What is chronic pain? It’s more than just a persistent ache; it’s a complex experience impacting every aspect of a person’s life. This exploration delves into the intricacies of chronic pain, from its definition and different types to its profound effects on the body, mind, and spirit. We’ll examine the diagnostic process, treatment options, and importantly, the coping mechanisms and support systems available for those living with this often-invisible illness.
Understanding chronic pain is crucial for anyone affected by it or those seeking to support someone they care about. This in-depth look will clarify the differences between acute and chronic pain, outlining the characteristics, triggers, and causes of various chronic pain types. We’ll explore the impact of chronic pain on daily life, relationships, and overall well-being. Crucially, the discussion will also touch upon the importance of personalized treatment plans and the role of support systems in managing this complex condition.
Defining Chronic Pain
Chronic pain is a significant health concern affecting millions worldwide. Unlike acute pain, which serves as a vital warning system for injury, chronic pain persists beyond the expected healing period, often causing significant disruption to daily life and impacting overall well-being. Understanding the nuances of chronic pain, its various manifestations, and its potential triggers is crucial for effective management and support.
Defining Chronic Pain vs. Acute Pain
Chronic pain is defined as pain that lasts for three months or longer. Acute pain, on the other hand, is a temporary response to injury or illness, typically lasting for a few days or weeks. Key distinctions lie in their duration, intensity, and the body’s response to the pain signal. Chronic pain often lacks a clear cause, and its intensity may fluctuate over time, complicating diagnosis and treatment.
Characteristics of Chronic Pain
Chronic pain distinguishes itself from other types of pain through several characteristics. It’s often described as a persistent, nagging sensation that can be localized or widespread. The intensity may vary, sometimes being mild but persistent, or escalating into debilitating episodes. Crucially, the pain’s duration exceeds the expected healing time, often leaving individuals with a constant sense of discomfort.
Chronic pain is tough, isn’t it? It’s that nagging ache that just won’t go away. But did you know sleep apnea, where you stop breathing in your sleep what happens if you stop breathing in your sleep , can actually contribute to chronic pain? The lack of oxygen can wreak havoc on your body, leading to various types of aches and pains.
It’s a vicious cycle, and understanding the connections between sleep disorders and chronic pain is key to finding relief.
Manifestations of Chronic Pain
Chronic pain impacts individuals physically and emotionally. Physically, it can manifest as aches, stiffness, shooting pains, numbness, or tingling sensations. These symptoms can affect mobility, sleep patterns, and overall physical function. Emotionally, chronic pain can lead to feelings of frustration, anxiety, depression, and isolation. The constant presence of pain can strain relationships and impact work or school performance.
Triggers and Contributing Factors
Various factors can trigger or contribute to chronic pain. These include injuries (such as back sprains or arthritis), underlying medical conditions (like fibromyalgia or nerve damage), and lifestyle factors (poor posture, stress, lack of exercise). Furthermore, psychological factors such as stress and anxiety can significantly influence the experience of chronic pain.
Acute vs. Chronic Pain Comparison
| Characteristic | Acute Pain | Chronic Pain |
|---|---|---|
| Duration | Brief (days to weeks) | Persistent (3 months or longer) |
| Intensity | Usually sharp, intense, and localized | Variable, ranging from mild to severe, sometimes widespread |
| Cause | Clear cause, often injury or illness | Often unclear, sometimes linked to underlying conditions |
| Treatment | Focused on relieving the symptoms of the injury or illness, often with short-term medications and physical therapy | Multifaceted, addressing both physical and emotional aspects, potentially requiring long-term management strategies, including medication, physical therapy, and psychological support. |
Types and Causes of Chronic Pain

Chronic pain isn’t just about the physical discomfort; it’s a complex interplay of various factors. Understanding the different types and potential causes can empower us to approach management strategies more effectively. This deeper understanding is crucial for navigating the complexities of this pervasive condition.Chronic pain often stems from a variety of sources, ranging from medical conditions and injuries to lifestyle choices.
Pinpointing the root cause is frequently the first step in developing an appropriate treatment plan.
Categories of Chronic Pain
Chronic pain can be broadly categorized into several types, each with its own set of underlying mechanisms and contributing factors. Recognizing these categories helps healthcare professionals tailor treatment strategies to individual needs.
- Nociceptive Pain: This type of pain arises from actual or potential tissue damage. Nociceptors, specialized nerve endings, detect noxious stimuli like heat, pressure, or chemicals, and transmit signals to the brain, resulting in the sensation of pain. Causes of nociceptive chronic pain often include injuries (sprains, fractures), arthritis (osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis), and musculoskeletal conditions (tendinitis, bursitis). Examples include persistent back pain after a fall or chronic knee pain due to osteoarthritis.
- Neuropathic Pain: This pain originates from damage or dysfunction in the nervous system. The damaged nerves can send incorrect signals to the brain, resulting in persistent pain, even without ongoing tissue damage. Causes include nerve compression (e.g., carpal tunnel syndrome), diabetes, multiple sclerosis, and certain infections. In some cases, even surgery can lead to neuropathic pain. For instance, postherpetic neuralgia, a common complication of shingles, is a type of neuropathic pain.
- Musculoskeletal Pain: This category encompasses pain originating from muscles, tendons, ligaments, bones, or joints. Causes include strains, sprains, arthritis, and repetitive stress injuries. Examples include chronic lower back pain due to poor posture or chronic neck pain from prolonged computer use.
Potential Causes of Chronic Pain
The causes of chronic pain are varied and complex. They can involve a combination of factors, including pre-existing medical conditions, past injuries, lifestyle habits, and even genetic predisposition.
Chronic pain is tough, isn’t it? It’s more than just a temporary ache; it’s a persistent discomfort that affects daily life. Interestingly, researchers are actively exploring new triggers for eczema, like those explored by the experts at ask an expert develop new eczema triggers , which might shed light on similar underlying mechanisms in chronic pain conditions.
Ultimately, understanding the complex interplay of factors causing chronic pain is crucial for effective treatment.
- Medical Conditions: Many medical conditions can contribute to chronic pain, including arthritis, fibromyalgia, cancer, and certain neurological disorders. For instance, rheumatoid arthritis can cause persistent joint pain, while fibromyalgia is characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain and tenderness.
- Injuries: Acute injuries, such as fractures or sprains, can sometimes evolve into chronic pain conditions if the healing process is disrupted or if the injury is severe. A fall resulting in a spinal injury can lead to persistent back pain, while a sports injury can cause chronic pain in the affected joint or muscle.
- Lifestyle Factors: Lifestyle choices, such as poor posture, inadequate sleep, lack of exercise, and stress, can also contribute to chronic pain. Prolonged sitting, without adequate breaks, can contribute to back pain, while chronic stress can trigger or worsen existing pain conditions.
- Genetics and Predisposition: Genetics plays a role in individual susceptibility to chronic pain conditions. Family history of chronic pain can indicate a potential predisposition. This is not a guarantee, but it can highlight the need for increased awareness and preventative measures.
Table of Chronic Pain Types, Causes, and Symptoms
This table summarizes the various types of chronic pain, their potential causes, and associated symptoms. It highlights the complexity and diversity of chronic pain conditions.
| Type of Chronic Pain | Potential Causes | Associated Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Nociceptive | Injuries, arthritis, musculoskeletal issues | Localized pain, tenderness, swelling, reduced range of motion |
| Neuropathic | Nerve damage, diabetes, infections, MS | Burning, shooting, tingling pain, numbness, altered sensation |
| Musculoskeletal | Strains, sprains, arthritis, repetitive stress | Muscle pain, joint pain, stiffness, limited mobility |
Impact of Chronic Pain
Chronic pain isn’t just a physical issue; it significantly impacts every aspect of a person’s life. It’s a complex condition that affects not only the body but also the mind and the relationships we have with others. Understanding the multifaceted impact of chronic pain is crucial for effective management and support.
Physical Effects of Chronic Pain
Chronic pain takes a substantial toll on the body. The constant discomfort and unpredictable nature of the pain can lead to a cascade of physical consequences. Prolonged muscle tension is a common response, causing stiffness, limited range of motion, and even contributing to other musculoskeletal issues. The body’s stress response, triggered by pain, can lead to significant fatigue.
This fatigue isn’t just tiredness; it’s a profound depletion of energy that makes even simple tasks feel overwhelming. Sleep disturbances are also frequent, as pain can make it difficult to fall asleep, stay asleep, or experience restful sleep. The lack of restorative sleep further exacerbates fatigue and other physical symptoms.
Emotional Toll of Chronic Pain
Chronic pain often triggers a complex emotional response. The constant struggle with pain can lead to feelings of anxiety and fear. The unpredictability of pain and the potential for its worsening can cause significant stress and worry. The frustration and helplessness associated with chronic pain can contribute to feelings of depression. The emotional burden of chronic pain can be isolating, as friends and family may struggle to fully understand the experience.
This isolation can exacerbate feelings of loneliness and hopelessness.
Social and Economic Impacts
Chronic pain can have a profound impact on social interactions and economic well-being. The pain itself can make it difficult to participate in social activities and maintain relationships. Individuals may withdraw from social gatherings, family events, or hobbies they once enjoyed. The need for frequent medical appointments, physical therapy, and medication can also strain personal finances. Lost work productivity due to pain and fatigue can lead to significant economic hardship, potentially impacting employment and overall financial stability.
Impact on Daily Life and Relationships
Chronic pain can significantly affect daily life activities. Simple tasks like getting dressed, showering, or preparing meals can become monumental challenges. Relationships with family and friends may suffer as individuals struggle to maintain their usual roles and responsibilities. Communication breakdowns, misunderstandings, and emotional distance can occur due to the demands of managing pain and its effects. The strain on relationships can be profound, impacting emotional well-being and potentially leading to conflict and estrangement.
Dimensions of the Impact of Chronic Pain, What is chronic pain
| Dimension | Impact |
|---|---|
| Physical | Fatigue, sleep disturbances, muscle tension, reduced mobility, decreased physical activity |
| Emotional | Anxiety, depression, fear, frustration, isolation, hopelessness |
| Social | Withdrawal from social activities, strained relationships, communication breakdowns, isolation |
| Economic | Lost productivity, increased medical expenses, reduced income, financial hardship, inability to work |
Diagnosis and Treatment
Chronic pain is a complex condition that requires a multifaceted approach to diagnosis and treatment. Accurate diagnosis is crucial to ensure the most effective treatment plan is implemented. A thorough understanding of the patient’s medical history, physical examination, and appropriate diagnostic tests are essential steps in this process. Treatment options range from medication to physical therapy, and alternative therapies, often employing interdisciplinary approaches to address the multifaceted nature of chronic pain.
Ultimately, patient-centered care and individualized treatment plans are paramount to achieving optimal outcomes.Effective diagnosis relies on a comprehensive evaluation. This involves gathering a detailed medical history, considering past injuries, illnesses, and treatments. The physical examination assesses the affected area for signs of inflammation, range of motion limitations, and tenderness. Specific diagnostic tests, such as imaging (X-rays, MRIs, CT scans), nerve conduction studies, or electromyography, may be necessary to identify the underlying cause of the pain.
These tests help determine the extent and nature of the condition, guiding the development of an appropriate treatment strategy.
Chronic pain is tough, isn’t it? It’s more than just a nagging ache; it’s a constant, often debilitating presence. Understanding how to support someone dealing with this kind of persistent discomfort is crucial. Think about how important it is to listen empathetically and create a safe space for them to express their feelings. Just like when someone is struggling with anxiety, a supportive approach, like the ones detailed in how to help someone with anxiety , is key.
Ultimately, chronic pain is about more than just the physical; it impacts their mental well-being, making empathy and understanding vital.
Diagnostic Process
The diagnostic process for chronic pain typically begins with a detailed medical history. This includes inquiries about the location, intensity, duration, and characteristics of the pain, as well as any associated symptoms. Past medical history, medications, and previous treatments for pain are also considered. A thorough physical examination follows, focusing on the affected area and the patient’s overall physical function.
This assessment includes evaluating range of motion, muscle strength, and neurological function. Diagnostic tests, when necessary, may be employed to pinpoint the underlying cause of the pain. Examples include imaging studies to assess for structural abnormalities or nerve conduction studies to evaluate nerve function.
Treatment Options
Various treatment options are available for chronic pain management. A comprehensive approach often involves a combination of strategies to address the multifaceted nature of the condition. These include medications, physical therapy, and alternative therapies.
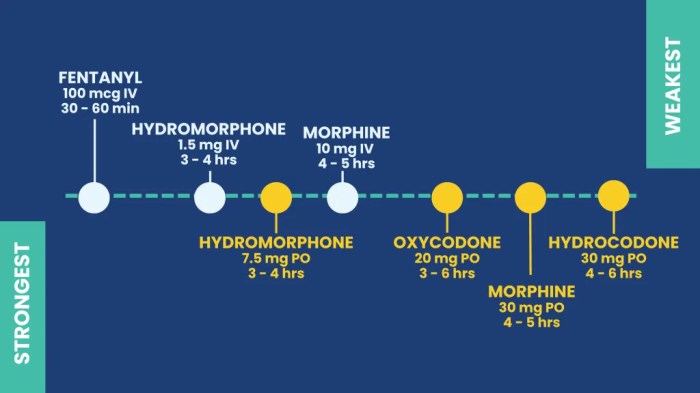
- Medications: Pain relievers, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), opioids (used cautiously and under strict medical supervision), and antidepressants, may be prescribed to manage pain intensity. Specific medications may be tailored to the type of chronic pain and the patient’s individual response.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy plays a significant role in restoring function, improving mobility, and managing pain. Exercises, manual therapy, and assistive devices can help improve strength, flexibility, and endurance, reducing pain and promoting a return to normal activities. Examples include targeted exercises, stretching routines, and the use of assistive devices like braces or splints.
- Alternative Therapies: Alternative therapies, such as acupuncture, massage therapy, and mindfulness-based techniques, may be beneficial for managing chronic pain. These therapies can complement conventional treatments and provide additional avenues for pain relief and symptom management. Individual experiences and responses vary, so careful consideration and consultation with healthcare providers are crucial.
Interdisciplinary Approaches
Interdisciplinary approaches are vital for comprehensive chronic pain management. These approaches involve collaboration among healthcare professionals with diverse expertise, such as pain specialists, physical therapists, psychologists, and social workers. This collaborative environment allows for a holistic assessment and treatment plan tailored to the patient’s unique needs. Shared decision-making ensures that the patient actively participates in their care and is fully informed about all treatment options.
Patient-Centered Care
Patient-centered care is paramount in chronic pain management. This approach emphasizes the individual patient’s preferences, values, and goals. Treatment plans are tailored to address the specific needs and circumstances of each patient. Active patient participation and open communication are essential components of this approach, allowing for adjustments to the treatment plan as needed.
Treatment Effectiveness Table
| Treatment Approach | Potential Effectiveness (Examples) | Types of Chronic Pain |
|---|---|---|
| Medications (NSAIDs, opioids, antidepressants) | Effective in reducing pain intensity in some cases, but may have side effects. | Neuropathic pain, musculoskeletal pain, some types of headaches. |
| Physical Therapy | Effective in improving function, mobility, and reducing pain in many chronic pain conditions. | Back pain, arthritis, fibromyalgia, musculoskeletal injuries. |
| Alternative Therapies (acupuncture, massage, mindfulness) | May provide complementary pain relief and symptom management, but evidence varies by condition. | Chronic tension headaches, musculoskeletal pain, fibromyalgia. |
Coping Mechanisms and Support Systems: What Is Chronic Pain
Living with chronic pain can be incredibly challenging, impacting not only physical well-being but also emotional and social life. Finding effective coping strategies and building a strong support system are crucial for navigating the daily realities of chronic pain. These strategies can help individuals regain control, improve their quality of life, and find ways to live fulfilling lives despite the pain.Understanding that chronic pain is more than just a physical condition, and that it affects all aspects of a person’s life, is paramount to effective management.
Coping mechanisms and strong support systems are vital tools for navigating the challenges and fostering a sense of well-being.
Relaxation Techniques for Pain Management
Relaxation techniques can significantly reduce pain perception and associated stress. Deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, and guided imagery are effective tools for calming the nervous system and promoting physical and mental relaxation. By practicing these techniques regularly, individuals can learn to manage pain triggers and improve overall well-being.
Mindfulness and Meditation Practices
Mindfulness practices, such as meditation and mindful movement, can help individuals focus on the present moment without judgment. This can reduce stress and anxiety associated with chronic pain. Mindfulness techniques encourage acceptance of pain without resistance, promoting a more balanced perspective on the experience. Regular practice can foster a sense of calm and clarity, allowing individuals to better manage their pain and overall emotional state.
Stress Management Strategies
Chronic pain often leads to heightened stress levels. Identifying and addressing stress triggers is essential. Effective stress management strategies include time management techniques, setting realistic goals, and engaging in activities that promote relaxation and enjoyment. This may include hobbies, spending time in nature, or connecting with loved ones. Developing healthy coping mechanisms for stress is critical for improving overall well-being.
Importance of Social Support and Emotional Well-being
Strong social support networks play a vital role in managing chronic pain. Connecting with friends, family, or support groups provides emotional validation, encouragement, and practical assistance. Maintaining strong social connections can significantly reduce feelings of isolation and loneliness, which are often exacerbated by chronic pain. Prioritizing emotional well-being is essential for managing the psychological impact of chronic pain.
Support Groups and Online Communities
Support groups and online communities offer a platform for individuals with chronic pain to connect with others who understand their experiences. These groups provide a safe space for sharing stories, exchanging coping strategies, and receiving encouragement. Online forums and support groups can offer a sense of community and belonging, especially for those who may not have local support networks.
The shared experience and understanding fostered in these groups can provide invaluable support.
Resources for Individuals with Chronic Pain
Numerous resources are available to assist individuals with chronic pain. These resources include healthcare professionals specializing in pain management, support groups tailored to specific pain conditions, and educational materials providing information about coping mechanisms and available treatments. Seeking out and utilizing these resources can significantly enhance the management and well-being of individuals living with chronic pain.
Coping Mechanisms and Their Benefits
| Coping Mechanism | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|
| Deep Breathing Exercises | Reduced anxiety, lowered heart rate, improved relaxation |
| Progressive Muscle Relaxation | Reduced muscle tension, decreased pain perception, improved sleep |
| Mindfulness Meditation | Improved focus, reduced stress, increased emotional regulation |
| Social Support Networks | Emotional validation, practical assistance, reduced isolation |
| Support Groups | Shared experience, encouragement, coping strategy exchange |
| Time Management Techniques | Reduced stress, improved organization, better overall well-being |
Living with Chronic Pain
Living with chronic pain is a significant challenge, impacting every aspect of daily life. It’s more than just physical discomfort; it often involves emotional and psychological distress. Adapting to this reality requires a multifaceted approach that considers both physical needs and mental well-being. This journey is unique to each individual, but shared strategies and support systems can make a substantial difference in navigating the complexities of chronic pain management.
Adapting Daily Routines
Chronic pain often necessitates adjustments to daily routines. These adjustments should focus on minimizing pain triggers and maximizing periods of rest and recovery. Prioritizing activities that don’t exacerbate pain, such as gentle exercise or relaxation techniques, is crucial. Planning for activities that cause pain flare-ups is also essential to avoid unnecessary stress and frustration. This can involve scheduling activities around pain management strategies.
Importance of Self-Care
Self-care is paramount for managing chronic pain effectively. It’s not a luxury but a necessity. Establishing healthy lifestyle habits, including a balanced diet, regular sleep patterns, and stress management techniques, plays a vital role in mitigating pain and improving overall well-being. Consistent self-care can enhance resilience and promote a sense of control over the condition. This includes incorporating activities that promote relaxation and emotional well-being, such as meditation, yoga, or spending time in nature.
Maintaining Purpose and Well-being
Maintaining a sense of purpose and well-being despite chronic pain is crucial. Finding ways to engage in meaningful activities, hobbies, or social connections can significantly improve mental health. This can involve joining support groups, pursuing creative outlets, or engaging in activities that bring joy and fulfillment. Remembering past accomplishments and focusing on personal growth can help maintain a positive outlook and contribute to overall well-being.
Inspiring Stories
Many individuals with chronic pain have found ways to thrive despite their challenges. One example is a former athlete who, after suffering a debilitating injury, transitioned to a career as a motivational speaker, sharing their experience to inspire others. This individual’s journey highlights the potential for finding purpose and resilience even in the face of significant adversity. Numerous stories of individuals navigating chronic pain demonstrate the importance of adapting, persevering, and maintaining hope.
Key Strategies for Adapting to Daily Life
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Prioritize rest and recovery | Scheduling regular breaks throughout the day to allow the body to recover from pain and fatigue. This might involve napping, using relaxation techniques, or simply sitting quietly. |
| Pain management techniques | Implementing various strategies like heat therapy, cold therapy, medication, or alternative therapies to manage pain levels. These methods may include yoga, tai chi, or massage. |
| Activity modification | Adjusting daily activities to accommodate pain limitations. This could involve breaking down tasks into smaller, manageable steps or finding alternative ways to accomplish tasks. |
| Building a support system | Connecting with friends, family, support groups, or healthcare professionals. Sharing experiences and receiving emotional support from others can significantly impact well-being. |
| Maintain a healthy lifestyle | Prioritizing a balanced diet, regular exercise (within pain limits), and adequate sleep. These elements are essential for overall health and pain management. |
Outcome Summary

In conclusion, chronic pain is a multifaceted condition with far-reaching consequences. From its varied forms and origins to the significant impact it has on physical and emotional well-being, understanding chronic pain is paramount. This exploration has highlighted the need for a comprehensive approach to diagnosis, treatment, and support. We’ve explored the diverse perspectives of those living with chronic pain, emphasizing the significance of individualized care, supportive environments, and practical coping mechanisms.
By fostering a greater understanding, we can create a more supportive and compassionate society for all those affected by chronic pain.


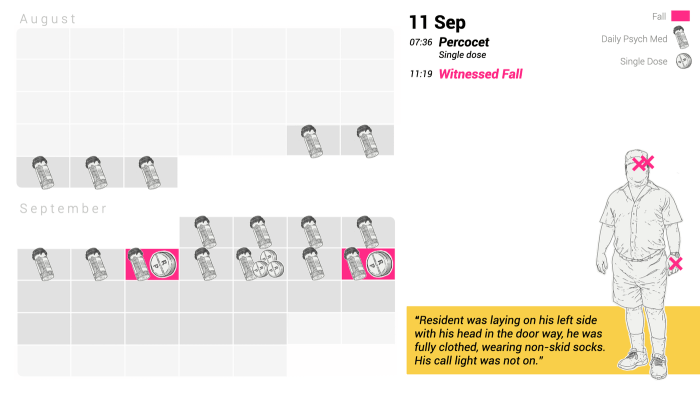
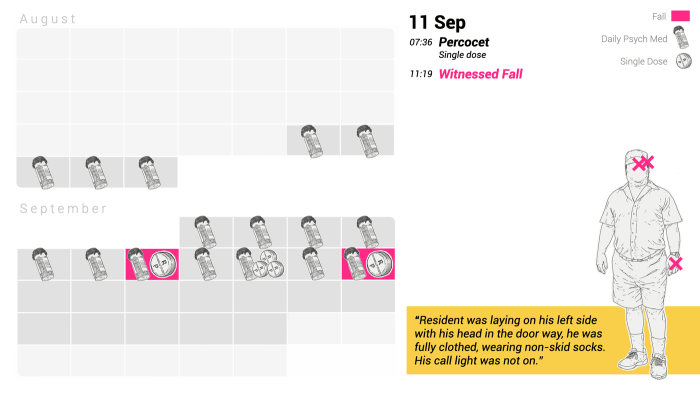
 The flowchart would visually depict the dynamic nature of chronic pain management, showcasing how patient needs may necessitate adjustments to treatment plans. It would clearly indicate points for reassessment and modification of the treatment plan based on the patient’s response. For instance, if a patient doesn’t respond well to initial therapy, the flowchart would guide clinicians toward alternative strategies or adjusting the dosage of buprenorphine. Furthermore, the flowchart would highlight the importance of ongoing monitoring and communication between the patient and the healthcare team.
The flowchart would visually depict the dynamic nature of chronic pain management, showcasing how patient needs may necessitate adjustments to treatment plans. It would clearly indicate points for reassessment and modification of the treatment plan based on the patient’s response. For instance, if a patient doesn’t respond well to initial therapy, the flowchart would guide clinicians toward alternative strategies or adjusting the dosage of buprenorphine. Furthermore, the flowchart would highlight the importance of ongoing monitoring and communication between the patient and the healthcare team.
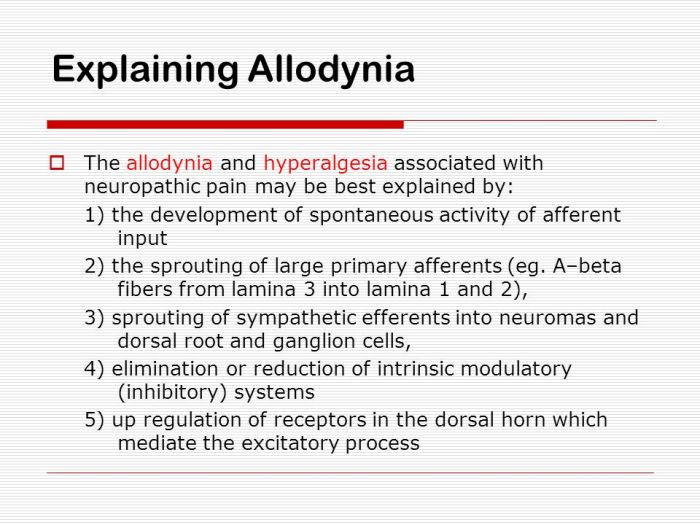

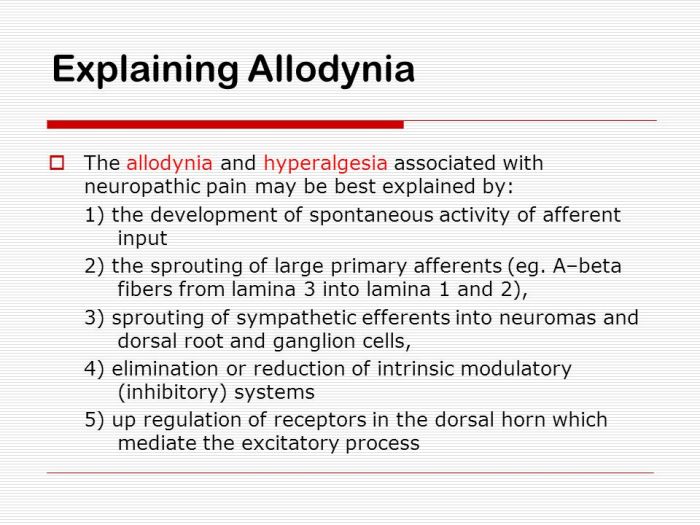
 (Description: A detailed diagram illustrating the neural pathways involved in allodynia. The diagram should clearly show the sensory neuron, the spinal cord, the brain stem, and the thalamus, highlighting the increased activity in the pain pathway. The diagram should also include annotations to point out the role of the brain regions involved in pain processing and the modulation of pain signals.)
(Description: A detailed diagram illustrating the neural pathways involved in allodynia. The diagram should clearly show the sensory neuron, the spinal cord, the brain stem, and the thalamus, highlighting the increased activity in the pain pathway. The diagram should also include annotations to point out the role of the brain regions involved in pain processing and the modulation of pain signals.)