and Adaptive Techniques
Navigating daily life with macular degeneration can be challenging, but various visual aids and adaptive techniques can significantly improve independence and quality of life. These tools and strategies empower individuals to maintain their activities and connections, fostering a sense of control and participation in their communities.
Visual Aids for Enhanced Vision
Understanding the specific needs of each individual with macular degeneration is crucial when selecting visual aids. The table below Artikels common visual aids and their applications, offering a starting point for exploring options.
| Visual Aid | Description | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Large-print materials | Printed text with larger font sizes | Reading books, newspapers, and other documents |
| Magnifiers | Optical devices that enlarge text and images | Examining small print, reading maps, and using computer screens |
| Telescopic devices | Optical aids that increase the apparent size of distant objects | Viewing objects from a distance, such as during outdoor activities or while watching television |
| Closed-circuit television (CCTV) | Systems that magnify images projected onto a screen | Reading documents, viewing small objects, and interacting with computer screens |
| Screen readers and screen magnifiers | Computer software that reads aloud text and enlarges screen elements | Accessing digital information, navigating websites, and using software applications |
Adjusting Lighting and Contrast
Proper lighting significantly impacts visibility for individuals with macular degeneration. Optimal lighting conditions reduce eye strain and improve clarity. Consider the following strategies:
- Use bright, but not harsh, lighting. Avoid overly dim or flickering lights, as these can exacerbate eye fatigue.
- Position lighting sources strategically to eliminate glare and shadows. For example, direct sunlight can be very harsh, and overhead lighting can cast shadows that obscure the intended reading material. A table lamp, placed to the side of the reading material, can provide a focused and balanced light source.
- Optimize the contrast between the text or object and the background. High contrast between the subject and its background is vital for clarity. Dark text on a light background, or vice-versa, is typically easier to read.
Large-Print Materials and Assistive Technologies
Large-print materials are a readily available and effective means to enhance readability. They can be utilized for various tasks such as reading books, newspapers, and magazines. Furthermore, a variety of assistive technologies exist to assist with navigating digital information.
- Many organizations provide large-print versions of books, magazines, and other documents. Libraries, bookstores, and specific online resources frequently offer such services.
- Assistive technologies, such as screen readers and screen magnifiers, can be installed on computers and mobile devices to provide voice-over text and enlarge display elements. This significantly increases accessibility to digital information for individuals with macular degeneration.
- Specialized computer software and tools are also available. These tools can include features that increase the font size, change text color, and improve the overall readability of digital content.
Specialized Computer Software and Tools
Numerous software applications and tools have been designed to enhance accessibility and usability for individuals with macular degeneration. These tools are invaluable for maintaining productivity and connectivity.
- Screen readers convert text into audible formats, enabling individuals to access digital content through sound. These tools are available for various operating systems and can be integrated with assistive technology devices.
- Screen magnifiers enlarge the content displayed on a computer screen, allowing individuals to clearly view and interact with digital materials. These tools can adjust zoom levels, font sizes, and other visual parameters.
- Text-to-speech software converts written text into spoken language. This feature can aid individuals in understanding documents and interacting with electronic devices more effectively.
Emotional Well-being and Mental Health
Living with macular degeneration can bring about a range of emotional challenges, impacting mental well-being significantly. The adjustment to changing vision, the potential for decreased independence, and the fear of the future can all contribute to feelings of anxiety, sadness, or isolation. Understanding these emotional responses is crucial for effective coping strategies.Macular degeneration isn’t just a visual impairment; it can also affect an individual’s emotional and mental state.
Coping with the loss of vision, and the uncertainty about the future, often necessitates a proactive approach to emotional well-being. This involves acknowledging the emotional responses, developing healthy coping mechanisms, and seeking support when needed.
Emotional Challenges Associated with Macular Degeneration, Macular degeneration coping support and living well
The emotional impact of macular degeneration is multifaceted. Individuals may experience feelings of grief, anger, frustration, and even depression as they adjust to the changing reality of their vision. It’s essential to acknowledge these feelings as a normal part of the adaptation process. Loss of independence, social isolation, and the fear of future limitations can also significantly impact mental health.
Understanding these emotional responses is the first step towards developing effective coping strategies.
Strategies for Managing Anxiety and Depression
Managing anxiety and depression related to vision loss requires a holistic approach. A crucial strategy is to acknowledge and validate your emotions. Journaling can be helpful in processing feelings and identifying patterns. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and sufficient sleep are fundamental to maintaining emotional well-being. Mindfulness and relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises and meditation, can also effectively reduce stress and anxiety.
Importance of Self-Care and Stress Reduction Techniques
Self-care is not a luxury, but a necessity for managing the emotional toll of macular degeneration. Regular self-care practices, like engaging in hobbies, spending time in nature, or pursuing creative outlets, can significantly reduce stress. Prioritizing adequate sleep, maintaining a healthy diet, and regular exercise can contribute significantly to emotional well-being. Learning and practicing relaxation techniques, such as progressive muscle relaxation or guided imagery, can help individuals manage stress and anxiety more effectively.
Connecting with others who understand the challenges can provide invaluable emotional support.
Resources for Mental Health Support and Counseling
Numerous resources are available to provide support and counseling for individuals dealing with the emotional challenges of macular degeneration. Support groups specifically for people with vision loss can offer a safe space to share experiences and connect with others facing similar challenges. Local organizations, eye care professionals, and mental health professionals can provide valuable guidance and resources. Online communities and forums can also offer a sense of connection and support.
These resources can provide invaluable assistance in navigating the emotional journey of macular degeneration.
Community Involvement and Support: Macular Degeneration Coping Support And Living Well
Connecting with others who understand the unique challenges of macular degeneration can be incredibly valuable. A supportive community provides emotional comfort, practical advice, and a sense of belonging. Shared experiences and mutual understanding can foster resilience and empower individuals to navigate the complexities of vision loss.Building a network of support is crucial for maintaining well-being. This community can offer invaluable assistance in accessing resources, sharing coping strategies, and providing encouragement during difficult times.
It’s important to remember that you are not alone in this journey.
Importance of Community Support
A supportive community plays a vital role in the overall well-being of individuals living with macular degeneration. This support system can ease the burden of adjusting to vision loss, offering practical assistance, and emotional encouragement. A sense of belonging and shared experiences can reduce feelings of isolation and foster a stronger sense of resilience.
Community Programs and Resources
Numerous community programs and resources cater to the needs of individuals with visual impairments. Local organizations often provide support groups, workshops, and educational sessions. These initiatives are designed to help individuals cope with the emotional and practical aspects of vision loss.
- Support Groups: These groups offer a safe space for sharing experiences, offering mutual support, and gaining valuable insights from others facing similar challenges. They provide a platform for discussing practical solutions and emotional well-being strategies.
- Educational Workshops: Workshops are frequently offered by organizations dedicated to visual impairments. These sessions typically cover topics such as adaptive techniques, assistive technologies, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Such programs equip participants with knowledge and skills to enhance their daily living.
- Advocacy Groups: These groups advocate for the rights and needs of individuals with visual impairments. They actively work to create more inclusive environments and improve access to resources and services.
Connecting with Local Organizations
Finding local organizations dedicated to visual impairment is often the first step in building a supportive community. Utilizing online search engines, contacting local eye care professionals, or visiting community centers are all effective strategies.
- Online Search: Online search engines can yield a wealth of information about local organizations and programs. s such as “visual impairment support groups,” “low vision rehabilitation,” and “Macular Degeneration support” can be highly effective in locating relevant resources.
- Local Eye Care Professionals: Eye care professionals, such as ophthalmologists and optometrists, are often well-versed in local resources and support networks. Asking them about available support groups or organizations can lead to immediate connections.
- Community Centers and Libraries: Community centers and libraries are often hubs for local organizations and programs. They can provide information on support groups, workshops, and other resources tailored to visual impairments.
Building Supportive Relationships
Building supportive relationships with others who share similar experiences can greatly enhance the journey of living with macular degeneration. Initiating conversations, joining support groups, and participating in community events are all effective ways to build a strong support network.
- Initiating Conversations: Don’t hesitate to reach out to others who share similar experiences. Sharing your story and concerns can foster a sense of connection and mutual understanding. It’s often a simple act of reaching out that can lead to profound support.
- Joining Support Groups: Support groups offer structured environments for interaction with others facing similar challenges. Sharing experiences, learning coping strategies, and receiving encouragement can create meaningful relationships.
- Participating in Community Events: Local organizations often host events that provide opportunities for socializing and networking with others facing similar circumstances. These gatherings can be a catalyst for building supportive relationships.
Last Point
In conclusion, living well with macular degeneration is achievable through a combination of understanding the condition, adopting effective coping strategies, and nurturing a strong support network. This guide has provided a roadmap to navigate the complexities of vision loss and has emphasized the importance of maintaining a positive outlook, embracing available resources, and actively participating in a supportive community. By integrating the practical advice and strategies presented here, individuals can confidently manage their condition and continue to thrive in life.











 (Diagram placeholder. A permanent pacemaker is typically implanted under the skin near the collarbone, with thin wires (leads) extending to the heart chambers. The pulse generator is housed within the implanted casing.)
(Diagram placeholder. A permanent pacemaker is typically implanted under the skin near the collarbone, with thin wires (leads) extending to the heart chambers. The pulse generator is housed within the implanted casing.)