Diarrhea and weight loss often occur together, signaling an underlying issue that needs attention. This comprehensive exploration delves into the complex relationship between these two symptoms, examining the various causes, from infections to dietary factors. We’ll also discuss medical treatments, lifestyle modifications, and the importance of seeking professional medical advice.
Understanding the possible causes of diarrhea and weight loss is crucial for effective management. This includes infections, inflammatory conditions, and digestive disorders. Dietary factors can also play a significant role, with certain food intolerances or nutrient deficiencies contributing to both symptoms. The physiological mechanisms behind these interactions will be discussed in detail.
Causes of Diarrhea and Weight Loss
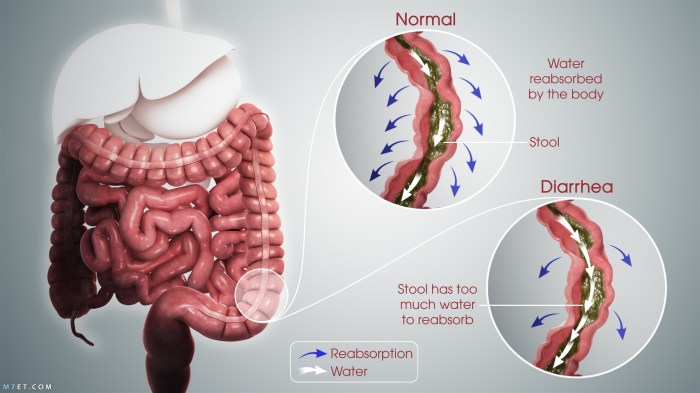
Diarrhea and weight loss, often occurring together, can signal underlying medical issues requiring prompt attention. Understanding the various causes and their associated mechanisms is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment. This exploration delves into the diverse factors contributing to these symptoms, emphasizing the importance of seeking professional medical advice for accurate evaluation and personalized care.A significant weight loss coupled with diarrhea can stem from a multitude of factors, ranging from easily treatable infections to more complex conditions.
This detailed look at the causes will provide a deeper understanding of the physiological processes behind these symptoms, enabling better recognition and management.
Infectious Causes
Infectious gastroenteritis, commonly known as food poisoning, is a frequent culprit behind both diarrhea and weight loss. Viruses, bacteria, and parasites can infect the intestines, disrupting normal function and leading to watery stools and decreased nutrient absorption. The inflammatory response triggered by these pathogens can also cause a loss of appetite, contributing to weight loss. Symptoms of infectious gastroenteritis typically include sudden onset of diarrhea, abdominal cramps, nausea, and vomiting.
Severity varies depending on the causative agent and individual response. Examples include norovirus, salmonella, and campylobacter infections. These infections often resolve within a few days with supportive care, including adequate hydration.
Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), such as Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, are chronic conditions characterized by inflammation of the digestive tract. The persistent inflammation damages the intestinal lining, disrupting nutrient absorption and leading to chronic diarrhea. Weight loss is common due to malabsorption, reduced appetite, and the body’s increased energy expenditure to fight the inflammation. Symptoms of IBD can vary, but often include chronic abdominal pain, bloody diarrhea, and fatigue.
The severity and frequency of these symptoms can fluctuate. In Crohn’s disease, inflammation can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract, while ulcerative colitis typically affects the colon and rectum.
Malabsorption Syndromes
Malabsorption syndromes are characterized by the inability of the small intestine to properly absorb nutrients from food. This can result from various conditions, including celiac disease, cystic fibrosis, and pancreatic insufficiency. The inadequate absorption of nutrients leads to malnutrition, resulting in weight loss and chronic diarrhea. Symptoms often include bulky, fatty stools, abdominal bloating, and gas. Celiac disease is an autoimmune response to gluten, leading to damage in the small intestine.
Cystic fibrosis impacts multiple organs, including the pancreas, leading to enzyme deficiency. Pancreatic insufficiency results in insufficient digestive enzyme production, impeding nutrient breakdown and absorption.
Other Medical Conditions
Other medical conditions can also contribute to both diarrhea and weight loss. Cancer, particularly those affecting the gastrointestinal tract, can cause significant weight loss due to the body’s metabolic response to the disease. Certain medications, such as some chemotherapy drugs, can also have diarrhea as a side effect. Hypothyroidism, an underactive thyroid gland, can slow down metabolism, affecting appetite and leading to weight gain or loss in some cases.
Additionally, certain hormonal imbalances can contribute to weight loss and diarrhea.
Losing weight with diarrhea can be tricky, especially when you’re feeling unwell. Sometimes, a sore throat accompanies the digestive issues, and a simple remedy like gargling salt water can offer some relief. This helps soothe the throat, but doesn’t directly address the underlying diarrhea, which can still contribute to weight loss, especially if the condition persists. For more information on the benefits of gargling salt water for sore throat , check out this helpful guide.
Ultimately, addressing the diarrhea is key for both comfort and regaining lost weight.
Summary Table
| Cause | Symptoms | Treatments |
|---|---|---|
| Infectious Gastroenteritis | Sudden onset diarrhea, abdominal cramps, nausea, vomiting, fever. | Rest, hydration, electrolyte replacement, and potentially antibiotics. |
| Inflammatory Bowel Diseases (IBD) | Chronic abdominal pain, bloody diarrhea, fatigue, weight loss, and malnutrition. | Anti-inflammatory medications, immunomodulators, and surgery in severe cases. |
| Malabsorption Syndromes | Bulky, fatty stools, abdominal bloating, gas, weight loss, and malnutrition. | Dietary modifications, enzyme replacement therapy, and specific treatments for the underlying condition (e.g., gluten-free diet for celiac disease). |
| Cancer | Weight loss, chronic diarrhea, fatigue, and other systemic symptoms depending on the location and type of cancer. | Targeted therapy, chemotherapy, surgery, radiation therapy, and supportive care. |
| Other Medical Conditions | Variable symptoms depending on the specific condition, including weight loss, diarrhea, and changes in appetite. | Treatment tailored to the specific condition, potentially including medication, lifestyle adjustments, or surgery. |
Dietary Factors Contributing to Diarrhea and Weight Loss
Dietary choices play a significant role in both the development and management of diarrhea and weight loss. Poor dietary habits can disrupt the delicate balance of gut health, leading to chronic digestive issues and impacting overall nutritional intake. Unhealthy eating patterns can also contribute to nutrient deficiencies, further exacerbating these symptoms. Understanding the specific dietary factors involved is crucial for developing effective strategies to address and prevent these conditions.Dietary factors can significantly influence the digestive system, triggering both diarrhea and impacting nutrient absorption, leading to weight loss.
Nutrient deficiencies resulting from poor dietary choices can create an environment conducive to digestive distress, while specific food intolerances or allergies can directly cause diarrhea and impair the body’s ability to absorb essential nutrients, impacting weight. The interplay between diet and these symptoms underscores the importance of mindful eating and a balanced approach to food selection.
Nutrient Deficiencies and Diarrhea/Weight Loss
Nutrient deficiencies can disrupt the normal functioning of the digestive system, leading to diarrhea and hindering weight gain. Certain vitamins and minerals are essential for proper gut health and nutrient absorption. For instance, deficiencies in vitamin D, zinc, or certain B vitamins can weaken the intestinal lining, making it more susceptible to infections and irritants, leading to diarrhea.
This compromised absorption can result in inadequate intake of essential nutrients, further contributing to weight loss.
Food Intolerances and Allergies
Food intolerances and allergies can directly trigger diarrhea and hinder weight gain. Substances like lactose, gluten, or certain food additives can irritate the digestive tract, causing inflammation and diarrhea. The immune system’s reaction to allergens can also trigger a cascade of inflammatory responses that can affect nutrient absorption, thus leading to weight loss. Individuals with sensitivities to specific foods may experience chronic diarrhea and have difficulties meeting their nutritional needs, which can manifest as significant weight loss.
Impact of Dietary Habits
Dietary habits can either exacerbate or mitigate the problem of diarrhea and weight loss. Regular consumption of processed foods, high-fat meals, or foods high in sugar and refined carbohydrates can disrupt the gut microbiome, increasing the risk of diarrhea and impairing nutrient absorption. Conversely, a diet rich in fiber, probiotics, and easily digestible foods can support a healthy gut microbiome, potentially reducing diarrhea and promoting nutrient absorption.
A balanced diet rich in whole foods, adequate hydration, and mindful eating practices can significantly improve gut health and aid in managing both diarrhea and weight loss.
Specific Dietary Patterns
Certain dietary patterns can contribute to both diarrhea and weight loss. For example, a diet overly reliant on processed foods, fast food, or sugary drinks often lacks essential nutrients and can disrupt gut health, potentially leading to diarrhea and preventing adequate calorie intake. Similarly, severely restrictive diets, such as fad diets, can deprive the body of essential nutrients, causing nutrient deficiencies and potentially resulting in diarrhea and weight loss.
Unbalanced diets that lack fiber or essential vitamins and minerals can contribute to these issues.
Experiencing diarrhea can sometimes lead to unexpected weight loss, which can be concerning. It’s important to address the underlying cause, and while it’s not directly related, dealing with acute low back pain try this first acute low back pain try this first might surprisingly affect your digestive system. If you’re experiencing both diarrhea and weight loss, it’s crucial to consult a doctor to rule out any serious health issues.
Dietary Triggers for Diarrhea and Weight Loss
| Dietary Factor | Impact on Diarrhea | Impact on Weight Loss | Modifications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Processed foods | Increased risk of diarrhea due to high content of additives and preservatives. | Reduced nutrient density, leading to inadequate calorie intake and weight loss. | Prioritize whole, unprocessed foods. |
| High-fat meals | Can trigger diarrhea in some individuals due to difficulty in digestion. | High-fat meals often lack fiber and essential nutrients, hindering weight gain. | Include more lean proteins and fiber-rich foods in meals. |
| Sugary drinks | Increased risk of diarrhea due to the high sugar content, potentially disrupting the gut microbiome. | Empty calories and lack of essential nutrients, contributing to weight loss. | Replace sugary drinks with water, unsweetened tea, or low-sugar options. |
| Spicy foods | Can cause diarrhea in sensitive individuals due to irritation of the digestive tract. | Spicy foods may be high in calories but often lack essential nutrients. | Moderate intake of spicy foods, focusing on balance. |
| Dairy products (lactose intolerance) | Lactose intolerance can cause diarrhea due to difficulty digesting lactose. | Dairy products can be a source of calories but might be difficult to digest for those with intolerance, leading to weight loss issues. | Reduce or eliminate dairy products if lactose intolerance is present, or opt for lactose-free options. |
| Gluten (Celiac disease or gluten sensitivity) | Gluten can cause diarrhea in individuals with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity. | Gluten-free diets may be lower in calories and nutrients for those who do not have celiac disease or gluten sensitivity. | Consult with a healthcare professional for personalized recommendations. |
Medical Treatments and Management Strategies
Addressing diarrhea and weight loss requires a multifaceted approach, focusing on identifying and treating the underlying cause. Effective management strategies encompass a range of medical treatments, dietary modifications, and lifestyle adjustments. This section explores various medical interventions, outlining their rationale, potential side effects, and comparative efficacy.Different medical treatments for diarrhea and weight loss are tailored to the specific cause.
For example, infections require antimicrobial therapy, while inflammatory bowel disease necessitates immunosuppressants. Understanding the root cause is crucial for selecting the appropriate and most effective treatment.
Pharmacological Treatments
Various medications are employed to address the symptoms and underlying causes of diarrhea and weight loss. Antidiarrheal medications, such as loperamide, can reduce the frequency and severity of bowel movements. These medications work by slowing down the movement of the intestines, allowing more water to be absorbed. However, these medications should be used cautiously, especially in cases of infectious diarrhea, as they may prolong the duration of the infection.
Another class of medications, such as bismuth subsalicylate, can help reduce inflammation and relieve symptoms of diarrhea.
Immunosuppressants
In cases of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), such as Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis, immunosuppressants are often prescribed to reduce inflammation in the digestive tract. These medications, like corticosteroids and immunomodulators, can effectively control symptoms and prevent relapses. The rationale behind their use lies in their ability to dampen the immune response, thereby lessening the inflammation and damage to the intestinal lining.
However, these medications can have significant side effects, including increased risk of infection, weakened immune system, and potential long-term complications.
Probiotics and Prebiotics
Probiotics, live microorganisms, and prebiotics, substances that promote the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut, may play a role in managing diarrhea and improving gut health. They are often used in conjunction with other treatments to restore the balance of gut microbiota and reduce the severity of symptoms. For example, studies have shown that certain strains of probiotics can effectively reduce the duration and frequency of diarrhea.
Nutritional Support, Diarrhea and weight loss
In cases of severe diarrhea and malnutrition, nutritional support may be crucial. This can include intravenous fluids to correct electrolyte imbalances, and nutritional supplements to provide essential nutrients and calories. The rationale behind this approach is to address the immediate nutritional needs of the body while the underlying cause is being treated. Intravenous fluids help replenish lost fluids and electrolytes, while nutritional supplements provide essential nutrients and calories to promote weight gain.
Table: Comparison of Treatment Approaches
| Treatment | Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
| Antidiarrheal medications (e.g., loperamide) | Reduce frequency and severity of diarrhea | May prolong infection, not suitable for all cases |
| Immunosuppressants (e.g., corticosteroids, immunomodulators) | Control symptoms, prevent relapses in IBD | Increased risk of infection, potential long-term complications |
| Probiotics/Prebiotics | Restore gut microbiota balance, reduce diarrhea | Limited efficacy in severe cases, potential allergic reactions |
| Nutritional support (IV fluids, supplements) | Address nutritional deficiencies, promote weight gain | Requires medical supervision, may not address underlying cause |
Lifestyle Modifications and Preventative Measures
Managing diarrhea and weight loss often involves more than just treating the symptoms. A holistic approach focusing on lifestyle modifications can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of these issues. These changes encompass dietary adjustments, stress management techniques, and proactive measures to prevent future infections. Implementing these strategies not only addresses the current problem but also contributes to overall health and well-being.Lifestyle changes are crucial in preventing and managing diarrhea and weight loss.
They go beyond simply addressing symptoms and focus on the root causes, which often involve underlying factors such as poor diet, stress, and infections. By adopting healthier habits, individuals can reduce their risk of experiencing these issues and improve their overall health.
Maintaining a Healthy Diet
A balanced diet plays a vital role in digestive health. Foods high in fiber, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, promote healthy bowel movements. Conversely, excessive consumption of processed foods, sugary drinks, and certain spices can irritate the digestive system and contribute to diarrhea. Limiting these foods can help prevent episodes of diarrhea and maintain a healthy weight.
Include plenty of fruits and vegetables in your daily meals to ensure your body gets the necessary nutrients. Choose lean protein sources and healthy fats.
Hydration
Adequate hydration is essential for overall health and digestive function. When experiencing diarrhea, the body loses fluids rapidly, leading to dehydration. Drinking plenty of water, clear broths, and electrolyte drinks can help replenish lost fluids and prevent dehydration. Aim for at least eight glasses of water a day, and increase intake if you’re experiencing diarrhea. Electrolyte drinks can be particularly helpful in replacing lost minerals and salts.
Stress Management
Stress can significantly impact the digestive system, potentially triggering or exacerbating diarrhea. Chronic stress can weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections. Effective stress management techniques, such as exercise, meditation, yoga, or spending time in nature, can help reduce stress levels and improve digestive health. These practices can also positively influence overall well-being.
Sanitation
Maintaining good hygiene practices is crucial in preventing infections that can cause diarrhea. Regular handwashing with soap and water, especially after using the restroom and before preparing food, is essential. Avoiding contaminated food and water is also vital. Proper food handling and storage practices are important to prevent the growth of harmful bacteria.
Dietary Habits
Following a diet tailored to your digestive needs is critical in managing and preventing diarrhea. This includes avoiding foods known to trigger symptoms, such as greasy or spicy foods, and consuming foods that promote healthy digestion, like yogurt and probiotics. Pay close attention to how your body reacts to different foods, and make adjustments accordingly.
Preventative Measures
- Hydration: Maintaining adequate hydration is paramount, especially during and after episodes of diarrhea. This prevents dehydration, a serious complication of diarrhea.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can weaken the immune system and exacerbate digestive issues. Implementing stress-reduction techniques like meditation, yoga, or spending time in nature can be beneficial.
- Dietary Habits: Adopting a balanced diet that includes plenty of fiber, fruits, and vegetables can promote healthy digestion. Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and trigger foods like spicy or greasy items.
- Sanitation: Maintaining good hygiene practices, such as regular handwashing, is crucial in preventing the spread of infections that cause diarrhea. Proper food handling and storage are equally important.
Underlying Conditions and Their Interrelation
Experiencing diarrhea and weight loss simultaneously can be a significant health concern, often signaling an underlying medical issue. These symptoms, while seemingly separate, frequently interact and exacerbate each other, making proper diagnosis and treatment crucial. Understanding the interplay between these conditions is vital for effective management and recovery.
Common Underlying Conditions
Many medical conditions can cause both diarrhea and weight loss. These conditions disrupt the body’s ability to absorb nutrients, leading to malabsorption and subsequent weight loss. Some of the most prevalent include inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), such as Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. Infections, particularly chronic infections, can also contribute to these symptoms. Furthermore, certain endocrine disorders and autoimmune diseases can also play a role.
Identifying the specific underlying cause is key to successful treatment.
Interaction and Exacerbation
The relationship between diarrhea and weight loss can be cyclical. Persistent diarrhea can lead to significant fluid and nutrient loss, which in turn contributes to weight loss. Simultaneously, the underlying condition causing the diarrhea may also impair the body’s ability to absorb nutrients, compounding the weight loss problem. This vicious cycle often necessitates a multi-faceted approach to treatment, addressing both the symptoms and the root cause.
Impact on Nutrient Absorption
Conditions that lead to diarrhea and weight loss often impair the body’s ability to absorb essential nutrients. For instance, inflammatory bowel diseases can cause inflammation in the intestines, reducing the surface area available for nutrient absorption. Chronic infections can also interfere with nutrient absorption by damaging the intestinal lining. This impaired absorption directly contributes to weight loss as the body is unable to acquire the necessary energy and building blocks for proper function.
Malabsorption can result in deficiencies of vitamins, minerals, and proteins, further impacting overall health.
Experiencing diarrhea can sometimes lead to unexpected weight loss. It’s crucial to understand the underlying causes before jumping to conclusions. If you’re considering medication like Zyrtec, it’s always wise to check out resources like before you buy Zyrtec to ensure it’s appropriate for your needs and doesn’t exacerbate any existing health issues, potentially affecting your weight or digestive system.
Ultimately, addressing diarrhea effectively is key to maintaining a healthy weight.
Hormonal Imbalances and Digestive Health
Hormonal imbalances can significantly impact digestive health and weight. For example, thyroid disorders can cause both diarrhea and weight loss. An underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism) can slow down metabolism, leading to weight gain in some cases. However, in some cases, an overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism) can increase metabolism, leading to weight loss, and simultaneously triggering digestive issues, such as diarrhea.
Other hormonal imbalances, such as those related to diabetes or adrenal disorders, can also contribute to these symptoms.
Underlying Conditions, Diarrhea, and Weight Loss
| Underlying Condition | Impact on Diarrhea | Impact on Weight Loss |
|---|---|---|
| Inflammatory Bowel Disease (Crohn’s Disease, Ulcerative Colitis) | Chronic, often bloody diarrhea; abdominal pain | Significant weight loss due to malabsorption and inflammation |
| Celiac Disease | Chronic diarrhea, abdominal bloating, and cramping | Significant weight loss due to gluten intolerance and malabsorption |
| Chronic Infections (e.g., Tuberculosis, HIV) | Frequent, watery diarrhea | Weight loss due to nutrient malabsorption and systemic inflammation |
| Cancer (e.g., Pancreatic Cancer, Gastrointestinal Cancer) | Diarrhea, sometimes with blood | Rapid weight loss due to tumor growth and nutrient malabsorption |
| Thyroid Disorders (Hyperthyroidism) | Diarrhea, increased appetite | Significant weight loss despite increased appetite |
| Diabetes | Frequent urination and diarrhea | Weight loss due to uncontrolled glucose levels and dehydration |
Importance of Professional Medical Advice
Persistent diarrhea and weight loss, while sometimes manageable with lifestyle changes and dietary adjustments, often signal an underlying health issue requiring professional medical attention. Ignoring these symptoms can lead to serious complications and delay appropriate treatment. Seeking timely medical advice is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective management.Professional medical guidance is essential because it allows for a comprehensive evaluation beyond self-diagnosis.
A healthcare provider can assess your overall health, medical history, and specific symptoms to determine the root cause of your diarrhea and weight loss. This assessment often involves a thorough physical examination, gathering detailed patient history, and potentially ordering diagnostic tests.
Diagnostic Tests for Identifying the Cause
Diagnostic tests are vital tools in identifying the specific cause of diarrhea and weight loss. These tests help rule out various potential underlying conditions and guide treatment decisions. Common tests may include stool samples to detect infections, blood tests to evaluate nutrient levels and organ function, and imaging studies to visualize the digestive tract. These tests provide objective data to aid in the diagnostic process.
Symptoms Requiring Immediate Medical Attention
Certain symptoms associated with diarrhea and weight loss necessitate immediate medical attention. These urgent situations often indicate severe complications or potentially life-threatening conditions. Prompt medical intervention is crucial to prevent further deterioration and ensure appropriate treatment.
- Severe abdominal pain or cramping:
- High fever (above 101°F or 38.3°C):
- Blood or mucus in the stool:
- Signs of dehydration:
- Sudden and significant weight loss:
Persistent or intense abdominal pain can indicate serious underlying conditions, such as appendicitis, inflammatory bowel disease, or even a bowel obstruction. This warrants immediate medical intervention.
Fever accompanying diarrhea can signify an infection or other serious illness. Prompt medical attention is necessary to prevent complications and identify the cause.
The presence of blood or mucus in stool is a significant warning sign that may indicate inflammation, infection, or other serious conditions in the digestive tract. Immediate medical evaluation is critical to determine the source of bleeding or inflammation.
Excessive diarrhea can lead to significant fluid loss, causing dehydration. Symptoms such as extreme thirst, dizziness, lightheadedness, and decreased urination signal the need for immediate medical attention to restore hydration.
Rapid weight loss accompanied by diarrhea often indicates a serious underlying issue. This warrants immediate investigation and intervention to prevent further health complications.
Importance of Timely Medical Care
Delaying medical care for persistent diarrhea and weight loss can have serious consequences. Untreated conditions can lead to complications like dehydration, malnutrition, electrolyte imbalances, and further damage to the digestive system. The sooner the cause is identified and addressed, the better the outcome. Early intervention often leads to more effective treatment and prevents potential long-term health problems.
Potential Risks of Delaying Treatment
The risks of delaying treatment for diarrhea and weight loss are substantial. Delayed intervention can exacerbate underlying conditions, potentially leading to complications such as severe dehydration, electrolyte disturbances, and malnutrition. This can result in a prolonged recovery period, increased medical costs, and potentially more serious health consequences.
Table of Symptoms Requiring Immediate Medical Attention
| Symptom | Action |
|---|---|
| Severe abdominal pain or cramping | Seek immediate medical attention |
| High fever (above 101°F or 38.3°C) | Seek immediate medical attention |
| Blood or mucus in the stool | Seek immediate medical attention |
| Signs of dehydration (extreme thirst, dizziness, lightheadedness, decreased urination) | Seek immediate medical attention |
| Sudden and significant weight loss | Seek immediate medical attention |
Wrap-Up

In conclusion, diarrhea and weight loss can stem from a multitude of factors, ranging from simple dietary indiscretions to severe underlying medical conditions. Understanding these causes, coupled with appropriate medical guidance, is vital for effective management and treatment. Remember, persistent diarrhea and weight loss require prompt medical attention to identify the root cause and prevent potential complications. This comprehensive overview provides a foundation for understanding the interplay between these symptoms and the importance of seeking professional medical advice.