Treatment of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) is a multifaceted approach addressing a complex condition. This in-depth look covers everything from understanding the underlying causes and varied symptoms to exploring diagnostic methods, dietary strategies, and medical management. We’ll delve into the principles of a low-FODMAP diet, the role of antibiotics, and the importance of long-term management to prevent recurrence.
Learn about potential complications and associated conditions, equipping yourself with the knowledge to navigate this health concern.
SIBO, a condition where an excessive amount of bacteria grows in the small intestine, can cause a wide array of symptoms. These symptoms can range from mild discomfort to severe digestive issues, making accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment crucial. This comprehensive guide provides a roadmap for understanding SIBO, empowering individuals to take an active role in their health journey.
Introduction to Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO)
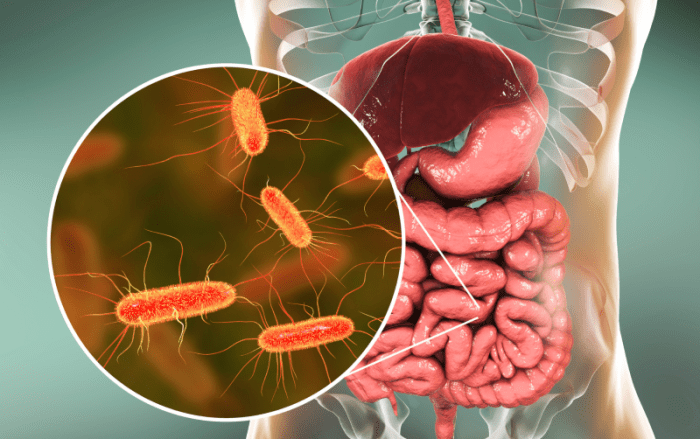
Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) is a digestive disorder characterized by an excessive amount of bacteria in the small intestine. Normally, the small intestine harbors a limited number of bacteria, primarily residing in the large intestine. In SIBO, this balance is disrupted, leading to a significant increase in bacterial populations. This imbalance can have various implications for nutrient absorption and overall health.The pathophysiology of SIBO is not fully understood, but several factors are implicated, including impaired motility of the small intestine, anatomical abnormalities, and immune system dysfunction.
These factors can create a favorable environment for bacterial proliferation, resulting in an overgrowth that can cause a range of symptoms. The prevalence of SIBO is estimated to be between 1 and 15% of the population, though it may be underdiagnosed.
Pathophysiology of SIBO
The small intestine’s normal function includes nutrient absorption. In SIBO, the excessive bacteria compete with the body for nutrients, leading to malabsorption. Furthermore, the bacteria produce various metabolites, including gases, acids, and toxins, which can contribute to the symptoms experienced by patients. The exact mechanisms by which SIBO develops are complex and not fully understood, but impaired motility is a significant factor, hindering the normal transit of food and bacteria through the small intestine.
Common Symptoms of SIBO
Symptoms associated with SIBO are highly variable, ranging from mild to severe. Common symptoms include bloating, abdominal distention, excessive flatulence, diarrhea, and weight loss. These symptoms can overlap with other digestive disorders, making diagnosis challenging. Additionally, some individuals may experience fatigue, nausea, or other systemic symptoms. This variability in symptoms makes accurate diagnosis critical.
Diagnostic Criteria and Methods
Diagnosing SIBO involves a combination of clinical evaluation, symptom analysis, and diagnostic tests. The evaluation focuses on identifying specific symptoms, such as the frequency and nature of bowel movements, the presence of bloating, and any associated pain. The diagnostic criteria also consider the patient’s medical history, including any prior digestive issues, and factors such as recent antibiotic use, which may contribute to the development of SIBO.
Comparison of Diagnostic Methods for SIBO
| Diagnostic Method | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Breath Tests | Measure the concentration of gases (e.g., hydrogen, methane) in exhaled breath after ingesting a specific substrate. | Non-invasive, relatively quick, and widely available. | May yield false-positive or false-negative results, and interpretation can be complex. |
| Endoscopy with small bowel biopsy | Visual inspection of the small intestine using a camera and potentially a small tissue sample. | Provides direct visualization of the small intestine and potential underlying abnormalities, can identify other potential causes. | More invasive, potentially more expensive, carries some risk of complications. |
| Capsule endoscopy | A small camera is swallowed that takes images of the small intestine. | Provides a detailed view of the small intestine, particularly useful for extensive evaluation. | Requires specialized equipment and personnel, may be less convenient. |
The table above highlights the advantages and disadvantages of various diagnostic methods for SIBO. The selection of the most appropriate method depends on individual patient factors and clinical context. Factors such as cost, accessibility, and the potential for complications need to be considered.
Diagnostic Approaches for SIBO
Identifying small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) relies on a combination of patient history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. The diagnostic journey aims to distinguish between SIBO and other conditions that might present with similar symptoms. A thorough understanding of the various diagnostic approaches and their limitations is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.The diagnostic process for SIBO involves a careful evaluation of symptoms, a detailed medical history, and a selection of tests tailored to the patient’s specific situation.
Different tests have varying degrees of sensitivity and specificity, and the choice of test often depends on the suspected cause and potential underlying conditions. It’s important to remember that a definitive diagnosis may require multiple tests and a thorough clinical assessment.
Rationale Behind Diagnostic Tests
Various diagnostic tests are used to identify SIBO, each with its own rationale. These tests are designed to detect an excessive amount of bacteria in the small intestine. Breath tests, for instance, measure the gases produced by bacterial metabolism, while culture tests directly identify and quantify bacteria. Each test has its own strengths and weaknesses in terms of accuracy and invasiveness.
Strengths and Limitations of Different Tests
The choice of diagnostic test for SIBO depends on factors like cost, invasiveness, and accuracy. Hydrogen breath tests are widely used, and while they are relatively non-invasive, they may not always be accurate, especially in cases with co-existing conditions that can affect gas production. Other tests, such as endoscopic biopsies and culture tests, provide more direct evidence of bacterial overgrowth but may be more invasive and costly.
Comparison of Diagnostic Approaches
Comparing the accuracy and reliability of different diagnostic approaches reveals that breath tests, particularly hydrogen breath tests, are commonly used due to their relative ease and safety. However, they may yield false-positive results if other factors affect gas production. While endoscopic biopsies offer a more direct view of the intestinal lining, they are more invasive and carry a small risk of complications.
Ultimately, the most accurate diagnosis often arises from a combination of tests and a comprehensive clinical assessment.
Summary Table of Breath Tests for SIBO
| Breath Test Type | Gas Measured | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen Breath Test | Hydrogen | Hydrogen is produced by bacteria fermenting carbohydrates in the small intestine. |
| Methane Breath Test | Methane | Methane is produced by certain types of bacteria. It is often used in conjunction with a hydrogen breath test to provide a more comprehensive picture of bacterial activity. |
| Lactose Breath Test | Hydrogen | This test specifically assesses the ability of the small intestine to digest lactose, a type of sugar. Elevated hydrogen levels suggest malabsorption and potential SIBO. |
Procedure for a Hydrogen Breath Test
The hydrogen breath test is a common and relatively non-invasive diagnostic procedure for SIBO. It involves the following steps:
- Fasting Period: The patient fasts for at least 8-12 hours before the test, avoiding foods that contain sugars and carbohydrates. This ensures that the baseline gas levels are representative of the patient’s natural state.
- Baseline Breath Sample: A breath sample is collected as a baseline measurement. This establishes a starting point for comparing subsequent readings.
- Ingestion of a Test Substance: The patient consumes a lactulose or glucose solution. Lactulose is often preferred due to its slow absorption and ability to produce a consistent level of gas.
- Subsequent Breath Samples: Breath samples are collected at specific time intervals (usually 30, 60, 90, 120, and 180 minutes) after the ingestion of the test substance. These samples are analyzed to measure hydrogen levels.
- Analysis: The collected breath samples are analyzed for hydrogen content. Elevated hydrogen levels at specific time points indicate bacterial fermentation in the small intestine, potentially suggesting SIBO.
Treatment Strategies for SIBO: Treatment Of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth
Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) is a condition characterized by an excessive amount of bacteria in the small intestine. Effective treatment aims to reduce bacterial load and alleviate associated symptoms. A multi-faceted approach is often necessary, combining dietary modifications, antibiotics, and sometimes probiotics.A comprehensive treatment plan for SIBO involves a careful evaluation of individual patient factors, symptom severity, and the specific bacterial species involved.
The primary goal is to restore a healthy balance of gut flora and improve overall digestive function.
Treating small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) often involves dietary changes and antibiotics. Understanding how to manage blood sugar levels is crucial for overall health, especially when dealing with conditions like SIBO, which can sometimes affect blood sugar control. For example, if you’re looking for information on the nuances of insulin versus blood sugar management in type 2 diabetes, this resource ( insulin vs blood sugar how to manage type 2 diabetes ) provides valuable insights.
Ultimately, addressing SIBO effectively often requires a multi-faceted approach that includes dietary modifications and possibly medical intervention.
Dietary Modifications
Dietary modifications play a crucial role in managing SIBO symptoms and reducing bacterial proliferation. A low-FODMAP diet is frequently recommended. This diet restricts fermentable carbohydrates that can be readily metabolized by bacteria, thereby decreasing their growth and activity. Examples of restricted foods include certain fruits, vegetables, legumes, and dairy products.The rationale behind dietary restrictions is that by limiting fermentable carbohydrates, the amount of nutrients available for bacterial growth decreases, contributing to a reduction in bacterial numbers.
Antibiotic Treatment
Antibiotics are frequently used to target and reduce the bacterial population in the small intestine. The selection of antibiotics depends on factors such as the suspected bacterial species, patient history, and potential side effects. Commonly prescribed antibiotics for SIBO include rifaximin, metronidazole, and neomycin. Rifaximin is often preferred due to its targeted action on the gut and relatively low systemic absorption, minimizing side effects.
Metronidazole and neomycin, while effective, can have more extensive side effects, necessitating careful monitoring.
Efficacy and Safety of Antibiotic Regimens
The efficacy of antibiotic regimens for SIBO varies. Some patients experience significant symptom improvement and bacterial reduction, while others may respond less effectively. Factors like adherence to the treatment regimen, the severity of the condition, and the presence of underlying conditions can influence treatment outcomes.The safety profile of antibiotics should be considered. While antibiotics are generally safe when used as prescribed, potential side effects like diarrhea, nausea, and abdominal discomfort can occur.
The use of antibiotics should be carefully evaluated by a healthcare professional to ensure the benefits outweigh the risks.
Duration of Antibiotic Treatment
The recommended duration of antibiotic treatment for SIBO is typically 10-14 days. Longer durations may not offer additional benefits and may increase the risk of antibiotic resistance. Individualized treatment durations might be necessary, depending on the patient’s response to therapy and the specific bacterial species involved.
Probiotics and Prebiotics
Probiotics and prebiotics are often considered adjunctive therapies in the management of SIBO. Probiotics, which contain beneficial bacteria, may help restore a more balanced gut microbiome. Prebiotics are non-digestible fibers that promote the growth of beneficial bacteria, indirectly influencing the gut environment.These strategies aim to support the establishment of a more favorable gut microbiome by introducing or fostering the growth of beneficial bacteria.
Antibiotic Options for SIBO
| Antibiotic | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|
| Rifaximin | Mild gastrointestinal upset, headache |
| Metronidazole | Headache, metallic taste, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and more severe neurological effects in rare cases |
| Neomycin | Ototoxicity (ear damage), nephrotoxicity (kidney damage), gastrointestinal distress, and others |
Dietary Management in SIBO Treatment
Dietary management plays a crucial role in managing small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO). A key component of this management is the low-FODMAP diet. This dietary approach focuses on reducing fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides, and polyols (FODMAPs), which are poorly absorbed by the small intestine and can promote bacterial fermentation and gas production. By minimizing the intake of these substances, individuals with SIBO can often experience significant symptom relief.
Principles of a Low-FODMAP Diet for SIBO Management
The low-FODMAP diet aims to reduce the intake of FODMAPs, thereby decreasing the substrate available for bacterial fermentation in the small intestine. This reduction can lessen symptoms like bloating, abdominal pain, and diarrhea, common in SIBO. The goal is not to eliminate all FODMAPs entirely but to reduce them to a manageable level that still allows for a balanced and nutritious diet.
Dealing with small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) can be tricky, but thankfully, there are treatments available. One thing that can be equally tricky is getting nail glue off skin, and luckily, there’s a helpful resource for that how to get nail glue off skin. While these situations are quite different, both involve careful attention to detail and potentially irritating substances.
Ultimately, the key to managing SIBO is a personalized approach tailored to your specific needs and symptoms.
This approach is usually implemented under the guidance of a registered dietitian or healthcare professional, as it requires careful planning and monitoring.
Treating small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) can be tricky, often requiring a combination of antibiotics and dietary changes. However, access to quality healthcare, especially for conditions like SIBO, isn’t always equitable, and this can disproportionately affect certain demographics. The health divide, particularly when considering menopause and Black women, highlights the disparities in treatment options and outcomes. Understanding these systemic factors is crucial for addressing SIBO effectively for all patients.
Further research into these disparities and improved access to care is needed to ensure equitable SIBO treatment for everyone. This article on health divide menopause and black women dives deeper into these critical issues.
High-FODMAP Foods to Avoid
A detailed list of high-FODMAP foods helps in identifying and eliminating these substances from the diet. This precise identification is critical for effectively reducing bacterial fermentation.
- Fruits: Apples, pears, mangoes, peaches, figs, watermelon, and many others.
- Vegetables: Onions, garlic, asparagus, mushrooms, broccoli, and many others.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, chickpeas, and many others.
- Dairy products: Milk, yogurt, and many other dairy products.
- Other: Honey, agave, and many other sweeteners.
- Grains: Barley, wheat, and many other grains.
Strategies for Implementing a Low-FODMAP Diet
Implementing a low-FODMAP diet requires careful planning and a phased approach. This approach minimizes the risk of nutritional deficiencies and allows for gradual adjustment to the dietary changes.
- Phase 1: Elimination Phase. During this phase, all high-FODMAP foods are removed from the diet. This allows the gut to rest and reduce the fermentation load.
- Phase 2: Reintroduction Phase. Gradually reintroduce low-FODMAP foods, one at a time, to identify which foods might trigger symptoms.
- Phase 3: Maintenance Phase. This involves maintaining a low-FODMAP diet that reduces symptoms without causing nutritional deficiencies.
Modifying Recipes to Accommodate a Low-FODMAP Diet
Modifying recipes to suit a low-FODMAP diet requires creativity and culinary knowledge. This approach ensures that meals remain enjoyable while adhering to the dietary restrictions.
- Substituting ingredients: For example, using low-FODMAP vegetables instead of high-FODMAP ones.
- Adjusting spices and herbs: This enhances the flavor profile of meals without relying on high-FODMAP ingredients.
- Utilizing different cooking methods: For example, grilling or roasting instead of stir-frying certain vegetables.
Low-FODMAP Alternatives to Common High-FODMAP Foods
This table provides practical alternatives to common high-FODMAP foods, enabling individuals to adapt their diet while maintaining nutritional adequacy.
| High-FODMAP Food | Low-FODMAP Alternative |
|---|---|
| Onions | Leeks, spring onions, or shallots |
| Garlic | Chives, or finely chopped fresh herbs |
| Apples | Berries, or other low-FODMAP fruits |
| Milk | Almond milk, soy milk, or other plant-based milks |
| Honey | Maple syrup, or other low-FODMAP sweeteners |
Medical Management of SIBO
Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) is often treated with antibiotics, which aim to reduce the excessive bacterial population in the small intestine. This approach is typically effective, but careful consideration of the antibiotic’s mechanism of action, potential side effects, and the importance of responsible antibiotic use is crucial.Antibiotics are a cornerstone of SIBO treatment due to their ability to target and eliminate the overgrowth of bacteria in the small intestine.
Selecting the right antibiotic and adhering to appropriate treatment duration are essential for efficacy and minimizing adverse effects.
Rationale for Using Antibiotics in SIBO Treatment
Antibiotics are employed to target and eliminate the excessive bacterial population in the small intestine. This approach is typically effective, but careful consideration of the antibiotic’s mechanism of action, potential side effects, and the importance of responsible antibiotic use is crucial. By reducing the bacterial load, symptoms associated with SIBO, such as bloating, abdominal pain, and diarrhea, can often be alleviated.
Mechanisms of Action of Commonly Used Antibiotics
Different antibiotics work through various mechanisms to inhibit bacterial growth. Some antibiotics, like tetracyclines, interfere with bacterial protein synthesis. Others, such as metronidazole, disrupt DNA synthesis. Understanding the specific mechanism allows for a better understanding of the antibiotic’s potential side effects and its efficacy against different bacterial species.
Efficacy of Different Antibiotic Classes
The efficacy of various antibiotic classes in treating SIBO varies. Some studies have shown that quinolones, such as ciprofloxacin, demonstrate good efficacy, particularly against gram-negative bacteria often implicated in SIBO. However, other classes, such as tetracyclines, also exhibit promising results. The choice of antibiotic depends on factors like the suspected bacterial species involved and the patient’s overall health status.
Potential Side Effects of Antibiotics Used in SIBO Treatment, Treatment of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth
Antibiotics, while effective, can have potential side effects. These include, but are not limited to, gastrointestinal upset like diarrhea or nausea, allergic reactions, and disruption of the gut microbiome, which can lead to secondary issues. Careful monitoring for side effects is crucial during antibiotic treatment.
Importance of Appropriate Antibiotic Stewardship in SIBO Management
Responsible antibiotic use is vital to minimize the development of antibiotic resistance. Overuse or inappropriate use can contribute to the emergence of resistant bacterial strains, potentially impacting future treatment options. This emphasizes the need for careful consideration of the specific bacterial species involved and the selection of the most appropriate antibiotic.
Comparison of Antibiotics for SIBO
| Antibiotic | Spectrum of Activity | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Metronidazole | Broad spectrum, effective against anaerobic bacteria | Nausea, vomiting, metallic taste, headache, peripheral neuropathy (especially with prolonged use) |
| Ciprofloxacin | Broad spectrum, effective against gram-negative bacteria | Nausea, diarrhea, headache, tendonitis (rare but serious), photosensitivity |
| Tetracycline | Broad spectrum, effective against various bacterial species | Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, photosensitivity, tooth discoloration (in children) |
| Rifaximin | Limited spectrum, primarily targets gram-positive bacteria and some gram-negative bacteria in the gut | Mild gastrointestinal upset, headache, dizziness |
This table provides a general overview of antibiotic classes used in SIBO treatment. The specific spectrum of activity and potential side effects can vary depending on the individual patient and the antibiotic used.
Long-Term Management and Prevention
Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) treatment isn’t a one-and-done affair. Sustained management and proactive strategies are crucial for preventing recurrence and maintaining overall well-being. Long-term strategies involve dietary modifications, lifestyle adjustments, and consistent medical follow-up.Effective long-term management of SIBO hinges on understanding the root causes and triggers that lead to bacterial overgrowth. This approach emphasizes proactive steps rather than simply treating symptoms as they arise.
Dietary Strategies for Long-Term Management
A key aspect of long-term SIBO management is the adoption of a dietary approach that minimizes the factors conducive to bacterial overgrowth. This involves a careful consideration of fermentable carbohydrates and the timing of food intake.
- Reducing Fermentable Carbohydrates: The diet should focus on limiting foods high in fermentable carbohydrates, such as certain fruits, vegetables, and grains. This dietary adjustment helps to reduce the readily available food source for the bacteria. Examples include limiting fructose-containing foods like high-fructose corn syrup, honey, and some fruits like grapes and mangoes, as well as avoiding excessive consumption of beans, lentils, and certain vegetables rich in fiber like cabbage, broccoli, and cauliflower.
This dietary approach is often a crucial element in preventing flare-ups.
- Strategic Meal Timing: Consider the timing of meals in relation to sleep. Avoid eating close to bedtime as this can increase the risk of bacterial overgrowth due to reduced motility in the gut during sleep.
- Careful Introduction of Foods: If you’ve been on a restricted diet, reintroduce foods gradually, monitoring for symptoms. This allows you to identify any trigger foods and adjust your diet accordingly. This step is crucial in identifying potential triggers, such as certain types of dairy or complex carbohydrates.
Lifestyle Modifications for Preventing Recurrence
Beyond diet, lifestyle modifications play a significant role in preventing SIBO recurrence. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can reduce the risk of developing or relapsing with SIBO.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can negatively impact gut motility and increase the risk of SIBO recurrence. Implementing stress-reducing techniques, such as yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature, can be beneficial. Stress management techniques, such as deep breathing exercises, can have a positive impact on overall gut health, reducing the risk of flare-ups.
- Adequate Hydration: Maintaining proper hydration is essential for gut health. Dehydration can impact gut motility, potentially contributing to SIBO recurrence. Drinking enough water throughout the day supports optimal gut function. This can help in preventing the conditions that lead to bacterial overgrowth.
- Regular Exercise: Regular physical activity promotes healthy gut motility. Exercise can help in maintaining a healthy gut environment.
Follow-Up Care and Monitoring
Regular check-ups and monitoring are vital for long-term SIBO management. This allows for early detection of any potential recurrence.
- Regular Check-ups: Schedule regular appointments with your doctor for monitoring and assessing your progress. This helps ensure your treatment plan is effective and adjusts it as needed.
- Symptom Tracking: Maintain a detailed log of your symptoms, including the types of foods consumed, to help identify potential triggers or patterns of recurrence. A detailed symptom journal allows for accurate identification of patterns and triggers, enabling better management of SIBO.
Strategies for Preventing SIBO Flare-Ups
Proactive steps can minimize the risk of SIBO flare-ups. This includes avoiding triggers and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
- Avoiding Triggers: Identifying and avoiding trigger foods and situations can significantly reduce the risk of SIBO flare-ups. This includes avoiding known triggers, such as excessive alcohol consumption or certain types of food.
- Maintaining Consistent Habits: Maintaining consistent dietary and lifestyle habits can help to prevent SIBO flare-ups. This helps in maintaining a stable gut environment.
Factors Contributing to SIBO Recurrence
Several factors can contribute to SIBO recurrence. Understanding these factors is essential for developing a comprehensive management plan.
- Dietary indiscretions: Returning to high-carbohydrate diets or eating large meals without adhering to the dietary recommendations can contribute to SIBO recurrence.
- Stressful periods: Increased stress levels can negatively affect gut motility and increase the risk of SIBO recurrence.
The Need for Regular Medical Check-ups
Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider are crucial for monitoring and managing SIBO long-term. This allows for early intervention if necessary.
- Early Detection: Regular check-ups enable early detection of any recurrence, which can lead to prompt intervention and prevent complications. Early detection is crucial in effective management and prevention of recurrence.
Complications and Associated Conditions
Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) isn’t just a digestive issue; it can have far-reaching consequences. Understanding the potential complications and associated conditions is crucial for effective management and prevention of long-term problems. This section delves into the various ways SIBO can impact overall health.
Potential Complications of Untreated SIBO
Untreated SIBO can lead to a cascade of problems, impacting not only the digestive system but also other bodily functions. One of the most significant consequences is nutrient deficiencies. The excessive bacteria in the small intestine can hinder the absorption of essential vitamins and minerals, leading to deficiencies in vitamin B12, iron, folate, and calcium. These deficiencies can manifest in various ways, from fatigue and anemia to bone weakness and neurological issues.
Relationship Between SIBO and Other Gastrointestinal Conditions
SIBO isn’t an isolated condition; it frequently co-occurs with other gastrointestinal issues. The overgrowth of bacteria in the small intestine can exacerbate existing problems or even contribute to the development of new ones. Conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), Crohn’s disease, and celiac disease are often linked to SIBO. The interplay between these conditions can make diagnosis and treatment more complex.
Link Between SIBO and Other Medical Conditions
Beyond the gastrointestinal tract, SIBO can have implications for other aspects of health. A strong correlation exists between SIBO and certain systemic conditions. For example, SIBO has been associated with conditions such as diabetes, cardiovascular issues, and autoimmune disorders. This highlights the importance of a comprehensive approach to SIBO management.
Examples of Co-occurring Conditions
Many conditions frequently accompany SIBO, adding complexity to the clinical picture.
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): IBS symptoms, such as abdominal pain, bloating, and altered bowel habits, can be exacerbated by SIBO. The mechanisms linking these two conditions are not fully understood but are thought to involve the altered microbial balance in the gut.
- Crohn’s Disease: Individuals with Crohn’s disease, an inflammatory bowel disease, often experience symptoms that overlap with SIBO. The presence of both conditions may require specialized treatment strategies.
- Celiac Disease: Celiac disease, an autoimmune disorder triggered by gluten, can affect nutrient absorption and create an environment conducive to SIBO. Diagnosing and managing both conditions concurrently requires careful consideration.
- Diabetes: Studies suggest a potential link between SIBO and diabetes, although the exact nature of the relationship remains under investigation. It’s possible that the bacterial imbalance in SIBO may contribute to glucose intolerance.
Potential Complications Associated with Untreated SIBO
Failure to address SIBO can result in significant long-term consequences. The persistent overgrowth of bacteria can lead to chronic inflammation in the small intestine, potentially increasing the risk of certain cancers. Moreover, the nutrient deficiencies associated with untreated SIBO can contribute to a range of health issues.
- Malnutrition: Chronic SIBO can disrupt nutrient absorption, leading to deficiencies in essential vitamins and minerals. This can lead to various health problems, from fatigue and anemia to bone weakness and neurological dysfunction.
- Chronic Fatigue: The impact of nutrient deficiencies on overall energy levels can contribute to chronic fatigue.
- Gastrointestinal Problems: Untreated SIBO can cause ongoing digestive issues like bloating, abdominal pain, and altered bowel habits, significantly impacting quality of life.
Last Recap
In conclusion, managing small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) requires a combination of careful diagnosis, personalized treatment plans, and a proactive approach to long-term management. This comprehensive guide provides a solid foundation for understanding the nuances of SIBO, enabling individuals to make informed decisions about their health. Remember, proper medical guidance is essential, and this information should not be considered a substitute for professional advice.