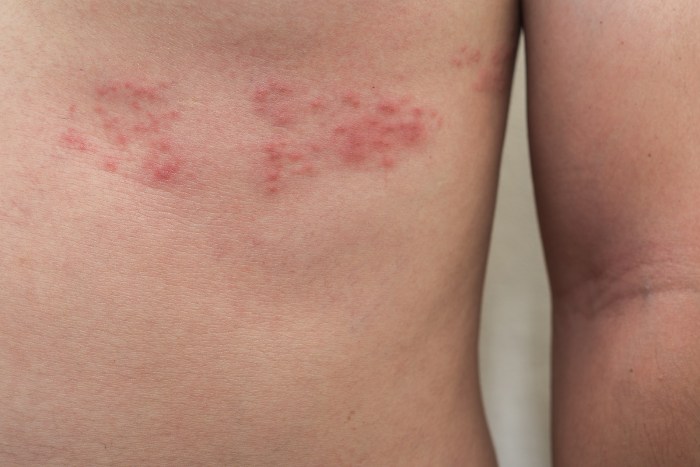
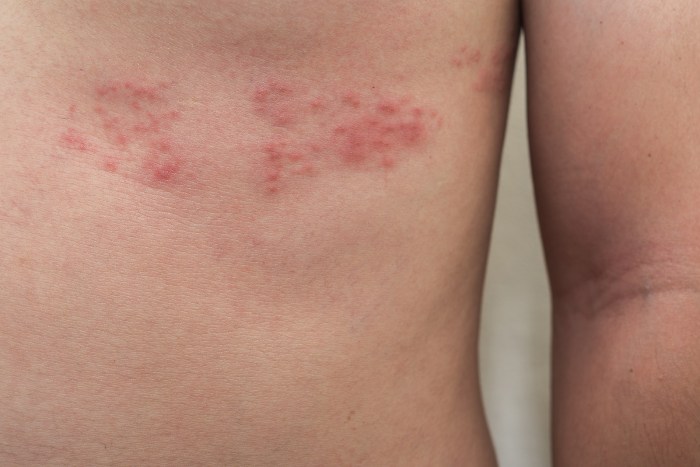
Shingles vaccine side effects can range from mild discomfort to more serious reactions. Understanding the potential effects, from common soreness to rare allergic responses, is crucial for making informed decisions about your health. This comprehensive guide explores the spectrum of side effects, from the most frequent to the less common but potentially serious, empowering you to navigate this important health topic with confidence.
This article provides a detailed overview of the potential side effects associated with shingles vaccines. We’ll examine common reactions, less frequent but serious complications, and strategies for managing them. We also address the importance of vaccine safety and how different vaccines might affect various individuals. Plus, we’ll look at interactions with other medications and offer information tailored to specific populations like the elderly and pregnant women.
Overview of Shingles Vaccine
The shingles vaccine is a crucial preventive measure against herpes zoster, the virus that causes shingles. This painful and sometimes debilitating skin rash can affect individuals of all ages, but the risk increases significantly with advancing years. Vaccination significantly reduces the risk of developing shingles and its complications.The vaccine works by introducing a weakened or inactive form of the varicella-zoster virus (VZV) into the body.
This prompts the immune system to create antibodies against the virus. These antibodies are then ready to fight off a future infection if exposure occurs. This anticipatory defense mechanism is a cornerstone of preventive medicine.
Available Shingles Vaccines
Several effective shingles vaccines are currently available, each with subtle differences in formulation and target populations. Understanding these differences is crucial for making informed decisions about vaccination.
| Vaccine Name | Purpose | Administration Method | Target Population |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shingrix | Provides protection against shingles. | Two injections, typically two to six months apart. | Adults aged 50 years and older. |
| Zostavax | Offers protection against shingles. | One injection. | Adults aged 50 to 60. |
Administration Schedule
The administration schedule for shingles vaccines varies depending on the specific vaccine chosen. Adherence to the recommended schedule is vital for optimal efficacy.
- Shingrix typically involves two injections, spaced two to six months apart. This two-dose regimen is designed to maximize immune response and long-term protection.
- Zostavax, in contrast, requires only a single injection.
Vaccine Selection and Considerations
Factors such as age, overall health, and prior vaccination history play a crucial role in determining the most appropriate vaccine choice. Consulting with a healthcare professional is essential for personalized recommendations. Healthcare providers can assess individual needs and guide patients towards the best vaccination strategy.
Common Side Effects
Getting vaccinated is a proactive step towards protecting your health, and while the benefits generally outweigh the risks, understanding potential side effects is crucial for informed decision-making. The shingles vaccine, like other vaccines, can trigger some mild to moderate reactions in some individuals. These reactions are usually temporary and resolve on their own without requiring medical intervention.Knowing what to expect can help you manage any discomfort and ensure you’re taking the right steps if anything seems unusual.
This section details the most common side effects associated with the shingles vaccine, their severity, and duration, providing a comprehensive understanding of the potential reactions.
Injection Site Reactions
A significant portion of vaccine recipients experience reactions directly at the injection site. These localized reactions are typically mild and temporary.
- Pain: Pain at the injection site is one of the most frequent side effects. It often manifests as a dull ache or sharp pain, ranging from mild to moderate in intensity. The pain usually subsides within a few days.
- Swelling: Swelling at the injection site is another common reaction. It may appear as a slight puffiness or a noticeable enlargement. The swelling typically resolves within a week.
- Redness: Redness is a frequent sign of inflammation at the injection site. The area may appear flushed or discolored. The redness generally fades within a few days.
Systemic Reactions
Some individuals may experience side effects beyond the injection site, affecting the whole body. These systemic reactions, while less common than local reactions, are still important to be aware of.
- Fatigue: Fatigue, or feeling unusually tired, is a possible systemic reaction. It’s often mild and can last for a few hours or a day. In some cases, fatigue might persist for a couple of days, but it usually resolves on its own.
- Headache: A headache is another possible systemic reaction, usually mild to moderate in intensity. It typically lasts for a day or two.
- Muscle aches: Muscle aches or soreness are a potential side effect. These are usually mild and temporary.
Frequency of Side Effects
The following table provides a comparison of the frequency of different side effects associated with the shingles vaccine. It’s important to note that these are general estimates, and individual experiences may vary.
| Side Effect | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Pain at injection site | Common |
| Swelling at injection site | Common |
| Redness at injection site | Common |
| Fatigue | Less Common |
| Headache | Less Common |
| Muscle aches | Less Common |
Less Common but Serious Side Effects
While most people experience only mild side effects from the shingles vaccine, some individuals may experience more serious, though less frequent, reactions. Understanding these potential complications is crucial for making informed decisions about your health. This section details the less common but serious side effects and emphasizes the importance of immediate medical attention if you notice anything unusual.
While researching shingles vaccine side effects, I stumbled upon some interesting information about itchy scalp at night. It turns out, some of the same underlying factors that can cause an itchy scalp at night, like certain allergies or even stress, might play a role in some shingles vaccine side effects. For a deeper dive into itchy scalp issues, check out this helpful resource on itchy scalp at night causes prevention and treatment.
Thankfully, most shingles vaccine side effects are mild and short-lived, but understanding potential connections can be reassuring.
Potential Allergic Reactions
Allergic reactions to the shingles vaccine, although rare, can be serious. These reactions typically manifest quickly after vaccination. Common symptoms include hives, swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat, difficulty breathing or swallowing, and a rapid heartbeat. It is important to remember that an allergic reaction can range in severity from mild to life-threatening.
While shingles vaccines generally have mild side effects like soreness at the injection site, some people experience more significant reactions. Interestingly, a related question often comes up, which is whether supplements like fish oil can influence cholesterol levels. For a deeper dive into that topic, check out this article on does fish oil lower cholesterol.
Ultimately, though, the best way to understand the potential side effects of the shingles vaccine is to discuss them with your doctor.
Importance of Immediate Reporting
If you experience any unusual or concerning symptoms after receiving the shingles vaccine, such as those mentioned above or any other unexpected reactions, seek immediate medical attention. Prompt reporting allows healthcare professionals to assess the situation and provide appropriate treatment, potentially preventing complications. Don’t hesitate to call your doctor or go to the nearest emergency room if you have any concerns.
So, I’ve been reading up on shingles vaccine side effects lately, and while some people experience mild reactions like soreness, others have reported more significant issues. It got me thinking about how different skin conditions can react to sun exposure, like eczema. Understanding how eczema and sun exposure interact is crucial for anyone with the condition, as it can affect treatment and overall well-being.
For example, eczema and sun exposure can sometimes lead to flare-ups, so it’s important to be aware of the relationship. Ultimately, though, the shingles vaccine side effects are something to keep a close eye on, regardless of other skin conditions.
Table of Less Common Side Effects
Recognizing potential side effects and understanding the appropriate actions is vital for your well-being. The following table provides a summary of less common, but serious, side effects, their potential symptoms, and the recommended actions.
| Side Effect | Symptoms | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Allergic Reaction | Hives, swelling of face/lips/tongue/throat, difficulty breathing/swallowing, rapid heartbeat, lightheadedness, loss of consciousness | Immediately seek emergency medical attention (call 911 or go to the nearest emergency room). |
| Severe Pain at Injection Site | Intense, persistent pain, redness, swelling, and/or warmth at the injection site that doesn’t improve within a few days. | Contact your healthcare provider for evaluation and potential treatment. |
| Severe Headache or Fever | A persistent and severe headache accompanied by a high fever (above 101°F or 38.3°C) that lasts for more than a day. | Contact your healthcare provider immediately. |
| Severe Dizziness or Lightheadedness | Dizziness or lightheadedness that is severe enough to cause loss of balance or fainting. | Seek immediate medical attention. |
| Seizures | Uncontrolled muscle spasms or convulsions. | Immediately seek emergency medical attention (call 911 or go to the nearest emergency room). |
Side Effect Management
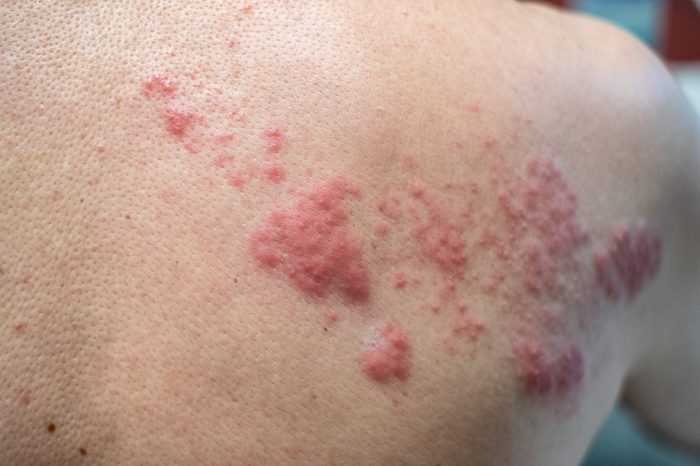
Managing the potential side effects of the shingles vaccine is crucial for a smooth recovery. While most side effects are mild and temporary, understanding how to address them effectively can significantly enhance your comfort and well-being. Knowing when to seek medical attention is equally important to ensure prompt and appropriate care for any serious reactions.Effective management of vaccine side effects involves a proactive approach, encompassing both self-care strategies and recognizing when professional medical intervention is necessary.
This approach will empower you to navigate the post-vaccination period with confidence and minimize any discomfort.
Managing Mild Side Effects
Mild side effects, such as soreness, redness, or swelling at the injection site, are common after vaccination. These are often temporary and can be effectively managed at home.
- Applying a cool compress or ice pack to the injection site for 15-20 minutes at a time can help reduce inflammation and discomfort. Repeat as needed, but avoid prolonged application to prevent tissue damage.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers, like ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help alleviate aches and pains. Always follow the dosage instructions carefully on the medication packaging.
- Elevating the affected limb (if applicable) can also reduce swelling and promote circulation.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While most side effects are manageable at home, some warrant immediate medical attention. Serious or persistent reactions require prompt evaluation by a healthcare professional.
- Seek immediate medical care if you experience difficulty breathing, severe dizziness, or a rapid heartbeat.
- If the injection site becomes excessively swollen, warm, or shows signs of infection (e.g., pus, redness spreading beyond the injection site), consult a healthcare professional.
- Persistent fever, severe headache, or other systemic symptoms, such as body aches or nausea, that don’t improve with home remedies, should be evaluated by a medical professional.
- If you experience any allergic reaction, including hives, swelling of the face or throat, or difficulty swallowing, immediately seek emergency medical attention.
Following Up with Your Healthcare Professional
Following up with your healthcare provider after vaccination is essential. This allows for monitoring and ensures any potential complications are addressed promptly.
- Schedule a follow-up appointment as recommended by your doctor to discuss any concerns or unusual symptoms that may arise after vaccination.
- Be prepared to discuss the specifics of your symptoms, their duration, and any other relevant medical history during your follow-up visit.
Step-by-Step Guide for Managing Common Side Effects
This guide provides a structured approach to managing common side effects, promoting a smooth post-vaccination recovery.
- Assessment: Immediately after vaccination, note the location and severity of any discomfort or reactions.
- Cooling: Apply a cool compress or ice pack to the injection site for 15-20 minutes, several times a day, if soreness or swelling is present.
- Pain Relief: If discomfort persists, consider taking over-the-counter pain relievers according to the recommended dosage instructions.
- Monitoring: Continue to monitor the injection site for any signs of infection (redness, swelling, warmth, or pus).
- Follow-up: Schedule a follow-up appointment as directed by your healthcare provider.
Vaccine Safety
The shingles vaccine, like all vaccines, undergoes rigorous testing and review to ensure its safety and effectiveness. This process, while meticulous, is designed to identify potential issues and mitigate risks before widespread use. Understanding the steps involved in vaccine development and approval provides a foundation for evaluating the overall safety profile of the shingles vaccine.
Safety Testing and Approval Process
The development of a shingles vaccine involves multiple phases of clinical trials. Phase 1 trials focus on safety and dosage, while Phase 2 trials expand the study group to further evaluate safety and effectiveness. Phase 3 trials, involving a larger group of participants, are crucial for confirming the vaccine’s effectiveness and safety in a diverse population. Data from these trials, along with rigorous analyses of potential side effects, are reviewed by regulatory agencies like the FDA (in the US) and similar bodies globally.
This rigorous review process ensures that the vaccine meets stringent safety standards before it is approved for widespread use.
Overall Safety Profile
Based on extensive clinical trials and post-marketing surveillance, the shingles vaccine demonstrates an excellent safety profile. While mild to moderate side effects are possible, serious adverse events are rare. Data consistently shows a favorable risk-benefit ratio, meaning the benefits of preventing shingles and its complications outweigh the potential risks of vaccine side effects.
Risk Comparison: Vaccine vs. Shingles
The risk of developing shingles is significantly higher than the risk of experiencing serious side effects from the vaccine. Shingles can lead to debilitating pain, nerve damage, and potentially serious complications, such as pneumonia or eye infections. The shingles vaccine, while having some potential side effects, dramatically reduces the likelihood of contracting shingles and its associated complications. The vaccine offers a proactive and preventative approach to a condition that can have a substantial negative impact on health and quality of life.
Measures Ensuring Vaccine Safety and Efficacy
Several measures are implemented to ensure the safety and efficacy of the shingles vaccine. These include rigorous quality control of the manufacturing process, ongoing monitoring of vaccine safety post-approval, and continuous research to further understand the vaccine’s effects. The commitment to ongoing monitoring and research ensures that any potential safety concerns are addressed promptly. Additionally, the development of vaccines often involves collaboration between scientists, researchers, and regulatory bodies, with a focus on gathering comprehensive data from various perspectives to optimize safety and effectiveness.
Comparing Different Shingles Vaccines
Different shingles vaccines are available, each with its own characteristics regarding side effects and effectiveness. Understanding the differences between these vaccines can help individuals make informed decisions about which vaccine is best suited for their needs. This comparison focuses on the currently available vaccines, highlighting potential variations in their side effect profiles and efficacy.Several factors influence the choice of a shingles vaccine.
Patient age, health conditions, and prior reactions to vaccines are crucial considerations. The specific side effects experienced can vary from person to person, even with the same vaccine.
Side Effect Profiles Across Shingles Vaccines
Different shingles vaccines may elicit varying degrees and types of side effects. This difference stems from the distinct formulations and manufacturing processes used in each vaccine. Understanding these nuances is vital for personalized vaccine selection.
- Shingles vaccines typically involve the use of either live attenuated or inactivated virus components. This difference in virus type might influence the overall side effect profile, with live attenuated vaccines potentially causing milder, more localized reactions compared to inactivated vaccines.
- The dose and administration method of the vaccine also contribute to the side effect profile. Different vaccines may utilize various dose levels or administration routes, leading to potentially different frequencies and severities of reactions.
- The composition of adjuvants, substances added to vaccines to enhance their immune response, can also affect side effect profiles. Different adjuvants might trigger different types of reactions in some individuals.
Efficacy and Safety Considerations
Efficacy and safety data for each shingles vaccine are crucial factors to consider. The scientific evidence supporting each vaccine’s effectiveness and safety profile is critical for informed decision-making.
- The effectiveness of each vaccine is measured by its ability to prevent shingles and postherpetic neuralgia (PHN). Studies comparing the effectiveness of different vaccines provide valuable insights into their potential benefits.
- The safety of each vaccine is evaluated based on the frequency and severity of adverse events reported in clinical trials and post-market surveillance. These data are used to assess the risk-benefit ratio of each vaccine.
- Rigorous clinical trials and ongoing monitoring play a vital role in assessing the long-term safety and efficacy of shingles vaccines.
Comparative Table of Shingles Vaccines
The table below summarizes the key differences in side effect profiles and efficacy among the currently available shingles vaccines. This table should not be considered exhaustive and individual patient circumstances should be considered in conjunction with a physician.
| Vaccine | Common Side Effects | Less Common but Serious Side Effects | Efficacy | Safety Data |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shingrix | Pain, redness, swelling at injection site; fatigue, headache, muscle aches | Allergic reactions, Guillain-Barré syndrome (very rare) | High efficacy in preventing shingles and postherpetic neuralgia | Extensive clinical trials demonstrate a strong safety profile. |
| Zostavax | Pain, redness, swelling at injection site; fever, headache, fatigue | Allergic reactions, skin reactions, neurological complications (very rare) | Demonstrated efficacy in preventing shingles | Data available from clinical trials; less extensive data compared to Shingrix. |
Interactions with Other Medications: Shingles Vaccine Side Effects
Understanding potential interactions between the shingles vaccine and other medications is crucial for ensuring both the vaccine’s effectiveness and your safety. Many medications can impact how your body responds to the vaccine, potentially affecting the immune response to the virus. Therefore, comprehensive disclosure of all medications you are taking is essential for your healthcare provider to make an informed decision about your vaccination.
Potential Interactions and Their Effects
Interactions can impact the effectiveness of the vaccine, potentially reducing its ability to prevent shingles. Some medications might also increase the risk of side effects, or alter the way the vaccine’s components are processed in the body. This is particularly relevant for individuals on immune-suppressing medications, as these can affect the body’s ability to mount an appropriate immune response.
Importance of Disclosure
Thorough disclosure of all medications is paramount. This includes prescription drugs, over-the-counter medications, supplements, and herbal remedies. Your healthcare provider needs this information to assess potential risks and determine if the vaccine is suitable for you. Even seemingly harmless over-the-counter medications can interact with the vaccine. Failing to disclose all medications can lead to complications or compromise the vaccine’s effectiveness.
Medications Potentially Interacting with the Shingles Vaccine
Several medications may interact with the shingles vaccine. It’s crucial to remember that this is not an exhaustive list, and your healthcare provider will assess your individual circumstances.
- Immunosuppressants:
- These medications, used to suppress the immune system (e.g., for organ transplant recipients or those with autoimmune diseases), can significantly affect the vaccine’s efficacy. The body’s ability to mount an immune response is diminished, potentially reducing the effectiveness of the vaccine in preventing shingles.
- Certain antiviral medications:
- In some cases, concurrent use of antiviral medications may impact the vaccine’s effectiveness. The interplay of different antiviral mechanisms might alter the vaccine’s response.
- Steroid medications:
- High doses of corticosteroids (steroids) can suppress the immune system, potentially affecting the vaccine’s ability to elicit an adequate immune response. This can impact the vaccine’s effectiveness in preventing shingles.
- Some Antibiotics:
- Certain antibiotics might impact the immune response, though this is less common. Your healthcare provider can assess whether your specific antibiotic may pose a concern.
Information for Specific Populations
Understanding the nuances of shingles vaccination is crucial for ensuring optimal protection and safety for everyone. Different demographics, including the elderly, pregnant women, and those with underlying health conditions, may have unique considerations regarding the vaccine’s effectiveness and potential side effects. This section delves into those specific needs.
Considerations for the Elderly
The elderly population often faces a unique set of circumstances when it comes to vaccinations. Their immune responses may be less robust, and they may have other health conditions that influence the decision to receive a shingles vaccine. Age-related factors can affect the vaccine’s efficacy and potential side effects.
- Reduced immune response: The elderly may not mount the same robust immune response to the shingles vaccine as younger adults. This can potentially impact the vaccine’s effectiveness in preventing shingles. However, the vaccine still offers substantial protection even in this demographic. For instance, older adults often experience a reduced immune response to any vaccine, but still benefit from protection.
- Co-existing health conditions: Many elderly individuals have other health conditions. Some medical conditions can interact with the vaccine, necessitating careful consideration. Pre-existing conditions, such as heart disease, diabetes, or autoimmune disorders, should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
- Medication interactions: Medications taken by elderly patients might influence how the vaccine works or increase the risk of side effects. A thorough review of current medications is crucial before vaccination.
Considerations for Pregnant Women, Shingles vaccine side effects
Pregnant women have unique physiological changes that can influence the effectiveness and safety of vaccines. The decision to receive the shingles vaccine during pregnancy should be made in consultation with a healthcare provider.
- Limited data: Studies on the vaccine’s safety during pregnancy are limited. Therefore, healthcare providers prioritize a risk-benefit assessment based on individual circumstances.
- Potential benefits outweigh risks: While data is limited, the potential benefits of shingles prevention for both the mother and the infant typically outweigh any potential risks associated with vaccination during pregnancy. In most cases, the benefits of preventing shingles far outweigh the potential risks for both the mother and the baby.
- Consult healthcare providers: Healthcare providers are best equipped to assess the specific needs of each pregnant woman and provide personalized recommendations.
Considerations for Individuals with Underlying Health Conditions
Individuals with underlying health conditions may have specific concerns about the shingles vaccine. Careful evaluation and consideration are necessary to ensure safety and efficacy.
| Population Group | Specific Considerations |
|---|---|
| Individuals with weakened immune systems | Individuals with compromised immune systems, such as those undergoing chemotherapy or with HIV, may need a different vaccine dose or schedule. Their immune response may be significantly altered. |
| Individuals with autoimmune disorders | Autoimmune disorders can potentially interact with the vaccine. The impact on the vaccine’s effectiveness and the possibility of adverse reactions should be discussed with the healthcare provider. |
| Individuals with severe allergies | Individuals with severe allergies to vaccine components should not receive the vaccine. An allergy to a vaccine component can trigger a serious reaction. Always disclose any allergies to the healthcare provider. |
Information for Healthcare Providers
This section provides crucial information for healthcare providers administering the shingles vaccine. Understanding administration guidelines, potential side effects, and appropriate management strategies is paramount for ensuring patient safety and optimal outcomes. Proper monitoring and intervention can significantly mitigate adverse events and enhance patient satisfaction.Effective management of vaccine-related side effects requires a nuanced approach, taking into account individual patient factors, pre-existing conditions, and the specific vaccine administered.
This section will Artikel procedures for managing side effects in various patient populations and provide guidance on recognizing and managing potential adverse reactions.
Shingles Vaccine Administration Guidelines
Proper administration techniques are essential to ensure vaccine efficacy and minimize the risk of complications. Adherence to recommended dosage and injection sites is crucial. Ensure the vaccine is stored and handled according to manufacturer guidelines to maintain its potency. Documentation of administration details, including date, time, lot number, and site of injection, is vital for tracking and potential future reference.
Monitoring for Side Effects
Post-vaccination monitoring is essential to detect and manage any adverse reactions promptly. This includes vigilant observation for local reactions (redness, swelling, pain at the injection site) and systemic reactions (fever, fatigue, headache). Detailed patient history, including any allergies or pre-existing medical conditions, is vital for anticipating potential complications. A standardized protocol for documenting and recording observed side effects is recommended.
Managing Side Effects in Different Patient Populations
Managing side effects varies based on the patient population. For example, elderly patients may exhibit different reactions compared to younger adults. Patients with pre-existing medical conditions, such as those with compromised immune systems, may require additional monitoring. Tailoring management strategies to individual patient needs is crucial. For instance, patients experiencing mild pain at the injection site may benefit from over-the-counter pain relievers, while those experiencing more severe reactions may require closer observation and potentially different interventions.
Recognizing and Managing Potential Adverse Reactions
Understanding the spectrum of potential adverse reactions is crucial for timely intervention. Recognizing symptoms such as severe allergic reactions (anaphylaxis) requires immediate action. A clear understanding of the different severity levels of reactions is essential for appropriate management. In cases of anaphylaxis, immediate administration of epinephrine and referral to an emergency department are critical.
Flowchart for Managing Side Effects
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1. Observe Patient | Monitor for local and systemic reactions, including injection site tenderness, redness, swelling, fever, fatigue, or headache. |
| 2. Assess Severity | Evaluate the intensity and duration of any observed side effects. |
| 3. Document Findings | Record the time, nature, and severity of the reaction in the patient’s medical record. |
| 4. Determine Appropriateness of Intervention | Based on the severity, consult with medical guidelines and consider if over-the-counter medication, close monitoring, or referral to a specialist is necessary. |
| 5. Administer Appropriate Intervention | If indicated, administer over-the-counter pain relievers or provide supportive care. |
| 6. Monitor Patient | Continue to monitor for any worsening of symptoms or new developments. |
| 7. Refer to Specialist | Refer to a specialist if the side effect is severe or concerning, such as anaphylaxis. |
Concluding Remarks
In conclusion, while shingles vaccines are generally safe and effective, understanding their potential side effects is essential. This guide equips you with knowledge to make well-informed decisions about your health. Remember, always consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice and to address any concerns about shingles vaccines or their potential side effects. This comprehensive resource empowers you to navigate the process with confidence.