What does gonorrhea look like? This guide dives deep into the visual manifestations of gonorrhea, exploring its appearance in different stages and body parts. Understanding the potential symptoms is crucial for early detection and treatment. We’ll examine the typical visual presentations in both men and women, highlighting key differences and comparing them to other sexually transmitted infections (STIs). This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice.
Gonorrhea, a common sexually transmitted infection (STI), can present with varying visual symptoms depending on the individual and the stage of infection. While some cases may be asymptomatic, others can manifest with noticeable signs. This comprehensive guide aims to provide a clear overview of the visual indicators of gonorrhea, helping individuals recognize potential issues and seek appropriate medical attention.
Overview of Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea, often referred to as “the clap,” is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacteriumNeisseria gonorrhoeae*. It primarily affects mucous membranes, including those in the genitals, rectum, and throat. Understanding its transmission, stages, and symptoms is crucial for early detection and treatment. Prompt diagnosis and appropriate medical intervention are essential to prevent potential complications.Gonorrhea is typically transmitted through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex.
While less common, it can also be passed from mother to child during childbirth. It’s important to remember that individuals can be infected without exhibiting any noticeable symptoms. This silent nature highlights the significance of regular STI screenings, particularly for those who are sexually active.
Transmission and Causative Agent
Gonorrhea is caused by the bacteriumNeisseria gonorrhoeae*, a gram-negative diplococcus. This bacterium primarily infects mucosal surfaces, establishing an infection through direct contact during sexual activity. The bacterium attaches to the cells lining the mucosal surfaces, initiating the infection process.
Stages of Gonorrhea Infection, What does gonorrhea look like
Gonorrhea infection progresses through distinct stages, although the clinical presentation can vary greatly. The initial phase often involves colonization of the mucous membranes. The infection can progress to an acute or chronic phase, depending on the host’s immune response and the virulence of the infecting strain. If left untreated, gonorrhea can lead to significant health consequences.
Symptoms of Gonorrhea in Men and Women
Gonorrhea manifests differently in men and women. While some individuals experience noticeable symptoms, many others remain asymptomatic, making early detection challenging. This variation in symptom presentation emphasizes the importance of routine STI testing for sexually active individuals.
Symptom Differences Between Genders
The clinical presentation of gonorrhea can differ significantly between men and women. In men, symptoms often manifest more readily, frequently involving the urethra. In women, symptoms are often less pronounced or absent altogether. This disparity highlights the need for tailored diagnostic approaches and awareness of potential variations in symptom presentation.
Comparison of Symptoms in Men and Women
| Characteristic | Men | Women |
|---|---|---|
| Common Symptoms | Painful urination (dysuria), pus-like discharge from the penis (urethral discharge), pain or swelling in the testicles (epididymitis). | Increased vaginal discharge (often thick, yellow, or green), painful urination (dysuria), vaginal bleeding between periods, pain during sex (dyspareunia), lower abdominal pain. |
| Less Common Symptoms | Sore throat, anal discharge or pain. | Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), ectopic pregnancy (pregnancy outside the uterus), infertility. |
| Asymptomatic Cases | Significant proportion of infected men may be asymptomatic. | A substantial percentage of infected women remain asymptomatic. |
Visual Manifestations
Gonorrhea, a sexually transmitted infection (STI), often presents subtly, making early detection challenging. Understanding the various visual manifestations across different genders is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment. While some cases may be asymptomatic, others display noticeable symptoms. Early intervention is key to preventing complications and the spread of the infection.Gonorrhea’s visual presentations can vary depending on the infected site.
Gonorrhea, unfortunately, doesn’t always have obvious symptoms. Sometimes, it can manifest as a discharge, but it’s crucial to remember that many people don’t experience any noticeable signs at all. Learning about the various uses and benefits of moringa, like its potential role in boosting the immune system, might seem unrelated, but a strong immune system is vital for overall health, including fighting off infections like gonorrhea.
So, while understanding the nuances of moringa’s potential health benefits is important, knowing the potential lack of outward signs of gonorrhea is equally vital for proactive health checks. the uses and benefits of moringa
The severity and type of symptoms can also differ between men and women. It’s important to remember that these symptoms are not always present, and a medical professional should always be consulted for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Visual Presentations in Men
Urethral discharge is a common visual manifestation in men. This discharge can range from a milky white to yellowish-green color and can be thick or thin. Painful urination (dysuria) is another frequent symptom. In some cases, men may experience testicular pain or swelling. The presence of these symptoms should prompt a visit to a healthcare provider.
Visual Presentations in Women
Women infected with gonorrhea may experience vaginal discharge, which can be similar in appearance to the discharge seen in men. Pain during urination (dysuria) is also a possible symptom. Pelvic pain and abnormal vaginal bleeding are also potential signs. However, it’s crucial to understand that these symptoms can mimic other conditions, emphasizing the importance of professional diagnosis.
Visual Manifestations Across Body Parts
The location of the infection significantly impacts the visible symptoms. A comprehensive visual examination plays a vital role in identifying the infection’s presence and extent.
| Body Part | Visual Manifestations |
|---|---|
| Urethra (Men) | Urethral discharge (white, yellow, or green; thick or thin), painful urination (dysuria). |
| Vagina (Women) | Vaginal discharge (similar appearance to men’s urethral discharge), painful urination (dysuria), pelvic pain, abnormal vaginal bleeding. |
| Rectum | Rectal discharge, pain during bowel movements (tenesmus), rectal bleeding. |
| Throat | Sore throat, difficulty swallowing. |
Role of Visual Examination in Diagnosis
A thorough visual examination, combined with a detailed medical history and laboratory tests, is essential for diagnosing gonorrhea. Healthcare professionals carefully assess the affected area for any abnormal discharge, redness, swelling, or pain. This examination helps in identifying the infection and guiding the appropriate treatment plan. The absence of visual symptoms does not rule out the possibility of gonorrhea, hence the necessity of further diagnostic tests.
Gonorrhea, sometimes, presents with no noticeable symptoms at all. Other times, it can manifest as unusual discharge, burning during urination, or even painful sores. Learning about different health conditions, like psoriasis, and how they impact your life is crucial. For a deeper understanding of how psoriasis can affect your overall well-being, check out this informative resource on psoriasis and your life.
Ultimately, it’s important to remember that seeking medical advice from a healthcare professional is the best way to determine what’s going on and get the right treatment for any potential health concerns, including gonorrhea.
Visual Differences Between Stages
Gonorrhea, a sexually transmitted infection (STI), can manifest visually in different ways depending on its stage of development. Early detection is crucial for effective treatment and preventing potential complications. Understanding the progression of visual symptoms can aid in early diagnosis and appropriate medical intervention. While the absence of symptoms is common, particularly in women, paying attention to any unusual signs can be vital.Early gonorrhea often presents with subtle or absent symptoms.
However, as the infection progresses, the visual signs might become more apparent and more noticeable. These visual changes are not universal, and individual responses can vary. This variability underscores the importance of seeking medical attention if any unusual symptoms arise, especially after potential exposure.
Early Stage Visual Manifestations
In the early stages, gonorrhea may not exhibit any noticeable visual symptoms at all. When symptoms do appear, they can be mild and easily overlooked. For example, some individuals might experience a slight burning sensation during urination or a mild discharge. These initial symptoms often resemble other common conditions, making self-diagnosis difficult and potentially delaying necessary medical care.
Late Stage Visual Manifestations
As gonorrhea progresses, visual symptoms can become more pronounced. This progression can involve increased discharge, which may become thicker or change in color. Painful urination, often accompanied by a burning sensation, becomes more intense. In severe cases, swelling and inflammation in the affected areas, such as the genitals or rectum, might be observed. Additionally, the discharge might become purulent (pus-like), making it more noticeable and obvious.
Individual Variations in Visual Symptoms
The visual presentation of gonorrhea can vary significantly based on individual factors. Gender plays a role, as symptoms might manifest differently in men and women. The presence of other underlying health conditions can also influence the development and presentation of visual symptoms. Furthermore, the individual’s immune response and overall health status can affect how the infection progresses.
This variability makes general guidelines less helpful than a thorough medical evaluation.
Progression of Visual Symptoms Over Time
| Stage | Timeframe | Possible Visual Symptoms | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Early | First few days/weeks | Mild or absent symptoms, slight burning during urination, minimal discharge. | Symptoms may be mistaken for other conditions. |
| Intermediate | Weeks to months | Increased discharge, potentially changing color (yellow, green, or white), more frequent and intense burning sensation, possible pain in the affected area. | Symptoms become more pronounced and noticeable. |
| Late | Months or more | Thick, purulent discharge, intense pain during urination, swelling and inflammation in the genital area, or rectal area. | Severe symptoms require immediate medical attention. |
Early detection is crucial for effective treatment and preventing potential complications.
Early diagnosis is paramount to minimize the risk of complications and ensure effective treatment. Prompt medical intervention is vital to halt the progression of the infection and prevent further complications. This table provides a general overview, but individual experiences may differ.
Visual Distinctions from Other Conditions
Recognizing gonorrhea involves more than just its symptoms. Accurate diagnosis often relies on differentiating it from other sexually transmitted infections (STIs) with similar presentations. Misdiagnosis can lead to inappropriate treatment and potential complications. This section focuses on visual distinctions to aid in proper identification.Differentiating gonorrhea from other STIs requires careful observation of symptoms and a thorough understanding of their distinct visual characteristics.
Gonorrhea, unfortunately, can sometimes manifest with no noticeable symptoms at all. Other times, it might present with a discharge, but it’s crucial to remember that those symptoms can easily be confused with other conditions. This highlights the importance of getting tested if you suspect you might have it. Learning how to encourage eating in dementia patients can be surprisingly similar, requiring a gentle, patient approach.
For more tips on that, check out this helpful resource: how to get dementia patients to eat. Ultimately, though, knowing what gonorrhea doesn’t look like is just as important as knowing its possible appearances.
Gonorrhea, while often accompanied by discharge, can manifest in ways that mimic other infections. Careful consideration of the location, consistency, and color of the discharge, along with other accompanying signs, is crucial.
Visual Differences Between Gonorrhea and Other STIs
Visual distinctions between gonorrhea and other STIs are critical for appropriate treatment. Observing the discharge, lesions, and other associated symptoms allows healthcare providers to make accurate diagnoses. The differences can be subtle, highlighting the importance of a comprehensive evaluation.
- Gonorrhea versus Chlamydia: Both infections can cause urethritis in males, characterized by urethral discharge. However, gonorrhea discharge is often thicker, pussier, and more yellow or greenish, compared to the often clear or milky discharge associated with chlamydia. Furthermore, gonorrhea can cause painful urination (dysuria) and sometimes swelling of the testicles (epididymitis) which are less commonly seen in chlamydia.
- Gonorrhea versus Genital Herpes: Genital herpes presents with characteristic blisters or sores, which can be painful and often rupture to form shallow ulcers. Gonorrhea, on the other hand, typically manifests as a discharge, though it can also cause painful sores, typically with a more diffuse or non-blistering presentation. The lesions associated with herpes tend to cluster together or appear in a pattern.
- Gonorrhea versus Trichomoniasis: Trichomoniasis, in women, can cause a frothy, greenish-yellow vaginal discharge with a strong odor. In men, it may cause urethral discharge, which can be thin and watery. Gonorrhea discharge is usually thicker, more purulent, and often has a yellow or greenish color. The presence of a distinctive odor can be helpful in differentiating between these infections.
Importance of Differential Diagnosis
Accurate identification of an STI is crucial for effective treatment. Mistaking one infection for another can lead to inappropriate therapies and the failure to address the actual condition. This can have long-term implications for the patient’s health. Appropriate treatment is essential for preventing complications and transmission to others.
Distinguishing Gonorrhea Visually from Other Infections
A combination of symptoms and careful visual examination is necessary to distinguish gonorrhea from other infections. The consistency, color, and location of discharge are important indicators. The presence of additional symptoms like pain or swelling can further aid in diagnosis.
| STI | Visual Characteristics | Key Differences from Gonorrhea |
|---|---|---|
| Gonorrhea | Thick, pus-like, yellow-green discharge from the penis or vagina; painful urination; sores; swelling. | Discharge consistency and color are typically more pronounced. |
| Chlamydia | Thin, milky discharge from the penis or vagina; often asymptomatic; painful urination. | Discharge is typically less thick and less visibly colored. |
| Genital Herpes | Painful blisters or sores that rupture; clusters of lesions. | Characteristic blisters or sores are absent in gonorrhea. |
| Trichomoniasis | Frothy, greenish-yellow, foul-smelling discharge from the vagina; painful urination. | Discharge is often more frothy and has a more pronounced odor. |
Illustrative Visuals (No image links): What Does Gonorrhea Look Like
Understanding the visual cues of gonorrhea is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment. While visual symptoms aren’t always present, recognizing potential patterns can aid in seeking medical attention promptly. This section provides detailed descriptions of possible appearances, but it’s vital to remember that these are just examples, and individual experiences can vary. A healthcare professional should always be consulted for accurate diagnosis.
Urethral Discharge in Men
Urethral discharge in men with gonorrhea can manifest as a thick, white, yellow, or greenish pus-like substance. The discharge may be present in small amounts or in larger quantities, and can sometimes be accompanied by pain or burning during urination.
“A thick, white, yellow, or greenish pus-like discharge from the penis is a possible symptom of gonorrhea in men.”
Vaginal Discharge in Women
Vaginal discharge in women with gonorrhea can exhibit similar characteristics to those in men, including thick, white, yellow, or greenish pus-like material. However, it’s also possible for women to experience a watery or increased amount of vaginal discharge. The discharge may also have an unusual odor.
“Possible vaginal discharge in women with gonorrhea can be thick, white, yellow, greenish, or watery and may have an unusual odor.”
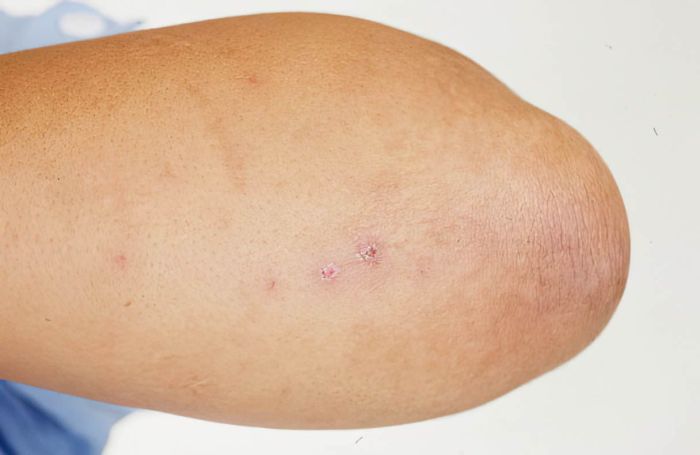
Lesions or Sores
While not always present, gonorrhea can sometimes cause lesions or sores, especially in the genital area. These sores can appear red, inflamed, and painful. They might be small or larger, and their appearance can vary depending on the individual. These sores are not the only indicator of the infection, and their presence does not necessarily confirm a gonorrhea diagnosis.
“Gonorrhea can sometimes cause red, inflamed, painful sores or lesions in the genital area, but these are not always present.”
Visual Acuity in Assessing Symptoms
Accurate visual assessment of potential symptoms is essential for seeking timely medical intervention. Paying attention to the color, consistency, and amount of any discharge, as well as the presence of sores or lesions, is vital. It’s important to note that these visual indicators should not be used to self-diagnose. Consult a healthcare provider for proper evaluation and diagnosis.
“Paying close attention to the color, consistency, and amount of any discharge, as well as the presence of sores or lesions, is crucial for early medical intervention.”
Diagnostic Considerations
Gonorrhea, often a silent infection, requires a meticulous diagnostic approach. A thorough understanding of the disease’s presentation, coupled with appropriate laboratory tests and a structured physical examination, is critical for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. This section will delve into the key elements of diagnosing gonorrhea.
Importance of a Comprehensive Physical Exam
A comprehensive physical exam is crucial in identifying potential symptoms of gonorrhea. It allows healthcare providers to assess for visible signs, such as discharge, pain, or inflammation, in various anatomical locations. This initial assessment guides the selection of appropriate laboratory tests and informs treatment strategies. Early detection and intervention are paramount to prevent complications and spread of the infection.
Role of Laboratory Tests in Confirming Diagnoses
Laboratory tests play a vital role in confirming a gonorrhea diagnosis. They provide definitive evidence of the presence or absence of the bacteriaNeisseria gonorrhoeae*. These tests offer a precise identification of the pathogen, aiding in targeted treatment and preventing misdiagnosis.
Proper Sample Collection for Laboratory Analysis
Accurate sample collection is critical for reliable laboratory results. The specific collection method depends on the site of suspected infection. For example, urethral swabs are used for male patients, while cervical swabs are typically collected from females. Proper collection techniques minimize contamination and maximize the chances of isolating the bacteria for accurate analysis. The use of sterile instruments and adherence to established protocols are essential for ensuring the validity of the laboratory results.
Structured Method for a Physical Examination
A structured approach to the physical examination is crucial for identifying potential gonorrhea symptoms. This method systematically assesses various anatomical areas. The examination should include visual inspection for discharge, swelling, redness, and tenderness. The provider should carefully document all observations.
- Genital Examination: Visual inspection of the urethra (in males) and cervix (in females) for discharge, swelling, redness, or any unusual lesions. Palpation of the affected area can detect tenderness or inflammation. This should be done with appropriate sterile equipment.
- Rectal Examination (if indicated): For patients who report rectal symptoms, a rectal examination might be necessary to assess for discharge, inflammation, or pain. This is crucial for identifying potential rectal gonorrhea.
- Throat Examination (if indicated): In cases of oral sex, a throat examination may be necessary to evaluate for pharyngeal gonorrhea, which is characterized by pain, swelling, or difficulty swallowing.
Table of Common Diagnostic Procedures and Expected Outcomes
| Diagnostic Procedure | Expected Outcome (Positive Result) | Expected Outcome (Negative Result) |
|---|---|---|
| Urethral Swab (Male) | Presence of
|
Absence of
|
| Cervical Swab (Female) | Presence of
|
Absence of
|
| Rectal Swab | Presence of
|
Absence of
|
| Urine Test | Presence of
|
Absence of
|
Outcome Summary
In conclusion, recognizing the visual signs of gonorrhea is vital for early intervention. While the appearance can vary, understanding the typical symptoms, including discharge, sores, and inflammation, is key. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent complications and protect overall health. Remember, this information is for educational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice.