What are heberdens nodes – What are Heberden’s nodes? These small, bony bumps, often appearing on the fingertips, can be a sign of a common condition affecting the joints. This informative guide delves into the specifics of Heberden’s nodes, exploring their causes, diagnosis, and treatment options. We’ll cover everything from the initial symptoms to the long-term impact on daily life, providing a comprehensive understanding of this often-overlooked issue.
Heberden’s nodes are a type of osteoarthritis, specifically affecting the distal interphalangeal joints. They manifest as bony enlargements at the end of the fingers, typically arising gradually over time. While often painless, they can eventually cause pain and stiffness, impacting a person’s ability to perform daily tasks. Understanding the underlying causes, risk factors, and treatment options is crucial for effective management.
Definition and Description
Heberden’s nodes are a common manifestation of osteoarthritis, particularly affecting the hands. They represent a specific type of joint change, often appearing as small, bony enlargements. Understanding their characteristics, location, and symptoms is crucial for diagnosis and management.Heberden’s nodes typically develop at the distal interphalangeal (DIP) joints of the fingers. These are the joints closest to the fingernails.
Their appearance varies, but they commonly present as hard, painless nodules or bumps. They can range in size from barely noticeable to quite prominent, potentially causing some restriction in finger movement.Common symptoms associated with Heberden’s nodes include pain, stiffness, and tenderness around the affected joints. The degree of these symptoms can vary greatly from person to person.
Some individuals may experience minimal discomfort, while others may find their daily activities significantly impacted by pain and restricted movement.
Comparison with Other Conditions
A clear understanding of Heberden’s nodes can be enhanced by comparing them with other conditions that may present with similar symptoms or characteristics. This comparison allows for a more precise diagnosis.
| Condition | Location | Appearance | Symptoms |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heberden’s Nodes | Distal interphalangeal (DIP) joints of the fingers | Hard, painless nodules or bumps, often bony enlargements | Pain, stiffness, tenderness around affected joints, potential for restricted finger movement |
| Rheumatoid Arthritis | Symetrical involvement of joints, including small joints of hands and feet. May also involve larger joints | Soft tissue swelling, warmth, and pain. Joint deformity may develop over time. | Morning stiffness, fatigue, symmetrical joint pain, systemic symptoms like fever and malaise. |
| Gout | Metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint of the big toe, but can also affect other joints | Sudden, intense, and throbbing pain, redness, swelling, warmth around affected joint. | Inflammation, extreme pain, often at night, acute onset |
| Psoriatic Arthritis | Distal interphalangeal (DIP) joints and the nail beds are commonly affected. | Redness, swelling, tenderness around affected joints, nail pitting, psoriasis skin lesions. | Pain, stiffness, swelling, skin lesions, nail changes, fatigue. |
Causes and Risk Factors: What Are Heberdens Nodes
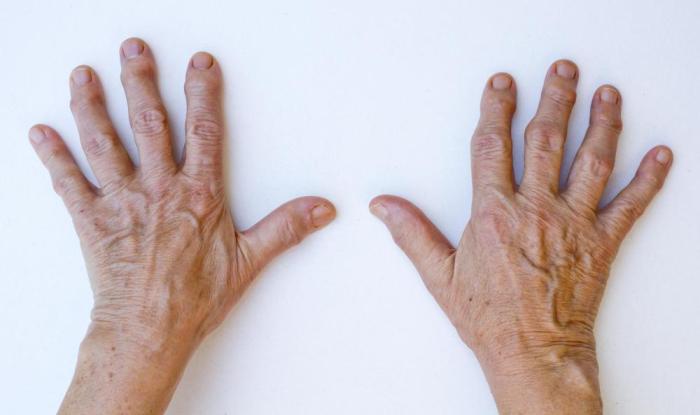
Heberden’s nodes, those characteristic bony bumps on the fingers, are often a sign of osteoarthritis. Understanding their causes and risk factors can help in prevention and management strategies. While the exact cause isn’t fully understood, a combination of factors contributes to their development.
Primary Cause of Heberden’s Nodes
The primary cause of Heberden’s nodes is osteoarthritis. This degenerative joint disease involves the breakdown of cartilage, the protective tissue cushioning the joints. As cartilage wears down, the bones rub against each other, leading to inflammation, pain, and the formation of bony outgrowths like Heberden’s nodes. This process is often gradual and can affect multiple joints in the body.
Risk Factors Associated with Heberden’s Nodes
Several factors increase the likelihood of developing Heberden’s nodes. These factors often interact and contribute to the overall risk.
Genetic Predisposition
A significant risk factor for Heberden’s nodes is a family history of the condition. Genetic predisposition plays a role in determining an individual’s susceptibility to osteoarthritis. Individuals with a family history of osteoarthritis or Heberden’s nodes are more likely to develop the condition themselves. This suggests a genetic component influencing the body’s response to joint wear and tear.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors can also play a role in the development of Heberden’s nodes, although their contribution is less understood than genetics. Certain repetitive movements or activities that put stress on the joints could potentially contribute to the development of Heberden’s nodes over time. However, this relationship isn’t definitively proven, and further research is needed to understand the precise role of environmental factors.
Lifestyle Factors
Lifestyle choices can significantly influence the risk of developing Heberden’s nodes. Maintaining a healthy weight and engaging in regular exercise are important for joint health. Obesity places extra stress on joints, potentially accelerating the progression of osteoarthritis and the formation of nodes. Similarly, a sedentary lifestyle can weaken the supporting muscles around the joints, making them more vulnerable to injury and contributing to osteoarthritis.
Table of Risk Factors
| Category | Factor | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Genetic | Family History | Having a family member with Heberden’s nodes or osteoarthritis increases the risk of developing the condition. |
| Genetic | Specific Genes | Certain genes may influence an individual’s susceptibility to joint diseases, although the exact genes involved are not fully identified yet. |
| Environmental | Repetitive Stress | Activities or jobs involving repetitive movements that put stress on the hands and joints might contribute to node formation. |
| Lifestyle | Obesity | Carrying excess weight places additional stress on joints, potentially accelerating osteoarthritis. |
| Lifestyle | Sedentary Lifestyle | Lack of exercise weakens the muscles supporting joints, increasing their vulnerability to damage and osteoarthritis. |
| Lifestyle | Poor Diet | A diet lacking in essential nutrients might negatively impact joint health, although this is not definitively proven. |
Diagnosis and Evaluation
Diagnosing Heberden’s nodes often involves a combination of clinical evaluation and sometimes imaging techniques. A thorough understanding of the patient’s medical history, coupled with a careful physical examination, is crucial in distinguishing Heberden’s nodes from other conditions that can present with similar symptoms. The goal is to confirm the presence of Heberden’s nodes, assess their severity, and rule out any underlying conditions that may be contributing to the symptoms.Accurate diagnosis allows for appropriate management strategies and helps to prevent potential complications.
A proper evaluation process involves a systematic approach that incorporates both subjective and objective data to arrive at an accurate diagnosis.
Typical Diagnostic Process
The diagnostic process for Heberden’s nodes typically begins with a comprehensive history taking. This includes inquiries about the onset, progression, and location of the symptoms, as well as any associated factors such as joint pain, stiffness, or other symptoms. Detailed information about the patient’s medical history, including any known underlying conditions or previous injuries, is also essential. This helps in determining potential contributing factors and differentiating Heberden’s nodes from other conditions.
Methods Used to Identify Heberden’s Nodes
The primary method for identifying Heberden’s nodes is a thorough physical examination. This involves careful palpation of the affected joints to assess the presence of bony enlargements, tenderness, and any associated inflammation. Observation of the joint alignment and range of motion can also provide valuable insights. The examiner will note the size, shape, and consistency of the nodes, and will compare the affected joint to the unaffected joint for comparison.
Role of Imaging Techniques
While physical examination is usually sufficient for diagnosing Heberden’s nodes, imaging techniques may be considered in certain cases. X-rays can reveal the underlying bony changes characteristic of osteoarthritis, which often accompanies Heberden’s nodes. Imaging plays a more crucial role in cases of uncertainty or suspicion of other conditions. For example, if there is concern about a fracture or another joint disorder, imaging might be necessary to provide a more definitive diagnosis.
Importance of Physical Examination
A thorough physical examination is paramount in assessing Heberden’s nodes. It allows for a direct evaluation of the affected joints, enabling the healthcare professional to assess the presence of tenderness, inflammation, and the extent of joint involvement. This assessment is crucial in determining the stage of the condition and tailoring appropriate management strategies.
Step-by-Step Procedure for Evaluation
- Patient History Collection: Gather detailed information about the patient’s symptoms, including their onset, progression, location, and any associated factors like pain or stiffness. This also involves inquiries about any relevant medical history, including previous injuries or underlying conditions.
- Physical Examination: Conduct a meticulous examination of the affected joints, focusing on the presence of bony enlargements (Heberden’s nodes), tenderness, inflammation, and any limitations in range of motion. Compare the affected joint with the unaffected joint.
- Imaging Studies (Optional): If there is doubt or suspicion of other conditions, consider X-rays to confirm the presence of osteoarthritis-related changes and rule out other potential causes.
- Differential Diagnosis: Based on the collected information, consider potential differential diagnoses, such as rheumatoid arthritis or other forms of arthritis, and rule them out based on the clinical findings.
- Diagnosis Confirmation: Based on the patient’s history, physical examination findings, and any relevant imaging studies, arrive at a definitive diagnosis of Heberden’s nodes or rule out the possibility in favor of other conditions.
Treatment and Management
Unfortunately, there’s no cure for Heberden’s nodes, but several treatment options can help manage pain and improve quality of life. These strategies focus on relieving symptoms, slowing disease progression, and preserving joint function. Understanding the various approaches and their potential benefits and risks is crucial for making informed decisions about care.
Non-Pharmacological Interventions
These methods aim to reduce pain and stiffness without medication. Physical therapy plays a significant role in managing Heberden’s nodes. Exercises and stretches, tailored to individual needs, can strengthen supporting muscles, improve flexibility, and reduce joint pain. A qualified physical therapist can create a personalized plan to target specific issues. Heat and cold therapy can also offer temporary pain relief.
Applying warm compresses can relax muscles and reduce stiffness, while cold packs can numb the area and decrease inflammation. Proper posture and ergonomic adjustments at work and home can significantly lessen stress on affected joints. Weight management is also crucial for individuals who are overweight or obese. The extra weight puts additional pressure on the joints, exacerbating pain and inflammation.
Adopting a healthy diet and exercise regimen can help maintain a healthy weight.
Pharmacological Interventions
Medications can help manage pain and inflammation associated with Heberden’s nodes. Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or naproxen, can provide short-term relief from mild to moderate pain. These medications work by reducing inflammation. However, long-term use of these medications should be discussed with a healthcare professional. For more severe pain, stronger pain relievers, such as opioids, might be considered, but these should be used with caution due to potential side effects and dependence.
In some cases, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) may be prescribed to slow the progression of the underlying condition if it’s considered rheumatoid arthritis or another inflammatory condition. Corticosteroids, administered orally or via injection, can reduce inflammation and pain but should be used cautiously due to potential side effects.
Treatment Options Summary
| Type | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Non-Pharmacological | Physical Therapy | Tailored exercises, stretches, and flexibility improvements. Addresses muscle strength, joint mobility, and pain reduction. |
| Non-Pharmacological | Heat/Cold Therapy | Application of warm or cold compresses to reduce muscle stiffness or inflammation, respectively. |
| Non-Pharmacological | Ergonomic Adjustments | Modifying work and home environments to reduce stress on affected joints. |
| Non-Pharmacological | Weight Management | Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce stress on joints. |
| Pharmacological | Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers | Ibuprofen or naproxen for short-term pain relief. |
| Pharmacological | Stronger Pain Relievers | Opioids for severe pain, but with caution due to potential side effects and dependence. |
| Pharmacological | Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs) | Potentially slow the progression of the underlying condition, if it’s considered rheumatoid arthritis or another inflammatory condition. |
| Pharmacological | Corticosteroids | Oral or injected corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and pain, but with caution due to potential side effects. |
Important Note: The choice of treatment depends on the severity of symptoms, the underlying cause, and individual patient factors. It’s crucial to discuss treatment options with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable approach. A personalized treatment plan can help manage Heberden’s nodes effectively.
Prevention and Prognosis
Navigating the journey with Heberden’s nodes involves understanding not just the current condition but also the potential future trajectory. This section delves into strategies to minimize the risk of progression and the typical outcomes for those affected. We’ll also explore the long-term implications for daily life and overall well-being.
So, Heberden’s nodes, those little bumps on your fingers, can be a real pain. They’re often linked to osteoarthritis, and maintaining a healthy weight can be beneficial for overall joint health. This is where cutting back on ultra-processed foods to avoid for weight loss comes in handy ultra processed foods to avoid for weight loss. Choosing nutritious options, and keeping an eye on your weight, could help lessen the impact of these annoying nodes in the long run.
After all, a healthy lifestyle can really make a difference in how you feel.
Preventive Measures
Implementing lifestyle adjustments can potentially lessen the likelihood of developing Heberden’s nodes or slowing their progression. A balanced approach that addresses various factors is crucial.
- Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Obesity is a recognized risk factor for many musculoskeletal conditions. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can significantly reduce the stress on joints, potentially lessening the development of Heberden’s nodes.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular low-impact exercises, such as swimming, walking, or cycling, strengthens the muscles surrounding the joints, providing support and reducing stress on the affected areas. This can help to alleviate symptoms and prevent further deterioration.
- Adequate Calcium and Vitamin D Intake: A diet rich in calcium and vitamin D is essential for maintaining strong bones. These nutrients play a crucial role in bone health, which is paramount in preventing the progression of conditions like osteoarthritis, a significant contributor to Heberden’s nodes.
Typical Prognosis
The prognosis for individuals with Heberden’s nodes is generally favorable, meaning the condition doesn’t typically lead to severe disability. While the nodes themselves may cause discomfort and limitations, significant functional impairment is usually not the case.
Heberden’s nodes are those bony bumps that can develop on the fingers, often a sign of osteoarthritis. While researching the best ways to manage joint pain, I stumbled upon the fascinating topic of vacuum therapy, particularly its potential benefits and drawbacks. Exploring the pros and cons of vacuum therapy here could offer insights into alternative pain relief methods for conditions like Heberden’s nodes, although more research is needed to confirm its efficacy.
Ultimately, it’s crucial to consult a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment recommendations for Heberden’s nodes.
The progression of Heberden’s nodes is typically gradual. Individuals may experience increasing pain and stiffness over time, but the rate of progression varies greatly between individuals. Early intervention and management strategies can significantly impact the severity of symptoms and the impact on daily activities.
Long-Term Implications on Daily Activities
Heberden’s nodes can impact daily activities, particularly those involving repetitive hand movements or gripping. The severity of this impact depends on the extent of the joint damage and the individual’s overall health.
- Activities Requiring Fine Motor Skills: Tasks like writing, buttoning clothes, or using small tools might become more challenging as the nodes progress.
- Household Chores: Simple household chores that involve gripping or repetitive hand movements may become difficult or painful. This can impact daily routines and independent living.
- Work-Related Tasks: For individuals with jobs requiring dexterity, Heberden’s nodes may limit their ability to perform certain tasks effectively, potentially leading to work-related issues.
Impact on Quality of Life
The impact of Heberden’s nodes on quality of life is multifaceted and varies greatly from person to person. Pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility can affect a person’s ability to engage in activities they enjoy, leading to emotional distress and social isolation.
The emotional well-being of those with Heberden’s nodes is often affected by the physical limitations and challenges they face. It’s crucial to acknowledge the importance of support systems and psychological well-being in managing the condition effectively.
Expected Course of the Disease and Potential Complications
The expected course of Heberden’s nodes is typically slow and progressive. While the condition rarely leads to severe complications, certain factors can influence the disease’s trajectory.
- Progression Rate: The rate at which Heberden’s nodes progress differs between individuals, ranging from slow to more rapid in some cases.
- Severity of Symptoms: The degree of pain, stiffness, and limitation in movement varies greatly. Some individuals experience minimal symptoms, while others may experience significant limitations.
- Potential Complications: While uncommon, complications such as joint instability or deformities can arise in advanced cases. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly minimize the likelihood of such complications.
Associated Conditions
Heberden’s nodes, while primarily affecting the hands, aren’t an isolated phenomenon. They frequently appear in the context of other joint conditions, and understanding these connections is crucial for comprehensive care and management. This section delves into the common conditions often seen alongside Heberden’s nodes.A significant relationship exists between Heberden’s nodes and other forms of osteoarthritis. This isn’t a case of one condition simply “causing” the other, but rather a pattern often observed.
So, Heberden’s nodes, those little bumps on your fingers, are a common sign of osteoarthritis. While they’re often associated with aging, understanding their development can help us look at similar conditions. Interestingly, some of the treatment options for calcific tendonitis of the shoulder, a condition where calcium deposits form in the shoulder tendons, can offer some insights into managing similar types of joint issues.
For example, exploring treatment options for calcific tendonitis of the shoulder , might help us understand how inflammation and calcium deposits can affect the joints in different ways. Ultimately, knowing more about Heberden’s nodes and their underlying causes is key to better managing their impact on our lives.
The underlying wear and tear on the joints, typical of osteoarthritis, can manifest in various ways, and Heberden’s nodes are one such manifestation.
Commonly Associated Joint Conditions
Osteoarthritis is the most prevalent condition associated with Heberden’s nodes. The shared underlying mechanisms, such as joint degeneration and inflammation, explain this connection. Furthermore, other forms of arthritis, while less common, can present with similar symptoms, making accurate diagnosis crucial.
- Osteoarthritis (OA): The most common association. OA involves the breakdown of cartilage within the joints, leading to pain, stiffness, and the formation of bony growths like Heberden’s nodes. The gradual deterioration of the joint structures in OA can affect multiple joints, potentially presenting with nodes in both the hands and feet.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): While less frequently associated with Heberden’s nodes, RA can occasionally present with similar joint changes. Differentiating between OA and RA is essential for appropriate treatment strategies, as RA requires a different approach to managing symptoms and progression.
- Psoriatic Arthritis: This type of arthritis is often linked to skin conditions like psoriasis. Psoriatic arthritis can lead to inflammation and damage in joints, sometimes resulting in node formation, though this is not as prominent a feature as in OA.
- Other forms of inflammatory arthritis: Several other inflammatory arthritic conditions exist, although they are less frequently associated with Heberden’s nodes. Each inflammatory arthritis presents with its own set of symptoms and characteristics, and it’s crucial to accurately diagnose the underlying cause to ensure effective treatment.
Other Conditions Often Co-occurring
Besides joint conditions, Heberden’s nodes can sometimes be observed in conjunction with other medical issues. This is not to say that one causes the other, but rather that they may share underlying risk factors or similar lifestyle influences.
- Metabolic Conditions: Conditions like gout or other metabolic disorders can affect the joints and contribute to the development of arthritis, which may manifest as Heberden’s nodes.
- Family History: A family history of osteoarthritis or other joint conditions can increase the risk of developing Heberden’s nodes, highlighting the importance of genetics in the development of these issues.
- Certain Medications: Some medications, while beneficial for other conditions, can have side effects that affect joint health. The precise mechanism and extent of these effects can vary significantly depending on the medication and the individual.
Important Considerations
It is crucial to remember that the presence of Heberden’s nodes does not definitively diagnose any of these associated conditions. A thorough assessment by a healthcare professional is essential to accurately identify the underlying cause of the joint symptoms.
Illustrations and Visual Aids
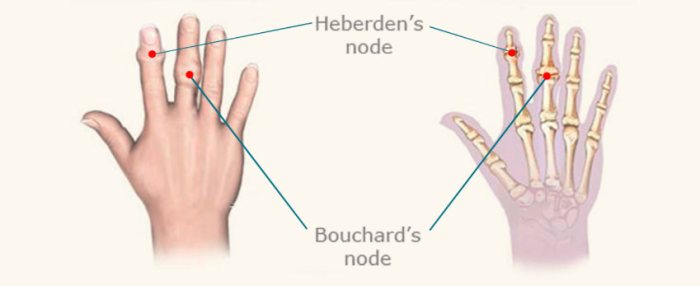
Visual representations are crucial for understanding Heberden’s nodes. They provide a tangible way to grasp the appearance, location, and progression of these bony enlargements. These aids are particularly helpful in educating patients and their families about the condition, enabling them to better visualize what they may be experiencing and understand the nature of the disease.
Visual Representation of Heberden’s Nodes
Heberden’s nodes manifest as small, hard, bony nodules that typically develop on the distal interphalangeal (DIP) joints of the fingers. These nodes appear as painless, slightly swollen protrusions. Imagine tiny bumps or enlargements on the finger joints, giving a slightly enlarged appearance. The nodes are often symmetrical, appearing on corresponding joints of both hands. The nodes’ size and prominence can vary significantly from person to person.
Progression of Heberden’s Nodes
The progression of Heberden’s nodes often mirrors the overall progression of osteoarthritis. Initially, the nodes might be subtle, appearing as slight irregularities or enlargements on the affected joints. As the disease progresses, these nodes can become more prominent, larger, and more noticeable, impacting the overall shape and functionality of the fingers. The process can take years, with some people experiencing a slow progression, while others may see more rapid development.
Anatomy of the Affected Joints
Understanding the anatomy of the affected joints provides valuable context. The DIP joints are located at the very tips of the fingers, connecting the middle and distal phalanges. These joints are crucial for fine motor movements, such as grasping and manipulating objects. A diagram illustrating the DIP joint would display the distal phalanx, middle phalanx, and the articular cartilage surrounding the joint.
The image would clearly delineate the area of the joint affected by the bony outgrowths of Heberden’s nodes.
Joint Structures Affected by Heberden’s Nodes, What are heberdens nodes
Heberden’s nodes primarily affect the articular cartilage and surrounding tissues of the DIP joints. The articular cartilage, a smooth layer of tissue covering the ends of the bones within the joint, is gradually worn away in osteoarthritis. The underlying bone is exposed, leading to the formation of bony spurs, or nodes. The diagram should illustrate the affected areas of the articular cartilage, the underlying bone, and the ligaments and tendons that support the joint.
This will visually show how the disease affects the structural integrity of the joint, leading to pain and limited movement.
Final Summary
In conclusion, Heberden’s nodes, though often associated with age and osteoarthritis, are a complex issue with a range of potential contributing factors. Early diagnosis and proactive management are key to minimizing the impact on quality of life. This guide has provided a starting point for understanding the condition, but it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment options.
Remember, knowledge is power when it comes to managing your health.










