Esophagus function and conditions are a fascinating aspect of human physiology. This exploration delves into the intricate workings of the esophagus, from its anatomy and structure to the various disorders that can affect it. We’ll examine the normal processes of swallowing, motility, and secretions, and then dive into specific conditions like GERD and esophageal cancer. We’ll also cover the diagnostic tools and treatment options available.
Understanding the esophagus is crucial for comprehending the overall digestive process. Its role in transporting food from the mouth to the stomach is fundamental, and any disruption in this pathway can have significant consequences. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview, covering everything from the basic anatomy to complex medical conditions, so readers can gain a deeper understanding of the esophagus and its importance.
Esophageal Anatomy and Structure
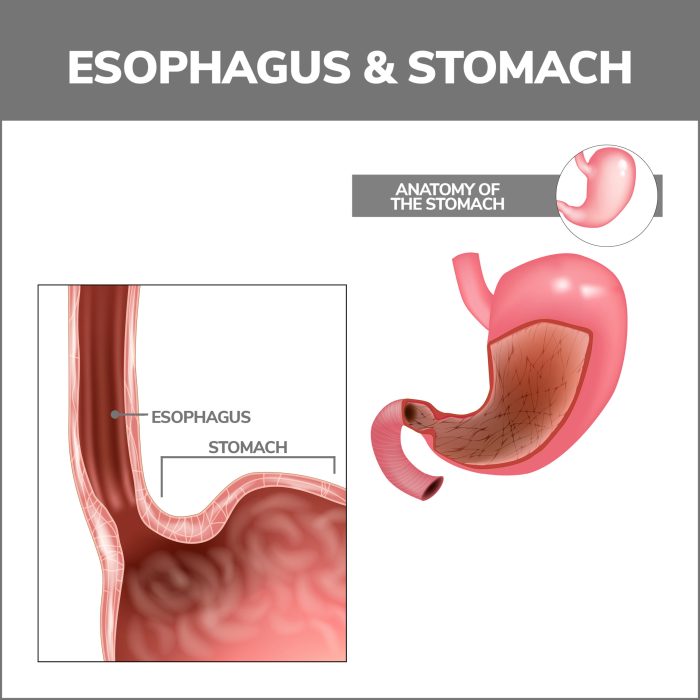
The esophagus, a muscular tube connecting the pharynx to the stomach, plays a crucial role in the digestive process. Understanding its structure and function is vital for comprehending various esophageal conditions. This section delves into the esophagus’s anatomy, from its location and length to the intricate layers of its wall and the critical role of sphincters in controlling its activity.The esophagus, approximately 10 inches (25 cm) long in adults, descends through the thorax, posterior to the trachea, and pierces the diaphragm before reaching the stomach.
Its precise location and the surrounding structures are important for understanding the potential sites of compression or injury.
Esophageal Location and Dimensions
The esophagus’s course through the thorax is crucial for its function. Its location, posterior to the trachea, allows for safe passage of food while avoiding interference with the airway. The length of the esophagus varies slightly among individuals, but the average adult esophagus is approximately 10 inches (25 cm) in length.
Layers of the Esophageal Wall
The esophageal wall, like that of other tubular organs in the digestive tract, is composed of four distinct layers. These layers work in concert to facilitate the transport of food and protect against mechanical and chemical stresses.
- The mucosa, the innermost layer, is a thin layer of epithelium that lines the lumen. It is responsible for secreting mucus, which lubricates the passage of food. It also plays a role in absorbing nutrients and protecting against pathogens.
- The submucosa, lying beneath the mucosa, contains connective tissue, blood vessels, and nerves. This layer supports the mucosa and provides nourishment to the surrounding tissues. Its elastic nature contributes to the esophagus’s ability to expand and contract.
- The muscularis, the middle layer, is composed of smooth muscle fibers arranged in circular and longitudinal layers. These layers work together to propel food downwards through peristalsis. This process is critical for efficient swallowing and digestion.
- The adventitia or serosa, the outermost layer, is a thin layer of connective tissue. In the thoracic portion, the adventitia is present. In the abdominal portion, the serosa (a specialized form of adventitia) lines the esophagus, which is covered by a mesothelial layer, providing a smooth surface that reduces friction during movement.
Comparison to Other Digestive Tract Organs
The following table provides a concise comparison of the esophageal structure to other parts of the digestive tract:
| Feature | Esophagus | Stomach | Small Intestine | Large Intestine |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Location | Thorax, posterior to trachea | Upper abdomen | Upper abdomen | Lower abdomen |
| Muscle Layer | Two layers of smooth muscle | Three layers of smooth muscle | Three layers of smooth muscle | Two layers of smooth muscle |
| Epithelium | Stratified squamous non-keratinized | Simple columnar epithelium | Simple columnar epithelium | Simple columnar epithelium |
| Function | Transport of food bolus | Food storage, mixing, and initial digestion | Nutrient absorption | Water absorption, waste compaction |
Role of Esophageal Sphincters
Sphincters are crucial for regulating the flow of food and preventing reflux. The presence of these specialized muscle structures maintains the integrity of the digestive system.
- The upper esophageal sphincter (UES) is located at the junction of the pharynx and esophagus. It prevents air from entering the esophagus during breathing and facilitates the passage of food into the esophagus.
- The lower esophageal sphincter (LES), also known as the gastroesophageal sphincter, is situated at the junction of the esophagus and stomach. Its primary function is to prevent stomach contents from refluxing back into the esophagus.
Normal Esophageal Function
The esophagus, a muscular tube connecting the pharynx to the stomach, plays a crucial role in the digestive process. Its primary function is to transport food and liquids from the mouth to the stomach efficiently and safely. This intricate process involves coordinated muscle contractions, secretions, and nervous system regulation. Understanding these mechanisms is vital for comprehending the various esophageal disorders.The act of swallowing, or deglutition, is a complex, multi-phased process that ensures the smooth transit of bolus (food or liquid) from the mouth to the stomach.
Swallowing Phases
The swallowing process is divided into three distinct phases: the oral, pharyngeal, and esophageal phases. Each phase involves specific muscle contractions and neural control to facilitate the movement of the bolus. The oral phase involves voluntary actions, whereas the pharyngeal and esophageal phases are involuntary, ensuring the food reaches the stomach without interruption.
- Oral Phase: This voluntary phase begins when the tongue pushes the bolus backward toward the oropharynx. The tongue’s movement and the soft palate’s elevation prevent food from entering the nasal cavity.
- Pharyngeal Phase: This involuntary phase starts when the bolus enters the oropharynx. The larynx elevates, and the epiglottis closes over the trachea to prevent aspiration. Sequential contractions of pharyngeal muscles propel the bolus into the esophagus.
- Esophageal Phase: This involuntary phase involves the coordinated peristaltic waves in the esophageal wall. Peristalsis propels the bolus through the esophagus and into the stomach. The lower esophageal sphincter (LES) relaxes to allow the bolus to pass into the stomach.
Muscles Involved in Swallowing
The coordinated action of various muscles ensures efficient swallowing. The muscles of the mouth, pharynx, and esophagus work together in a precise sequence to propel the bolus.
- Oral Muscles: These muscles are involved in manipulating the bolus for swallowing.
- Pharyngeal Muscles: These muscles facilitate the movement of the bolus through the pharynx.
- Esophageal Muscles: The esophagus contains two types of muscle layers: an inner circular layer and an outer longitudinal layer. Their coordinated contractions, known as peristalsis, propel the bolus down the esophagus.
Esophageal Motility and Peristalsis
Peristalsis, a wave-like contraction of the esophageal muscles, is crucial for propelling food through the esophagus. This coordinated muscular activity ensures that the bolus moves in a unidirectional manner, preventing reflux or backflow. This action is controlled by the autonomic nervous system.
The esophagus, that crucial tube connecting our mouths to our stomachs, plays a vital role in swallowing and getting food to where it needs to go. Various conditions can affect its function, like esophageal spasms or even more serious issues. Interestingly, some research suggests that certain factors linked to stage 4 prostate cancer might also have a subtle impact on esophageal health, though this area requires further investigation.
Ultimately, understanding esophageal function and conditions is key to maintaining overall digestive health.
Peristaltic waves are initiated in the upper esophagus and propagate towards the stomach, ensuring efficient transit of the bolus.
Esophageal Secretions
The esophagus produces a small amount of mucus to lubricate the passage of the bolus. This mucus plays a crucial role in preventing the bolus from adhering to the esophageal walls. The mucus also aids in the smooth transit of the food material.
Esophageal Function Across Age Groups
Esophageal function varies across different age groups. Infants and children have a shorter and wider esophagus compared to adults, impacting the swallowing mechanism. Furthermore, the development of the esophageal sphincters may not be fully matured in infants and young children, which can increase the risk of gastroesophageal reflux. In the elderly, esophageal motility can slow down, potentially leading to dysphagia (difficulty swallowing).
Autonomic Nervous System Regulation
The autonomic nervous system, specifically the vagus nerve, plays a vital role in regulating esophageal function. The vagus nerve transmits signals to the esophageal muscles, controlling peristaltic movements and the relaxation of the lower esophageal sphincter.
Conditions Affecting Esophageal Function
The esophagus, a vital conduit for food and liquids, can be susceptible to various disorders that disrupt its normal function. These conditions can range from relatively minor issues to life-threatening complications, impacting the quality of life for those affected. Understanding these conditions is crucial for early diagnosis and effective treatment.
Esophageal Motility Disorders
Esophageal motility disorders affect the coordinated muscular contractions that propel food through the esophagus. These disorders disrupt the normal peristaltic wave, leading to difficulties with swallowing. Common examples include achalasia, esophageal spasm, and diffuse esophageal spasm.
- Achalasia: Characterized by impaired relaxation of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), resulting in difficulty swallowing both solids and liquids. Symptoms often include dysphagia (difficulty swallowing), regurgitation, and chest pain.
- Esophageal Spasm: This condition involves intermittent, uncoordinated contractions of the esophageal muscles, leading to chest pain that mimics heart attack symptoms. Symptoms can range from mild discomfort to severe pain.
- Diffuse Esophageal Spasm: A more severe form of esophageal spasm, characterized by non-peristaltic contractions throughout the esophagus. This often causes episodic pain and dysphagia.
Infections of the Esophagus
Infections can also compromise esophageal function. Infectious esophagitis, often caused by fungal, viral, or bacterial agents, can inflame the esophageal lining, leading to discomfort and swallowing problems.
- Candidiasis (Fungal Infection): A common cause of esophageal infection, particularly in immunocompromised individuals. Symptoms include dysphagia, odynophagia (painful swallowing), and retrosternal pain.
- Viral Esophagitis: While less common than fungal infections, viral infections can also cause inflammation of the esophagus. Symptoms may include fever, sore throat, and dysphagia.
- Bacterial Esophagitis: Infections caused by bacteria can occur, although less frequently than fungal or viral infections. Symptoms may include inflammation, pain, and difficulty swallowing.
Structural Abnormalities
Structural abnormalities in the esophagus can impede the normal passage of food. These abnormalities can result from a variety of causes, including tumors, strictures, or foreign bodies.
- Esophageal Strictures: Narrowing of the esophageal lumen, often caused by inflammation, scarring, or tumors. Symptoms include dysphagia, initially mild but progressively worsening as the stricture becomes more severe.
- Esophageal Tumors: Cancerous or non-cancerous growths within the esophagus can obstruct the lumen. Symptoms can include dysphagia, weight loss, and pain.
- Foreign Body Impaction: A foreign object lodged in the esophagus can cause significant obstruction. Symptoms include sudden and severe dysphagia, and sometimes pain.
Diagnostic Procedures
Diagnostic procedures for esophageal disorders vary depending on the suspected cause. Common methods include endoscopy, esophageal manometry, and esophageal pH monitoring.
- Endoscopy: A flexible tube with a camera is inserted into the esophagus to visualize the lining and identify abnormalities.
- Esophageal Manometry: Measures the pressure and motility patterns within the esophagus to assess the function of the esophageal muscles.
- Esophageal pH Monitoring: Tracks the acidity levels in the esophagus to identify reflux or other acid-related problems.
Treatment Options
Treatment options for esophageal conditions vary widely, depending on the specific disorder and its severity. Pharmacological interventions, endoscopic procedures, and surgical interventions are common approaches.
- Pharmacological Treatment: Medications like proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) or H2 blockers can treat acid reflux, while specific medications may be used to address motility disorders.
- Endoscopic Procedures: Techniques like dilation or endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) can address strictures, tumors, or other structural abnormalities.
- Surgical Interventions: Surgical procedures are sometimes necessary to correct severe structural abnormalities or motility disorders.
Categorization of Esophageal Conditions
| Category | Conditions |
|---|---|
| Motility Disorders | Achalasia, esophageal spasm, diffuse esophageal spasm |
| Infections | Candidiasis, viral esophagitis, bacterial esophagitis |
| Structural Abnormalities | Esophageal strictures, esophageal tumors, foreign body impaction |
Motility Disorders
Esophageal motility disorders are conditions that affect the ability of the esophagus to move food and liquids from the mouth to the stomach. These disorders can cause a range of symptoms, from mild discomfort to severe complications, significantly impacting a person’s quality of life. Understanding the different types, causes, and treatment options is crucial for proper diagnosis and management.Esophageal motility disorders stem from problems with the coordinated contractions and relaxations of the esophageal muscles.
These rhythmic waves, known as peristalsis, propel food down the esophagus. Disruptions in this process can lead to a variety of symptoms, and recognizing the specific pattern of dysfunction is key to diagnosis and treatment.
Types of Esophageal Motility Disorders
Esophageal motility disorders manifest in diverse ways. Different patterns of abnormal esophageal contractions give rise to various types of motility disorders. These can be broadly categorized as follows:
- Achalasia: Characterized by the failure of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) to relax properly, achalasia prevents the food from entering the stomach. This results in a buildup of food in the esophagus and difficulties in swallowing.
- Diffuse esophageal spasm (DES): In DES, the esophageal muscles contract in a disorganized and non-peristaltic manner. This can cause chest pain, often described as squeezing or burning, along with difficulty swallowing.
- Nutcracker esophagus: In this condition, the esophageal muscles contract with excessive force, causing increased pressure within the esophagus. The symptoms are similar to DES, including chest pain and dysphagia (difficulty swallowing).
- Sandifer syndrome: Often seen in infants, Sandifer syndrome presents with esophageal motility issues, which are coupled with torticollis (a twisting of the neck). The spasms in the esophagus cause the neck to twist in an effort to relieve the pain.
- Esophageal spasm: This broad term encompasses various patterns of esophageal muscle contractions. They can manifest in different ways, and the exact cause isn’t always clear. It can lead to episodic chest pain.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact causes of esophageal motility disorders are often unknown, but various factors are thought to play a role.
- Achalasia: A common theory suggests a problem with the nerves that control the lower esophageal sphincter. Autoimmune responses or infections may also be implicated.
- Diffuse esophageal spasm (DES): The exact cause is unknown but potential contributors include esophageal inflammation, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), and neurological conditions.
- Nutcracker esophagus: While the exact mechanism is unknown, potential factors may include esophageal inflammation, stress, and certain medications.
- Sandifer syndrome: The cause is linked to the interaction between neurological conditions and esophageal motility problems, often stemming from underlying neurological issues. Genetic predispositions may also play a role.
- Esophageal spasm: In some cases, certain medications, stress, or underlying neurological conditions can trigger or worsen esophageal spasm. The exact mechanism is often unclear.
Symptoms
Different esophageal motility disorders can share similar symptoms, yet each type often presents a unique symptom profile.
- Achalasia: Symptoms frequently include dysphagia (difficulty swallowing), chest pain, regurgitation of food, and a feeling of fullness in the chest after eating.
- Diffuse esophageal spasm (DES): Chest pain, often described as squeezing or burning, is a hallmark symptom, along with dysphagia, and sometimes heartburn.
- Nutcracker esophagus: Chest pain, often similar to DES, is common, along with dysphagia and regurgitation.
- Sandifer syndrome: In addition to esophageal issues, the twisting of the neck is a significant symptom. Vomiting and difficulty feeding are also frequently reported.
- Esophageal spasm: Symptoms vary but typically include episodic chest pain and difficulty swallowing, sometimes accompanied by a feeling of pressure in the chest.
Diagnostic Procedures
Diagnosing esophageal motility disorders requires specialized tests.
- Upper endoscopy: A flexible tube with a camera is inserted through the mouth to visualize the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum. This can identify structural abnormalities but isn’t specific to motility issues.
- Esophageal manometry: A thin tube is inserted through the nose or mouth into the esophagus. This measures the pressure and contractions of the esophageal muscles during swallowing. This is a crucial diagnostic tool.
- Barium swallow: A contrast material is swallowed, and X-rays are taken to visualize the esophagus and identify any structural abnormalities or motility issues. This can help evaluate swallowing function.
Treatment Options
Treatment for esophageal motility disorders depends on the specific type and severity of the condition.
- Achalasia: Treatment options include pneumatic dilation (inflating a balloon to stretch the lower esophageal sphincter) or surgery to create an opening in the sphincter.
- Diffuse esophageal spasm (DES): Treatments often involve medications to relax the esophageal muscles, such as calcium channel blockers. In severe cases, surgical options may be considered.
- Nutcracker esophagus: Similar to DES, medications to relax the esophageal muscles are a common treatment approach. Other treatments include lifestyle modifications and, in severe cases, surgery.
- Sandifer syndrome: Treatment is primarily focused on managing the underlying neurological condition. Esophageal issues are addressed through symptom relief and medications.
- Esophageal spasm: Treatment approaches are varied and depend on the underlying cause. Medications, lifestyle changes, or, in severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary.
Structural Abnormalities
The esophagus, a crucial part of our digestive system, is susceptible to various structural abnormalities. These abnormalities can arise from congenital defects, acquired diseases, or trauma. Understanding these conditions is vital for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment, as they can significantly impact esophageal function and overall health. Structural issues can lead to swallowing difficulties, pain, and even life-threatening complications.Structural abnormalities of the esophagus can manifest in diverse forms, ranging from subtle narrowing to significant dilatations.
These variations can be congenital, meaning present at birth, or acquired later in life. Recognizing the specific characteristics of each abnormality, along with their underlying causes and associated symptoms, is paramount in the diagnostic and therapeutic approach. Accurate identification of the precise nature of the structural defect allows for appropriate treatment strategies and improved patient outcomes.
Congenital Esophageal Atresia and Tracheoesophageal Fistula
Congenital esophageal atresia (EA) and tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF) are conditions that involve abnormal connections between the esophagus and trachea. These birth defects disrupt the normal development of the esophagus, often resulting in a blockage or a connection between the esophagus and trachea. The severity of these defects varies, and symptoms can range from mild to severe. Babies with these defects frequently exhibit difficulty swallowing and may aspirate, leading to breathing problems and respiratory infections.
- Causes: The exact causes of EA and TEF are often unknown, but genetic factors and environmental influences during pregnancy are suspected. The precise etiology remains largely elusive. Some cases may be associated with specific genetic syndromes, highlighting the complexity of these conditions.
- Risk Factors: While precise risk factors are elusive, some research suggests a potential link to maternal factors during pregnancy. For instance, exposure to certain medications or infections during gestation might be implicated. However, definitive risk factors remain unclear.
- Symptoms: Symptoms in infants include difficulty swallowing (dysphagia), excessive drooling, and coughing or choking during feeding. These symptoms typically appear soon after birth.
- Diagnostic Procedures: Diagnostic procedures often include X-rays to visualize the esophagus and trachea. Further investigations like endoscopy might be necessary to confirm the diagnosis and assess the extent of the abnormalities. Endoscopy allows for direct visualization of the esophageal and tracheal structures.
- Treatment Options: Treatment for EA and TEF typically involves surgical intervention to correct the structural abnormalities and restore the normal pathway for swallowing. The surgical approach varies depending on the specific defect.
Esophageal Strictures
Esophageal strictures are narrowing of the esophageal lumen, potentially impacting the passage of food. These strictures can be caused by a variety of factors, including chronic acid reflux, radiation therapy, or even certain infections. They may also be a complication of prior esophageal surgery. Esophageal strictures are a frequent cause of dysphagia.
- Causes: Chronic gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a significant cause of esophageal strictures, as repeated exposure to stomach acid damages the esophageal lining. Other potential causes include prolonged use of certain medications, radiation therapy to the chest, or infections.
- Risk Factors: Individuals with a history of GERD, those who have undergone radiation therapy to the chest, and those with a history of esophageal infections are at an elevated risk of developing esophageal strictures. Certain genetic predispositions may also play a role.
- Symptoms: Symptoms of esophageal strictures typically include progressive dysphagia (difficulty swallowing). Initially, patients may experience difficulty swallowing solid foods, progressing to difficulties with liquids. Pain may also accompany swallowing.
- Diagnostic Procedures: Diagnostic procedures commonly include endoscopy, a technique that allows visualization of the esophageal lining. Further tests, such as esophageal manometry, might be necessary to assess esophageal motility and function.
- Treatment Options: Treatment options for esophageal strictures may range from dilation procedures to surgical interventions. Dilation involves widening the narrowed area using specialized instruments. Surgery might be necessary in severe or persistent cases.
Esophageal Diverticula
Esophageal diverticula are pouches or sacs that protrude from the esophageal wall. These outpouchings can be caused by a variety of factors and are classified based on their location and structure. Symptoms associated with esophageal diverticula can vary, often manifesting as dysphagia and regurgitation.
- Causes: The precise causes of esophageal diverticula are not always clear, but factors like chronic esophageal irritation, muscle weakness, and increased pressure in the esophagus are believed to contribute to their development.
- Risk Factors: Individuals with a history of esophageal motility disorders, those with a history of chronic cough, and those with certain systemic diseases are potentially at increased risk. However, a definitive risk factor profile remains elusive.
- Symptoms: Symptoms associated with esophageal diverticula can vary depending on the size and location of the diverticulum. These may include dysphagia, regurgitation of undigested food, and pain.
- Diagnostic Procedures: Diagnostic procedures include endoscopy, barium swallow studies, and esophageal manometry to visualize the esophagus and identify the diverticulum. Barium swallow studies are crucial for visualizing the structure and function of the esophagus.
- Treatment Options: Treatment for esophageal diverticula is often determined by the severity and location of the diverticulum. Minimally invasive endoscopic procedures are commonly employed to remove or treat the diverticulum. Surgical interventions may be necessary in severe cases.
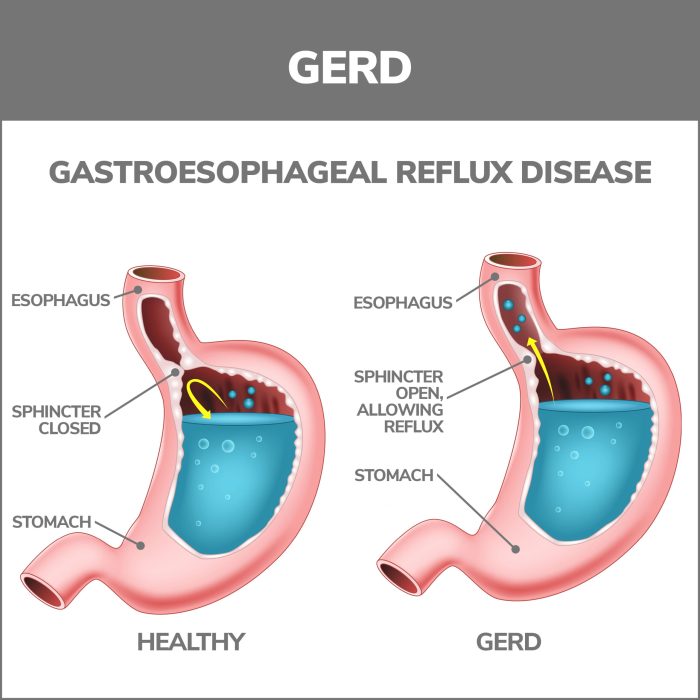
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
Heartburn, a burning sensation in the chest, is a common symptom, often associated with a sour taste in the mouth. This discomfort is frequently caused by gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), a chronic condition that arises when stomach acid frequently flows back into the esophagus. Understanding the pathophysiology, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for GERD is crucial for effective management and prevention of potential complications.
Pathophysiology of GERD
GERD occurs when the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), a ring of muscle at the junction between the esophagus and stomach, doesn’t function properly. Normally, the LES prevents stomach acid from refluxing into the esophagus. In GERD, this barrier is weakened or relaxes inappropriately, allowing stomach acid to back up into the esophagus. The prolonged exposure of the esophageal lining to stomach acid is the key driver of GERD symptoms and complications.
Esophageal acid exposure is a key factor in the development of esophageal damage, ranging from mild inflammation to severe erosion and ulcers.
Symptoms of GERD
Common symptoms of GERD include heartburn, a burning sensation in the chest, often radiating to the neck and throat. Other frequent symptoms encompass regurgitation of stomach contents into the mouth, a sour or bitter taste in the mouth, difficulty swallowing (dysphagia), and chest pain, which can mimic angina (heart pain). The severity of symptoms varies among individuals and can fluctuate over time.
Complications of GERD
Prolonged and severe GERD can lead to several complications. Esophagitis, an inflammation of the esophagus, is a frequent consequence. Chronic esophagitis can progress to more severe conditions like esophageal strictures (narrowing of the esophagus), Barrett’s esophagus (precancerous changes in the esophageal lining), and esophageal cancer. Careful monitoring and management of GERD are essential to mitigate the risk of these serious complications.
Understanding the esophagus’s role in swallowing and digestion is crucial, but sometimes things go wrong. For example, acid reflux or esophageal spasms can cause discomfort. While exploring home remedies for spider bites can be helpful, home remedies for spider bites aren’t going to help with these digestive issues. Ultimately, proper medical care is essential for diagnosing and treating esophageal problems.
Diagnostic Methods for GERD
Diagnosing GERD involves a combination of patient history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. A detailed history of symptoms, including frequency, duration, and triggers, is crucial. An upper endoscopy, a procedure that uses a flexible tube with a camera to visualize the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum, is often employed to directly assess the esophageal lining for damage and identify the presence of Barrett’s esophagus.
In some cases, a 24-hour pH monitoring test may be necessary to measure the amount of acid reflux over a period of time. This test provides a more quantitative assessment of reflux events and the duration of acid exposure.
Treatment Options for GERD
Treatment strategies for GERD focus on reducing acid reflux and alleviating symptoms. Lifestyle modifications play a significant role. These include weight loss (if overweight or obese), avoiding trigger foods (e.g., fatty foods, caffeine, chocolate), and elevating the head of the bed to improve nighttime reflux. Medications, such as proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and H2 blockers, can effectively reduce stomach acid production, providing relief from symptoms.
In some cases, surgery, such as fundoplication, may be considered for more severe or refractory GERD. Surgery involves wrapping the upper portion of the stomach around the lower esophagus to strengthen the LES and prevent reflux.
Esophageal Cancer
Esophageal cancer is a serious disease that develops in the lining of the esophagus, the tube that carries food from the mouth to the stomach. It’s a significant health concern, often requiring aggressive treatment. Early detection and appropriate intervention are crucial for improving outcomes.
Types of Esophageal Cancers
Esophageal cancers are broadly categorized based on their cellular structure. Understanding the different types helps in tailoring treatment strategies and predicting prognosis.
- Adenocarcinoma: This type originates from the glandular cells lining the esophagus. It’s the most common type of esophageal cancer in developed countries, often linked to chronic gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). The increased acidity in the esophagus can damage the cells over time, potentially leading to the development of this type of cancer.
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma: This type originates from the squamous cells that form the outer lining of the esophagus. It’s more prevalent in areas with high rates of tobacco use and alcohol consumption, particularly in parts of Asia and Africa. Exposure to these carcinogens is a key risk factor for the development of this type of cancer.
Risk Factors for Esophageal Cancer
Several factors increase the likelihood of developing esophageal cancer. Identifying and managing these risks is crucial for preventative measures.
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): Chronic acid reflux can damage the esophageal lining, increasing the risk of adenocarcinoma. Patients with long-standing GERD are at higher risk, particularly if left untreated.
- Tobacco Use: Smoking is a significant risk factor for both adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. The carcinogens in tobacco smoke damage the esophageal cells, leading to uncontrolled cell growth.
- Alcohol Consumption: Heavy alcohol use is a contributing factor to squamous cell carcinoma. The combination of alcohol and tobacco significantly increases the risk.
- Obesity: Obesity is associated with a higher risk of esophageal adenocarcinoma. Excess weight can increase pressure on the esophagus and potentially contribute to acid reflux.
- Diet Deficiencies: A diet lacking in fruits and vegetables and high in processed foods may contribute to the development of esophageal cancer. A balanced diet rich in antioxidants and micronutrients can support overall health.
- Previous Esophageal Conditions: Individuals with a history of esophageal conditions like Barrett’s esophagus or Plummer-Vinson syndrome are at increased risk. Barrett’s esophagus, in particular, is a precancerous condition that significantly raises the risk of esophageal adenocarcinoma.
Symptoms of Esophageal Cancer
Recognizing the symptoms of esophageal cancer early is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment.
- Difficulty Swallowing (Dysphagia): This is a common symptom, initially affecting solids and progressing to liquids. As the tumor grows, the difficulty swallowing becomes more pronounced. This is a key indicator for seeking medical attention.
- Painful Swallowing (Odynophagia): This symptom involves pain or discomfort during the act of swallowing. It is often a later manifestation of the disease as the tumor grows and impinges on surrounding structures.
- Weight Loss: Unexplained weight loss is a frequent symptom, often due to the difficulty in eating and absorbing nutrients. This can significantly impact the patient’s overall health.
- Heartburn and Acid Reflux: While common in GERD, persistent and worsening heartburn or acid reflux can be associated with esophageal cancer, particularly adenocarcinoma.
- Chest Pain: Some individuals may experience chest pain, which can be confused with other cardiac conditions. It’s important to seek medical evaluation for any persistent chest pain.
Diagnostic Methods for Esophageal Cancer
Accurate diagnosis is essential for appropriate treatment planning.
- Upper Endoscopy: A flexible tube with a camera is used to visualize the esophagus. This procedure allows for direct observation of the esophageal lining and potential abnormalities.
- Biopsy: A small tissue sample is collected from suspicious areas during endoscopy for microscopic examination to determine the presence and type of cancer cells.
- Imaging Studies (CT, MRI): These imaging techniques provide detailed images of the esophagus and surrounding structures, helping assess the extent of the cancer and potential spread.
- Esophageal Manometry: This procedure measures the pressure and movement of the esophagus during swallowing to evaluate motility disorders. It is not the primary diagnostic tool for esophageal cancer but can provide important contextual information in conjunction with other tests.
Treatment Options for Esophageal Cancer
Treatment strategies vary depending on the stage and type of cancer.
- Surgery: Surgical removal of the cancerous portion of the esophagus is often a primary treatment option, especially in early-stage cancers. Surgical procedures can involve a portion or complete removal of the esophagus. In advanced cases, a combination of procedures might be needed.
- Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams to target and destroy cancer cells. It can be used as a standalone treatment or in conjunction with other treatments, like surgery or chemotherapy.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells. It can be administered before, during, or after surgery or radiation therapy. It is often combined with other treatments to enhance effectiveness.
- Targeted Therapy: This type of therapy targets specific molecules or pathways involved in cancer growth and spread. It’s becoming increasingly important in the treatment of esophageal cancer, offering more specific and potentially less damaging treatments.
Imaging Techniques
Unveiling the esophageal landscape requires sophisticated imaging techniques. These methods provide detailed views of the esophagus’s structure and function, enabling clinicians to diagnose and monitor various conditions. From visualizing the esophagus’s anatomy to assessing its motility, these techniques are essential tools in modern esophageal medicine.
Esophageal Imaging Techniques
Various imaging techniques are employed to evaluate the esophagus, each with unique capabilities. These techniques provide different levels of detail, allowing for a comprehensive assessment of the esophagus’s structure and function.
The esophagus, that crucial tube connecting your mouth to your stomach, has a pretty important job. It’s responsible for moving food down smoothly. However, various conditions can disrupt this vital process. Considering the complexities of different treatments, like hip labrum surgery is it the right treatment , it’s essential to understand the specific issues and potential solutions.
Ultimately, understanding the proper function of the esophagus is key to overall health.
Radiographic Studies
Radiographic studies, including standard X-rays and fluoroscopy, offer a valuable initial assessment of the esophagus’s structural integrity. These techniques are relatively inexpensive and readily available.
- Plain X-rays: A plain X-ray uses ionizing radiation to create an image of the esophagus. It primarily assesses the overall shape, size, and position of the esophagus, as well as detecting any significant abnormalities like narrowing or foreign bodies. Contrast agents may be used to enhance visualization.
- Barium Swallow (Esophagram): This technique involves ingesting a barium suspension, which coats the esophagus. Subsequent X-rays reveal the esophagus’s anatomy and passage of the contrast material. This method allows for detailed visualization of the esophageal lumen, helping to identify strictures, diverticula, or other structural abnormalities. It is often performed in conjunction with fluoroscopy.
- Fluoroscopy: Fluoroscopy uses continuous X-ray imaging to visualize the esophagus’s function during swallowing. It provides dynamic information about esophageal motility, identifying problems like dysphagia (difficulty swallowing) or esophageal spasms. The real-time nature of fluoroscopy is crucial for assessing the coordination of esophageal contractions.
Endoscopic Procedures
Endoscopy provides direct visualization of the esophageal lining and surrounding structures. It allows for the collection of tissue samples (biopsies) for pathological analysis.
- Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD): EGD involves inserting a flexible endoscope through the mouth and into the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum. This procedure allows for direct visualization of the esophageal mucosa, identifying inflammation, ulcers, or tumors. Biopsies can be taken for diagnostic purposes, and certain interventions, such as dilation of strictures, can be performed simultaneously.
Manometry
Manometry measures the pressure changes in the esophagus during swallowing. This technique assesses the esophageal motility patterns, revealing abnormalities in the coordination of contractions.
- Esophageal Manometry: A thin, flexible catheter with pressure sensors is inserted into the esophagus. The catheter measures the pressure exerted by the esophageal muscles during swallowing, providing data on the timing, strength, and coordination of esophageal contractions. This technique is invaluable for diagnosing motility disorders, such as achalasia or esophageal spasm.
Other Imaging Techniques
Other advanced imaging techniques provide more detailed structural information.
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: A CT scan uses X-rays and computer processing to create cross-sectional images of the esophagus. It provides detailed anatomical information, aiding in the detection of tumors, masses, or other structural abnormalities. It can also assess the relationship of the esophagus to surrounding structures.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI uses magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the esophagus. It provides superior soft tissue contrast compared to CT scans, allowing for better visualization of subtle structural changes. MRI can be helpful in assessing the extent of esophageal lesions and their relationship to surrounding tissues.
Comparison of Imaging Techniques
| Technique | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Plain X-ray | Inexpensive, readily available | Limited visualization, may require contrast |
| Barium Swallow | Useful for structural assessment, identifies abnormalities | Requires patient cooperation, potential for barium residue |
| Fluoroscopy | Dynamic visualization of motility | Exposure to radiation, limited visualization of mucosal detail |
| EGD | Direct visualization of mucosa, biopsy capability | Invasive procedure, potential for complications |
| Esophageal Manometry | Assesses motility, diagnoses motility disorders | Invasive procedure, limited visualization |
| CT Scan | Detailed structural information, detects masses | Exposure to radiation, less detailed soft tissue visualization |
| MRI | Superior soft tissue contrast, assesses extent of lesions | Longer examination time, potentially less readily available |
Procedures and Risks
The specific procedures for each technique vary, but generally involve preparing the patient, positioning them appropriately, and using specialized equipment. Potential risks vary depending on the technique. Radiation exposure is a concern with radiographic studies. Complications from endoscopic procedures include bleeding, perforation, and infection. Patient preparation and careful technique minimize these risks.
Illustrative Examples (Esophageal Conditions): Esophagus Function And Conditions
Understanding esophageal conditions requires delving into real-world cases to grasp their complexity and impact on patients’ lives. This section presents a detailed case study of a specific esophageal condition, highlighting the symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, prognosis, and long-term implications.A crucial aspect of comprehending esophageal disorders is to consider individual patient experiences, and this case study is designed to provide a concrete example.
The specific condition detailed below, while not a comprehensive overview of all esophageal pathologies, offers a useful illustration of the challenges and considerations involved in patient care.
Case Study: Achalasia, Esophagus function and conditions
Achalasia is a motility disorder of the esophagus, characterized by impaired relaxation of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) and peristalsis. This leads to difficulty swallowing (dysphagia) and, in severe cases, esophageal dilation and potential complications.
Patient Medical History
A 45-year-old female presented with progressive dysphagia over the past 18 months. She initially experienced difficulty swallowing solids, which later progressed to include liquids. She reported occasional chest pain, particularly after meals, and a sensation of food getting stuck in her chest. There was no significant past medical history except for occasional heartburn. She is a non-smoker and has no known allergies.
Symptoms
The patient’s primary symptom was progressive dysphagia, initially affecting solids and eventually liquids. She also experienced chest pain, particularly after meals, and a sensation of food becoming lodged in her chest. These symptoms were gradually worsening, impacting her quality of life.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of achalasia was confirmed through a combination of diagnostic tests. Endoscopy revealed an absence of esophageal strictures or other structural abnormalities, while esophageal manometry demonstrated impaired relaxation of the LES. Barium swallow radiography showed a dilated esophagus, a classic feature of achalasia, and a “bird’s beak” appearance at the LES, indicating a narrowing at the lower esophageal sphincter.
Treatment Plan
Given the progressive nature of the patient’s condition, a combination of treatment options was implemented. Initially, pharmacologic interventions were attempted to improve LES relaxation, but these proved insufficient. The patient was then advised on dietary modifications, including a softer diet to aid in swallowing. Ultimately, an endoscopic pneumatic dilation procedure was recommended to improve LES function and allow for improved swallowing.
This procedure involves using a balloon to gently dilate the narrowed LES.
Prognosis and Long-Term Implications
The prognosis for achalasia varies depending on the severity of the condition and the effectiveness of treatment. With successful endoscopic dilation, the patient experienced significant improvement in dysphagia. However, the risk of recurrence exists, and the need for periodic follow-up evaluations is essential. Long-term implications include potential esophageal damage if the condition is not managed appropriately. Regular medical check-ups and potential future interventions are necessary to maintain good health.
Visual Representation
A visual representation of the condition, achalasia, would demonstrate the following structural changes:
A radiograph (Barium Swallow) of the esophagus would show a dilated esophageal segment proximal to the LES, and a characteristic “bird’s beak” narrowing at the lower esophageal sphincter. Endoscopic images might also reveal the smooth, muscular esophageal wall without any significant inflammation.
A diagram comparing a healthy esophagus to one with achalasia could visually depict the differences in esophageal peristalsis, and LES function. A healthy esophagus exhibits rhythmic contractions for effective food transport, while in achalasia, this process is significantly impaired.
Final Review
In conclusion, the esophagus, though seemingly a simple conduit, plays a vital role in our digestive health. Its intricate structure and function are crucial for proper nutrition. From the mechanics of swallowing to the various conditions that can impact its performance, this exploration has illuminated the complexities of the esophagus. Hopefully, this overview provides a solid foundation for understanding this critical component of the human body.