Difference between acne pimple and ingrown hair: Understanding these skin conditions is crucial for proper care and treatment. This comprehensive guide explores the nuanced differences between acne, pimples, and ingrown hairs, delving into their causes, appearances, symptoms, and treatment options.
Acne and ingrown hairs, while both causing skin irritation, are distinct conditions. Acne, a common skin issue, involves the inflammation of hair follicles and sebaceous glands. Ingrown hairs, on the other hand, occur when a hair curls back into the skin, leading to inflammation and discomfort. This article provides a detailed comparison, making it easy to differentiate between these two types of skin problems.
Introduction to Skin Conditions
Understanding skin conditions like acne and ingrown hairs requires recognizing their similarities and key differences. Both can cause discomfort, inflammation, and blemishes, but their underlying causes and treatment approaches vary. This section delves into the specifics of these skin issues, outlining the anatomical structures involved and the typical locations where they manifest.Skin health is crucial for overall well-being. Identifying the root causes of skin problems is essential for effective management and treatment.
Proper knowledge allows for informed decisions regarding personal care routines and professional medical interventions.
Overview of Acne and Ingrown Hairs
Acne and ingrown hairs are common skin conditions affecting individuals of all ages and backgrounds. While both result in skin blemishes, their underlying mechanisms and anatomical involvement differ significantly. Acne involves the pilosebaceous unit, while ingrown hairs stem from follicle-related issues. Understanding these differences is critical for appropriate diagnosis and treatment.
Causes and Mechanisms of Acne
Acne develops when sebaceous glands, associated with hair follicles, produce excess oil (sebum). This overproduction, combined with dead skin cells and bacteria, clogs pores. The resulting inflammation and infection lead to the formation of pimples, papules, pustules, and sometimes nodules or cysts. Genetics, hormonal fluctuations, and certain medications can contribute to acne severity.
Causes and Mechanisms of Ingrown Hairs
Ingrown hairs occur when a hair follicle becomes blocked, preventing the hair from growing out normally. This blockage can be caused by friction, shaving, or waxing. The hair then grows back into the skin, triggering inflammation and potentially infection. Factors like skin texture and hair thickness can also play a role in ingrown hair susceptibility.
Anatomical Structures Involved
Both acne and ingrown hairs involve the pilosebaceous unit, a complex structure composed of hair follicles, sebaceous glands, and surrounding skin tissues. In acne, the primary issue stems from sebaceous gland activity and pore blockage. In ingrown hairs, the follicle itself is the primary focus, with blockage and subsequent hair growth inward.
Locations of Acne and Ingrown Hairs
The following table highlights the typical locations where acne and ingrown hairs commonly appear on the body:
| Skin Condition | Typical Locations |
|---|---|
| Acne | Face, back, chest, shoulders |
| Ingrown Hairs | Shaved areas (legs, underarms, face), areas with friction (groin, buttocks), or areas with coarse hair |
The table clearly demonstrates the different predilections of each condition. Acne frequently appears in areas with higher sebaceous gland activity, whereas ingrown hairs are more common in areas subject to shaving or friction.
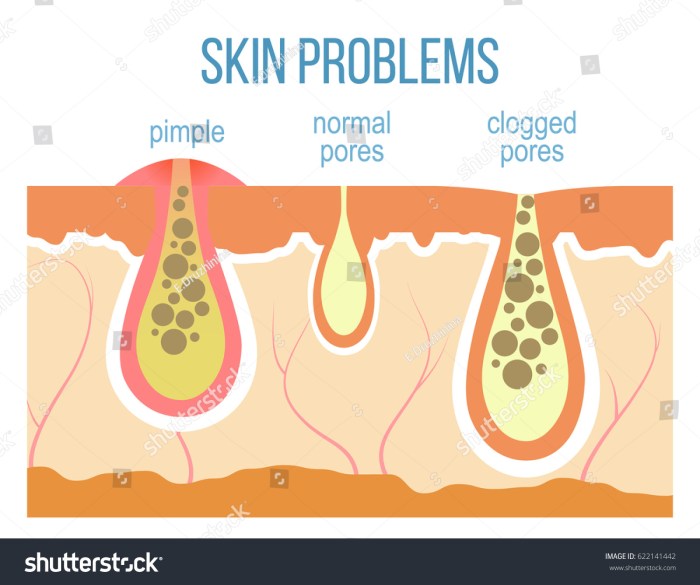
Visual Differences
Spotting the difference between an acne pimple and an ingrown hair can be tricky, but understanding their visual characteristics is key to proper self-care and seeking appropriate treatment. Both can cause discomfort and redness, but their underlying causes and appearances differ significantly. Careful observation of the location, size, and shape can provide valuable clues to the nature of the skin issue.
Comparing Acne and Ingrown Hair Appearances
Identifying acne and ingrown hairs relies heavily on visual cues. Acne lesions arise from clogged pores and inflammation, while ingrown hairs result from hair follicles that are blocked by the hair shaft itself. This leads to different visual presentations, and understanding these differences is crucial for accurate diagnosis.
Types of Acne Lesions
Acne manifests in various forms, each with a distinct visual presentation. Comedones, the earliest stage, appear as blackheads (open comedones) or whiteheads (closed comedones). Papules are small, red, inflamed bumps, while pustules are similar but contain pus. Nodules are deeper, painful, and inflamed lesions that may even form under the skin. Each type of acne lesion differs in size, color, and texture from ingrown hairs.
Ingrown Hair Characteristics
Ingrown hairs are characterized by a small, inflamed bump or a cluster of bumps, typically appearing around the hair follicle. The inflammation often results in redness, swelling, and sometimes, pus. The presence of the hair shaft embedded beneath the skin is a key visual distinction.
Visual Comparison Table
| Feature | Acne Lesion | Ingrown Hair |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Variable; comedones (blackheads/whiteheads), papules (red bumps), pustules (pus-filled bumps), nodules (deep, inflamed bumps) | Small, inflamed bump(s) around a hair follicle; sometimes pus-filled; may appear as a cluster |
| Location | Can occur anywhere on the skin, especially on the face, back, chest, and shoulders. | Often found on areas with frequent hair growth, such as the legs, bikini line, or underarms. |
| Size | Comedones can be small; papules, pustules, and nodules can range from a few millimeters to a centimeter or more in diameter. | Typically small, a few millimeters in diameter. |
| Color | Comedones can be black or white; papules and pustules are red; nodules can be red, inflamed, or even bluish. | Red, inflamed, potentially with pus. |
| Texture | Comedones can be smooth or rough; papules and pustules are typically firm; nodules are firm and sometimes hard. | Usually firm or slightly raised. |
Size and Color Variations, Difference between acne pimple and ingrown hair
The size of an acne lesion can vary considerably, from tiny comedones to larger nodules. Ingrown hairs, conversely, are usually small, a few millimeters in diameter. Color variations also play a part. Acne can manifest in various shades of red, while ingrown hairs are generally red, inflamed, or possibly even have a yellowish tinge from the presence of pus.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Understanding the differences between acne and ingrown hairs is crucial for effective treatment. Accurate diagnosis is essential, as both conditions share some similar symptoms, potentially leading to misdiagnosis and inappropriate treatment. Incorrect treatment approaches can prolong the healing process or worsen the condition.Precise identification allows for personalized care plans, focusing on the specific needs of the skin issue.
Differentiating between these two conditions often relies on a thorough examination of the symptoms, location, and overall skin context.
Common Symptoms of Acne Pimples
Acne pimples manifest as inflamed lesions on the skin. These lesions vary in size and severity, ranging from small, red bumps to large, pus-filled cysts. Common symptoms include redness, swelling, pain, and sometimes, the presence of whiteheads or blackheads. The affected area might be tender to the touch. The location is often associated with sebaceous glands, commonly found on the face, back, chest, and shoulders.
Common Symptoms of Ingrown Hairs
Ingrown hairs occur when a hair follicle becomes blocked, causing the hair to grow back into the skin. This leads to inflammation and irritation. Symptoms typically include small, red bumps, often accompanied by tenderness, pain, and itchiness. These bumps may appear similar to acne lesions, but often present in areas where hair follicles are concentrated, such as the legs, underarms, and bikini line.
Comparing Pain Levels and Sensations
The pain and sensation associated with acne and ingrown hairs can differ. Acne pimples, particularly those that progress to cysts, often cause throbbing or sharp pain. Ingrown hairs typically produce a more localized, persistent, and often itchy sensation. The pain intensity can vary significantly between individuals and the stage of the condition.
Importance of Proper Diagnosis and Dermatologist’s Role
Accurate diagnosis is vital to ensure the appropriate treatment plan. A dermatologist possesses specialized knowledge and tools to differentiate between acne and ingrown hairs. They can assess the skin’s condition comprehensively, including the location, size, and appearance of the lesions. Dermatologists can perform diagnostic tests to rule out other potential skin conditions that may mimic acne or ingrown hairs.
Ever wondered what’s the difference between a pesky pimple and an ingrown hair? It’s not always easy to tell, but understanding the root causes can help. Learning how to properly care for your skin is key, and that often involves knowing the difference between a simple breakout and a more stubborn ingrown hair. For instance, understanding how to use a tampon how to use a tampon can help with hygiene, and knowing the difference between ingrown hairs and acne pimples is equally important.
Ultimately, proper hygiene and understanding your skin type are crucial for keeping those annoying spots at bay.
Potential Complications of Misdiagnosis
Misdiagnosis can lead to several complications. Applying inappropriate treatments for ingrown hairs, for example, may exacerbate the inflammation and prolong healing. Conversely, treating acne with methods intended for ingrown hairs may prove ineffective and delay the resolution of the acne. This can also affect the patient’s self-esteem and confidence.
Table Comparing Severity Levels of Acne and Ingrown Hair Symptoms
| Characteristic | Acne Pimple | Ingrown Hair |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Red bumps, pustules, cysts | Red bumps, inflamed follicles |
| Location | Face, back, chest, shoulders | Legs, underarms, bikini line |
| Pain | Throbbing, sharp, varying | Localized, persistent, itchy |
| Severity | Can range from mild to severe | Typically mild to moderate |
| Treatment | Specific acne treatments | Exfoliation, topical treatments |
Treatment Approaches
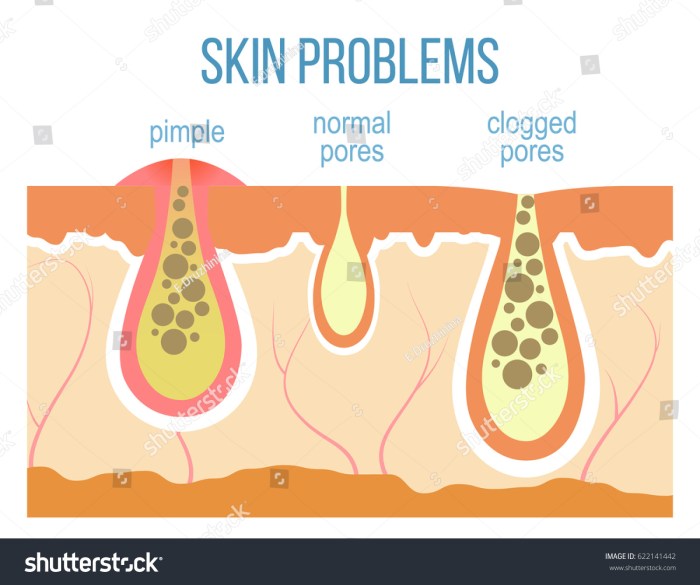
Treating acne and ingrown hairs effectively requires understanding the root causes and employing appropriate strategies. Different approaches work for different individuals, and a personalized treatment plan is often the most successful. Consistency and patience are key to achieving lasting results.
Acne Treatments
Effective acne treatments aim to reduce inflammation, control bacteria, and promote skin cell turnover. Topical medications, oral medications, and procedures are common approaches.
- Topical Medications: These are applied directly to the skin and often contain ingredients like benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, or retinoids. Benzoyl peroxide works by killing bacteria and reducing inflammation. Salicylic acid exfoliates the skin, unclogging pores. Retinoids promote cell turnover, preventing future breakouts and improving overall skin texture. Examples of topical medications include Differin and Proactiv.
- Oral Medications: Oral medications, often prescribed by a dermatologist, are typically used for moderate to severe acne. These medications, such as antibiotics and birth control pills, address the underlying hormonal imbalances or bacterial overgrowth contributing to acne. Antibiotics help control the bacteria, while birth control pills can regulate hormone levels. It’s important to note that long-term antibiotic use can lead to antibiotic resistance, so doctors usually prescribe them only when necessary.
Ever wondered what the difference is between an acne pimple and an ingrown hair? It’s more than just a visual difference; understanding the root causes can help target the right treatment. A DIY cervical roll, like the one demonstrated in this helpful guide on diy cervical roll to manage neck pain while sleeping , can help alleviate neck pain and improve sleep quality, which in turn can positively impact your skin health.
Ultimately, knowing the distinction between these skin issues will help you take better care of your skin.
- Procedures: Procedures such as chemical peels, microdermabrasion, and laser treatments can help improve acne scarring and promote healthy skin cell turnover. These procedures are often used in conjunction with topical or oral medications to achieve optimal results. For example, chemical peels can remove dead skin cells, revealing healthier skin beneath.
Ingrown Hair Treatments
Ingrown hair treatments focus on preventing the hair from becoming trapped beneath the skin’s surface and addressing any inflammation. Exfoliation, extraction, and topical solutions are common approaches.
- Exfoliation: Regular exfoliation can help remove dead skin cells and prevent hair from becoming trapped in pores. This is crucial to prevent ingrown hairs. Gentle exfoliation using products with salicylic acid or glycolic acid can promote smoother skin and prevent hair entrapment. A proper exfoliation routine can prevent future ingrown hairs and improve the overall skin texture.
- Extraction: If an ingrown hair is already present, extraction can be performed by a dermatologist or esthetician. This involves gently removing the hair from beneath the skin’s surface. Proper extraction techniques, performed by a professional, are crucial to avoid further irritation or infection.
- Topical Solutions: Topical solutions containing ingredients like tea tree oil, aloe vera, or hydrocortisone can help soothe inflammation and promote healing. These solutions are particularly effective in reducing redness and discomfort associated with ingrown hairs.
Comparison of Treatments
The efficacy and potential side effects of treatments for acne and ingrown hairs vary significantly. Careful consideration of individual needs and potential risks is vital.
| Treatment Approach | Acne | Ingrown Hairs | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Topical Medications (Benzoyl Peroxide, Salicylic Acid, Retinoids) | Effective for mild to moderate acne | Can help prevent future ingrown hairs | Relatively low risk of serious side effects | May cause skin irritation or dryness |
| Oral Medications (Antibiotics, Birth Control Pills) | Effective for moderate to severe acne | Not typically used | Can control underlying causes | Potential side effects (antibiotics), hormonal imbalances (birth control) |
| Procedures (Chemical Peels, Microdermabrasion, Laser Treatments) | Can improve acne scars | Not usually needed for ingrown hairs | Potential for significant improvement | Can be expensive, potentially painful |
| Exfoliation | Can help prevent breakouts | Crucial to prevent future ingrown hairs | Gentle, often part of a skincare routine | Requires consistent use to be effective |
| Extraction | Not a primary treatment | Can remove existing ingrown hairs | Provides immediate results | Requires professional expertise to avoid infection |
| Topical Solutions (Tea Tree Oil, Aloe Vera) | Can help soothe inflammation | Can soothe inflammation and promote healing | Often inexpensive, readily available | May not be as effective as other treatments |
Home Remedies
Some home remedies can complement professional treatments, but they should not replace them entirely. Consult a dermatologist for personalized advice.
- Acne: Applying a cold compress to a pimple can reduce inflammation. Using a gentle cleanser can help prevent breakouts. Avoid harsh scrubbing, as this can worsen acne.
- Ingrown Hairs: Soaking the affected area in warm water can soften the hair. Applying a gentle moisturizer can help prevent future ingrown hairs.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing acne and ingrown hairs requires a multifaceted approach that addresses both external factors and internal health. A proactive approach to skincare and lifestyle choices can significantly reduce the likelihood of breakouts and ingrown hair development. By understanding the triggers for each condition, you can develop tailored strategies to minimize their occurrence.Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and implementing specific skincare practices are crucial in preventing both acne and ingrown hairs.
Effective prevention involves understanding the underlying causes and taking proactive steps to minimize their impact.
Acne Prevention
Proper hygiene plays a pivotal role in acne prevention. Regular cleansing, exfoliation, and moisturizing are essential to remove excess oil, dirt, and dead skin cells that can clog pores. A gentle, non-comedogenic cleanser is recommended to avoid irritating the skin further. Choosing the right cleanser, moisturizer, and sunscreen is crucial for acne-prone skin.
“A consistent skincare routine, including gentle cleansing, exfoliation, and moisturizing, is fundamental to preventing acne.”
Dietary choices can influence acne development. Reducing the intake of sugary and processed foods, and focusing on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins can contribute to improved skin health. Hydration is also essential for overall skin health.Stress management is an often overlooked aspect of acne prevention. Chronic stress can trigger hormonal imbalances that exacerbate acne.
Practices like yoga, meditation, and spending time in nature can help manage stress levels and contribute to improved skin health.
Ingrown Hair Prevention
Shaving techniques significantly impact the likelihood of ingrown hairs. Using a sharp razor, applying a shaving cream or gel, and ensuring smooth strokes can help reduce friction and irritation. Avoiding harsh scrubbing after shaving is also important.Hair removal methods can influence ingrown hair risk. Methods like waxing or sugaring, if performed correctly, can minimize the risk of ingrown hairs.
Electrolysis and laser hair removal are also long-term solutions that can significantly reduce or eliminate hair growth, thus minimizing ingrown hairs.Skin care routines are essential for preventing ingrown hairs. Using gentle exfoliants, and avoiding harsh scrubbing can help prevent ingrown hairs. Applying moisturizers and using products that promote skin elasticity can help prevent ingrown hairs.
Preventing Both Acne and Ingrown Hairs
Several preventative measures can be effective for both acne and ingrown hairs. Maintaining a healthy diet, avoiding excessive stress, and practicing good hygiene are beneficial for both conditions. Using non-comedogenic products and choosing gentle hair removal methods are also beneficial for both.
“Consistent skincare routines, stress management, and a balanced diet are key for preventing both acne and ingrown hairs.”
While both acne pimples and ingrown hairs can be frustrating, they’re distinctly different. Ingrown hairs often occur after shaving or waxing, and appear as small, red bumps. Acne, on the other hand, is more complex, usually involving clogged pores. Interestingly, if you’re experiencing a cough, exploring natural remedies might help. For instance, check out this article on natural remedies for cough for some ideas.
Ultimately, knowing the difference between these skin issues can help you choose the right treatment approach.
| Preventive Measure | Acne | Ingrown Hairs |
|---|---|---|
| Proper Hygiene | Regular cleansing, exfoliation, and moisturizing | Gentle cleansing, avoiding harsh scrubbing after hair removal |
| Diet | Reducing sugary and processed foods, focusing on balanced diet | No specific dietary considerations, but a healthy diet is beneficial overall |
| Stress Management | Managing stress through relaxation techniques | Stress management can indirectly help reduce skin irritation |
| Shaving Techniques | N/A | Using a sharp razor, shaving cream, and gentle strokes |
| Hair Removal Methods | N/A | Choosing methods that minimize friction (e.g., waxing, sugaring, electrolysis) |
| Skincare Routines | Using non-comedogenic products | Using gentle exfoliants and moisturizers |
Visual Representation (Illustrative Content): Difference Between Acne Pimple And Ingrown Hair
Understanding the subtle differences between acne and ingrown hairs is crucial for effective treatment. Visual aids play a vital role in this process, enabling clear identification of various stages, types, and locations of these skin conditions. Visual representations also aid in differentiating between them, and appreciating the variety of treatment approaches available.
Acne Pimple vs. Ingrown Hair
A helpful visual would show a side-by-side comparison of an acne pimple and an ingrown hair. The acne pimple would likely be depicted as a red, inflamed bump, potentially with a white or yellow head, while the ingrown hair would appear as a small, red, inflamed bump, often with a small, dark hair follicle visible within or next to it.
The texture of the lesions might also be noted, with the acne pimple potentially having a slightly softer, more pus-like center, and the ingrown hair exhibiting a more solid, perhaps slightly raised, texture.
Stages of Acne Development
Visualizing the different stages of acne development is essential for appropriate treatment. An image could showcase a progression from a small, red, non-inflamed papule to a larger, inflamed pustule, and eventually a deep, cystic lesion. The image would show the increasing redness, swelling, and pus formation as acne progresses. The images should highlight the varying appearances and sizes, enabling one to understand how acne evolves over time.
Types of Ingrown Hairs
Different types of ingrown hairs result from various factors. An illustrative image would show several examples: one depicting an ingrown hair with a small, inflamed bump, another showcasing an ingrown hair surrounded by a larger, more inflamed, red area, and another showing multiple ingrown hairs clustered together. These visuals would help differentiate between isolated ingrown hairs and more extensive ingrown hair clusters.
Treatment Options for Acne and Ingrown Hairs
A visual representation of treatment options could feature several common topical treatments, such as benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, retinoids, and over-the-counter acne spot treatments. For ingrown hairs, the image could display the application of a topical solution, such as salicylic acid or benzoyl peroxide, along with gentle exfoliation. It might also depict the use of topical creams or gels for both conditions, highlighting their role in managing symptoms and promoting healing.
The image could also show professional treatments like laser therapy or chemical peels for more severe cases.
Location Differences
An image demonstrating the location differences between acne and ingrown hairs would be helpful. The image should illustrate the typical areas where acne commonly occurs, such as the face, back, chest, and shoulders. In contrast, the image would also highlight areas prone to ingrown hairs, such as the legs, armpits, and bikini line. This would underscore the connection between specific locations and the types of skin conditions that can occur there.
Concluding Remarks
In conclusion, recognizing the differences between acne, pimples, and ingrown hairs is essential for effective treatment and prevention. While both can be frustrating, understanding their unique characteristics, symptoms, and treatment options allows for personalized care. This guide provides a valuable resource for anyone seeking to better understand and manage these common skin concerns. By grasping the nuances of each condition, you can take proactive steps toward healthier, clearer skin.