Enterovirus strains and facts cover a wide range of topics, from the basics of what enteroviruses are to their impact on public health. This exploration delves into the diverse families and genera within this group, highlighting their classification methods and common characteristics. We’ll examine their global distribution, seasonal patterns, and transmission routes, as well as the specific symptoms associated with various strains.
The discussion also covers the pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention strategies for enterovirus infections. Finally, we’ll explore the public health impact of enterovirus outbreaks, including emerging strains and variants, their impact on different populations, and strategies for monitoring their emergence.
Understanding enteroviruses is crucial, not only for recognizing symptoms and seeking appropriate medical care but also for appreciating the complexity of viral infections and the vital role of public health measures in controlling outbreaks.
Introduction to Enterovirus Strains
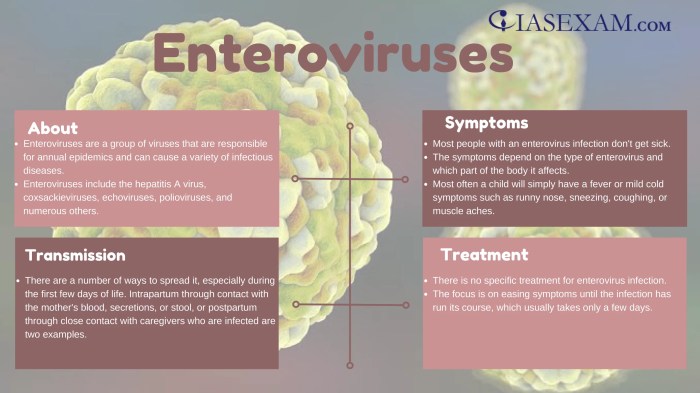
Enteroviruses are a diverse group of viruses that commonly infect humans and other animals. They are known for their ability to replicate in the gastrointestinal tract, hence the name “entero.” These viruses are widespread and can cause a range of illnesses, from mild respiratory infections to more severe neurological diseases. Understanding the different strains and their characteristics is crucial for effective prevention and treatment strategies.Enteroviruses are classified within the Picornaviridae family, a large family of small, non-enveloped viruses.
This family is further subdivided into various genera, with Enterovirus being one of the most significant. These genera contain numerous species, each with its own characteristics and potential pathogenic impact. This categorization allows scientists to better understand the diversity and relatedness of these viruses.
Enterovirus Classification and Categorization
Enteroviruses are categorized based on their genetic and antigenic characteristics. Genetic analysis, particularly of the viral RNA sequences, is a fundamental tool for differentiating various enterovirus strains. This approach allows for precise identification and tracking of viral evolution and transmission. Furthermore, serological methods, based on antibody responses, are also employed to classify and differentiate different strains. These methods rely on the unique proteins on the surface of the virus to identify specific strains.
Common Characteristics of Enterovirus Strains
Enteroviruses share several common characteristics that contribute to their ability to infect and replicate. These include their small, non-enveloped structure, their preference for replication in the gastrointestinal tract, and their capacity to cause a wide spectrum of clinical presentations. Their RNA genome allows for rapid replication and mutation, contributing to the diverse range of strains and the challenges in developing universal vaccines.
Enterovirus Species Comparison
| Enterovirus Species | Common Symptoms | Transmission | Severity | Notable Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enterovirus 71 (EV-71) | Hand, foot, and mouth disease; neurological complications (encephalitis, meningitis) | Fecal-oral route; respiratory droplets | Can be severe, particularly in infants and young children | Associated with severe neurological outcomes in some cases |
| Coxsackievirus A | Hand, foot, and mouth disease; herpangina (sore throat, fever); skin rashes | Fecal-oral route; respiratory droplets | Generally mild | Diverse group with multiple serotypes |
| Coxsackievirus B | Meningitis; myocarditis (inflammation of the heart muscle); pericarditis (inflammation of the heart lining); other organ involvement | Fecal-oral route | Can range from mild to severe, with potential for severe complications | Associated with more severe systemic infections |
| Enterovirus D68 | Respiratory illness, including bronchiolitis and pneumonia | Respiratory droplets | Generally mild, but some cases have been severe | Associated with respiratory illnesses and potentially causing complications in individuals with pre-existing conditions |
This table provides a concise overview of several key enterovirus species, highlighting their common symptoms, transmission routes, severity levels, and notable characteristics. Further research is ongoing to deepen our understanding of these viruses and develop more effective preventative measures.
Epidemiology of Enterovirus Strains: Enterovirus Strains And Facts
Enteroviruses, a diverse group of viruses, are a significant cause of human illness worldwide. Understanding their epidemiology is crucial for developing effective prevention strategies and managing outbreaks. This involves analyzing their global distribution, seasonal patterns, high-risk populations, and transmission routes. Detailed knowledge of these factors empowers public health officials to implement targeted interventions and minimize the impact of enterovirus infections.Enterovirus infections often manifest with mild symptoms, but they can also lead to severe complications, particularly in vulnerable populations.
Enterovirus strains are fascinating, with a surprising number of types. Understanding these strains is crucial for public health, but they’re also linked to a range of health issues, including potential complications like liver inflammation. This inflammation can sometimes be a factor in the development of fatty liver disease, a condition requiring further investigation, which you can learn more about in this comprehensive overview: overview of fatty liver disease.
Ultimately, research into enterovirus strains is vital for better disease prevention and treatment strategies.
The epidemiological characteristics of these viruses, including their prevalence, seasonality, and modes of transmission, influence the development of public health policies and interventions to control their spread.
Global Distribution of Enterovirus Strains
Enteroviruses are globally distributed, with varying prevalence across different regions. Their presence is not uniform; factors like hygiene standards, socioeconomic conditions, and access to healthcare influence the frequency of infections in various populations. Some regions experience higher rates of enterovirus infections due to specific environmental or socioeconomic conditions.
Seasonal Patterns of Enterovirus Outbreaks
Enterovirus outbreaks frequently exhibit seasonal patterns, often peaking during warmer months. Warmer temperatures and increased human contact in crowded environments, like schools and daycare centers, are thought to contribute to the amplified spread. The prevalence of enterovirus infections fluctuates seasonally, correlating with climate and social behaviors. For instance, summer outbreaks in North America are common, often coinciding with increased outdoor activities and gatherings.
High-Risk Populations for Enterovirus Infections, Enterovirus strains and facts
Certain populations are more susceptible to severe enterovirus infections. Infants and young children, the elderly, and immunocompromised individuals often experience more severe outcomes compared to healthy adults. These individuals, due to their reduced immune response, are at increased risk for developing complications. For example, newborns and infants with underdeveloped immune systems are more vulnerable to serious enterovirus illnesses.
Transmission Routes of Enteroviruses
Enteroviruses spread primarily through the fecal-oral route, meaning they enter the body through contaminated food or water. Direct contact with infected individuals, especially through respiratory droplets, also plays a role in transmission. These viruses can also spread through fomites, which are inanimate objects contaminated with the virus. This mode of transmission highlights the importance of hygiene practices to prevent spread.
For example, handwashing after using the restroom and before preparing food are crucial preventive measures.
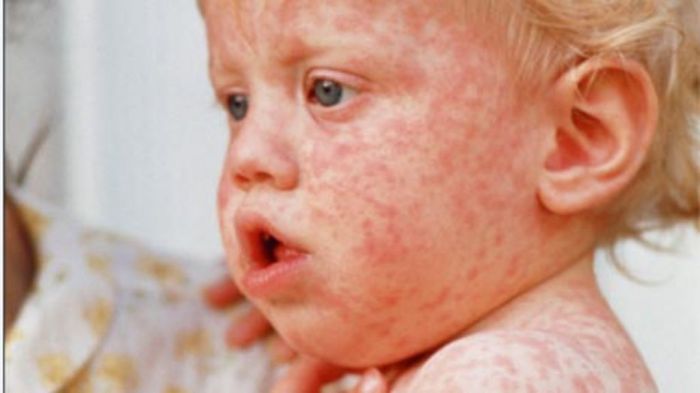
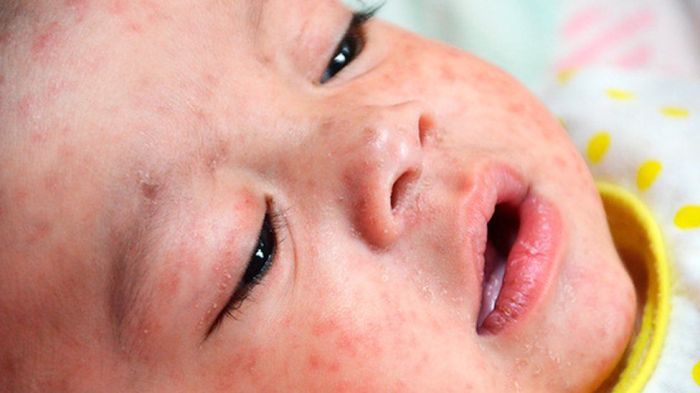
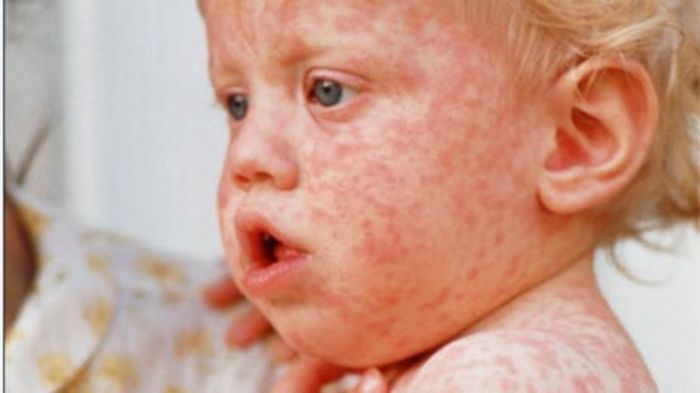
Symptoms Associated with Different Enterovirus Strains
The symptoms of enterovirus infections can vary significantly depending on the specific strain. Some enteroviruses cause mild symptoms, while others can result in more severe complications. A detailed understanding of the symptoms associated with each strain is crucial for diagnosis and treatment.
| Enterovirus Strain | Common Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Coxsackievirus A | Hand, foot, and mouth disease; herpangina |
| Coxsackievirus B | Meningitis, myocarditis, pleurodynia |
| Enterovirus 71 | Hand, foot, and mouth disease; encephalitis |
| Poliovirus | Paralysis |
Enterovirus Pathogenesis
Enteroviruses, a diverse group of viruses, cause a wide range of illnesses, from mild to severe. Understanding their pathogenesis, the steps involved in their infection and replication within the host, is crucial for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies. This intricate process involves several key steps, starting from initial cellular entry to the eventual immune response. This exploration delves into the mechanisms of enterovirus infection, the replication cycle, host factors, and the immune system’s reaction.
Cellular Infection Mechanisms
Enteroviruses employ various strategies to gain entry into host cells. They typically bind to specific cell surface receptors, triggering cellular uptake via endocytosis. This process is crucial for initiating the infection cascade. The specific receptor utilized often dictates the cell tropism of the virus, meaning which cell types are preferentially infected. For example, some enterovirus serotypes preferentially infect intestinal cells, while others target the respiratory tract.
This selective binding and entry into susceptible cells are essential steps in the enteroviral replication cycle.
Replication Cycle
The enterovirus replication cycle is a complex process involving several stages. Once inside the host cell, the viral genome is released from the capsid. The viral RNA then directs the synthesis of viral proteins, using the host cell’s machinery. These newly synthesized viral components assemble to form new virions. This assembly process involves the intricate coordination of viral proteins, which are vital for encapsulating the viral RNA genome.
Enterovirus strains are a fascinating but sometimes tricky bunch. Learning about their various types and how they spread is important. Finding natural remedies to soothe skin conditions like eczema can also be beneficial, and using aloe vera is a popular option. For detailed information on how to use aloe vera for eczema, check out this helpful guide: how to use aloe vera for eczema.
Ultimately, staying informed about enteroviruses and other health concerns is key to maintaining well-being.
The final step involves the release of these newly assembled virions from the host cell, often causing cell lysis. This release of new viral particles leads to the continued spread of the infection.
Host Factors in Infection
Host factors significantly influence the course of enterovirus infections. Genetic predisposition, nutritional status, and the presence of co-infections or pre-existing immune conditions can affect the severity of the disease. For instance, individuals with weakened immune systems may experience more severe outcomes compared to those with robust immune responses. Furthermore, the presence of specific host proteins or cellular pathways can either facilitate or hinder viral replication.
Immune Response
The host immune system mounts a multifaceted response to enterovirus infections. Both innate and adaptive immune responses are activated. Innate immunity, the first line of defense, involves the activation of antiviral proteins and immune cells like natural killer (NK) cells. Adaptive immunity, including antibody production and cellular immunity, develops over time and provides long-term protection. The strength and type of immune response influence the outcome of the infection, determining whether it resolves with minimal symptoms or progresses to more severe disease.
Enterovirus Replication Stages
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Attachment | Virus binds to specific receptors on the host cell surface. |
| Entry | Virus enters the host cell via endocytosis. |
| Uncoating | Viral RNA genome is released from the capsid. |
| Replication | Viral RNA serves as a template for the synthesis of viral proteins and new RNA genomes. |
| Assembly | New viral components assemble to form new virions. |
| Release | New virions are released from the host cell, often causing cell lysis. |
Clinical Manifestations of Enterovirus Infections
Enteroviruses, a diverse group of viruses, cause a wide range of illnesses, from mild, self-limiting fevers to severe, life-threatening complications. Understanding the spectrum of clinical manifestations is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management. This understanding helps healthcare providers distinguish between various enterovirus strains and tailor treatment strategies to individual patient needs.The clinical presentation of enterovirus infections is highly variable, depending on the specific enterovirus strain, the age and overall health of the infected individual, and the immune response.
While some infections are asymptomatic, others manifest with a constellation of symptoms that can mimic other viral or bacterial illnesses. This variability underscores the importance of considering enterovirus as a potential cause in cases with unexplained symptoms, especially in vulnerable populations.
Enterovirus strains are fascinating, aren’t they? They’re a diverse group, and understanding their various facts is key. Sometimes, these infections can surprisingly lead to complications like skin issues, especially in individuals with pre-existing conditions such as diabetes and skin problems. But ultimately, learning about enterovirus strains and facts is crucial for overall health awareness.
Spectrum of Clinical Manifestations
Enterovirus infections can manifest in a wide array of ways, ranging from mild, non-specific symptoms to severe complications. The severity of the illness depends on several factors. These factors include the specific enterovirus type, the immune status of the host, and the age of the individual.
Common Symptoms
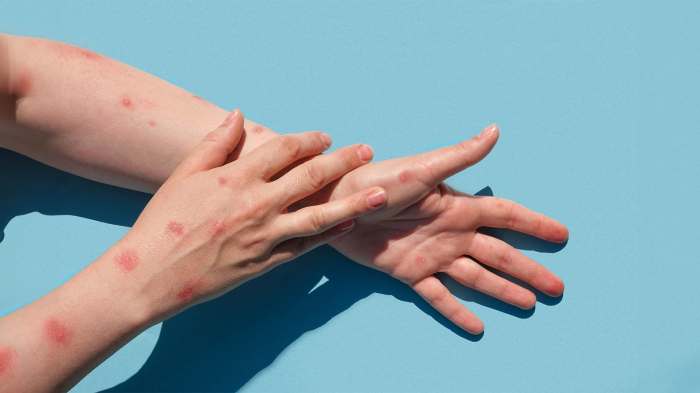
Common symptoms associated with enterovirus infections include fever, rash, and gastrointestinal issues. Fever is a frequent and often prominent symptom, presenting as a sustained elevation in body temperature. Skin rashes, characterized by various patterns and distributions, are another frequent manifestation. Diarrhea, ranging from mild loose stools to severe dehydration, is also a common gastrointestinal manifestation. These symptoms are often accompanied by other symptoms such as headache, malaise, and muscle aches.
Severe Complications
While most enterovirus infections resolve without lasting sequelae, some infections can lead to severe complications. These complications can range from myocarditis (inflammation of the heart muscle) to meningitis (inflammation of the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord). In infants and young children, severe complications can be particularly concerning. Examples of severe complications include encephalitis (inflammation of the brain), which can lead to long-term neurological deficits.
Another significant complication is myocarditis, which can potentially cause heart failure.
Differences in Symptoms Between Strains
Different enterovirus strains can exhibit varying clinical presentations. For instance, Coxsackievirus A strains are often associated with hand, foot, and mouth disease, characterized by a specific rash on the hands, feet, and mouth. Enterovirus 71, a more severe strain, can be associated with more significant neurological complications.
Categorization of Enterovirus Infections by Severity
| Severity | Symptoms | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Mild | Fever, mild rash, mild gastrointestinal issues (e.g., diarrhea) | Hand, foot, and mouth disease in healthy children |
| Moderate | High fever, more significant rash, moderate gastrointestinal issues (e.g., vomiting, severe diarrhea), possible neurological symptoms (e.g., headache, stiff neck) | Enterovirus 71 infections, some cases of aseptic meningitis |
| Severe | High fever, severe rash, severe gastrointestinal issues, neurological complications (e.g., encephalitis, meningitis, myocarditis), respiratory distress | Severe cases of enterovirus 71 infections, cases involving a compromised immune system |
Diagnosis and Treatment of Enterovirus Infections
Enterovirus infections, while often mild, can sometimes lead to severe complications, particularly in vulnerable populations. Accurate and timely diagnosis is crucial for appropriate management and preventing the spread of these infections. Treatment primarily focuses on supportive care, addressing symptoms, and preventing secondary infections.Effective strategies for diagnosing and managing enterovirus infections involve a multi-faceted approach, incorporating laboratory tests, clinical evaluation, and understanding the potential spectrum of disease presentations.
This section will delve into the diagnostic methods, the importance of timely diagnosis, supportive care options, and available treatment strategies.
Diagnostic Methods for Enterovirus Infections
Accurate diagnosis of enterovirus infections is essential for appropriate management and public health interventions. Various laboratory tests can identify the specific enterovirus strain and confirm the infection.
- Viral Culture: Viral culture remains a valuable method for isolating and identifying enteroviruses. Samples, such as throat swabs or stool specimens, are cultured in specific cell lines. Positive results confirm the presence of the virus. However, this method can be time-consuming, requiring several days for results.
- Molecular Assays: Molecular assays, including polymerase chain reaction (PCR) techniques, are widely used for detecting enterovirus RNA in clinical samples. PCR is highly sensitive and can detect even low viral loads, enabling earlier diagnosis. These methods are faster than viral culture and provide more rapid results.
- Serological Testing: Serological tests, such as enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA), can detect antibodies produced by the body in response to the infection. These tests are useful for retrospective diagnosis or to determine if an individual has previously been exposed to a specific enterovirus. They may not be as useful for acute infections.
Importance of Timely Diagnosis
Prompt diagnosis is crucial in managing enterovirus infections, especially in high-risk populations. Early detection allows for timely implementation of supportive care and appropriate public health measures to prevent further transmission. Delay in diagnosis can lead to prolonged illness, potentially severe complications, and increased transmission to others. For instance, in a hospital outbreak, rapid diagnosis through PCR can help quickly isolate infected patients, prevent further spread, and implement appropriate infection control measures.
Supportive Care for Enterovirus Infections
Supportive care plays a critical role in managing enterovirus infections, particularly in mild cases. The primary focus is on alleviating symptoms and preventing complications.
- Rest and Hydration: Encouraging rest and providing adequate hydration are essential for the body’s recovery process. Fluids help prevent dehydration, a common concern, especially in children.
- Symptom Management: Symptomatic relief through over-the-counter medications, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, can help manage fever, pain, and discomfort. However, it is crucial to follow dosage recommendations carefully.
- Monitoring for Complications: Close monitoring for complications, such as severe respiratory distress or neurological symptoms, is essential. Early intervention for complications can significantly improve outcomes.
Treatment Strategies for Enterovirus Infections
Currently, no specific antiviral treatments exist for enterovirus infections. Treatment strategies primarily focus on supportive care to manage symptoms and prevent complications.
- Antiviral Medications: While no antiviral medications are currently approved for treating enterovirus infections, research is ongoing. Future developments may lead to more targeted treatments.
- Symptom-Based Treatment: Treatment is generally supportive, focusing on relieving symptoms such as fever, muscle aches, and rash. Over-the-counter medications, like acetaminophen or ibuprofen, are often used to manage symptoms.
- Preventative Measures: Good hygiene practices, like frequent handwashing, are crucial in preventing the spread of enterovirus infections.
Diagnostic Tests and Procedures
The table below Artikels the common diagnostic tests for enterovirus infections, their procedures, and turnaround times.
| Diagnostic Test | Procedure | Turnaround Time |
|---|---|---|
| Viral Culture | Isolation of virus in cell culture | 3-7 days |
| Molecular Assays (PCR) | Detection of viral RNA using PCR | 1-3 days |
| Serological Testing (ELISA) | Detection of antibodies against enteroviruses | 1-2 days |
Prevention and Control of Enterovirus Infections
Enteroviruses are a common cause of illness, particularly in children. Effective prevention and control strategies are crucial to minimizing the spread of these infections and protecting vulnerable populations. Implementing robust hygiene practices, vaccination programs, and public health measures are key components in mitigating the impact of enterovirus outbreaks.Understanding the diverse transmission routes and environmental factors influencing enterovirus spread is critical for developing targeted and effective prevention strategies.
This knowledge allows for the implementation of tailored interventions in various settings, ranging from homes and schools to healthcare facilities and communities.
Importance of Hygiene Practices
Maintaining meticulous hygiene standards is fundamental in preventing enterovirus transmission. Frequent handwashing with soap and water, especially after using the restroom and before eating, is a cornerstone of infection control. Proper hand hygiene significantly reduces the risk of viral spread. This is particularly important in communal settings like schools and daycare centers where frequent contact between individuals occurs.
Role of Vaccination
Vaccination plays a vital role in controlling enterovirus outbreaks, though a universal enterovirus vaccine is not yet available. While specific enterovirus vaccines are currently not widely used, research and development in this area are ongoing. The effectiveness of vaccines against specific enterovirus strains can vary. Developing and implementing vaccines against prevalent enterovirus strains could substantially reduce the incidence of severe infections.
Public Health Measures
Public health measures are crucial in controlling the transmission of enteroviruses. These measures include monitoring the prevalence of enterovirus infections, promptly identifying and isolating cases, and implementing appropriate infection control protocols in healthcare settings. Tracing and quarantining close contacts of infected individuals can help to limit the spread of the virus. This can include advising on proper hygiene, especially in environments with high population density.
The implementation of these strategies is essential in managing and controlling enterovirus outbreaks.
Examples of Effective Prevention Strategies
Effective prevention strategies can be tailored to different settings. In schools, promoting handwashing and encouraging the use of hand sanitizers can significantly reduce transmission. In healthcare facilities, strict adherence to infection control protocols, including proper disinfection of surfaces and equipment, is critical. Community-wide awareness campaigns can educate individuals about preventive measures, including proper hygiene and infection control protocols.
For instance, distributing educational materials on how to prevent enterovirus infections in public areas and organizing community health fairs can be highly effective.
Recommended Hygiene Practices
| Hygiene Practice | Description |
|---|---|
| Frequent Handwashing | Washing hands with soap and water for at least 20 seconds, especially after using the restroom, before eating, and after contact with potentially contaminated surfaces. |
| Proper Hand Sanitizer Use | Using hand sanitizer with at least 60% alcohol content when soap and water are not readily available. |
| Disinfection of Surfaces | Regularly disinfecting frequently touched surfaces, such as doorknobs, countertops, and toys, with appropriate disinfectants. |
| Proper Food Handling | Maintaining proper food safety practices to prevent contamination, including thorough cooking of food and proper food storage. |
| Avoiding Close Contact | Reducing close contact with individuals who are showing symptoms of enterovirus infection. |
Enterovirus Strains and Public Health Impact
Enteroviruses, a diverse group of viruses, pose a significant public health concern, particularly during outbreaks. These infections can range from mild, self-limiting illnesses to severe, life-threatening conditions. Understanding the public health impact of enterovirus outbreaks is crucial for developing effective prevention and control strategies. This section explores the multifaceted consequences of enterovirus infections, including their economic and social burdens.
Impact of Enterovirus Outbreaks on Public Health
Enterovirus outbreaks strain healthcare resources, leading to increased demand for hospital beds, intensive care units, and medical personnel. This surge in demand can overwhelm existing systems, potentially affecting the care of other patients. Outbreaks can also disrupt educational institutions and workplaces, impacting productivity and economic activity. Moreover, the potential for severe complications, such as myocarditis (inflammation of the heart muscle) or meningitis (inflammation of the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord), highlights the need for vigilant public health monitoring and response.
Economic Burden of Enterovirus Infections
Enterovirus infections impose a substantial economic burden on society. Direct costs include medical expenses, such as hospitalizations, laboratory tests, and medications. Indirect costs encompass lost productivity due to illness, absenteeism from work or school, and caregiver time. The economic impact varies depending on the severity and extent of the outbreak, but it can be substantial, particularly in vulnerable populations.
For example, a large-scale enterovirus outbreak in a community can lead to significant disruptions in the local economy, impacting businesses and the overall quality of life.
Social Consequences of Enterovirus Outbreaks
Enterovirus outbreaks can have profound social consequences, impacting families and communities. Parents may experience anxiety and stress due to the illness of their children. Outbreaks can also lead to social isolation and stigmatization, particularly for those with chronic conditions or weakened immune systems. Moreover, the emotional toll on families and caregivers during outbreaks is significant. Fear and uncertainty about the virus can also contribute to social disruption and tension within communities.
Long-Term Health Effects of Enterovirus Infections
While most enterovirus infections are self-limiting, some individuals may experience long-term health effects. Post-viral fatigue syndrome, characterized by persistent fatigue and other symptoms, can occur following an enterovirus infection. Additionally, some enterovirus infections can lead to long-term neurological complications, such as permanent neurological damage. The potential for long-term sequelae emphasizes the importance of prompt diagnosis and treatment.
Table: Economic and Social Consequences of Different Enterovirus Outbreaks
| Enterovirus Strain | Economic Consequences | Social Consequences |
|---|---|---|
| Enterovirus D68 | Significant disruption of schools and businesses, leading to lost productivity and increased healthcare costs. | Increased anxiety and stress among parents, disruption of family routines, and potential stigmatization. |
| Enterovirus 71 | Increased demand on healthcare facilities, leading to higher medical expenses and potential strain on the healthcare system. | Community-wide fear and uncertainty, potential for social unrest, and disruption of community activities. |
| Coxsackievirus A | Increased demand for healthcare services, leading to higher medical expenses. Indirect costs from lost productivity. | Increased anxiety and stress for parents, potential disruption of family routines, and social isolation for vulnerable individuals. |
Emerging Enterovirus Strains and Variants
Enteroviruses, a diverse group of viruses, are constantly evolving. This evolution, coupled with global travel and interconnected populations, leads to the emergence of new strains and variants. Understanding these emerging strains is crucial for public health preparedness and response. Recognizing patterns of emergence, potential impacts, and effective monitoring strategies are essential components in mitigating the risks associated with these new viral forms.
Identifying Emerging Strains and Variants
Emerging enterovirus strains and variants are often identified through surveillance systems. These systems track the genetic characteristics of enteroviruses circulating in different populations and geographic areas. Laboratory-based methods, such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and sequencing, play a key role in detecting these changes. The analysis of these genetic sequences allows researchers to identify new variants and determine their relationship to previously identified strains.
This process often involves comparing the genetic makeup of the new strain to existing enterovirus strains, looking for significant mutations.
Factors Driving Emergence
Several factors contribute to the emergence of new enterovirus strains. High viral replication rates and the large number of enterovirus types within a host population contribute to the potential for rapid mutation and evolution. This high mutation rate increases the likelihood of new strains arising. Additionally, the viral RNA genome, which has a high error rate during replication, contributes to the creation of new genetic variations.
Environmental conditions, such as temperature and humidity, and the host population’s immune status also play a role in determining which strains flourish. Furthermore, human behaviors, including global travel and migration, can facilitate the spread of emerging strains across different geographical regions.
Potential Impact on Public Health
The emergence of new enterovirus strains can have significant public health consequences. These consequences can vary depending on the specific strain, including the severity of the illness, the number of people affected, and the availability of effective treatments. The impact on public health can be considerable, potentially leading to outbreaks, especially if the new strain exhibits increased virulence or evades existing immunity in a population.
For example, the emergence of new poliovirus strains has historically demonstrated a substantial impact on public health.
Strategies for Monitoring and Tracking
Effective monitoring and tracking of emerging enterovirus strains are crucial for public health. Robust surveillance systems are vital for detecting new strains early, tracking their spread, and assessing their potential impact. These systems should incorporate multiple data sources, including laboratory-based surveillance data and clinical reports. Genomic sequencing, in particular, allows for the identification of mutations that could contribute to a strain’s increased transmissibility or virulence.
Characteristics of Emerging Enterovirus Strains (Table)
| Strain Name | Geographic Origin | Key Characteristics | Impact on Public Health |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enterovirus X | North America | Increased transmissibility, higher replication rate | Potential for widespread outbreaks, strain-specific complications |
| Enterovirus Y | Europe | Reduced sensitivity to existing antiviral treatments | Potential for treatment challenges, longer recovery times |
| Enterovirus Z | Asia | Unique combination of genetic mutations, new clinical symptoms | Requires further investigation, potential for novel disease presentations |
Conclusion
In conclusion, enterovirus strains present a significant public health concern, with a wide range of clinical manifestations and varied impact depending on the specific strain and the population affected. This overview has highlighted the importance of understanding the epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical presentation, and management of enterovirus infections. Further research and ongoing surveillance are crucial to address the evolving nature of these viruses and improve strategies for prevention, diagnosis, and treatment.
By understanding these viruses, we can better protect ourselves and our communities from the potential health risks they pose.