Overview of fatty liver disease is a prevalent health concern impacting global well-being. This condition involves the accumulation of fat in the liver, which can lead to various health issues. Different types exist, including non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), each with unique characteristics. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and potential complications is crucial for proactive health management.
This detailed overview explores the intricacies of fatty liver disease, examining its pathophysiology, diagnostic methods, management strategies, potential complications, and preventive measures. We will delve into the underlying mechanisms driving fat buildup in the liver, the role of insulin resistance, and the factors influencing disease progression. The information presented aims to equip readers with a comprehensive understanding of this significant health challenge.
Introduction to Fatty Liver Disease: Overview Of Fatty Liver Disease
Fatty liver disease, a common condition affecting millions globally, encompasses a spectrum of liver disorders characterized by the accumulation of excess fat within liver cells. This buildup of fat can lead to inflammation and, in some cases, severe liver damage. Understanding the different types, prevalence, and risk factors is crucial for early detection and effective management.
Types of Fatty Liver Disease
Fatty liver disease isn’t a single entity; rather, it exists in various forms. The most prevalent types are non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). NAFLD is characterized by the simple accumulation of fat in the liver, often without inflammation. NASH, however, involves inflammation alongside the fat accumulation, increasing the risk of liver damage and potentially leading to cirrhosis or liver cancer.
Prevalence and Impact
Fatty liver disease is a significant global health concern. Its prevalence is rising in parallel with the increasing prevalence of obesity and metabolic syndrome. This rise poses a substantial burden on healthcare systems, leading to increased healthcare costs and a higher risk of liver-related complications. The global burden of fatty liver disease highlights the importance of preventative measures and early intervention strategies.
Risk Factors
Several factors increase the likelihood of developing fatty liver disease. These risk factors often intersect, creating a complex interplay that contributes to the development of the condition. Obesity, diabetes, high cholesterol, and a sedentary lifestyle are frequently cited as significant contributors. Understanding these risk factors is critical for developing personalized prevention strategies.
Understanding fatty liver disease is crucial for overall health. It’s often linked to lifestyle choices, and managing it involves a multifaceted approach. While exploring natural remedies like applying pressure to specific points for migraine relief, like those detailed in this guide on migraine relief pressure points , isn’t a direct treatment for fatty liver, the underlying principles of stress reduction and mindful living can positively impact both conditions.
Ultimately, a balanced diet and regular exercise remain key components in managing fatty liver disease.
| Disease Type | Description | Prevalence |
|---|---|---|
| Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) | Accumulation of fat in the liver in the absence of excessive alcohol consumption. This often presents without noticeable symptoms. | Highly prevalent, affecting a significant portion of the population, particularly those with obesity or metabolic syndrome. |
| Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) | A more severe form of fatty liver disease characterized by inflammation and liver cell damage alongside fat accumulation. It carries a higher risk of progressing to cirrhosis and liver failure. | Less prevalent than NAFLD, but still a significant concern due to its potential for serious complications. |
Pathophysiology of Fatty Liver Disease
Fatty liver disease, a condition characterized by the accumulation of excess fat in the liver, encompasses a spectrum of pathologies with varying degrees of severity. Understanding the underlying mechanisms driving this fat buildup is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment. This accumulation, if left unmanaged, can lead to serious complications like liver inflammation, fibrosis, and cirrhosis.The pathophysiology of fatty liver disease is complex and involves a multitude of interconnected factors.
These factors often act in concert, exacerbating the accumulation of fat and contributing to the progression of the disease. The fundamental process involves an imbalance between the intake and utilization of lipids within the liver.
Mechanisms of Fat Accumulation
The accumulation of fat in the liver stems from an intricate interplay of factors. The liver plays a pivotal role in lipid metabolism, synthesizing, storing, and releasing lipids. Disruptions in this intricate process can lead to the accumulation of fat. Excess caloric intake, especially from dietary fat and sugars, surpasses the liver’s capacity for proper lipid utilization, resulting in a buildup of triglycerides.
Furthermore, reduced lipoprotein secretion can trap fat within the liver.
Role of Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance is a critical factor in the development and progression of fatty liver disease. Insulin, a hormone crucial for glucose regulation, signals the body to absorb glucose from the bloodstream. In insulin resistance, the body’s cells do not respond effectively to insulin, leading to elevated blood glucose levels. The liver, in response to elevated insulin levels, increases the production of fatty acids.
This increased production, coupled with the reduced ability of the body to utilize these fatty acids, results in fat accumulation within the liver cells.
Metabolic Factors in Fatty Liver Disease
Numerous metabolic factors contribute to the development and progression of fatty liver disease. These include dyslipidemia (abnormal blood lipid levels), elevated blood pressure, and a pro-inflammatory state. Dyslipidemia, characterized by high levels of triglycerides and low levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, directly contributes to fat accumulation in the liver. Chronic inflammation, a key player in the progression to more severe forms of the disease, further exacerbates the damage.
Comparison of Pathophysiological Processes in Different Types
Fatty liver disease can be categorized into alcoholic and non-alcoholic forms. While both involve fat accumulation, the underlying mechanisms differ significantly. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is primarily linked to metabolic factors like insulin resistance, while alcoholic fatty liver disease (AFLD) is directly associated with chronic alcohol consumption and its detrimental effects on liver function. In AFLD, alcohol directly damages liver cells, impairing their ability to process lipids, and triggering inflammation.
Cellular and Molecular Pathways
The progression of fatty liver disease involves intricate cellular and molecular pathways. One crucial pathway involves the accumulation of triglycerides within the liver cells. Elevated levels of fatty acids and triglycerides can lead to cellular stress and inflammation. This inflammatory response further contributes to the progression of the disease. Moreover, oxidative stress, resulting from an imbalance between the production of reactive oxygen species and the body’s antioxidant defenses, plays a significant role.
The interplay of these factors creates a vicious cycle that drives the progression from simple fat accumulation to more severe forms of the disease.
Flowchart of NAFLD Development
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Excess Caloric Intake | High intake of calories, particularly from processed foods and sugary drinks, exceeds energy expenditure. |
| 2. Insulin Resistance | Cells become less responsive to insulin, leading to elevated blood glucose levels. |
| 3. Increased Lipogenesis | The liver increases the production of fatty acids from glucose and other sources. |
| 4. Triglyceride Accumulation | The liver’s capacity to process and release lipids is overwhelmed, resulting in a buildup of triglycerides in hepatocytes. |
| 5. Liver Inflammation | Accumulation of fat triggers an inflammatory response within the liver. |
| 6. Fibrosis and Steatosis | Chronic inflammation can lead to fibrosis (scarring) and further fat accumulation, progressing to more severe stages. |
This flowchart depicts a simplified representation of the sequence of events in NAFLD development. The interplay of these steps highlights the complex nature of this condition.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Fatty Liver Disease
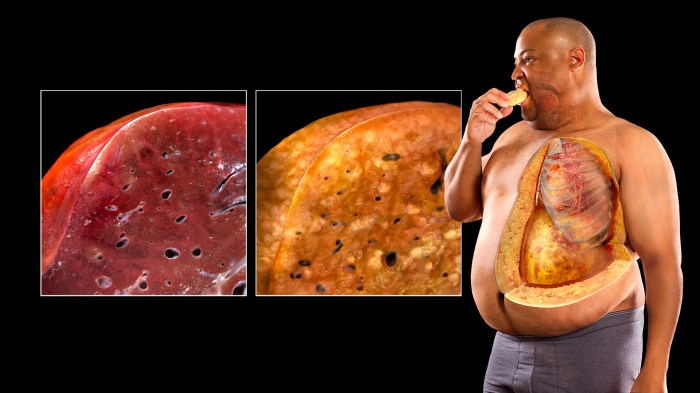
Fatty liver disease, a condition characterized by excessive fat accumulation in the liver, can often progress silently without noticeable symptoms in its early stages. However, as the disease progresses, certain symptoms may manifest, and accurate diagnosis is crucial for timely intervention and management. Understanding the various diagnostic methods employed, including imaging techniques and liver biopsies, is essential for assessing the severity of the condition and tailoring treatment strategies.
Common Symptoms
Many individuals with fatty liver disease experience no symptoms, especially in the early stages. This asymptomatic nature underscores the importance of regular health check-ups and screenings, particularly for individuals at risk. When symptoms do arise, they can vary and often mimic other health problems. Common symptoms include fatigue, mild abdominal discomfort, and, in some cases, a feeling of fullness in the upper abdomen.
In more severe cases, individuals might experience jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), nausea, and vomiting. It is important to note that these symptoms can also be associated with other liver conditions or unrelated illnesses, emphasizing the need for proper medical evaluation.
Diagnostic Methods
Several methods are used to diagnose and assess the severity of fatty liver disease. These methods typically involve a combination of blood tests, imaging techniques, and, in certain cases, liver biopsies. The selection of diagnostic tools depends on the suspected severity and underlying causes of the disease.
Blood Tests
Blood tests are commonly performed to evaluate liver function and identify potential markers of liver damage. These tests measure the levels of liver enzymes, such as alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), which can indicate inflammation or damage to the liver. Elevated levels of these enzymes may suggest the presence of fatty liver disease, but additional tests and imaging are often necessary to confirm the diagnosis.
Blood tests also assess liver function by checking levels of bilirubin, albumin, and prothrombin time (PT), providing further insights into the overall health of the liver.
Imaging Techniques
Imaging techniques, such as ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), play a crucial role in diagnosing and assessing the severity of fatty liver disease. Ultrasound, a non-invasive imaging method, uses sound waves to create images of the liver and surrounding structures. It can help visualize the amount of fat accumulation and identify any structural abnormalities in the liver.
MRI provides detailed images of the liver, offering a more comprehensive view of the extent and distribution of fatty infiltration. These techniques can be particularly helpful in identifying signs of cirrhosis, a late-stage complication of fatty liver disease. The choice between ultrasound and MRI depends on the specific clinical question and available resources.
Liver Biopsy
Liver biopsies are considered the gold standard for definitively diagnosing and assessing the severity of fatty liver disease. A small tissue sample is extracted from the liver using a needle, and then examined under a microscope by a pathologist. This procedure provides a direct visualization of the extent of fat accumulation, inflammation, and potential fibrosis. However, liver biopsies carry a small risk of complications, such as bleeding or infection, and are usually reserved for cases where other diagnostic methods are inconclusive or when the doctor suspects more severe liver damage.
Diagnostic Criteria and Procedures
| Type of Fatty Liver Disease | Diagnostic Criteria | Diagnostic Procedures |
|---|---|---|
| Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD) | History of significant alcohol consumption | Blood tests (liver function tests), imaging (ultrasound), and possibly liver biopsy |
| Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) | Absence of significant alcohol consumption; presence of other risk factors such as obesity, diabetes, or metabolic syndrome | Blood tests (liver function tests), imaging (ultrasound or MRI), and possibly liver biopsy |
| Steatohepatitis | Presence of inflammation in addition to fat accumulation in the liver | Blood tests (liver function tests), imaging (ultrasound or MRI), and possibly liver biopsy |
This table Artikels the general diagnostic criteria and procedures for various types of fatty liver disease. The specific diagnostic approach may vary depending on individual circumstances and clinical presentation.
Management and Treatment Strategies
Navigating fatty liver disease often involves a multifaceted approach, moving beyond simply identifying the condition to actively managing its progression and mitigating its potential complications. This phase focuses on practical strategies for controlling the disease, encompassing lifestyle adjustments, dietary modifications, and, in some cases, pharmacological interventions. Effective management hinges on early intervention, consistent adherence to treatment plans, and proactive monitoring of liver function.
Non-Pharmacological Interventions
Lifestyle modifications are crucial in managing fatty liver disease, particularly in its early stages. These interventions aim to address the underlying causes and prevent further liver damage. A cornerstone of this approach is the commitment to sustainable changes in daily habits.
So, you’re learning about fatty liver disease? It’s basically when your liver gets too much fat. Understanding how vitamins function is key to this topic. Knowing more about vitamins what are they and how do they work is super helpful in understanding how certain vitamins can either help or hinder the health of your liver.
Ultimately, a healthy diet and lifestyle play a crucial role in preventing and managing fatty liver disease.
- Weight Management: Sustained weight loss, even modest amounts, can significantly reduce liver fat content and improve liver function. This often involves a combination of a balanced diet and regular physical activity. For instance, a person losing 5-10% of their body weight can experience noticeable improvements in liver health. A consistent calorie deficit, achieved through a combination of reduced calorie intake and increased physical activity, is key.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity plays a pivotal role in improving insulin sensitivity and promoting weight loss. Aerobic exercises, such as brisk walking, jogging, swimming, or cycling, are beneficial. Consistency is key; aiming for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week is generally recommended.
- Dietary Changes: A balanced diet low in saturated and trans fats, processed foods, and sugary drinks is essential. Focusing on whole foods, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins is crucial. Reducing sugar intake is especially important as it contributes to insulin resistance, a significant factor in the development of fatty liver disease. Examples of healthy dietary choices include whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
Pharmacological Options
Currently, there are no medications specifically approved to treat non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) itself. However, certain medications may be prescribed to address associated conditions, such as type 2 diabetes or high cholesterol, which can contribute to the development or progression of the disease.
- Medications for Associated Conditions: Management of associated conditions like type 2 diabetes and dyslipidemia (high cholesterol) is critical. These conditions often worsen NAFLD. For instance, metformin, a common diabetes medication, has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity and potentially reduce liver fat in some cases.
Dietary Changes in Management
Dietary modifications are fundamental in managing fatty liver disease. A diet rich in whole foods, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins, while limiting processed foods, saturated fats, and sugary drinks, is essential.
- Reducing Sugar Intake: High sugar consumption, often found in sugary drinks and processed foods, can lead to insulin resistance, which contributes to the accumulation of fat in the liver. This necessitates a significant reduction in the intake of sugary beverages, processed foods, and desserts.
- Prioritizing Whole Foods: Whole foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, are rich in essential nutrients and fiber, supporting overall health and potentially improving liver function.
Monitoring Liver Function Tests
Regular monitoring of liver function tests (LFTs) is crucial during treatment. These tests provide valuable insights into the health of the liver and allow for adjustments to the treatment plan as needed.
- Importance of Regular Monitoring: Regular LFTs are essential for tracking the effectiveness of the treatment and identifying any potential adverse effects. They provide a snapshot of the liver’s current health, allowing healthcare providers to make informed decisions about treatment adjustments. For example, if liver enzymes show a significant increase, it may signal a need to modify the treatment plan or lifestyle interventions.
Treatment Approaches and Efficacy
| Treatment Approach | Description | Efficacy |
|---|---|---|
| Lifestyle Modifications | Weight loss, regular exercise, dietary changes | Generally effective in early stages, can prevent progression |
| Pharmacological Interventions (for associated conditions) | Medications for diabetes, dyslipidemia | Can improve liver function by addressing the underlying cause |
Complications and Prognosis
Fatty liver disease, while often initially asymptomatic, can progress to more severe conditions if left unmanaged. Understanding the potential complications and long-term prognosis is crucial for effective patient care. This section delves into the potential complications associated with fatty liver disease, from cirrhosis to liver cancer, and explores the factors influencing disease progression.The severity of fatty liver disease significantly impacts the likelihood and type of complications that may arise.
Early intervention and lifestyle modifications can often slow or halt the progression of the disease, reducing the risk of long-term complications.
Learning about fatty liver disease is crucial for overall health. While researching, I stumbled upon an interesting development in early cancer detection: an experimental blood test for early pancreatic cancer. This innovative test, which you can read more about here , could potentially revolutionize how we approach early diagnosis. Hopefully, similar advancements will eventually lead to improved detection and treatment options for fatty liver disease too.
Potential Complications, Overview of fatty liver disease
Fatty liver disease, if not addressed, can lead to a range of complications. The most significant complications include cirrhosis and liver cancer. Other potential complications, although less common, can still affect overall health and well-being.
- Cirrhosis: This is a late-stage scarring of the liver, often resulting from chronic liver damage. Cirrhosis can lead to impaired liver function, increasing the risk of complications like portal hypertension, ascites, and encephalopathy.
- Liver Cancer: Chronic liver inflammation and scarring associated with fatty liver disease can increase the risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most common type of liver cancer. The risk is higher with more severe disease stages and associated factors like obesity, diabetes, and alcohol abuse.
- Portal Hypertension: Damaged liver tissue can disrupt normal blood flow through the liver, leading to elevated blood pressure in the portal vein. This can cause complications like esophageal varices (enlarged veins in the esophagus) which can bleed.
- Ascites: Fluid buildup in the abdomen is a common symptom of advanced liver disease, often linked to portal hypertension and impaired liver function.
- Encephalopathy: This condition involves impaired brain function, caused by toxins building up in the blood due to impaired liver function.
Factors Influencing Disease Progression
Several factors influence the progression of fatty liver disease from a mild condition to more severe complications. Lifestyle choices and underlying health conditions play a significant role.
- Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol intake is a significant risk factor for alcoholic fatty liver disease and can accelerate its progression to cirrhosis and liver cancer.
- Obesity and Diabetes: Individuals with obesity and type 2 diabetes are at higher risk for developing non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and its progression to more serious conditions. Maintaining a healthy weight and managing blood sugar levels are critical.
- Metabolic Syndrome: This cluster of conditions, including high blood pressure, high blood sugar, and high cholesterol, increases the risk of NAFLD and its complications.
- Chronic Inflammation: Persistent inflammation within the liver tissue can contribute to the progression of fatty liver disease and the development of cirrhosis and liver cancer.
Correlation between Severity and Complications
The severity of fatty liver disease directly correlates with the potential for long-term health consequences.
| Severity Level | Potential Complications | Risk Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Mild | No significant complications typically. Lifestyle changes may be sufficient. | Healthy diet, regular exercise, normal weight, absence of other health conditions. |
| Moderate | Increased risk of liver inflammation and fibrosis (scarring). Careful monitoring and lifestyle modifications are recommended. | Overweight, insulin resistance, high blood pressure, family history of fatty liver disease. |
| Severe | Cirrhosis, liver cancer, portal hypertension, ascites, and encephalopathy. Medical intervention may be necessary. | Alcohol abuse, uncontrolled diabetes, obesity, severe metabolic syndrome. |
Prognosis
The long-term prognosis for individuals with fatty liver disease varies significantly based on the stage of the disease and the presence of associated risk factors. Early diagnosis and prompt intervention can significantly improve the outcome. Individuals with mild to moderate NAFLD can often manage the condition through lifestyle modifications, leading to a favorable prognosis. However, individuals with severe disease or those with significant underlying health conditions may experience a poorer prognosis.
Examples include patients with advanced fibrosis or cirrhosis who may require more extensive interventions like liver transplantation.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing fatty liver disease hinges on proactive lifestyle choices. Early intervention is crucial, as many cases of fatty liver disease are preventable through simple, sustainable changes. Addressing the underlying factors contributing to the condition is paramount in reducing the risk of developing more serious complications.Maintaining a healthy weight and adopting a balanced diet are key components in preventing fatty liver disease.
Regular physical activity plays a significant role in improving overall health and reducing the risk of developing this condition. Implementing these strategies can substantially decrease the chances of progressing to more severe stages of the disease.
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications are fundamental to preventing fatty liver disease. These modifications address the root causes of the condition, promoting overall health and reducing the risk of developing complications. A holistic approach, encompassing dietary changes, exercise, and stress management, is highly effective in preventing and managing fatty liver disease.
- Maintaining a healthy weight:
- Maintaining a healthy weight is essential in preventing fatty liver disease. Excess weight, particularly abdominal obesity, is a significant risk factor for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Weight loss through a combination of diet and exercise can significantly reduce the amount of fat in the liver and improve overall health.
- Regular Exercise:
- Regular physical activity is crucial for preventing fatty liver disease. Exercise helps regulate blood sugar levels, improve insulin sensitivity, and promote weight loss. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise per week, along with muscle-strengthening activities on two or more days a week.
Dietary Strategies
Dietary strategies are essential for preventing and managing fatty liver disease. A balanced diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, is vital for reducing the risk of developing the condition. Limiting processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive saturated and trans fats is also crucial.
- Nutritional Recommendations:
- A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provides essential nutrients and fiber, which can help regulate blood sugar and promote overall health. Reducing intake of processed foods, sugary drinks, and foods high in saturated and trans fats is equally important. A Mediterranean-style diet, characterized by olive oil, lean protein, and plenty of fruits and vegetables, has shown promising results in reducing the risk of fatty liver disease.
Comprehensive Lifestyle Changes
A comprehensive approach encompassing lifestyle changes is crucial for minimizing the risk of developing fatty liver disease. These changes should address dietary habits, physical activity levels, and stress management techniques. Combining these strategies effectively reduces the likelihood of developing NAFLD and its associated complications.
- Dietary changes:
- Prioritizing whole foods, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins is vital. Reducing processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive saturated fats is equally important. This shift towards a balanced diet improves overall health and can significantly decrease the risk of fatty liver disease.
- Increased Physical Activity:
- Regular exercise, including aerobic activities and strength training, helps improve insulin sensitivity, regulate blood sugar levels, and promote weight loss. This contributes to overall health and reduces the risk of developing fatty liver disease.
- Stress Management Techniques:
- Chronic stress can negatively impact metabolic health, increasing the risk of developing fatty liver disease. Stress management techniques, such as yoga, meditation, and mindfulness practices, can help regulate stress hormones and improve overall health.
Closure

In conclusion, overview of fatty liver disease is a serious health concern that warrants attention. By understanding the various aspects of this condition, from its causes and symptoms to its management and prevention, individuals can take proactive steps towards better health outcomes. Remember that early detection and lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in mitigating the risks and potential complications associated with fatty liver disease.
Consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and support.

