Lower back pain when walking can be debilitating, significantly impacting daily life. This comprehensive guide explores the multifaceted causes, symptoms, and potential treatments for this common ailment. From musculoskeletal issues to lifestyle factors, we’ll delve into everything you need to understand about managing and preventing lower back pain while walking.
Understanding the underlying mechanisms is crucial to effectively address the problem. This involves exploring various contributing factors, including postural abnormalities, muscle imbalances, and potential joint problems. The pain itself can manifest in different ways, from sharp to dull, and its intensity and location provide valuable clues for diagnosis.
Causes of Lower Back Pain When Walking
Lower back pain during walking can stem from a multitude of interconnected factors, often originating from musculoskeletal issues. Understanding these underlying causes is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment. This exploration delves into the various musculoskeletal contributors, encompassing posture, gait, muscle imbalances, joint problems, and specific medical conditions.A detailed analysis of these factors can help pinpoint the root cause of the pain, allowing for targeted interventions and preventing future episodes.
Proper understanding is paramount for managing this prevalent issue effectively.
Musculoskeletal Issues Contributing to Lower Back Pain During Walking
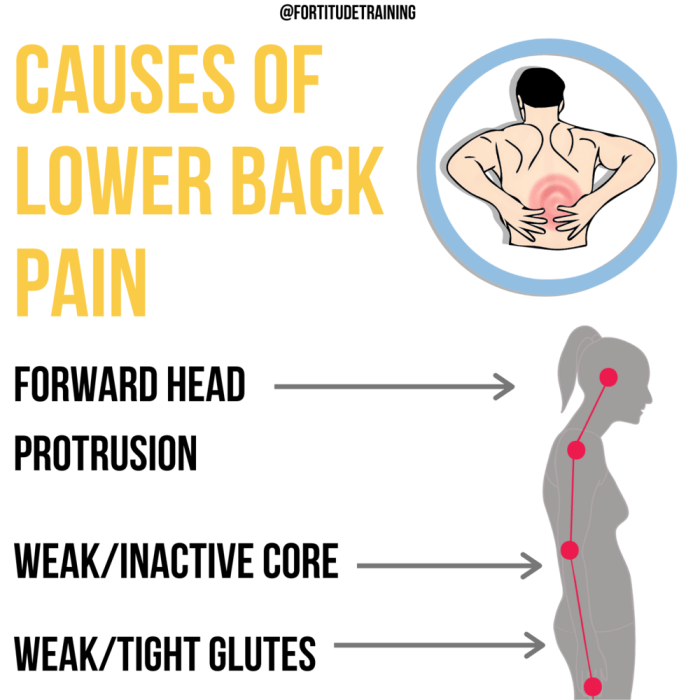
Various musculoskeletal issues can contribute to lower back pain while walking. These include problems with the spine, surrounding muscles, and associated joints. Muscle imbalances, poor posture, and gait abnormalities can all place undue stress on the lower back, leading to pain.
- Posture and Gait Abnormalities: Poor posture during walking, such as slouching or excessive forward leaning, can increase stress on the lumbar spine. Similarly, gait abnormalities, like uneven strides or excessive pronation, can alter the distribution of forces across the body, leading to lower back pain. For instance, someone with a significant hip or knee problem may compensate by altering their gait, placing additional strain on the lower back.
- Muscle Imbalances and Weaknesses: Muscle imbalances, particularly in the core, hip, and gluteal muscles, can disrupt the normal biomechanics of walking. Weak or tight muscles can’t effectively support the spine during movement, leading to pain. For example, weak abdominal muscles may not provide sufficient support for the spine during walking, leading to lower back pain. Tight hip flexors can also contribute by pulling the pelvis forward, leading to an exaggerated lumbar curve.
- Joint Problems (Hip, Knee): Problems in the hip or knee joints can significantly impact the mechanics of walking. Conditions such as osteoarthritis, bursitis, or meniscus tears can cause pain and stiffness, potentially altering gait and placing stress on the lower back. For instance, a hip impingement may force the individual to adopt a limping gait, transferring undue stress to the lower back.
Specific Medical Conditions and Their Manifestations
Certain medical conditions can present as lower back pain during walking. Understanding these conditions is critical for appropriate diagnosis and management.
Lower back pain when walking can be a real drag, making everyday activities tough. Sometimes, underlying conditions like pulmonary hypertension can contribute to this discomfort. Fortunately, there are various medications available to help manage pulmonary hypertension, such as those listed on this page for available pulmonary arterial hypertension medications. While these treatments can significantly improve overall health, it’s crucial to remember that addressing the root cause of the back pain is also vital for long-term relief.
- Spinal Stenosis: Spinal stenosis is a narrowing of the spinal canal, often impacting the nerves exiting the spinal cord. During walking, the increased pressure on the nerves can cause pain, numbness, or tingling in the lower back, buttocks, and legs. This pain often subsides with rest. A patient with spinal stenosis may report a gradual worsening of pain with prolonged walking.
- Herniated Discs: A herniated disc occurs when the soft inner material of a spinal disc bulges or ruptures, potentially pressing on nearby nerves. Walking can aggravate the pressure on these nerves, leading to lower back pain, radiating pain down the leg, and possible numbness or tingling. Individuals with herniated discs often experience pain that worsens with prolonged activity.
Comparison of Musculoskeletal Causes of Lower Back Pain During Walking
| Condition | Symptoms | Location of Pain | Possible Treatments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Muscle Imbalances | Lower back pain, stiffness, tightness in specific muscle groups, reduced range of motion. | Lower back, buttocks, hips. | Physical therapy, stretching, strengthening exercises, massage therapy. |
| Spinal Stenosis | Lower back pain that worsens with walking, numbness or tingling in legs, weakness in legs. | Lower back, buttocks, and radiating down the legs. | Physical therapy, medication, spinal decompression surgery (in severe cases). |
| Herniated Disc | Lower back pain, radiating pain down the leg, numbness or tingling in the leg, weakness in the leg. | Lower back and radiating down the leg. | Physical therapy, pain medication, epidural injections, surgery (in severe cases). |
| Posture and Gait Abnormalities | Chronic lower back pain, pain in the hips and knees, muscle fatigue. | Lower back, hips, and knees. | Physical therapy, posture correction exercises, orthotics, footwear modifications. |
Identifying the Pain Characteristics
Understanding the nuances of your lower back pain when walking is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. Paying close attention to the specific qualities of the pain, like its type, intensity, location, and relationship to walking, can significantly aid healthcare professionals in pinpointing the source of the discomfort.Pinpointing the exact nature of the pain is a vital step in determining the cause and developing an appropriate treatment strategy.
Different types of pain, varying intensities, and the correlation between pain and walking patterns offer clues to the underlying problem. The location of the pain can also provide valuable insights into the potential source of the issue.
Types of Pain
Lower back pain when walking can manifest in various ways, from a dull ache to a sharp, stabbing sensation. Understanding these different pain types is essential for communicating effectively with healthcare providers. A sharp pain typically indicates a sudden, acute injury, while a dull, aching pain might suggest a more gradual, chronic condition.
Intensity and Duration, Lower back pain when walking
The intensity of the pain, measured on a scale of 1 to 10 (1 being mild, 10 being the worst imaginable pain), can vary significantly. Similarly, the duration of the pain, whether it lasts for a few seconds or persists for hours, plays a role in determining the underlying cause. For instance, a sharp, intense pain lasting only a few seconds during a sudden movement might indicate a muscle strain, whereas a dull, persistent ache lasting for hours after a prolonged walk could suggest a more serious condition.
Relationship to Walking
The relationship between the pain and the pace or duration of walking can also be helpful. Does the pain intensify with faster walking or longer distances? Does it subside when resting? Understanding these factors can help determine if the pain is mechanical, resulting from the repetitive motion of walking, or if it’s linked to a more systemic issue.
For example, someone experiencing pain that worsens after 30 minutes of brisk walking might have a problem with their joint mechanics or disc degeneration.
Pain Location
The location of the pain can significantly help in pinpointing the source of the problem. Is the pain concentrated in a specific area of the lower back, or does it radiate to other parts of the body, like the buttocks or legs? Pain localized to the lower lumbar region might indicate a problem with the lumbar spine, while radiating pain might suggest nerve impingement.
A precise description of the pain’s location is invaluable for diagnosis.
Pain Characteristics Table
| Pain Type | Intensity (Scale 1-10) | Location | Aggravating Factors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sharp, stabbing | 7-10 | Lower lumbar, radiating to buttock | Sudden movements, prolonged walking |
| Dull, aching | 3-6 | Lower back, especially after prolonged walking | Prolonged standing, sitting |
| Burning | 5-9 | Lower back, radiating to leg | Walking downhill, prolonged walking |
| Numbness/Tingling | 2-7 | Buttocks, lower legs | Walking for long durations, sitting for long durations |
Associated Symptoms and Risk Factors
Lower back pain when walking can stem from a variety of issues, and understanding the accompanying symptoms and potential risk factors is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. Identifying these factors allows for more targeted interventions and potentially prevents the pain from worsening. This section will delve into additional symptoms that often accompany lower back pain during ambulation, explore lifestyle choices that may increase the risk, and discuss the role of age and genetics in the development of this type of pain.
Additional Symptoms
Besides the primary pain, several other symptoms frequently accompany lower back pain when walking. These additional sensations can provide valuable clues to the underlying cause. Numbness, tingling, and weakness in the legs are common occurrences. These neurological symptoms may indicate nerve compression or irritation in the lower back, which can be indicative of conditions like spinal stenosis or herniated discs.
Pain radiating down the leg (sciatica) is another significant associated symptom. Understanding the specific characteristics of these additional sensations can help healthcare professionals differentiate between various potential causes and tailor appropriate treatment strategies.
Lifestyle Risk Factors
Certain lifestyle choices can significantly increase the risk of developing lower back pain during walking. Obesity, for example, places excessive strain on the spine, leading to increased pressure and potential inflammation. Poor posture, characterized by slouching or improper alignment, also contributes to spinal stress and may trigger or exacerbate existing conditions. A lack of regular exercise weakens supporting muscles, decreasing spinal stability and making the individual more susceptible to pain.
Incorporating regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, and practicing good posture are crucial for mitigating these risks.
Age and Genetics
Age plays a role in the development of lower back pain. As we age, our spinal discs naturally lose hydration and elasticity, making them more prone to injury and degeneration. This age-related decline in spinal health can increase the risk of developing conditions like osteoarthritis and spinal stenosis. Genetic predisposition also influences an individual’s susceptibility to lower back pain.
Certain genetic factors may increase the risk of developing specific conditions that contribute to pain during walking. Understanding these factors can be helpful in determining individual risk levels and tailoring preventive measures.
Risk Factor Table
| Risk Factor | Description | Example | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Obesity | Excess body weight puts excessive pressure on the spine, increasing the risk of injury and pain. | An individual with a BMI of 35 is at higher risk compared to someone with a BMI of 25. | Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise. Consider consulting a nutritionist or a physical therapist. |
| Poor Posture | Slouching or incorrect spinal alignment puts undue stress on the back muscles and ligaments, increasing the risk of pain. | Prolonged sitting at a desk without proper lumbar support. | Improving posture through ergonomic adjustments at work or home, and practicing mindful posture awareness throughout the day. |
| Lack of Exercise | Weak core and back muscles provide insufficient support for the spine, making it more vulnerable to injury. | A sedentary lifestyle with minimal physical activity. | Regular exercise that strengthens core and back muscles, including yoga, Pilates, and weight training. |
| Age | The natural aging process can lead to disc degeneration and reduced spinal flexibility, increasing pain risk. | An individual in their 60s is more susceptible to spinal problems compared to someone in their 20s. | Maintaining an active lifestyle, staying hydrated, and incorporating regular stretching and mobility exercises. Consulting a physician for age-related concerns. |
| Genetics | Certain genetic predispositions can increase the likelihood of developing conditions that cause lower back pain. | A family history of spinal stenosis or herniated discs. | Maintaining a healthy lifestyle to mitigate potential genetic risks. Regular check-ups with a doctor to monitor for any potential issues. |
Diagnostic Considerations
Figuring out the precise cause of lower back pain that worsens when walking is crucial for effective treatment. A thorough evaluation process, combining a detailed medical history with appropriate diagnostic tests, helps pinpoint the underlying issue and guides the most suitable course of action. This involves understanding the nuances of the pain, identifying potential contributing factors, and eliminating any potentially serious conditions.A structured approach to evaluating lower back pain during walking is essential.
It should begin with a comprehensive history, exploring the onset, duration, location, and character of the pain. Factors like the timing of the pain (e.g., after a certain distance, with certain movements) and any relieving or aggravating factors should be noted. This initial assessment is a critical foundation for subsequent investigations.
Evaluating Lower Back Pain During Walking
A systematic evaluation involves gathering a detailed medical history and performing a physical examination. This includes a neurological examination to assess reflexes, muscle strength, and sensation in the lower extremities. The examination should also include palpation of the spine and surrounding soft tissues to identify any areas of tenderness or muscle spasm.
Potential Diagnostic Tests and Procedures
Several diagnostic tests and procedures may be employed to pinpoint the source of lower back pain when walking. These tests range from straightforward imaging techniques to more specialized procedures. The selection of tests will depend on the initial evaluation and suspected diagnoses.
Medical History in Diagnosis
A thorough medical history is paramount in diagnosing the cause of lower back pain. Information about past injuries, surgeries, underlying medical conditions, and lifestyle factors can provide valuable insights into the potential causes. This information helps in narrowing down the possibilities and guiding the selection of appropriate diagnostic tests. For example, a history of cancer or inflammatory conditions can suggest certain etiologies, while a history of repetitive strain injuries might point to mechanical causes.
Diagnostic Tests and Procedures
| Test | Purpose | Procedure | Potential Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| X-ray | To visualize the bones of the spine for fractures, dislocations, or other bony abnormalities. | A low-dose X-ray is taken of the lower back. | Potential results include evidence of fractures, scoliosis, spondylolisthesis, or degenerative joint disease. |
| MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) | To visualize soft tissues, including ligaments, tendons, muscles, and nerves, to detect herniated discs, spinal stenosis, or other soft tissue abnormalities. | The patient lies inside a large magnet, and detailed images of the spinal structures are generated. | Potential results include identification of herniated discs, spinal stenosis, tumors, or inflammation. The quality and detail of the images are critical for accurate interpretation. |
| CT (Computed Tomography) Scan | To provide detailed images of the bones and soft tissues of the spine. Especially useful for evaluating complex bony structures. | The patient lies on a table that moves through a scanner that uses X-rays to create cross-sectional images. | Potential results include identification of fractures, tumors, or bony abnormalities that may not be visible on an X-ray. A CT scan can also provide detailed images of the spinal canal and its contents. |
| Electromyography (EMG) | To assess the electrical activity of muscles and nerves to identify nerve compression or damage. | Small needles are inserted into muscles to record their electrical activity. | Potential results include evidence of nerve root impingement, muscle damage, or other neurological issues. |
Management Strategies and Treatment Options
Lower back pain when walking can significantly impact daily life, making movement challenging and frustrating. Fortunately, several effective strategies and treatment options can help manage and alleviate this discomfort. This section explores conservative approaches, non-pharmacological interventions, the role of medications, and the process of creating a personalized treatment plan.
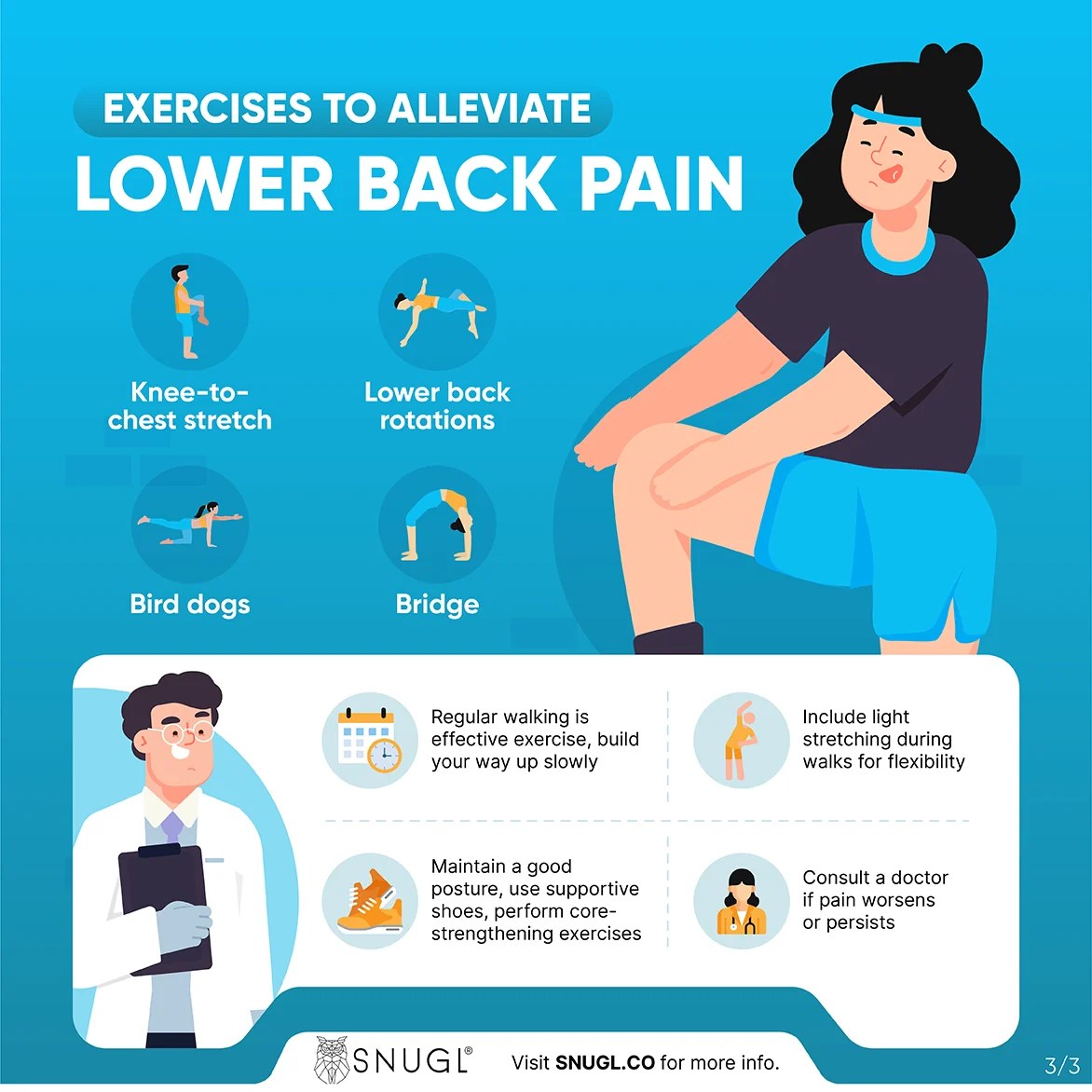
Conservative Approaches
Conservative management focuses on non-surgical methods to alleviate pain and improve function. Physical therapy plays a crucial role in this approach. A physical therapist can assess the root cause of the pain and develop a tailored exercise program to strengthen core muscles, improve posture, and increase flexibility. This can significantly reduce pain and improve mobility. Exercises targeting specific muscle groups and stretches can help alleviate pain and improve movement.
Proper posture and movement techniques are crucial in preventing future episodes.
Ugh, lower back pain when walking is the worst. It can really throw a wrench in your day, making even simple tasks feel monumental. Sometimes, those nagging aches can feel like a never-ending cycle of discomfort, mirroring the repetitive thoughts and behaviors associated with coping with obsessive compulsive behavior, like checking locks repeatedly or constantly needing to rearrange objects.
Learning strategies to manage those unwanted thoughts and behaviors, like those discussed in this helpful resource on coping with obsessive compulsive behavior , might surprisingly help with the persistent lower back pain, as mental clarity and reduced stress can contribute to physical well-being.
Non-Pharmacological Interventions
Non-pharmacological interventions are often the first line of defense in managing lower back pain. Lifestyle modifications are essential. Maintaining a healthy weight, adopting good posture habits, and avoiding prolonged periods of sitting or standing can significantly reduce the strain on the lower back. Regular physical activity, including walking, swimming, or cycling, can help improve overall fitness and reduce pain.
Lower back pain when walking can be a real drag, right? It’s frustrating, especially when you’re trying to enjoy a simple stroll. Sometimes, though, it’s not as straightforward as a simple stretching routine. For example, if you’ve got a sore or cut inside your mouth, it can be tricky to figure out what to do. Fortunately, there are great resources out there to help you understand how to treat a cut inside your mouth.
Check out this helpful guide: how to treat a cut inside your mouth. Ultimately, dealing with any kind of pain, from a cut to a back ache, needs to be approached with care and proper care. Addressing these issues promptly and correctly can get you back on your feet and walking pain-free.
Heat and ice therapy can also provide temporary relief. Applying heat can relax muscles and improve blood flow, while ice can reduce inflammation and pain. These methods are often used in conjunction with other treatments.
Role of Medications
Medications can be used to manage lower back pain when walking, but should be considered supplementary to other treatments. Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help reduce pain and inflammation. Prescription medications, such as stronger anti-inflammatory drugs, may be necessary in more severe cases. However, it is crucial to discuss medication options with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate course of action, considering potential side effects and interactions with other medications.
Following a healthcare professional’s advice is crucial for safe and effective medication use.
Creating a Personalized Treatment Plan
A personalized treatment plan for lower back pain when walking is crucial for optimal outcomes. This plan should be developed in collaboration with a healthcare provider, taking into account the individual’s specific needs, medical history, and lifestyle. The plan should include a combination of therapies, exercises, and lifestyle modifications. Factors such as age, occupation, and pre-existing conditions should be carefully considered to create a comprehensive strategy.
The plan should be regularly reviewed and adjusted as needed.
Comparison of Treatment Options
| Treatment Type | Description | Benefits | Potential Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Therapy | A structured program of exercises, stretches, and manual therapy to improve strength, flexibility, and posture. | Improved muscle strength, reduced pain, increased mobility, and long-term pain relief. | Requires commitment to regular sessions, may not be suitable for all individuals, and may take time to see results. |
| Lifestyle Modifications | Changes in daily habits, such as maintaining a healthy weight, improving posture, and avoiding prolonged periods of sitting or standing. | Reduces strain on the lower back, improves overall health, and can prevent future episodes of pain. | Requires consistent effort and dedication, and may not be sufficient for severe pain. |
| Heat/Ice Therapy | Applying heat or ice to the affected area to reduce pain and inflammation. | Provides temporary relief from pain and inflammation, and is a safe and inexpensive treatment option. | May not be effective for all individuals, and should be used in conjunction with other therapies. |
| Medications | Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs to manage pain and inflammation. | Provides fast pain relief, and may be necessary for severe cases. | Potential side effects, such as stomach upset or interactions with other medications, and may not address the underlying cause of pain. |
Prevention Strategies
Preventing lower back pain when walking involves a proactive approach that combines proper posture, regular exercise, and mindful activity modification. A comprehensive strategy focuses on building core strength, maintaining flexibility, and understanding how to adapt daily routines to minimize stress on the lower back. This proactive approach is key to long-term pain management and overall well-being.
Maintaining Good Posture and Proper Gait
Maintaining correct posture while walking is crucial for preventing lower back pain. Proper posture involves aligning the spine, keeping the head erect, and engaging the core muscles. A good gait involves a smooth, controlled stride, avoiding excessive twisting or leaning. This requires conscious awareness and practice. Think of it like a well-rehearsed dance move; the more you practice, the more natural it becomes.
Importance of Regular Exercise and Stretching
Regular exercise, including activities like walking, swimming, and yoga, strengthens core muscles, improving spinal stability. Stretching exercises, such as hamstring stretches, hip flexor stretches, and back extensions, increase flexibility and range of motion, further reducing the risk of injury. Consistency is key, aiming for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week. Incorporate stretching routines before and after walks to improve muscle flexibility and reduce muscle strain.
Modifying Activities to Minimize Pain Risk
Activities that place excessive stress on the lower back should be modified or avoided. Heavy lifting, prolonged standing, and repetitive bending should be approached with caution and awareness. Consider using proper lifting techniques, employing assistive devices, and adjusting the duration of activities to prevent overuse. For example, if you’re carrying groceries, break down the task into smaller portions and take frequent breaks.
Adjusting posture and technique while working can also minimize strain.
Preventive Measures for Daily Routines
Incorporating preventive measures into daily routines can significantly reduce the risk of lower back pain. This includes using supportive footwear, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding prolonged periods of sitting or standing. Prioritizing proper sleep hygiene and managing stress are also essential components.
- Use supportive footwear: Choosing shoes with proper arch support and cushioning can lessen the stress on your lower back during walks. Consider orthotics for added support if needed.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Excess weight puts extra strain on the lower back, increasing the risk of pain. A balanced diet and regular exercise are crucial.
- Avoid prolonged sitting or standing: Take frequent breaks to stretch and move around. Adjust your workspace to encourage better posture. Standing desks can be beneficial for those who work at a desk.
- Prioritize sleep hygiene: Adequate sleep allows your body to recover and repair itself, which is essential for preventing pain.
- Manage stress: Stress can exacerbate existing back pain and lead to new problems. Incorporate stress-reducing activities into your daily routine, such as meditation or yoga.
Illustrative Case Studies (Example scenarios)
Understanding lower back pain when walking requires exploring real-world examples. Case studies offer valuable insights into the diverse presentations, contributing factors, and effective management strategies for this common condition. They allow us to connect theoretical knowledge with practical application, ultimately leading to a better comprehension of individual patient needs.
Hypothetical Case Study 1: Mechanical Back Pain
A 45-year-old female office worker reports experiencing lower back pain that intensifies when walking. The pain is described as a dull ache, localized to the lower lumbar region, and is exacerbated by prolonged standing or repetitive movements. She reports no significant medical history, but admits to recent increased physical demands at work, including carrying heavy boxes. Potential diagnoses could include lumbar strain, facet joint syndrome, or spondylolisthesis.
Imaging studies, such as X-rays or MRI, might be necessary to rule out more serious conditions.
Hypothetical Case Study 2: Radicular Pain
A 62-year-old male construction worker presents with lower back pain radiating down his left leg. The pain is described as sharp and shooting, worsened by coughing or sneezing. He has a history of osteoarthritis and reports experiencing numbness and tingling in his left foot. Risk factors include his occupation involving heavy lifting and potential nerve impingement. Potential diagnoses could include lumbar herniated disc, spinal stenosis, or sciatica.
Neurological examination and diagnostic imaging are crucial for accurate assessment.
Hypothetical Case Study 3: Successful Management
A 30-year-old female experiences lower back pain when walking, aggravated by prolonged periods of sitting. She initially tried over-the-counter pain relievers without significant relief. She subsequently consulted a physical therapist, who prescribed a combination of exercises focusing on core strengthening and flexibility. She also implemented lifestyle changes, such as improved posture, regular walking, and ergonomic adjustments at her workplace.
Her pain significantly reduced after several weeks of therapy. This demonstrates the importance of multifaceted approaches to lower back pain management.
Table of Case Studies
| Patient Profile | Symptoms | Diagnosis (Potential) | Treatment Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 45-year-old female office worker | Dull ache in lower lumbar region, exacerbated by prolonged standing/repetitive movements | Lumbar strain, facet joint syndrome, or spondylolisthesis | Further evaluation and potential physical therapy, ergonomic adjustments, and lifestyle modifications. |
| 62-year-old male construction worker | Sharp, shooting pain radiating down left leg, worsened by coughing/sneezing; numbness/tingling in left foot | Lumbar herniated disc, spinal stenosis, or sciatica | Neurological examination, imaging studies, and potential surgery or physical therapy, pain management, and lifestyle changes. |
| 30-year-old female | Lower back pain when walking, aggravated by prolonged sitting; initially unresponsive to OTC pain relievers. | Potential musculoskeletal issues related to prolonged sitting or posture | Successful pain reduction after physical therapy (core strengthening/flexibility), lifestyle changes (improved posture, regular walking, ergonomic adjustments). |
Final Review
In conclusion, lower back pain when walking can stem from a variety of sources, requiring a multifaceted approach to diagnosis and treatment. Understanding the interplay of musculoskeletal issues, pain characteristics, associated symptoms, and risk factors is essential. By exploring diagnostic considerations, management strategies, and preventive measures, we empower individuals to take control of their well-being and regain mobility.
Remember that consulting a healthcare professional is crucial for personalized guidance and effective treatment.