What is patulous eustachian tube? This condition, where the Eustachian tube remains abnormally open, can lead to a range of ear issues. Understanding the normal function of this vital tube, and how its persistent openness differs from the norm, is key to grasping the nuances of this condition. This in-depth look will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis associated with patulous eustachian tube, providing a comprehensive overview of this often-misunderstood ear problem.
The Eustachian tube, a crucial part of our auditory system, normally regulates pressure in the middle ear. When it’s patulous, this delicate balance is disrupted, leading to a cascade of potential complications. This article will delve into the specific anatomy of the Eustachian tube, highlighting the critical components involved and how their malfunction can manifest in various ways.
Definition and Overview
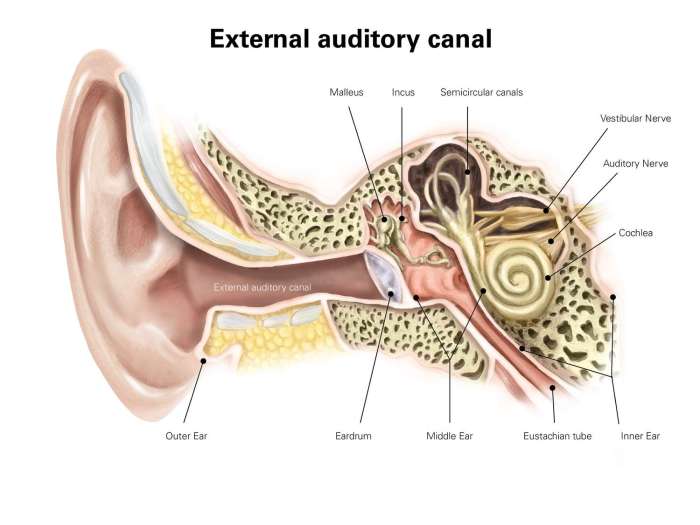
The Eustachian tube, a vital part of our ear, plays a crucial role in maintaining pressure equilibrium between the middle ear and the nasopharynx. A patulous Eustachian tube, however, deviates significantly from this normal function, impacting the delicate balance within the ear. This blog post will delve into the specifics of a patulous Eustachian tube, examining its definition, normal function, and anatomical structure.Understanding the patulous Eustachian tube requires first comprehending the normal function of the Eustachian tube.
A patulous eustachian tube is essentially when that tiny tube connecting your throat to your middle ear stays open all the time. This can lead to all sorts of ear issues, and surprisingly, it can be linked to dietary habits, like consuming excessive amounts of foods high in sodium. A high-sodium diet can potentially impact fluid balance, which might indirectly affect the Eustachian tube’s function, although more research is needed.
Ultimately, understanding patulous eustachian tube involves looking at various factors, including diet, but it’s a complex condition.
The tube, a narrow channel connecting the middle ear to the nasopharynx, acts as a pressure valve. It opens periodically to equalize air pressure in the middle ear with the atmospheric pressure outside the body, ensuring optimal function of the eardrum and hearing. This normal opening and closing is a crucial aspect of auditory health.
Normal Function of the Eustachian Tube, What is patulous eustachian tube
The Eustachian tube’s normal function is essential for maintaining optimal middle ear pressure. This pressure regulation is critical for clear hearing and prevents discomfort. The tube opens and closes in response to various factors, including swallowing, yawning, and changes in atmospheric pressure. These actions facilitate the passage of air, maintaining the proper pressure differential between the middle ear and the external environment.
This process is crucial for normal hearing and preventing earaches.
Comparison of Normal and Patulous Eustachian Tubes
A normal Eustachian tube functions effectively, regulating middle ear pressure in response to external changes. It opens and closes periodically to maintain the necessary pressure balance. Conversely, a patulous Eustachian tube remains persistently open. This continuous openness leads to a constant flow of air between the middle ear and the nasopharynx, which disrupts the delicate pressure balance and can lead to various symptoms.
This persistent openness can impact hearing and create a sensation of fullness or pressure in the ear.
Anatomical Location and Structure of the Eustachian Tube
The Eustachian tube is situated within the skull, connecting the middle ear cavity to the nasopharynx. It originates from the anterior wall of the middle ear cavity, descending obliquely towards the nasopharynx. Its course is roughly horizontal and slightly downward, with the opening of the tube positioned near the posterior portion of the nasal cavity. This specific location, relative to the nasopharynx and the middle ear, dictates its role in pressure regulation.
Key Components of the Eustachian Tube
| Component | Description | Location | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tubal Ostium | The opening of the Eustachian tube into the nasopharynx. | Nasopharynx | Allows air to enter the middle ear to equalize pressure. |
| Tubal Wall | The muscular and cartilaginous structure of the tube. | Between the middle ear and nasopharynx. | Provides support and facilitates the opening and closing of the tube. |
| Pharyngeal Ostium | The opening of the Eustachian tube into the nasopharynx. | Nasopharynx | Allows air to enter the middle ear to equalize pressure. |
| Tubal Muscles | Muscles that control the opening and closing of the tube. | Surrounding the Eustachian tube | Regulate air pressure in the middle ear. |
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding the causes and risk factors of a patulous Eustachian tube is crucial for diagnosis and management. While the exact mechanisms aren’t always clear, several contributing factors have been identified. A deeper dive into these factors helps individuals and healthcare providers better anticipate and address this condition.The patulous Eustachian tube is a condition where the Eustachian tube, a vital pathway connecting the middle ear to the back of the nose and throat, remains open or inadequately closed.
This persistent opening disrupts the normal pressure equilibrium in the middle ear, potentially leading to various symptoms and complications.
Potential Causes
Several factors can contribute to a patulous Eustachian tube, some of which are better understood than others. Underlying conditions and lifestyle choices may play a role.
- Upper respiratory infections (URIs): Frequent or chronic infections can weaken the muscles responsible for closing the Eustachian tube, potentially leading to a patulous state. This weakening may be a temporary response to the infection, or in some cases, a long-term consequence.
- Allergies and environmental irritants: Chronic exposure to allergens or irritants can inflame the Eustachian tube area, impacting the tube’s ability to close properly. This can result in prolonged opening of the tube.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as nasal decongestants and antihistamines, can impact the function of the Eustachian tube, sometimes contributing to patulousness. Specific types and dosages may increase the risk.
- Barotrauma and altitude changes: Exposure to rapid changes in pressure, such as during air travel or scuba diving, can stress the Eustachian tube, potentially causing it to remain open. Frequent or extreme exposure to these situations might increase the likelihood of patulousness.
- Neurological conditions: Certain neurological disorders, affecting the muscles controlling the Eustachian tube, can disrupt the normal closure mechanism, increasing the likelihood of a patulous Eustachian tube. Examples include multiple sclerosis or certain cranial nerve palsies.
- Anatomical variations: Some individuals might have variations in the structure of their Eustachian tube or surrounding tissues, potentially predisposing them to patulousness. This may affect the effectiveness of the tube’s closing mechanism.
Risk Factors
Various factors can increase the susceptibility to developing a patulous Eustachian tube. Understanding these factors can help identify individuals who might be at higher risk.
A patulous eustachian tube is basically when the tube connecting your ear to your throat stays open all the time, which can lead to some annoying ear issues. Sometimes, a lack of iron in your diet can affect your overall health, impacting things like energy levels and even ear function, which might make it seem like your tube is staying open more often.
Fortunately, there are effective treatments for iron deficiency anemia that can help address this underlying issue. Finding out about treatments for iron deficiency anemia can provide insights into improving your overall health and, consequently, potentially easing the symptoms of a patulous eustachian tube. Ultimately, understanding the root causes of this condition is key to finding the best solutions.
- Age: While patulous Eustachian tube can affect individuals of any age, some studies suggest that the condition might be more common in certain age groups. Children and adolescents might be particularly susceptible due to developmental factors and a higher incidence of upper respiratory infections.
- Gender: Some studies have suggested a possible correlation between gender and the occurrence of patulous Eustachian tube, although the findings aren’t entirely consistent. Further research is needed to determine if there’s a significant gender disparity.
- Family history: A family history of ear infections or similar conditions could potentially indicate a predisposition to patulous Eustachian tube. This could involve genetic factors or shared environmental exposures.
- Certain occupations or activities: Individuals involved in activities requiring frequent or prolonged changes in pressure, such as airplane pilots or scuba divers, may be at a higher risk. The repeated pressure changes can strain the Eustachian tube.
Summary Table
| Cause | Risk Factor | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Upper Respiratory Infections | Frequent infections | Chronic or frequent infections can weaken muscles controlling Eustachian tube closure. |
| Allergies/Irritants | Chronic exposure | Prolonged exposure can inflame the Eustachian tube area, hindering proper closure. |
| Medications | Certain types | Specific nasal decongestants and antihistamines can impact tube function. |
| Barotrauma/Altitude Changes | Frequent exposure | Rapid pressure changes can stress the tube, potentially leading to an open state. |
| Neurological Conditions | Disorders affecting controlling muscles | Conditions affecting muscles controlling the tube can disrupt closure mechanisms. |
| Anatomical Variations | Structural differences | Variations in Eustachian tube structure may impact its closing efficiency. |
| Age | Developmental factors | Children and adolescents may be more susceptible due to developmental aspects and higher infection rates. |
| Gender | Possible correlation | Some studies suggest a potential correlation, but further research is needed. |
| Family History | Ear infections/related conditions | Family history may indicate a predisposition to the condition. |
| Occupation/Activities | Frequent pressure changes | Jobs or activities involving pressure fluctuations may increase risk. |
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Understanding the symptoms and diagnostic methods for patulous Eustachian tube dysfunction is crucial for early intervention and effective management. Early detection allows for prompt treatment, potentially preventing further complications. This section delves into the common signs and the various techniques used to confirm the diagnosis.The symptoms of patulous Eustachian tube dysfunction can be subtle and often overlap with other ear, nose, and throat conditions.
Careful attention to the presented symptoms, coupled with a thorough examination, is key to accurate diagnosis.
Common Symptoms
The most prevalent symptoms of patulous Eustachian tube dysfunction stem from the persistent opening of the Eustachian tube. This allows air to enter the middle ear more freely, but also allows the entry of unwanted sounds or foreign matter. This can result in a variety of symptoms, including:
- Persistent ear fullness: A feeling of pressure or congestion in the ear, often described as a “plugged” sensation. This is a very common symptom and can be intermittent or constant.
- Tinnitus: A ringing, buzzing, or hissing sound in the ears, which may be exacerbated by patulous Eustachian tube.
- Hearing loss: While not always present, hearing loss can occur due to the constant pressure fluctuations or middle ear infections.
- Earaches: In some cases, ear pain may be experienced. This can be mild to moderate and may be accompanied by other symptoms.
- Discomfort or pain in the jaw or face: Some patients experience pain in the jaw or face area, often related to the proximity of the Eustachian tube to these structures.
Diagnostic Methods
Several diagnostic methods are used to identify patulous Eustachian tube dysfunction. These methods are usually integrated to gain a comprehensive picture of the patient’s condition.
- Otoscopic Examination: This involves visually inspecting the external ear canal and tympanic membrane (eardrum) using an otoscope. The examiner looks for any signs of inflammation, perforation, or other abnormalities that may suggest the presence of an underlying ear condition. Crucially, the examiner should note any unusual characteristics of the eardrum’s movement or the presence of a retracted or bulging eardrum.
A patulous eustachian tube is basically when the tube connecting your ear to your throat stays open all the time. This can lead to some ear issues, but did you know that managing blood pressure can indirectly impact ear health? For example, adopting healthy habits like eating a balanced diet and exercising regularly, which are also important for how to lower blood pressure , might also contribute to a healthier Eustachian tube function.
Ultimately, understanding patulous eustachian tube involves looking at various factors, including overall well-being.
The tympanic membrane may appear unusually mobile or demonstrate abnormal mobility patterns.
- Acoustic Reflex Testing: This test assesses the function of the middle ear muscles in response to sound. An absence of an acoustic reflex, or an abnormal acoustic reflex, can be an indication of a dysfunction in the middle ear. The presence or absence of the acoustic reflex is an important diagnostic sign.
- Tympanometry: This test measures the pressure within the middle ear. Abnormal pressure readings, or the absence of a pressure reading, can be indicative of patulous Eustachian tube. An unusual lack of mobility or resistance in the tympanic membrane to changes in pressure suggests a patulous Eustachian tube.
Thorough Ear Examination Procedures
A thorough ear examination should include careful observation of the external ear, the ear canal, and the eardrum. The examiner should use appropriate lighting and magnification to ensure a clear view of the structures. Visual inspection should include a detailed assessment of the eardrum’s appearance and any signs of fluid buildup. Further, the examiner must assess the mobility of the eardrum in response to changes in pressure.
| Test | Procedure | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Otoscopic Examination | Visual inspection of the ear canal and eardrum using an otoscope. | Identifies any visible abnormalities like inflammation, perforation, or fluid buildup. |
| Acoustic Reflex Testing | Measuring the middle ear muscle response to sound. | Indicates potential middle ear dysfunction, which can be linked to patulous Eustachian tube. |
| Tympanometry | Measuring middle ear pressure. | Detects abnormal pressure levels, which are often associated with patulous Eustachian tube. |
Treatment and Management
Managing patulous Eustachian tube involves a multifaceted approach, focusing on alleviating symptoms and improving Eustachian tube function. While a complete cure isn’t always possible, various strategies can significantly improve quality of life for those affected. The choice of treatment often depends on the severity of symptoms, individual response, and the underlying cause of the patulous condition.Effective management of patulous Eustachian tube often involves a combination of non-surgical and, in some cases, surgical interventions.
The goal is to reduce the frequency and intensity of symptoms, allowing for improved hearing and overall well-being. This requires careful consideration of individual needs and a collaborative approach between patients and healthcare professionals.
Non-Surgical Interventions
Non-surgical interventions are often the first line of treatment for patulous Eustachian tube. These strategies aim to reduce pressure and irritation in the middle ear while promoting Eustachian tube closure.
- Avoiding Irritants: Identifying and avoiding triggers such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and certain medications can be beneficial. For example, someone with patulous Eustachian tube experiencing symptoms after consuming caffeinated beverages might find that reducing caffeine intake helps alleviate their symptoms. This personalized approach is crucial for effective management.
- Nasal Saline Irrigation: Regular rinsing of the nasal passages with saline solution can help keep the nasal passages moist and reduce inflammation. This can, in turn, decrease pressure on the Eustachian tube, potentially relieving symptoms. The use of a neti pot or similar devices is common.
- Ear Plugs/Earmuffs: Using earplugs or earmuffs, especially in noisy environments, can help reduce pressure fluctuations that can trigger or exacerbate symptoms. This is particularly helpful for individuals who work in noisy environments or frequently experience loud noises. This simple measure can make a considerable difference.
- Positional Changes: Maintaining an upright posture or avoiding lying down during certain periods, especially at night, might reduce pressure changes that could impact the Eustachian tube. This is a simple but potentially valuable strategy to consider.
Medical Therapies
Certain medications may help to reduce inflammation or manage associated symptoms. However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable medical therapies for an individual.
- Decongestants: These medications can help reduce nasal congestion, potentially alleviating some of the symptoms related to patulous Eustachian tube. However, long-term use of decongestants can be problematic, so it’s crucial to follow medical advice carefully.
- Antihistamines: For individuals with allergies that might contribute to inflammation and symptoms, antihistamines can be helpful. These are effective in reducing allergic reactions and improving overall comfort.
- Corticosteroids: In some cases, topical or oral corticosteroids may be used to reduce inflammation in the Eustachian tube and surrounding tissues. However, the use of corticosteroids requires careful consideration of potential side effects.
Surgical Procedures
Surgical intervention is typically considered only when non-surgical approaches prove insufficient.
- Tympanoplasty: This procedure involves reconstructing the eardrum and/or middle ear structures. It may be considered in certain cases of patulous Eustachian tube, where structural abnormalities are contributing to the condition. This surgical intervention aims to correct the anatomical structure.
- Eustachian Tube Tuboplasty: This procedure focuses on modifying the Eustachian tube itself to improve its function and control its opening and closing. This is a specialized surgical approach that targets the Eustachian tube directly.
Treatment Effectiveness Comparison
| Treatment | Description | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Non-Surgical Interventions | Lifestyle adjustments, nasal irrigation, earplugs, and positional changes | Generally effective for mild to moderate symptoms. Highly recommended as first-line approach. |
| Medical Therapies | Decongestants, antihistamines, corticosteroids | Can provide symptomatic relief but often not a long-term solution. Individual responses vary. |
| Surgical Procedures (Tympanoplasty, Eustachian Tube Tuboplasty) | Reconstruction of eardrum and middle ear structures, or direct modification of the Eustachian tube. | Generally reserved for cases where non-surgical approaches are ineffective or when structural issues are present. Results vary. |
Prognosis and Complications
Living with a patulous Eustachian tube can be challenging, but the long-term prognosis is generally good. While the condition itself doesn’t typically cause lasting damage, the persistent pressure changes and associated symptoms can significantly impact quality of life. Understanding the potential complications and how they affect daily activities is crucial for effective management.The outlook for someone with patulous Eustachian tube hinges largely on the severity of the condition and the individual’s response to treatment.
Mild cases might only present occasional discomfort, while more severe cases can lead to more significant issues. The key is proactive management and understanding how to minimize potential complications.
Long-Term Prognosis
The long-term prognosis for patulous Eustachian tube is generally favorable. Most individuals can maintain a good quality of life with appropriate management strategies. However, some may experience persistent symptoms or complications if the condition isn’t adequately addressed. The severity of symptoms and the presence of associated conditions can influence the overall prognosis.
Potential Complications
Several complications can arise from chronic Eustachian tube dysfunction. These complications can range from mild discomfort to more serious health concerns. Proactive monitoring and early intervention are essential to mitigate the risk of these issues.
- Hearing Loss: Persistent pressure fluctuations and fluid buildup can lead to temporary or even permanent hearing loss. This is a significant concern, as it can affect communication and overall quality of life. Individuals may experience fluctuating hearing loss that varies throughout the day, often correlated with changes in barometric pressure or activity.
- Ear Infections (Otitis Media): Repeated infections can occur due to the Eustachian tube’s inability to properly drain fluids. This can lead to inflammation, pain, and further hearing damage. Recurring ear infections can impact daily routines, especially for children, and require frequent medical attention.
- Tinnitus: The persistent pressure changes can cause tinnitus, or ringing in the ears. This can be a distressing symptom that affects sleep and concentration, making daily activities less enjoyable.
- Facial Pain: Pressure buildup in the middle ear can lead to facial pain or discomfort. This pain can vary in intensity and may be associated with other symptoms like headaches or a feeling of fullness in the ear.
- Discomfort and Reduced Quality of Life: Chronic ear pressure, fullness, and tinnitus can significantly impact daily activities. Individuals may experience difficulty concentrating, sleeping, or enjoying social activities.
Impact on Daily Activities
Patulous Eustachian tube can significantly impact daily activities. The persistent pressure, discomfort, and potential hearing loss can affect concentration, sleep, and overall well-being. Some individuals may need to avoid activities that exacerbate symptoms, such as flying or scuba diving. The degree of impact varies depending on the severity of the condition and the individual’s response to treatment.
Summary of Potential Outcomes
The potential outcomes of patulous Eustachian tube vary. While most individuals can manage the condition and maintain a good quality of life, some may experience persistent symptoms or complications. The likelihood of complications depends on the severity of the condition, the individual’s response to treatment, and the presence of other health conditions.
Potential Complications and Associated Risk Factors
| Complication | Description | Risk Factor |
|---|---|---|
| Hearing Loss | Permanent or temporary reduction in hearing ability due to persistent pressure changes and fluid buildup. | Severity of patulous Eustachian tube, duration of untreated condition, presence of other ear conditions. |
| Ear Infections (Otitis Media) | Inflammation of the middle ear due to repeated infections from impaired fluid drainage. | Weakened immune system, exposure to respiratory infections, chronic Eustachian tube dysfunction. |
| Tinnitus | Ringing, buzzing, or other sounds in the ears, often caused by ongoing pressure changes. | Severity of patulous Eustachian tube, presence of other ear conditions, stress or anxiety. |
| Facial Pain | Discomfort or pain in the facial area due to pressure buildup in the middle ear. | Severity of patulous Eustachian tube, presence of other facial conditions, associated tension headaches. |
| Reduced Quality of Life | Significant impact on daily activities due to chronic ear pressure, discomfort, and potential hearing loss. | Severity of patulous Eustachian tube, presence of other health conditions, lack of effective treatment strategies. |
Illustrative Case Studies
Understanding patulous Eustachian tube requires examining how it manifests in real-life situations. These case studies highlight the variability in symptoms, diagnoses, and treatment approaches, emphasizing the importance of personalized care for each individual.The following case studies present hypothetical scenarios to illustrate the diverse ways patulous Eustachian tube can impact a person’s life. These examples are designed to showcase the range of symptom severity and treatment responses, recognizing that actual experiences will vary greatly.
Case Study Examples
These case studies demonstrate how patulous Eustachian tube can present with different symptom profiles and require tailored treatment plans.
| Case Study | Symptoms | Diagnosis | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1: The Frequent Flyer | Chronic ear fullness, mild tinnitus, and intermittent episodes of mild hearing loss. The patient notes the symptoms worsen during airplane travel. | Detailed audiological testing, including tympanometry and acoustic reflex testing, revealed consistent evidence of middle ear pressure equalization issues. A thorough medical history, including travel patterns, was also crucial for diagnosis. | The patient was advised to use a nasal decongestant spray before and during flights, and earplugs during flights. A recommendation for avoiding situations that exacerbate the condition was also given. |
| Case 2: The Musician | Persistent ear pressure, fluctuating hearing loss, and discomfort during high-volume activities like singing. The patient also experiences intermittent dizziness and headaches. | Diagnosis involved a combination of audiological testing, a thorough medical history, and consideration of the patient’s profession. The doctor explored the possibility of a patulous Eustachian tube as a contributing factor to the patient’s symptoms. | The musician was advised to minimize exposure to loud sounds and use earplugs during rehearsals and performances. Hearing protection and strategies for managing pressure equalization were crucial parts of the treatment plan. The patient was also advised to consult an otolaryngologist for further assessment. |
| Case 3: The Athlete | Experiences frequent ear fullness and pain, particularly during strenuous physical activity. This was coupled with a sensation of blocked ears and reduced hearing acuity. | A combination of detailed medical history and a physical examination was used to evaluate the potential for patulous Eustachian tube. Audiometric testing helped in diagnosing the condition. | The athlete was advised to avoid activities that increase pressure changes in the middle ear, such as diving and high-altitude activities. The patient was also instructed on how to perform the Valsalva maneuver and was encouraged to monitor symptoms carefully. A referral to a specialist for further evaluation was recommended. |
Variability in Presentation and Treatment
The presented case studies highlight the diverse range of symptoms and treatment strategies required for effective management of patulous Eustachian tube. Recognizing this variability is crucial for providing appropriate care to each patient. No two individuals will experience or require the same treatment plan. Factors like lifestyle, profession, and underlying medical conditions influence the most effective approach.
Closing Summary: What Is Patulous Eustachian Tube
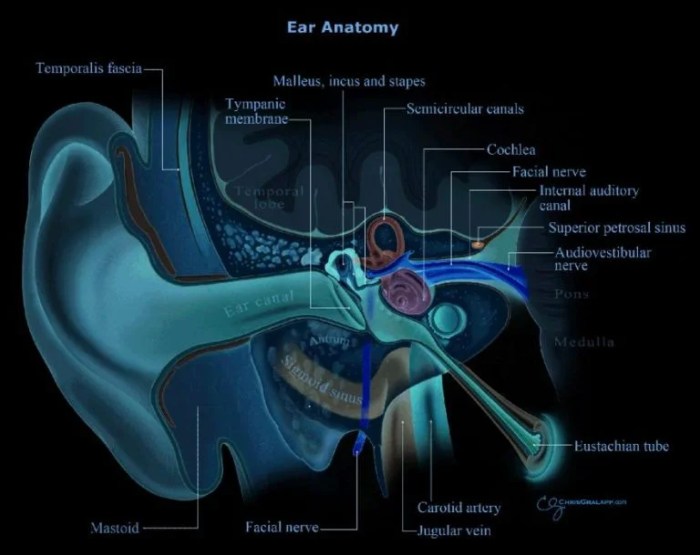
In conclusion, patulous eustachian tube is a condition that warrants attention and understanding. While the exact causes are still being explored, the potential symptoms and complications can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. A thorough understanding of the diagnosis and treatment options is crucial for effectively managing the condition. This exploration should help those affected, or those interested in learning more, to approach the condition with greater awareness and knowledge.










