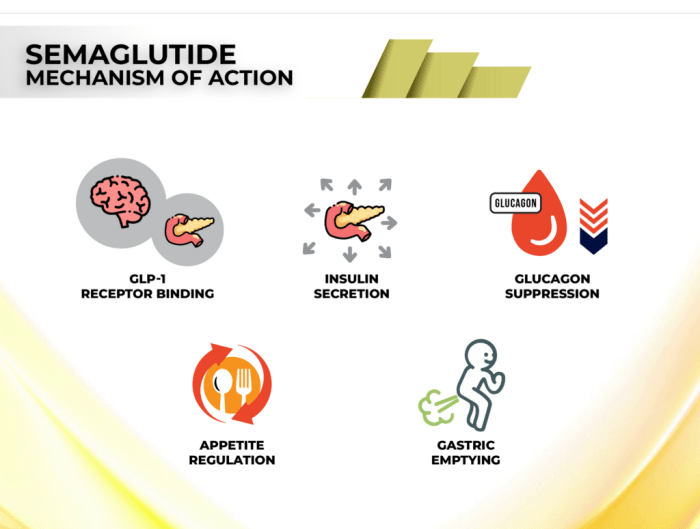
Medication changes after semaglutide can be a complex process, impacting various aspects of a patient’s health. This guide explores potential interactions, side effects, patient considerations, clinical aspects, lifestyle adjustments, and monitoring parameters. Understanding these factors is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers to navigate this transition effectively.
We’ll delve into the specifics of potential drug interactions, common side effects, and the importance of open communication between patients and doctors. This comprehensive overview provides practical insights into managing the complexities of medication changes after starting semaglutide.
Potential Interactions and Side Effects
Navigating medication changes after starting semaglutide requires careful consideration of potential interactions and side effects. This section delves into the complexities of these changes, exploring potential drug interactions, common side effects, and adjustments frequently made by healthcare professionals. Understanding these factors is crucial for patient safety and optimal treatment outcomes.
Ever wondered about medication changes after you’ve started semaglutide? It’s a common question, and understanding how your other prescriptions might need adjustment is crucial. This often intertwines with the broader issue of when prescription drugs are the right approach for heart disease. For a deeper dive into this complex topic, check out our expert’s advice on ask an expert when should prescription drugs be used to heart disease.
Ultimately, talking to your doctor about potential medication adjustments after starting semaglutide is key for a safe and effective treatment plan.
Medication Interactions
Semaglutide, a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist, can interact with various medications. These interactions can impact the effectiveness or safety of both semaglutide and the interacting drug. Careful monitoring is essential to manage these potential complications.
- Blood Pressure Medications: Some blood pressure medications, particularly those that lower blood pressure significantly, might interact with semaglutide, potentially leading to hypotension (low blood pressure). This is a particularly important consideration when adjusting doses of antihypertensive medications.
- Diabetes Medications: Semaglutide’s mechanism of action overlaps with some diabetes medications. Combining semaglutide with certain other diabetes medications can lead to increased risk of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) or other adverse effects. Careful monitoring of blood glucose levels is essential.
- Gastrointestinal Medications: Semaglutide can sometimes affect the absorption of certain gastrointestinal medications. This can influence their effectiveness. It is important to discuss any gastrointestinal medications with your doctor.
- Thyroid Medications: Semaglutide can influence thyroid function in some cases. Careful monitoring of thyroid function is essential, especially in patients with pre-existing thyroid conditions.
- Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs): PPIs can affect the absorption of semaglutide, which might affect its efficacy. The impact of this interaction can vary based on the specific PPI and dosage.
Potential Side Effects
While semaglutide is generally well-tolerated, some side effects can occur, particularly during the initial stages of treatment or when adjusting to new medications. These side effects can vary in severity and duration.
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Common gastrointestinal side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation. These effects are often mild and transient, but they can be severe in some cases. Adjusting the dose or frequency of semaglutide, or adding medications to mitigate the side effects, may be necessary.
- Endocrine Issues: Changes in thyroid function and other endocrine issues are rare but possible. Monitoring thyroid function and other relevant hormones is essential.
- Pancreatitis: Pancreatitis is a rare but serious side effect. Symptoms include severe abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Immediate medical attention is necessary.
- Kidney Problems: In some cases, semaglutide may be associated with kidney issues. It is crucial to monitor kidney function regularly, especially in patients with pre-existing kidney conditions.
Medication Adjustments After Starting Semaglutide
Adjusting medications after starting semaglutide is common. These adjustments often aim to optimize blood glucose control, manage side effects, or address potential interactions.
- Reducing or discontinuing sulfonylureas or insulin: This is a common adjustment to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia, as semaglutide can lower blood sugar levels. This reduction is often gradual and monitored closely by healthcare providers.
- Adjusting doses of other diabetes medications: Adjusting doses of other diabetes medications, such as metformin, can be necessary to balance blood sugar control with semaglutide. The specific adjustments depend on the individual’s response to semaglutide.
- Adding medications to manage side effects: Adding anti-nausea medications or other gastrointestinal remedies can help manage the side effects associated with semaglutide, like nausea or diarrhea. This approach often provides comfort and allows for better adherence to the treatment.
Comparison of Side Effects
| Medication | Common Side Effects |
|---|---|
| Semaglutide | Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, abdominal pain, headache, fatigue |
| Metformin | Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, metallic taste |
| Insulin | Hypoglycemia, weight gain, edema |
Potential Drug Interactions Table
| Medication Class | Potential Interactions with Semaglutide |
|---|---|
| Antihypertensives | Possible hypotension (low blood pressure) |
| Diabetes Medications | Increased risk of hypoglycemia, altered efficacy |
| Gastrointestinal Medications | Potential changes in absorption |
| Thyroid Medications | Potential influence on thyroid function |
| Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs) | Potential changes in absorption |
Patient Considerations and Communication
Navigating medication changes, especially after initiating a new treatment like semaglutide, requires open communication and a proactive approach from both patients and healthcare providers. Understanding the process and your role in it can make the transition smoother and more effective. This section will delve into the crucial aspects of patient-provider communication, highlighting the importance of your medical history and the factors influencing medication adjustments.Effective communication is paramount in managing your health, especially when adjustments to your medication regimen are being considered.
Open dialogue with your healthcare provider about your concerns and experiences is key to achieving optimal results.
Importance of Open Communication, Medication changes after semaglutide
A strong patient-provider relationship fosters trust and understanding, which are vital in navigating the complexities of medication changes. This allows for a collaborative approach to care, where both parties work together to ensure the best possible outcome. Clear communication prevents misunderstandings and ensures that both the patient and provider are on the same page regarding treatment goals and potential challenges.
Steps for Discussing Medication Changes
When discussing medication changes with your healthcare provider, preparation is key. Documenting your concerns, questions, and desired outcomes in advance will streamline the conversation. Actively listening to the provider’s explanations and asking clarifying questions demonstrates your commitment to understanding the changes and their rationale.
Role of Medical History in Medication Adjustments
A comprehensive medical history is crucial in determining appropriate medication adjustments. Past diagnoses, allergies, and responses to previous medications all provide valuable context for the healthcare provider. This information aids in predicting potential interactions and side effects, allowing for safer and more effective adjustments. Understanding your personal medical history enables your healthcare provider to make informed decisions that align with your unique health needs.
Factors for Healthcare Providers in Making Adjustments
When making medication adjustments after semaglutide initiation, healthcare providers must consider various factors beyond just the current medication. These include your overall health status, other medications you are taking, and potential interactions between semaglutide and other drugs. The provider also needs to consider your response to semaglutide, any side effects you’ve experienced, and the goals of your treatment.
Understanding the potential impact of these factors ensures the best possible outcome for your health.
Effective Communication of Concerns
Expressing your concerns about medication changes effectively is essential. Instead of simply stating “I don’t like this,” try to provide specific reasons. For example, “I’m concerned about the potential for increased heart rate with this new medication, given my history of palpitations.” Framing your concerns in a clear and concise manner helps the provider understand your perspective and address your anxieties.
Questions to Ask Your Doctor
A proactive approach to asking questions ensures you fully understand the rationale behind any medication changes. Consider these questions:
- What is the rationale behind this medication change?
- What are the potential benefits and risks of this new medication?
- Are there any potential interactions between this medication and other medications I’m currently taking?
- What are the expected side effects, and what should I do if I experience them?
- How long will it take for this new medication to take effect?
- How will this new medication be monitored?
- What are the alternative treatment options if this medication doesn’t work?
- How can I manage potential side effects?
- How will this medication affect my existing health conditions?
- Are there any specific dietary recommendations or lifestyle adjustments that would be beneficial with this medication?
Clinical Considerations for Healthcare Providers
Navigating medication changes after semaglutide initiation requires careful consideration of individual patient needs and potential interactions. This section Artikels the crucial criteria healthcare providers should use to evaluate the necessity of adjustments, the monitoring procedures to follow, and strategies for managing potential side effects. Understanding the long-term implications and various patient scenarios is vital for successful management.Healthcare providers must meticulously assess patients’ responses to semaglutide before considering adjustments.
Factors like weight loss progress, gastrointestinal tolerability, and overall health status need to be evaluated. Changes in blood glucose levels, blood pressure, and lipid profiles also play a significant role in determining the need for alterations. A thorough review of the patient’s medical history, including any pre-existing conditions or allergies, is paramount.
Assessing the Need for Medication Changes
Careful monitoring of patient response to semaglutide is essential. Factors such as the patient’s weight loss trajectory, side effect profile, and overall health condition should be meticulously tracked. The provider should also consider any new symptoms or changes in existing conditions. Changes in blood glucose, blood pressure, and lipid levels should be documented to aid in the decision-making process.
A patient’s medical history, including any pre-existing conditions, allergies, or medications, should be reviewed and updated as needed.
Monitoring Patients After Medication Adjustments
A structured monitoring plan is crucial after adjusting medications related to semaglutide. This plan should detail the frequency of follow-up appointments, blood tests, and vital sign checks. Specific parameters, like weight, blood glucose, blood pressure, and lipid levels, should be tracked over time. Patients should be educated on recognizing and reporting any new or worsening side effects.
Documentation of these parameters is critical for identifying trends and potential complications.
Managing Potential Side Effects
Strategies for managing potential side effects after medication changes related to semaglutide should focus on patient education and supportive interventions. For example, gradual dose adjustments and/or modifying the administration schedule can help mitigate gastrointestinal side effects. If nausea or vomiting persists, antiemetic medications may be necessary. Close monitoring and communication with the patient are vital to address any concerns promptly.
It is crucial to be prepared to address potential side effects such as thyroid issues, gallbladder problems, or pancreatitis.
Long-Term Implications of Medication Changes
Long-term implications of medication changes related to semaglutide include the potential for interactions with other medications. It’s vital to understand the long-term effects of semaglutide and its interactions with other drugs. A thorough understanding of the patient’s overall health status and medication regimen is essential for proactive management. Healthcare providers must carefully consider the potential long-term impact on various organ systems.
Patient Scenarios Requiring Medication Adjustments
Different patient scenarios might necessitate adjustments to their medication regimen after initiating semaglutide. For example, a patient with pre-existing hypertension might require adjustments to their antihypertensive medication due to changes in their blood pressure readings. Another patient experiencing severe nausea after dose escalation might require a reduction in the semaglutide dosage. Additionally, patients with underlying thyroid conditions may require monitoring of thyroid function.
Medication Interactions with Semaglutide
Understanding potential interactions between semaglutide and other medications is crucial. This table provides a summary of various medication classes and their potential interactions with semaglutide.
Navigating medication changes after semaglutide can be tricky, especially if you’re considering a career shift. If you’re thinking about becoming a surgical technologist, understanding the different procedures and steps involved is crucial. how to become a surgical technologist is a great resource to explore this field further. Ultimately, any medication adjustments after semaglutide will depend on your individual needs and your healthcare provider’s guidance.
Remember, research and open communication are key to a smooth transition.
| Medication Class | Potential Interaction | Clinical Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Antihypertensives | Possible potentiation of hypotensive effects | Monitor blood pressure closely, adjust dosages as needed |
| Diuretics | Potential for electrolyte imbalances | Monitor electrolytes regularly, consider potassium supplementation |
| Anti-diabetic agents | Potential for altered blood glucose control | Monitor blood glucose levels closely, adjust dosages as needed |
| Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs) | May decrease absorption of semaglutide | Consider administering semaglutide at least 1 hour before or 4 hours after PPI intake |
| Other medications affecting GI motility | Potential for increased or decreased absorption | Adjust administration times as needed to maximize absorption and minimize GI discomfort |
Lifestyle Adjustments and Dietary Considerations: Medication Changes After Semaglutide
Semaglutide, often used for weight management, interacts with various lifestyle factors. Understanding how dietary changes and exercise impact medication adjustments is crucial for optimizing treatment outcomes. This section delves into the intricate relationship between diet, exercise, stress, and semaglutide’s effectiveness, offering practical advice for patients.Dietary changes play a significant role in managing the effects of semaglutide and adjusting dosages.
A balanced diet, alongside consistent exercise, can either enhance or hinder the medication’s impact. Understanding these nuances is key to achieving sustained weight loss and overall well-being.
Dietary Modifications for Optimal Medication Adjustment
Dietary modifications can significantly influence how the body processes semaglutide. Certain dietary patterns can enhance or hinder the medication’s effects. The goal is to create a supportive environment for the medication to work optimally.
- A balanced diet rich in whole foods, fruits, and vegetables, coupled with controlled portion sizes, can contribute to a healthier response to semaglutide. This supports sustained weight loss and minimizes potential side effects.
- Reducing processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats is crucial. These foods often lead to rapid blood sugar fluctuations, potentially impacting medication efficacy.
- Increasing fiber intake can promote satiety, leading to better appetite control. Fiber-rich foods also aid in digestion, which can be important when adjusting to a new medication.
Impact of Lifestyle Factors on Medication Changes
Lifestyle factors like exercise, stress levels, and sleep quality can modulate the body’s response to semaglutide. Consistent exercise, alongside a balanced diet, is a cornerstone of a successful treatment plan.
Adjusting medications after a semaglutide course can sometimes lead to unexpected side effects. One such potential issue is an allergic reaction, particularly on the face. This could manifest as swelling, redness, or itching, mirroring other skin reactions. If you experience these changes after altering your medication regimen, it’s crucial to consult a doctor immediately. Remember, understanding the potential for a reaction like an allergic reaction on the face, like this one , is part of responsible medication management following semaglutide.
Your doctor will guide you through the best approach to manage any adjustments and ensure your well-being.
- Regular exercise helps to burn calories, enhance insulin sensitivity, and support weight loss, all of which can affect semaglutide’s effectiveness.
- Chronic stress can negatively impact metabolism and lead to increased cortisol levels. This can sometimes interfere with weight loss efforts and potentially necessitate medication adjustments.
- Adequate sleep is crucial for hormone regulation and metabolic processes. Sleep deprivation can disrupt the body’s natural rhythms, which can influence how the body responds to semaglutide.
Dietary Patterns and Medication Responses
Different dietary patterns can impact how patients respond to semaglutide. Individual responses to the medication can vary significantly depending on factors such as overall health and pre-existing conditions.
- Low-carbohydrate diets may result in faster weight loss in some individuals, potentially influencing the need for semaglutide dosage adjustments.
- Mediterranean diets, rich in fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats, have shown positive associations with weight management and can complement semaglutide therapy.
- High-protein diets may also influence the efficacy of semaglutide by promoting satiety and preserving lean body mass.
Patient Education for Optimal Outcomes
Patient education on lifestyle modifications is essential to optimize medication outcomes. Providing clear instructions and support is key to achieving successful results. This education should encompass practical advice and support for long-term adherence.
- Clear communication about the importance of dietary modifications and exercise is crucial for patient engagement and adherence.
- Educational materials, including handouts and online resources, can reinforce these concepts and provide accessible information.
- Regular follow-up appointments allow for personalized guidance and support, addressing any challenges or questions that may arise during the adjustment period.
Potential Dietary Considerations and Their Influence on Medication Adjustments
| Dietary Consideration | Influence on Medication Adjustments |
|---|---|
| High-fat, low-fiber diet | May hinder weight loss, potentially requiring dosage adjustments or lifestyle modifications. |
| Balanced diet with controlled portions | Generally supports weight loss, potentially minimizing the need for dosage adjustments. |
| High-protein, low-carbohydrate diet | May accelerate weight loss, possibly influencing semaglutide dosage adjustments. |
| Stressful lifestyle | May negatively impact medication response and require addressing stress levels for optimal results. |
| Regular exercise | Enhances medication efficacy, potentially leading to more favorable weight loss outcomes. |
Monitoring and Evaluation
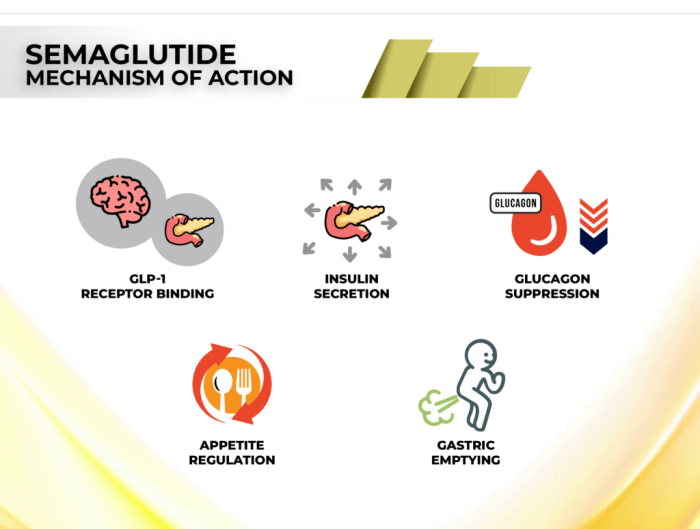
Post-semaglutide medication adjustments require meticulous monitoring to ensure efficacy and safety. Close observation allows healthcare providers to fine-tune treatment plans, address any emerging issues, and ultimately optimize patient outcomes. This vigilance is crucial, as the impact of medication changes can vary significantly between individuals.Monitoring parameters and frequency are key factors in determining the effectiveness and safety of the adjustments.
Effective monitoring facilitates proactive intervention and avoids potential complications. Understanding the role of laboratory tests and evaluating the effectiveness of the adjustments is also vital.
Monitoring Parameters for Medication Adjustments
Effective monitoring of patients after medication changes related to semaglutide necessitates a systematic approach. This includes regular assessments of key parameters to gauge the impact of the adjustments on patient health. This allows for timely interventions and ensures patient safety and optimal outcomes.
- Weight: Regular weight measurements are essential to track the effectiveness of the medication in achieving weight loss goals. Significant fluctuations or plateaus may indicate a need for adjustments to the treatment plan. For example, if a patient’s weight loss stalls after a medication adjustment, the healthcare provider can investigate potential underlying causes and modify the regimen accordingly.
Weight loss should be gradual and sustainable.
- Blood Glucose Levels: Monitoring blood glucose levels is critical, particularly for patients with pre-existing diabetes or those at risk. Changes in semaglutide dosage can influence glucose control, and consistent monitoring helps prevent complications. Regular testing can reveal how the adjustments affect glucose management. A patient experiencing hypoglycemia after a dosage increase, for instance, might require a dose reduction or dietary modifications.
- Blood Pressure: Monitoring blood pressure is crucial as some medications can affect blood pressure. Regular checks are essential to identify any potential hypertension or hypotension issues and adjust the medication as needed. Blood pressure fluctuations following medication changes should be carefully noted to ensure the patient’s cardiovascular health.
- Adverse Events: A thorough review of reported adverse events is vital. This includes noting the frequency, severity, and duration of any side effects. Detailed documentation is essential to promptly address any emerging problems. For instance, if a patient experiences persistent nausea after a dose increase, the provider can adjust the medication or implement supportive measures.
Frequency of Monitoring
The frequency of monitoring after medication adjustments depends on several factors, including the patient’s baseline health, the nature of the adjustment, and the specific medication involved. Establishing a tailored monitoring schedule ensures timely intervention while minimizing unnecessary testing.
- Initial Period: The first few weeks following a medication change require more frequent monitoring to detect any immediate reactions or changes. This ensures early detection of potential complications.
- Stable Period: Once the patient’s condition stabilizes, the frequency of monitoring can be reduced to less frequent visits or home monitoring. This approach optimizes patient care by reducing the burden of frequent appointments and testing.
- Patient Factors: Patients with pre-existing conditions or those experiencing more pronounced side effects may require more frequent monitoring than those without such issues.
Evaluation of Medication Effectiveness
Evaluating the effectiveness of medication adjustments requires a comprehensive approach that goes beyond just the observed parameters. This necessitates a careful assessment of the impact on the patient’s overall well-being.
- Patient Reports: Patient feedback plays a crucial role in evaluating the effectiveness of the adjustments. Regular communication with patients about their experiences and symptoms provides valuable insights into the impact of the changes.
- Objective Measures: Objective measures, such as weight loss, blood glucose control, and blood pressure stabilization, provide concrete evidence of the medication’s effectiveness.
Potential Complications of Inappropriate Medication Changes
Inappropriate medication changes can lead to a variety of complications. These range from mild side effects to more severe health issues. Properly managing the transition period minimizes these risks.
- Adverse Reactions: Inappropriate changes can lead to severe adverse reactions, necessitating immediate medical intervention.
- Treatment Ineffectiveness: Adjustments that do not effectively address the underlying condition can lead to a lack of improvement or even deterioration.
Role of Laboratory Tests
Laboratory tests are essential tools for evaluating the impact of medication changes. They provide objective data on various physiological parameters, enabling a more accurate assessment of the patient’s response to treatment.
- Monitoring Kidney and Liver Function: Laboratory tests can assess kidney and liver function, ensuring that these vital organs are not being adversely affected by the medication changes.
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): A CBC helps identify any potential hematological complications related to the medications.
Monitoring Parameters and Frequency Table
| Monitoring Parameter | Frequency (Initial Period) | Frequency (Stable Period) |
|---|---|---|
| Weight | Weekly | Monthly |
| Blood Glucose | Daily | Weekly |
| Blood Pressure | Weekly | Monthly |
| Adverse Events | Daily | Weekly |
Ending Remarks
In conclusion, medication changes after semaglutide require careful consideration of potential interactions, side effects, and patient factors. Open communication, thorough monitoring, and understanding lifestyle impacts are vital for successful management. This guide aims to empower both patients and healthcare providers with the knowledge needed to navigate this process effectively, ensuring optimal health outcomes.