Scabs on scalp causes diagnosis and treatment is a crucial guide for understanding the various factors contributing to scalp issues. This comprehensive exploration dives deep into the different types of scalp scabs, potential causes ranging from skin conditions to infections, and effective diagnostic methods. We’ll also cover a spectrum of treatment options, from topical remedies to antifungal medications, and even explore some helpful home remedies.
Finally, we’ll touch on prevention strategies and provide detailed descriptions of various types of scalp scabs.
From identifying the telltale signs of dry, crusty, or oozing scabs to pinpointing the underlying cause, this guide empowers you with the knowledge to address your scalp concerns effectively. Whether you’re dealing with a fungal infection, seborrheic dermatitis, or another potential cause, this guide provides a detailed roadmap for understanding and managing your scalp health.
Introduction to Scalp Scabs
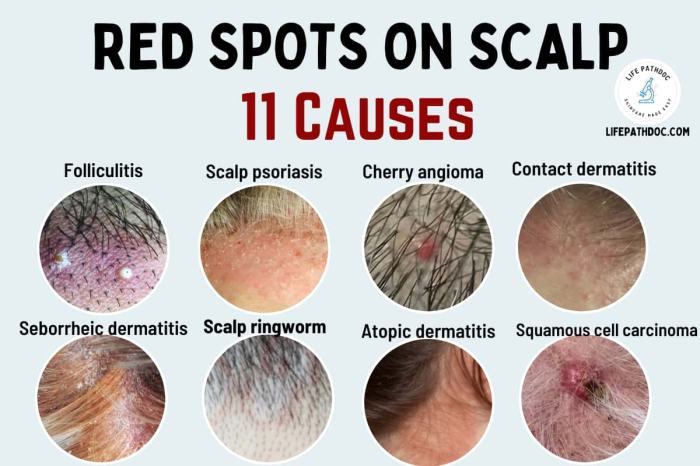
Scalp scabs, those unsightly patches of hardened skin on your scalp, can be a source of concern and discomfort. They can range from minor irritations to more serious underlying conditions. Understanding the different types of scalp scabs, their appearances, and common locations can be helpful in determining the cause and appropriate course of action. This section will delve into the specifics of scalp scabs, enabling you to better recognize and address them.
Types of Scalp Scabs
Scalp scabs manifest in various forms, each reflecting a possible cause. Dry, crusty, and oozing scabs represent distinct conditions, and their appearance provides clues to potential diagnoses. Understanding the visual characteristics of each type can aid in self-assessment and prompt appropriate medical attention when necessary.
Common Locations of Scalp Scabs
Scalp scabs aren’t confined to specific areas. They can appear anywhere on the scalp, though certain regions may be more prone to irritation or injury, leading to scab formation. Common areas include the crown, the sides, and the hairline, where hair density or scalp exposure might be different. Sometimes, scabs can be clustered, or they may appear as a single, isolated lesion.
Dealing with scabs on your scalp can be frustrating, but understanding the potential causes and how to diagnose them is key to effective treatment. Sometimes, these scabs might be a symptom of a more serious issue, like an infection. Knowing if there’s a link to other health concerns like HIV transmission through casual contact is crucial.
But, in most cases, scabs on the scalp are easily treatable with a combination of good hygiene and potentially some over-the-counter remedies. Proper diagnosis and following a suitable treatment plan are essential to restoring scalp health.
Visual Characteristics of Scalp Scabs
Identifying the type of scab is crucial for understanding its potential cause. The appearance can vary significantly, influenced by the underlying condition. The consistency, color, and size of the scab offer valuable insights into the nature of the problem.
| Type of Scalp Scab | Visual Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Dry | These scabs appear as thin, flaky, or papery patches. They might be light beige or a similar shade to the surrounding skin. Often, they are accompanied by dryness and itching. |
| Crusty | Crusty scabs are thicker and rougher than dry scabs. They are often more raised and may appear as hardened, rough patches of various shades, from light brown to dark brown, or even black. The consistency is more solid than dry scabs. |
| Oozing | Oozing scabs are characterized by a moist or wet appearance. They may have a yellowish or whitish discharge, often accompanied by redness and inflammation. The area surrounding the scab might be swollen or tender to the touch. |
Potential Causes of Scalp Scabs: Scabs On Scalp Causes Diagnosis And Treatment
Scalp scabs, a common skin issue, can have various underlying causes. Understanding these causes is crucial for proper diagnosis and effective treatment. They range from relatively benign conditions to more serious ones, requiring prompt medical attention. This section will delve into the common reasons behind these skin imperfections.A multitude of factors can contribute to the development of scalp scabs.
From infections to allergic reactions, and even underlying skin conditions, a careful examination is needed to identify the root cause. Knowing these causes can guide appropriate treatment strategies and prevent potential complications.
Common Skin Conditions
Various skin conditions can manifest as scalp scabs. These conditions often involve inflammation and irritation, leading to the formation of crusty or scaly patches. Identifying the specific condition is important for tailoring the right treatment.
- Seborrheic dermatitis: This chronic inflammatory skin condition is a frequent culprit behind scalp scabs. It’s characterized by greasy, yellowish scales and often causes significant discomfort.
- Psoriasis: Another chronic autoimmune condition, psoriasis can lead to inflamed patches on the scalp, accompanied by scaling and sometimes scabs. The appearance can vary significantly between individuals.
- Eczema: Atopic dermatitis, or eczema, can also affect the scalp, resulting in dry, itchy skin, and potentially scabs. This condition often involves a strong genetic component.
Fungal Infections and Scalp Scabs
Fungal infections, particularly tinea capitis, are significant contributors to scalp scabs. These infections are often characterized by inflammation, scaling, and sometimes, the formation of pustules and crusts. Different types of fungi can cause these infections.
- Tinea capitis: This fungal infection is commonly referred to as ringworm. It’s important to note that while the name suggests a circular pattern, the appearance can be diverse. Tinea capitis can cause patchy hair loss, and the affected areas can be inflamed and have scaling or crusting. The infection is contagious and requires appropriate antifungal treatment.
- Malassezia furfur: This yeast can cause dandruff, but in some cases, it can lead to more severe inflammation and scabs, particularly in individuals with underlying skin conditions or weakened immune systems.
Seborrheic Dermatitis and Scalp Scabs
Seborrheic dermatitis is closely linked to scalp scabs. This chronic inflammatory condition causes greasy, yellowish scales and often presents as patches of red, inflamed skin. It’s important to recognize the connection to prevent misdiagnosis and to provide effective treatment.
Seborrheic dermatitis can affect various areas of the body, including the scalp, eyebrows, and face, often manifesting as greasy scales and redness.
Comparison of Fungal Infections
Different fungal infections can lead to similar symptoms, making accurate diagnosis crucial. Understanding the distinctions can guide treatment strategies.
Scalp scabs can be a real nuisance, and figuring out the cause is key to effective treatment. Sometimes, they’re linked to underlying skin conditions or even dietary factors like excessive sodium intake. Eating a balanced diet, including foods high in sodium, can contribute to inflammation and potentially exacerbate the issue. Consulting a dermatologist is crucial for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan, addressing any underlying causes, including possible allergic reactions or infections.
Identifying the root cause is vital for successful treatment of scalp scabs. foods high in sodium should be consumed in moderation, as excess sodium can be problematic for various health concerns. A proper diagnosis from a healthcare professional is always recommended.
- Comparison of Different Types of Tinea Capitis: While all types of tinea capitis involve fungal infection, the appearance and severity can differ. Some types may present with more pronounced inflammation, scaling, or hair loss than others. Proper identification is critical for effective antifungal therapy.
Table of Scalp Conditions and Scabs
The following table summarizes the appearance and causes of various scalp conditions that can lead to scabs:
| Condition | Appearance | Causes |
|---|---|---|
| Seborrheic Dermatitis | Greasy, yellowish scales, red patches | Yeast overgrowth, inflammatory response |
| Tinea Capitis (Ringworm) | Scaly patches, hair loss, sometimes pustules | Fungal infection (various types) |
| Psoriasis | Thick, silvery scales, red patches | Autoimmune response |
| Eczema | Dry, itchy skin, inflamed patches | Allergic reaction, environmental factors |
Diagnosing Scalp Scabs
Pinpointing the cause of scalp scabs is crucial for effective treatment. A thorough diagnostic approach involves a multifaceted evaluation considering various factors, from the patient’s medical history to physical examination findings. This process aims to differentiate between benign and potentially more serious underlying conditions.Accurate diagnosis is essential to tailor the treatment plan to the specific cause, avoiding ineffective or even harmful interventions.
A clear understanding of the diverse conditions that can manifest as scalp scabs is vital to ensure the most appropriate course of action.
Diagnostic Methods for Scalp Scabs
A comprehensive diagnostic process for scalp scabs begins with a detailed evaluation of the affected area. Physical examination allows for visual assessment of the scabs, their distribution, and any associated symptoms, such as redness, inflammation, or itching. The consistency and appearance of the scabs themselves—whether they are dry, crusted, or oozing—can provide clues about the underlying cause. This assessment is complemented by a careful review of the patient’s medical history.
- Physical examination, including visual inspection of the scalp, and palpation to detect any underlying lumps or tenderness.
- Skin biopsy, a procedure involving the removal of a small skin sample for microscopic examination, can identify specific skin conditions, like fungal infections or certain inflammatory diseases. This method is crucial for diagnosing conditions not easily identified by visual inspection alone.
- Scraping and microscopic examination of the affected area to detect fungal elements or parasites, a simple procedure that can help in diagnosing certain types of infections.
- Blood tests, particularly in cases where systemic conditions might be suspected, to rule out underlying medical issues contributing to the scalp scabs. For example, a complete blood count (CBC) can identify signs of anemia or infection.
- Allergy testing, if an allergic reaction is suspected as a possible cause, can identify potential allergens triggering the scalp condition.
Role of Medical History in Diagnosing Scalp Scabs
A detailed medical history provides valuable context for interpreting the physical findings. Knowing about any pre-existing skin conditions, recent illnesses, medications, or exposures to irritants or allergens can significantly aid in narrowing down the potential causes. For instance, a history of eczema might suggest a predisposition to certain types of scalp inflammation. Likewise, a recent use of a new hair product or a known allergy to certain substances might be crucial clues.
Furthermore, a history of stress or other factors that might affect immune function can provide a broader perspective on the problem.
Differentiating Scalp Conditions Causing Scabs
Differentiating between various scalp conditions is essential. Seborrheic dermatitis, for example, often presents with yellowish, greasy scales, while psoriasis shows silvery, flaky patches. Fungal infections like tinea capitis might present with pustules or inflamed areas. Understanding these differences is critical for choosing the right treatment. This meticulous process ensures the chosen treatment addresses the specific underlying condition, minimizing the risk of ineffective or inappropriate interventions.
Importance of Ruling Out Other Possible Causes
It is essential to rule out other possible causes of scalp scabs. These could include:
- Infections (bacterial, viral, fungal).
- Autoimmune diseases.
- Allergies.
- Nutritional deficiencies.
- Medications or other external irritants.
Diagnostic Steps for Scalp Scabs
| Diagnostic Step | Potential Tests | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Evaluation | Physical examination, medical history | Identify the nature of the scabs, associated symptoms, and potential contributing factors. |
| Further Evaluation (if needed) | Skin biopsy, fungal culture, blood tests, allergy testing | Confirm suspected diagnoses, rule out other conditions, and identify underlying causes. |
Treatment Options for Scalp Scabs
Scalp scabs, while often a minor nuisance, can be indicative of underlying skin conditions requiring specific treatment. Proper diagnosis is crucial to selecting the most effective approach. Identifying the cause allows for targeted interventions, leading to faster healing and preventing recurrence.Effective treatment for scalp scabs hinges on addressing the root cause. A dermatologist or primary care physician can accurately assess the situation, determine the specific condition, and recommend the most suitable course of action.
This personalized approach ensures optimal results and minimizes potential complications.
Common Topical Treatments
Topical treatments are frequently used for various scalp conditions causing scabs. Their effectiveness depends heavily on the underlying cause. For example, topical corticosteroids can be helpful for inflammatory conditions like seborrheic dermatitis, while antifungal creams target fungal infections. The selection of topical treatment will be determined by the cause identified by the doctor.
Antifungal Medications
Antifungal medications, both topical and oral, are crucial in treating fungal infections that manifest as scalp scabs. These medications work by inhibiting the growth of fungal organisms, thereby controlling the infection and promoting healing. Examples include clotrimazole, ketoconazole, and miconazole, which are available in various formulations for topical application. Oral antifungals are often prescribed for more extensive or systemic infections.
So, you’ve got those pesky scabs on your scalp? Figuring out the cause and best treatment is key. Sometimes, a simple fungal infection is the culprit, other times it could be a more serious issue. Knowing whether your diet might play a role is also important. Eating a healthy diet, including plenty of nutritious foods like nuts, can be beneficial for overall health, and you might want to explore if are nuts good for you in the context of your scalp health.
Ultimately, a visit to a dermatologist is crucial for proper diagnosis and a personalized treatment plan to get rid of those pesky scabs.
Home Remedies
Many home remedies can provide temporary relief from minor scalp scabs. However, these remedies are not substitutes for professional medical advice, especially when dealing with persistent or worsening conditions.
| Home Remedy | Potential Benefits | Important Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Aloe vera gel | Soothes irritation, promotes healing | May not be effective for all types of scalp scabs |
| Tea tree oil | Anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial properties | Potentially irritating to sensitive skin; dilute before application |
| Apple cider vinegar rinse | May help with fungal infections | Can be drying; use cautiously and dilute with water |
| Coconut oil | Moisturizing properties | May not be effective for all types of scalp scabs; can clog pores if used excessively |
Comparison of Treatment Approaches
The effectiveness and potential side effects of various treatment approaches differ significantly. Topical corticosteroids, for instance, can effectively reduce inflammation but may cause thinning of the skin with prolonged use. Antifungal medications are generally safe but may cause allergic reactions in some individuals. Home remedies, while generally safe, may not be effective for severe or persistent conditions.
Consulting a healthcare professional is essential for a proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
Step-by-Step Home Treatment Guide
Important Note: This guide is for informational purposes only and should not be considered a substitute for professional medical advice. If your scalp scabs are persistent or worsening, consult a dermatologist or primary care physician immediately.
- Cleanse the affected area gently with a mild, fragrance-free cleanser.
- Apply a thin layer of the recommended topical treatment (if prescribed by a doctor).
- Avoid scratching or picking at the scabs.
- Maintain good hygiene by regularly washing hair and using a gentle shampoo.
- Monitor the condition regularly for any changes or worsening symptoms. If symptoms persist or worsen, seek medical attention.
Prevention of Scalp Scabs
Preventing scalp scabs involves understanding the factors that contribute to their formation and implementing proactive measures to minimize the risk. A proactive approach to scalp health is crucial for overall well-being, as consistent scalp irritation can lead to discomfort and potentially more serious conditions.Scalp scabs are often a symptom of underlying issues, and preventing them hinges on addressing these root causes.
This involves a multifaceted approach focusing on hygiene, product selection, and overall scalp health. By taking preventive steps, individuals can significantly reduce the likelihood of experiencing scalp scabs.
Identifying Contributing Factors
Scalp scabs can arise from various factors, including dryness, infections, and even certain medical conditions. Understanding these factors is key to preventing future occurrences. Dryness, for example, can be caused by environmental conditions or a lack of hydration. Fungal infections or bacterial infestations can also lead to scabs. Furthermore, certain medical conditions like eczema or psoriasis can manifest as scalp scabs.
Good Hygiene Practices
Maintaining good hygiene is fundamental to preventing scalp scabs. Regular, gentle cleansing with a mild shampoo is crucial. Over-washing, however, can strip the scalp of its natural oils, leading to dryness and irritation. Furthermore, ensuring the scalp is completely dry after washing is important to avoid moisture-related issues.
Avoiding Harsh Chemicals and Products
Harsh chemicals and products can irritate the scalp, increasing the risk of scabs. Avoid using shampoos or hair products containing strong fragrances, dyes, or sulfates. Opt for products specifically formulated for sensitive scalps or those free of harsh chemicals. These products often contain gentler cleansers and moisturizers, reducing the risk of irritation.
Scalp Care Tips, Scabs on scalp causes diagnosis and treatment
Implementing consistent scalp care practices is vital in preventing scab formation. These measures can significantly contribute to a healthy scalp.
- Gentle Cleansing: Use a mild, sulfate-free shampoo to cleanse the scalp without stripping natural oils. Avoid harsh scrubbing motions, which can irritate the scalp.
- Proper Drying: Ensure the scalp is completely dry after washing to prevent moisture-related issues. Use a soft towel to gently pat the scalp dry, avoiding vigorous rubbing.
- Regular Checks: Inspect your scalp regularly for any signs of irritation, redness, or unusual scaling. Early detection allows for prompt treatment.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in nutrients can support overall health, including scalp health. Sufficient intake of vitamins and minerals is crucial.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can affect the scalp’s health. Practicing stress-reducing techniques like meditation or yoga can help maintain a healthy scalp.
- Hair Product Selection: Choose hair products carefully, prioritizing those free of harsh chemicals and fragrances. Look for products specifically designed for sensitive scalps or those with natural ingredients.
- Avoid Over-Styling: Excessive heat styling, chemical treatments, and other damaging hair practices can contribute to scalp irritation and scab formation.
- Regular Medical Checkups: If scalp issues persist, consult a dermatologist or healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. This is especially important for persistent scabs or associated symptoms.
Illustrations of Scalp Scabs
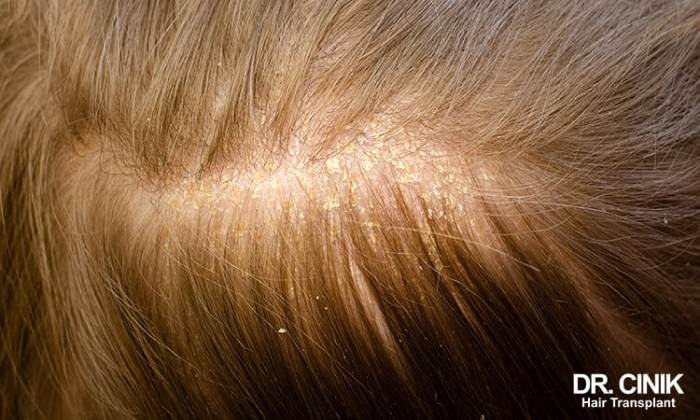
Visualizing scalp scabs is crucial for accurate diagnosis. Understanding the various appearances, locations, and stages of development helps distinguish between different underlying causes. This section provides detailed descriptions of common types of scalp scabs.Different types of scalp scabs exhibit varying characteristics. These characteristics can offer clues about the potential cause. Color, texture, size, and location patterns on the scalp provide valuable diagnostic information.
Observing how scabs evolve over time can further aid in the assessment.
Types of Scalp Scabs
Scalp scabs can manifest in diverse forms, reflecting different underlying conditions. Careful observation of these visual cues can be a vital step in diagnosis.
- Small, Crusty Scabs: These scabs are typically small, dry, and flaky, resembling tiny, light-brown or tan-colored flakes. They might be scattered across the scalp or clustered in specific areas. These scabs often appear in conditions like seborrheic dermatitis, a common scalp inflammation, and are commonly seen in the scalp’s oily areas, like the forehead, sides, and the hairline. The texture is rough and easily removable.
The scabs may look like dandruff but are thicker and more firmly attached to the scalp.
- Larger, Thickened Scabs: These scabs are larger, and raised, with a rough or uneven surface. Their color can vary from light brown to dark brown or even black. The thickness suggests a longer duration of the underlying condition. These larger scabs often occur in conditions like psoriasis or fungal infections, which may present with patches of inflamed skin and thick, adherent scabs.
The location might be concentrated on the scalp’s edges or in particular areas.
- Fluid-Filled Blisters with Scabs: In cases of infection or skin conditions involving blisters, scabs can form over the dried-up fluid in the blister. These scabs might be moist or slightly sticky initially, with a yellowish or whitish color. As the blisters heal, the scabs often dry and become darker, and the texture can vary from slightly sticky to firmly attached to the skin.
They can appear on any part of the scalp and vary in size, sometimes forming large, crusted areas.
- Ring-Shaped or Patchy Scabs: These scabs can form in a circular or ring-like pattern, often indicative of fungal infections or specific skin conditions. The scabs may be raised or flat, and their color might vary from light red to dark brown or even black, depending on the infection and the stage of development. The ring shape can be a diagnostic indicator, as well as the appearance of scaling or inflammation around the scabs.
Stages of Scalp Scab Development
Understanding the stages of scab development can provide valuable clues to the underlying cause.
- Initial Stage: Initially, the scalp may show redness or inflammation. Small, pinpoint lesions or blisters may appear, which gradually develop into crusty or fluid-filled scabs. The scabs are usually small and may be difficult to distinguish from the surrounding skin initially.
- Maturation Stage: As the scab matures, it thickens, and its color might deepen. The texture becomes more coarse, and the scab’s size may increase. This stage can take several days to several weeks, depending on the underlying condition.
- Healing Stage: The scab’s color usually lightens, and the texture becomes smoother. The scab starts to shrink and eventually falls off, leaving behind the healed skin. This process can take several weeks or months, depending on the extent of the damage and the healing process.
A Scalp with Scabs: Visual Cues
A detailed description of a scalp with scabs is essential for diagnosis.
- Description 1: A patient presents with a scalp exhibiting numerous small, crusty scabs, predominantly located on the forehead and hairline. The scabs are a light brown color, and the scalp shows mild redness around the affected areas. The scabs are easily removable. This description suggests a potential case of seborrheic dermatitis or dandruff.
- Description 2: A patient presents with a scalp displaying large, thick, raised scabs. The scabs are dark brown and concentrated around the temples and crown. The affected areas show scaling and inflammation. This description suggests a possible case of psoriasis or a fungal infection.
- Description 3: A patient presents with a scalp showing ring-shaped scabs with inflamed skin around the edges. The scabs are a dark reddish-brown color. The rings are approximately 2-3 cm in diameter and are scattered throughout the scalp. This description suggests a possible fungal infection or a specific skin condition requiring further evaluation.
Conclusive Thoughts
In conclusion, addressing scalp scabs requires a multifaceted approach that considers the potential causes, accurate diagnosis, and tailored treatment options. This comprehensive guide has explored the various aspects of scalp scabs, from their different types and appearances to the effective methods of diagnosis and treatment. We’ve also emphasized the importance of prevention through good hygiene and avoiding harsh chemicals.
By understanding the causes, diagnoses, and treatment options presented here, you’re well-equipped to take control of your scalp health and well-being.