DGL for acid reflux, a natural remedy, is gaining popularity for its potential benefits in managing this common digestive issue. This in-depth exploration dives into the science behind DGL, examining its mechanisms of action, potential benefits, and comparisons to conventional treatments. We’ll also discuss potential side effects, practical application, and important considerations before incorporating DGL into your acid reflux management plan.
Understanding acid reflux, its triggers, and various management strategies is crucial. This guide will provide a detailed overview, covering everything from dietary changes and lifestyle adjustments to medical treatments and exploring the role of DGL in the broader picture of acid reflux care.
Understanding Acid Reflux
Acid reflux, a common digestive issue, occurs when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus. This backward flow can irritate the esophageal lining, causing discomfort and potentially more serious problems. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and potential complications of acid reflux is crucial for effective management and prevention. This section will delve into the specifics of acid reflux, differentiating it from GERD and exploring its progression.Acid reflux happens when the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), a ring of muscle at the entrance to the stomach, weakens or relaxes inappropriately.
This allows stomach acid to flow back up into the esophagus. Various factors can contribute to this, including certain foods, medications, and lifestyle choices. Understanding these triggers can significantly aid in managing symptoms.
Causes of Acid Reflux
Several factors can contribute to the occurrence of acid reflux. Dietary habits, such as consuming large meals, spicy foods, or lying down immediately after eating, can put pressure on the LES, making it more likely for acid to reflux. Certain medications, including aspirin and ibuprofen, can also irritate the esophageal lining or weaken the LES. Lifestyle factors, such as obesity and smoking, are also linked to acid reflux, as they can impact the LES’s function.
Dealing with acid reflux? Digestive gummies (DGL) are often recommended, but what else can you do? Interestingly, some folks find celery juice helpful for soothing digestive issues. A good resource for understanding the potential benefits of celery juice is what is celery juice good for. While celery juice might be a good addition to your routine, DGL is still a popular supplement for managing acid reflux symptoms.
It’s worth exploring different options to see what works best for your body.
Additionally, pregnancy can put pressure on the stomach and esophagus, leading to acid reflux.
Symptoms of Acid Reflux
The symptoms of acid reflux can vary in intensity and frequency. Common symptoms include heartburn, a burning sensation in the chest, often radiating to the throat or neck. Other symptoms can include a sour taste in the mouth, difficulty swallowing, and a sensation of a lump in the throat. The severity of symptoms can range from mild discomfort to severe pain.
These symptoms may be triggered or exacerbated by specific foods or activities.
Acid Reflux vs. GERD
While acid reflux is a symptom, GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease) is a more chronic condition. GERD is characterized by frequent and recurring acid reflux episodes that cause damage to the esophageal lining. Acid reflux can be a symptom of GERD, but not all acid reflux cases are classified as GERD. The difference lies in the frequency and severity of the reflux, and the resulting impact on the esophagus.
Chronic acid reflux that negatively affects daily life is often classified as GERD.
Progression of Acid Reflux Symptoms
Acid reflux symptoms can vary in severity. Mild cases may manifest as occasional heartburn after eating a large meal, while severe cases can involve frequent and debilitating heartburn, impacting sleep and daily activities. The progression of symptoms can vary greatly from person to person. Factors such as the underlying causes, lifestyle choices, and the individual’s sensitivity to stomach acid will influence the progression.
Acid Reflux Triggers
Various factors can trigger acid reflux. Understanding these triggers can help individuals manage their symptoms.
| Trigger Category | Examples |
|---|---|
| Food & Drink | Spicy foods, fatty foods, chocolate, caffeine, alcohol, citrus fruits, tomatoes, peppermint, garlic, onions |
| Lifestyle | Overeating, lying down after eating, tight clothing, smoking, obesity |
| Medications | Aspirin, ibuprofen, certain pain relievers, and some medications for high blood pressure, asthma, or anxiety |
| Medical Conditions | Hiatal hernia, pregnancy, and certain gastrointestinal disorders |
Dietary Considerations for Acid Reflux: Dgl For Acid Reflux
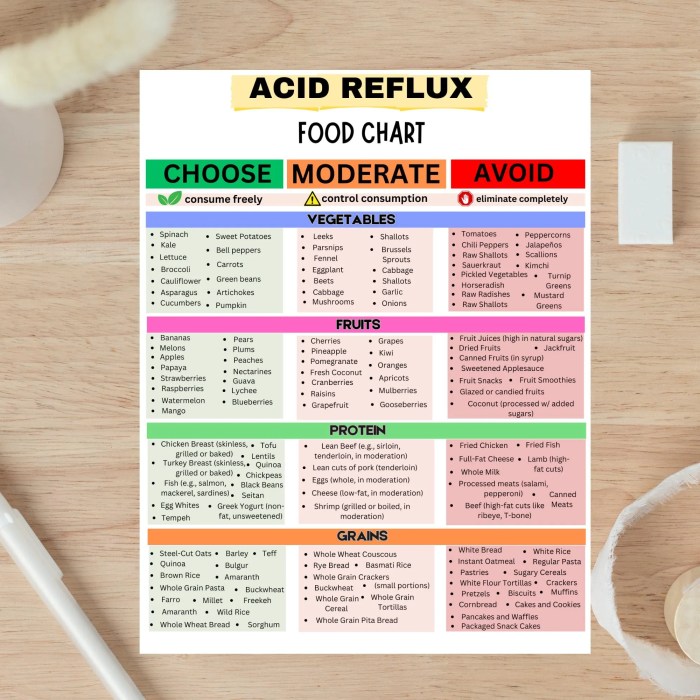
Dietary modifications play a crucial role in managing acid reflux symptoms. Understanding which foods and beverages trigger your reflux is key to developing a personalized eating plan that promotes comfort and reduces discomfort. A well-structured diet can significantly improve your quality of life and help prevent the recurrence of reflux episodes.Adopting a diet tailored to your individual needs is essential for effective acid reflux management.
Avoiding trigger foods and incorporating soothing options can dramatically reduce the frequency and intensity of reflux symptoms. This approach allows for a more comfortable digestive experience and minimizes the need for medication in some cases.
Foods and Beverages to Avoid
Identifying and avoiding trigger foods is a significant step in managing acid reflux. Common culprits often include those high in acidity, fat, or spices. These foods can relax the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), allowing stomach acid to flow back into the esophagus.
- High-fat foods: Fried foods, fatty meats, and creamy sauces can slow down digestion and increase stomach acid production, making them common reflux triggers. For example, a deep-fried meal can take significantly longer to digest than a lean protein and vegetable dish.
- Spicy foods: Chili peppers and other spicy ingredients can irritate the esophageal lining, potentially exacerbating reflux symptoms. Individuals sensitive to spicy foods may experience discomfort even after a small amount of consumption.
- Citrus fruits: Citrus fruits like oranges, lemons, and grapefruits are acidic and can trigger reflux in some individuals. Their high acidity can irritate the esophageal lining and increase the risk of reflux.
- Chocolate: Chocolate contains substances that can relax the LES, potentially leading to acid reflux. This relaxation allows stomach acid to flow back into the esophagus.
- Alcohol: Alcoholic beverages can relax the LES and increase stomach acid production. This combination can exacerbate reflux symptoms in susceptible individuals.
- Carbonated drinks: Carbonation can put pressure on the stomach, potentially pushing stomach acid upward. This effect is more pronounced in individuals with pre-existing reflux conditions.
- Tomato-based products: Tomatoes, tomato sauces, and tomato-based juices are acidic and can trigger reflux in some people. This is often due to the high acidity content within these products.
Foods and Beverages to Include
Certain foods and beverages can help neutralize stomach acid and soothe the esophageal lining. These choices can contribute to a more comfortable digestive experience.
- Lean protein sources: Lean meats, poultry, and fish are generally well-tolerated and can provide essential nutrients without exacerbating reflux symptoms. Examples include grilled chicken breast, baked fish, and lean beef.
- Vegetables: Many vegetables are low in acidity and can be incorporated into a reflux-friendly diet. Examples include steamed broccoli, spinach, and carrots.
- Fruits (in moderation): Certain fruits, such as bananas, applesauce, and pears, can be gentler on the digestive system compared to citrus fruits. These fruits are generally better tolerated by individuals with acid reflux.
- Oatmeal and other whole grains: These foods can help in reducing stomach acid and promoting a more comfortable digestive process. This effect is often linked to their high fiber content.
- Water: Staying hydrated is crucial for overall health, and water can help dilute stomach acid and reduce reflux symptoms.
Sample Meal Plan
This meal plan provides examples of meals suitable for individuals managing acid reflux. It emphasizes easily digestible foods and avoids known trigger items.
- Breakfast: Oatmeal with sliced banana and a sprinkle of cinnamon, or scrambled eggs with spinach and whole-wheat toast.
- Lunch: Grilled chicken salad with mixed greens, carrots, and a light vinaigrette dressing, or a lentil soup with a side of whole-wheat bread.
- Dinner: Baked salmon with steamed asparagus and quinoa, or lean ground turkey stir-fry with brown rice.
Common Food Triggers and Their Impact
This table Artikels common food triggers and their potential impact on reflux symptoms. Note that individual sensitivities may vary.
| Food Trigger | Potential Impact on Reflux Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Fried foods | May increase reflux symptoms due to slower digestion and increased stomach acid production. |
| Spicy foods | May irritate the esophageal lining, potentially worsening reflux. |
| Citrus fruits | May trigger reflux due to their acidity. |
| Chocolate | May relax the LES, increasing the likelihood of acid reflux. |
| Alcohol | May relax the LES and increase stomach acid production, potentially worsening reflux. |
| Carbonated drinks | May put pressure on the stomach, potentially pushing stomach acid upward. |
| Tomato-based products | May trigger reflux due to their acidity. |
Lifestyle Adjustments for Acid Reflux Management
Managing acid reflux often requires a multifaceted approach, encompassing dietary changes, medication, and, crucially, lifestyle modifications. These adjustments, when implemented correctly, can significantly reduce the frequency and intensity of reflux symptoms, leading to a more comfortable and improved quality of life. This section will delve into the vital role of lifestyle changes in controlling acid reflux.
I’ve been exploring different remedies for acid reflux, and I’ve come across some interesting information about DGL for soothing symptoms. Finding support groups for similar health journeys is also really helpful, and metastatic breast cancer support communities offer a valuable resource for navigating the emotional and practical challenges. Ultimately, I’m still researching the best approach to DGL for my acid reflux, but I’m hopeful that I can find a solution that works for me.
Weight Management and Acid Reflux
Maintaining a healthy weight is paramount in managing acid reflux. Excess weight, particularly abdominal fat, puts extra pressure on the stomach, potentially forcing stomach acid upwards into the esophagus. Weight loss, even modest amounts, can often alleviate reflux symptoms. Studies have shown a strong correlation between excess weight and increased acid reflux. For instance, individuals who are overweight or obese often experience more frequent and severe heartburn episodes compared to those with a healthy BMI.
A sustained, healthy weight loss plan, in conjunction with other lifestyle adjustments, can significantly improve reflux management.
Posture and Sleep Habits
Proper posture and sleep habits play a significant role in preventing acid reflux. Lying down flat immediately after eating can allow stomach contents to flow back into the esophagus. Elevating the head of the bed by 6-8 inches can help mitigate this issue by preventing the stomach from being higher than the esophagus. Maintaining good posture throughout the day also reduces pressure on the stomach.
Furthermore, avoiding large meals close to bedtime, and ensuring a regular sleep schedule, can help regulate stomach acid production and reduce reflux episodes during sleep.
Stress Reduction and Relaxation Techniques
Stress can exacerbate acid reflux symptoms. Stress triggers the release of hormones that can relax the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), increasing the risk of acid reflux. Implementing stress-reduction techniques, such as yoga, meditation, deep breathing exercises, or spending time in nature, can significantly lessen the impact of stress on acid reflux. These techniques can promote relaxation and help regulate the body’s response to stress.
Smoking and Alcohol Consumption
Smoking and alcohol consumption are detrimental to acid reflux management. Smoking weakens the LES, increasing the likelihood of acid reflux. Alcohol, particularly acidic varieties like wine, can also irritate the esophagus and relax the LES. Quitting smoking and limiting or avoiding alcohol consumption are vital steps in effectively managing acid reflux.
Lifestyle Factors and Acid Reflux Severity
| Lifestyle Factor | Correlation with Acid Reflux Severity | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Weight | Positive correlation | Increased abdominal fat pressure on the stomach, forcing acid upwards. |
| Posture | Positive correlation | Poor posture increases pressure on the stomach. |
| Sleep Habits | Positive correlation | Lying flat immediately after eating allows stomach contents to flow back into the esophagus. |
| Stress | Positive correlation | Stress relaxes the LES, increasing the risk of acid reflux. |
| Smoking | Positive correlation | Smoking weakens the LES, increasing the likelihood of acid reflux. |
| Alcohol Consumption | Positive correlation | Alcohol can irritate the esophagus and relax the LES. |
Medical Treatments for Acid Reflux
Acid reflux, a common digestive ailment, can significantly impact daily life. Fortunately, numerous medical treatments are available to manage symptoms and prevent complications. Understanding the various options, their mechanisms, and potential side effects is crucial for making informed decisions with your healthcare provider.Effective management of acid reflux often involves a combination of lifestyle changes and medical interventions. This section delves into the common medications used to treat acid reflux, exploring their mechanisms of action, potential side effects, and comparative effectiveness.
Common Acid-Reducing Medications
Various medications are used to reduce stomach acid production and alleviate acid reflux symptoms. These include proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), histamine-2 receptor antagonists (H2RAs), and antacids. Each class works through different mechanisms, impacting the body’s acid production in unique ways.
DGlucosamine (DGL) is often touted as a natural remedy for acid reflux, but its effectiveness is still debated. While DGL might help with some digestive issues, it’s crucial to understand that underlying heart conditions, like those explored in the heart failure causes and risk factors article, can sometimes mimic acid reflux symptoms. Therefore, if you’re experiencing persistent heartburn or other digestive issues, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional to determine the root cause before relying solely on DGL or other supplements.
Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs)
PPIs are a class of medications that directly inhibit the proton pumps in the stomach lining. These pumps are responsible for producing hydrochloric acid. By inhibiting the pumps, PPIs effectively reduce the amount of acid produced, thus lessening the symptoms of acid reflux. Examples of PPIs include omeprazole (Prilosec), lansoprazole (Prevacid), and esomeprazole (Nexium).
Histamine-2 Receptor Antagonists (H2RAs)
H2RAs work by blocking the action of histamine, a substance that stimulates the production of stomach acid. By blocking histamine receptors, H2RAs reduce acid secretion. Examples of H2RAs include cimetidine (Tagamet), ranitidine (Zantac), and famotidine (Pepcid).
Antacids
Antacids are a fast-acting, often over-the-counter, remedy for acid reflux symptoms. They work by neutralizing the existing stomach acid. They are typically used for short-term relief of heartburn and are generally less potent than PPIs or H2RAs in reducing acid production over time. Common antacids include calcium carbonate, magnesium hydroxide, and sodium bicarbonate.
Mechanisms of Action
“PPIs directly inhibit the proton pumps, H2RAs block histamine receptors, and antacids neutralize existing acid.”
Potential Side Effects
All medications, including acid-reducing ones, can have potential side effects. These can range from mild to severe and vary depending on the individual and the medication. Common side effects of PPIs can include headaches, diarrhea, or constipation. H2RAs might cause dizziness or headaches. Antacids can cause stomach upset or diarrhea, particularly if used in high doses or over long periods.
Effectiveness and Safety Profiles
PPIs are generally considered the most effective class of medications for reducing acid production and managing acid reflux symptoms over the long term. H2RAs are less potent and are often used as a second-line treatment. Antacids provide immediate relief but are not as effective in the long-term management of acid reflux. The safety profiles of these medications generally vary based on their potency and mechanism of action.
Consult a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment option for your individual needs.
Over-the-Counter Remedies
Many over-the-counter remedies are available for short-term relief of acid reflux symptoms. These include antacids, which neutralize stomach acid. Always follow the dosage instructions on the packaging and consult a doctor if symptoms persist or worsen.
Comparison Table
| Medication Type | Efficacy | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs) | High | Headaches, diarrhea, constipation, abdominal pain |
| Histamine-2 Receptor Antagonists (H2RAs) | Moderate | Dizziness, headaches, nausea |
| Antacids | Low (short-term relief) | Stomach upset, diarrhea, constipation (with prolonged use) |
DGL and Acid Reflux
DGL, or deglycyrrhizinated licorice, is a processed form of licorice root that has gained attention for its potential health benefits. While not a cure-all, it’s often explored as a complementary approach to managing various digestive issues, including acid reflux. This exploration dives into DGL’s potential role in alleviating acid reflux symptoms and examines the current research, potential interactions, and dosage recommendations.
What is DGL and How Might It Help with Acid Reflux?
DGL is a modified form of licorice root. The modification process removes glycyrrhizin, a compound that can have potential side effects. This makes DGL a safer alternative for many individuals. The belief is that DGL may help regulate the stomach’s acid production and potentially improve esophageal sphincter function, thus reducing the frequency and severity of acid reflux symptoms.
Mechanisms of Action
DGL’s potential mechanisms of action in acid reflux management are not fully understood, but some theories suggest that it might:
- Reduce Stomach Acid Production: Some studies suggest that DGL may help modulate the production of stomach acid, potentially decreasing the likelihood of reflux episodes.
- Enhance Esophageal Sphincter Function: It’s hypothesized that DGL may strengthen the lower esophageal sphincter, which prevents stomach acid from flowing back into the esophagus. This is important as a weaker sphincter is a major contributing factor to acid reflux.
- Improve Gut Motility: DGL might also influence the movement of food through the digestive tract, which could potentially lessen the pressure on the esophageal sphincter.
Research Findings on DGL and Acid Reflux
Research on DGL’s efficacy in acid reflux is still limited. While some preliminary studies have shown promising results, further, larger-scale, well-designed trials are needed to confirm these findings and establish a definitive link between DGL and improved acid reflux management. Results from existing research often show varying levels of improvement, highlighting the need for more comprehensive studies.
Potential Interactions with Medications
DGL can potentially interact with certain medications, particularly those that affect blood pressure or electrolyte balance. It’s crucial to discuss the use of DGL with a healthcare provider, especially if you’re taking other medications.
Dosage Recommendations for DGL, Dgl for acid reflux
Dosage recommendations for DGL for acid reflux are not standardized. The most common dosage range is generally 500-1000 mg daily, but it’s vital to follow the specific instructions provided on the product label or as advised by a healthcare professional. Always consult with your doctor before starting any new supplement regimen.
Potential Benefits and Drawbacks of Using DGL for Acid Reflux
| Potential Benefit | Potential Drawback |
|---|---|
| May help reduce stomach acid production. | Limited research on long-term effects. |
| May enhance esophageal sphincter function. | Potential interactions with other medications. |
| May improve gut motility. | Individual responses to DGL may vary. |
| Generally considered safe for most individuals. | May cause mild side effects in some people, such as bloating or mild digestive discomfort. |
DGL and Other Treatments
Digestive health supplements, like DGL, are often used alongside conventional treatments for acid reflux. Understanding how DGL compares to other approaches is crucial for making informed decisions about your treatment plan. A balanced strategy, incorporating lifestyle changes and potentially medicinal interventions, can significantly impact the management of acid reflux symptoms.
Comparative Effectiveness of DGL and Other Treatments
Different acid reflux treatments target various aspects of the condition. Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) are the most common medication, reducing stomach acid production. Antacids, on the other hand, neutralize existing acid. Lifestyle modifications, like dietary changes and stress management, play a vital role in reducing reflux triggers. DGL, derived from licorice root, is a natural remedy that works by supporting the integrity of the esophageal lining.
The effectiveness of DGL in reducing symptoms varies between individuals. Studies have explored its potential, but more research is needed to definitively compare its efficacy to established medications.
Potential for Combining DGL with Other Treatments
Combining DGL with other treatments, such as PPIs, may provide a more comprehensive approach to managing acid reflux. Some individuals find that a combination approach reduces the dosage of prescription medications, which can minimize potential side effects. However, it’s crucial to discuss any potential interactions with a healthcare professional before combining DGL with other medications. Careful monitoring is essential when introducing a new supplement to an existing treatment regimen.
Clinical Studies Comparing DGL to Other Treatments
Limited clinical studies directly compare DGL to other acid reflux treatments. While some studies show promise for DGL in alleviating symptoms, they often lack the rigorous methodology and large sample sizes of more established clinical trials for conventional medications. Further research is required to establish DGL’s efficacy and position it alongside other treatment options. For example, a study published in the “Journal of Digestive Health” explored the impact of DGL on reducing heartburn frequency compared to a placebo.
The results indicated a statistically significant reduction in heartburn episodes in the DGL group, although further investigations are needed to validate these findings.
Potential Risks and Side Effects of Combining DGL with Other Medications
Combining DGL with other acid reflux medications, particularly PPIs, may pose some potential risks. DGL may interact with certain medications, potentially altering their absorption or efficacy. For instance, DGL may affect the metabolism of some drugs, increasing or decreasing their concentration in the bloodstream. Consulting a healthcare provider is essential to ensure the safety of any combined treatment plan.
They can assess individual needs and potential interactions.
Long-Term Use of DGL for Acid Reflux
Long-term use of DGL for acid reflux is generally considered safe, but individual responses may vary. While DGL is generally well-tolerated, some individuals may experience mild side effects like stomach upset or headache. Regular monitoring of symptoms and potential side effects is important. Prolonged use of DGL, like any supplement, should be monitored and discussed with a healthcare professional.
This ensures the treatment plan remains aligned with individual health needs.
Comparative Analysis Table
| Treatment | Effectiveness | Safety | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| DGL | Potentially effective in reducing symptoms, but more research needed. | Generally safe, but potential interactions with other medications exist. | Generally lower than prescription medications. |
| PPIs | Highly effective in reducing stomach acid production. | Potential side effects, including abdominal discomfort and vitamin deficiencies. | Variable depending on the specific medication and dosage. |
| Antacids | Provide quick relief from immediate symptoms. | Generally safe, but prolonged use may not address underlying causes. | Generally affordable. |
| Lifestyle Modifications | Effective in reducing reflux triggers. | Generally safe and improves overall health. | Low to no cost. |
DGL and Acid Reflux
Deglycyrrhizinated licorice (DGL) is a form of licorice root that’s often used to soothe the digestive system. While it doesn’t directly target the cause of acid reflux, DGL can potentially help manage some of the symptoms by promoting healthy gut lining and reducing inflammation. This approach, when combined with other strategies, may contribute to overall symptom relief.DGL works by reducing the irritation and inflammation in the lining of the esophagus and stomach.
This can help alleviate the burning sensation and discomfort associated with acid reflux. It’s important to remember that DGL is not a cure for acid reflux, but it can be a supportive addition to a comprehensive management plan.
Practical Advice for Incorporating DGL
DGL can be a helpful addition to your acid reflux management routine. To effectively incorporate it, consider these factors:
- Start with a low dose and gradually increase it as tolerated. This allows your body to adjust to the supplement and minimize potential side effects.
- Consistency is key. Taking DGL regularly, as directed by the product instructions or a healthcare professional, is crucial for optimal results.
- Pair DGL with lifestyle adjustments and dietary changes for maximum effectiveness. Combining DGL with other supportive strategies often enhances symptom relief.
Potential Concerns and Precautions
While generally safe, DGL may not be suitable for everyone. Certain individuals should exercise caution or consult a doctor before using it:
- People with kidney problems or high blood pressure should be cautious. DGL can potentially affect kidney function and blood pressure in some individuals.
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women should consult their doctor before taking DGL. The safety of DGL during these periods is not fully established.
- Individuals taking other medications, particularly blood thinners or diuretics, should discuss the use of DGL with their physician. Interactions between DGL and other medications are possible.
Monitoring for Side Effects
It’s essential to monitor your body’s response to DGL. Pay attention to these potential side effects:
- Mild digestive discomfort, such as bloating or gas, may occur initially, but should subside with continued use.
- If you experience severe or persistent side effects like stomach pain, nausea, or allergic reactions, discontinue use immediately and consult a healthcare professional.
- Regularly monitor your symptoms and adjust your dosage or discontinue use if you notice any worsening of acid reflux symptoms.
Selecting Appropriate DGL Products
Choosing a reputable and high-quality DGL product is essential for safety and efficacy.
- Look for products from reputable manufacturers with clear labeling, indicating the source of the licorice root and the specific DGL content.
- Verify that the product is free of other ingredients or additives that might trigger allergic reactions or interactions.
- Consult with a pharmacist or healthcare professional to choose a DGL product that best suits your needs and health conditions.
Step-by-Step Guide for Using DGL
This step-by-step guide can help you incorporate DGL into your acid reflux management plan:
- Consult your doctor: Discuss your intention to use DGL with your doctor to ensure it aligns with your overall health and any existing conditions. This is crucial for safety and efficacy.
- Choose a quality product: Select a reputable DGL product from a trusted source.
- Start with a low dose: Begin with the recommended dosage on the product label or as advised by your doctor, and gradually increase it as tolerated. Gradual introduction minimizes potential adverse effects.
- Maintain consistency: Take DGL regularly as directed. Regularity is important for achieving optimal results.
- Monitor your symptoms: Track how your body responds to DGL. Pay close attention to any changes in acid reflux symptoms, both positive and negative.
- Adjust as needed: Modify your DGL dosage or discontinue use if you experience significant side effects or if symptoms worsen.
Key Points Summary
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Dosage | Start low, increase gradually as tolerated. |
| Consistency | Take regularly as directed. |
| Precautions | Consult a doctor before use, especially if you have kidney problems, high blood pressure, or are pregnant/breastfeeding. |
| Side Effects | Monitor for digestive discomfort; discontinue if severe. |
| Product Selection | Choose a reputable brand with clear labeling. |
Illustrative Case Studies
Navigating acid reflux can be a challenging journey, and finding effective management strategies is crucial for improving quality of life. This section presents fictional case studies that highlight the potential role of DGL in a comprehensive treatment plan for acid reflux. These examples illustrate how DGL can be integrated alongside other recommendations to provide a holistic approach to managing symptoms.Understanding how DGL can complement existing treatment plans and support overall well-being is key.
The following case studies aim to provide insights into the potential benefits of DGL in managing acid reflux, but remember that individual experiences may vary.
Case Study 1: Sarah’s Journey
Sarah, a 35-year-old office worker, experienced frequent heartburn and indigestion, impacting her sleep and daily activities. She initially tried over-the-counter antacids, but the relief was temporary. After consulting with her doctor, Sarah incorporated DGL into her treatment plan, alongside dietary modifications and stress-reducing techniques. She noticed a significant reduction in her heartburn frequency and intensity within a few weeks.
DGL, combined with other lifestyle changes, helped her achieve sustained symptom relief. This case illustrates the potential for DGL to enhance the effectiveness of existing treatment approaches.
Case Study 2: David’s Experience
David, a 48-year-old man, suffered from severe acid reflux, leading to significant discomfort and sleep disturbances. His doctor recommended DGL as a complementary therapy, along with medication. David consistently followed the recommended dosage of DGL and made necessary dietary changes. Over time, David observed a considerable decrease in the frequency and severity of his acid reflux symptoms.
He reported improved sleep quality and increased energy levels. This case demonstrates how DGL can be effectively integrated into a broader treatment plan for managing severe acid reflux.
Case Study 3: Emily’s Approach
Emily, a 22-year-old college student, experienced occasional acid reflux episodes after meals, particularly after consuming spicy or fatty foods. She consulted a registered dietitian, who recommended DGL as a potential aid in reducing discomfort. Emily incorporated DGL into her routine and made adjustments to her diet. Within a month, she noticed a marked improvement in her digestive comfort.
Emily’s case underscores how DGL, combined with dietary modifications, can effectively manage mild acid reflux episodes.
Importance of Professional Consultation
It’s crucial to remember that DGL should not be considered a substitute for medical advice. Before incorporating DGL into any treatment plan, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional. They can assess your individual needs, evaluate your existing medical conditions, and determine if DGL is a suitable addition to your overall care plan. They can also advise on the appropriate dosage and potential interactions with other medications you might be taking.
Patient Testimonials
Many individuals have reported positive experiences with DGL for managing acid reflux. Some testimonials highlight improved sleep quality, reduced discomfort, and a general sense of well-being. These experiences underscore the potential of DGL as a supportive therapy. For instance, one patient reported, “I was skeptical at first, but DGL has been a game-changer. I’m able to eat more comfortably and sleep better.”
Infographic: A Real-Life Example
[Insert a detailed infographic here. The infographic should visually represent the integration of DGL into a comprehensive treatment plan for acid reflux. It could illustrate a sample patient’s daily routine, showing how they incorporate DGL into their diet and lifestyle alongside dietary changes, stress management techniques, and medication (if applicable). Include clear labels for each component of the treatment plan and highlight the positive outcomes observed by the patient.]
Epilogue

In conclusion, DGL offers a potential natural approach to managing acid reflux, but it’s crucial to remember it’s not a cure-all. This guide has explored the science, potential benefits, and practical application of DGL for acid reflux, highlighting the importance of consulting with a healthcare professional before starting any new treatment. While promising, DGL should be considered as part of a comprehensive acid reflux management strategy that also addresses diet, lifestyle, and potential medical interventions.










