Breast cancer staging stage zero, often overlooked, represents a critical early detection stage. This early diagnosis is crucial because it typically involves a small, non-invasive lesion that hasn’t spread beyond the milk ducts or lobules of the breast. Understanding the characteristics, diagnosis, and treatment options associated with stage zero breast cancer is essential for individuals and healthcare professionals alike.
Early intervention significantly improves outcomes.
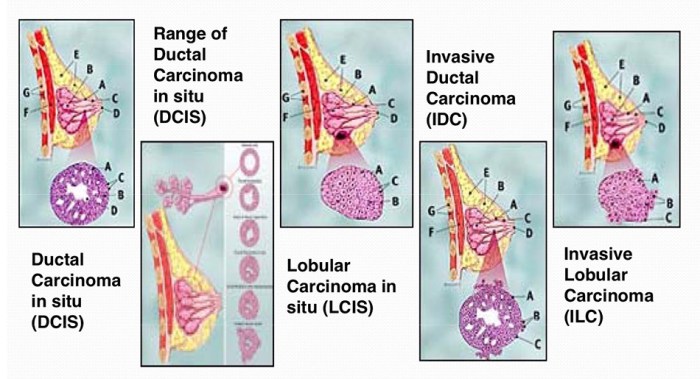
Stage zero breast cancer, also known as ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) or lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS), is characterized by abnormal cells confined to the milk ducts or lobules. It’s important to note that these abnormal cells haven’t yet invaded surrounding tissues, which distinguishes it from more advanced stages. This article will explore the key aspects of this often-overlooked stage of breast cancer, from diagnosis and treatment to prognosis and prevention.
Introduction to Breast Cancer Staging Stage Zero
Stage zero breast cancer, also known as ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) or lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS), represents an early stage of breast cancer. It’s characterized by abnormal cells that have not yet invaded the surrounding breast tissue. This non-invasive form is often detected through screening mammograms, highlighting the importance of regular breast cancer screenings. While these abnormal cells can potentially develop into invasive cancer, they haven’t yet spread beyond the milk ducts or lobules.
So, I’ve been learning about breast cancer staging, specifically stage zero. It’s fascinating how early detection is key, and stage zero means the cancer is very early. But did you know there’s a potential connection between migraines and breast cancer? Migraines and breast cancer research is ongoing, but it’s an area of interest. Regardless, understanding stage zero breast cancer is crucial for early intervention and better outcomes.
Definition of Stage Zero Breast Cancer
Stage zero breast cancer, formally known as ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) or lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS), is characterized by the presence of abnormal cells within the milk ducts (DCIS) or lobules (LCIS) of the breast. These abnormal cells haven’t broken through the walls of the ducts or lobules, and haven’t spread to surrounding tissues. Early detection and treatment are crucial at this stage to prevent progression to invasive cancer.
Key Characteristics of Stage Zero Breast Cancer
The key characteristics of stage zero breast cancer revolve around the localized nature of the abnormal cells. These cells are often detected through mammograms and/or biopsies, and they haven’t spread beyond the milk ducts or lobules. The absence of invasion into surrounding tissues distinguishes stage zero from other, more advanced stages. This early detection is critical for successful treatment.
Types of Breast Cancer in Stage Zero
Stage zero breast cancer primarily presents as two main types: ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS). DCIS involves abnormal cells within the milk ducts, while LCIS involves abnormal cells within the milk-producing glands (lobules). Understanding these distinctions helps in tailoring treatment strategies.
Prevalence and Incidence Rates of Stage Zero Breast Cancer
The prevalence and incidence rates of stage zero breast cancer are significant. While it’s considered an early stage, it’s a fairly common finding in breast cancer screening programs. Specific numbers vary depending on the population studied and the screening methods used. The precise prevalence and incidence rates are subject to ongoing research and data collection.
Comparison of Stage Zero Breast Cancer to Other Stages
| Cancer Type | Tumor Size | Lymph Node Involvement | Distant Metastasis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stage Zero (DCIS/LCIS) | Usually microscopic; not palpable | Absent | Absent |
| Stage 1 | Less than 2 centimeters | Absent | Absent |
| Stage 2 | 2-5 centimeters | Present or absent | Absent |
| Stage 3 | Can vary | Present | Absent |
| Stage 4 | Can vary | Present | Present |
This table highlights the key differences in tumor size, lymph node involvement, and distant metastasis between stage zero and other stages of breast cancer. Note that stage zero breast cancer is fundamentally different in its lack of invasive growth, a crucial distinction for treatment planning.
Learning about breast cancer staging, specifically stage zero, is crucial for understanding the early detection and treatment of this disease. While there’s a lot of focus on proactive health measures, like proper nutrition, the effectiveness of gummy vitamins in supporting overall health is a subject of ongoing discussion. Researching the topic of are gummy vitamins effective can offer insight into how supplements might complement existing treatment plans.
Ultimately, stage zero breast cancer is characterized by the absence of invasive cancer cells, making early intervention and treatment highly effective.
Diagnosis and Detection of Stage Zero Breast Cancer
Early detection is crucial in the fight against breast cancer, and stage zero, also known as ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), is no exception. Understanding the diagnostic methods used to identify this early-stage cancer is essential for prompt treatment and improved outcomes. The key lies in recognizing the subtle changes that might indicate the presence of abnormal cells.The diagnosis of stage zero breast cancer often involves a multi-step process, combining various imaging techniques and tissue analysis.
A combination of approaches allows healthcare providers to build a comprehensive picture of the situation, increasing the chances of accurate diagnosis. This allows for timely intervention and the best possible treatment strategy.
Common Diagnostic Methods
Early detection is paramount in managing stage zero breast cancer effectively. Various diagnostic methods are employed to identify and characterize the abnormal cells. These methods provide a more detailed picture of the condition, guiding healthcare professionals in making informed decisions.
Mammograms
Mammograms are a vital tool in the early detection of breast abnormalities. This low-dose X-ray imaging technique can reveal subtle changes in breast tissue, including microcalcifications that might indicate the presence of DCIS. Regular mammograms are essential for women at varying ages, allowing for the identification of any potentially cancerous changes in a timely manner.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound, another imaging modality, plays a significant role in evaluating breast abnormalities detected on mammograms or during physical examinations. It utilizes sound waves to create images of the breast tissue, providing a different perspective than mammograms. Ultrasound is particularly useful in distinguishing between solid and fluid-filled masses and can help determine the characteristics of the abnormality.
Biopsies, Breast cancer staging stage zero
A biopsy is a procedure where a small tissue sample is removed from the breast for examination under a microscope. It’s a crucial step in confirming a diagnosis of DCIS or other breast abnormalities detected by imaging. Different biopsy techniques exist, each with its own advantages and disadvantages, and the appropriate technique is chosen based on the nature of the abnormality and its location within the breast.
Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of stage zero breast cancer is critical because it often means the cancer has not yet spread beyond the milk ducts. This translates into a higher likelihood of successful treatment and a better prognosis. The earlier the detection, the more effective and less invasive the treatment can be, potentially preventing the need for aggressive therapies.
Breast cancer staging, specifically stage zero, is often a relief for patients. It indicates the cancer is contained and hasn’t spread. Interestingly, while researching the prevalence of breast cancer, I stumbled upon information about how common erectile dysfunction is in men. Knowing this, I was curious to explore how the potential physiological impacts of different cancers could correlate with other health issues.
Ultimately, understanding stage zero breast cancer, like the statistics on how common is erectile dysfunction , provides valuable insight for patients and healthcare professionals.
Symptoms and Warning Signs
While stage zero breast cancer often presents with no noticeable symptoms, some women may experience certain signs. These are not specific to stage zero breast cancer and can occur in other conditions. Therefore, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for evaluation. Regular self-exams and mammograms are key to early detection.
Diagnostic Tests and Accuracy
| Test Type | Accuracy | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Mammogram | High accuracy in detecting abnormalities, especially microcalcifications. | May not detect all cancers, particularly in dense breast tissue. Can sometimes produce false positives. |
| Ultrasound | Helpful in differentiating between solid and fluid-filled masses. | Can sometimes be less accurate in identifying microcalcifications compared to mammograms. |
| Biopsy | Confirmatory diagnosis. | Involves a small procedure that can carry risks, though these are typically minimal. |
Treatment Options for Stage Zero Breast Cancer
Stage zero breast cancer, also known as ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), is a non-invasive form of breast cancer. This means the abnormal cells are confined to the milk ducts and haven’t spread to surrounding tissues. While it’s not considered a true cancer in the sense that it hasn’t yet invaded surrounding tissue, it still requires careful management to prevent potential progression to invasive cancer.
Treatment approaches are designed to minimize the risk of this progression and maintain a healthy outcome.Treatment for stage zero breast cancer is primarily focused on eradicating the abnormal cells to prevent future issues. This typically involves methods that effectively target the affected area, avoiding unnecessary procedures and side effects. The goal is to remove the cancer completely and prevent its recurrence.
Surgical Procedures
Surgical removal of the affected tissue is a common treatment for stage zero breast cancer. The type of surgery depends on the size and location of the abnormal cells and the individual’s overall health. A lumpectomy, which involves removing only the affected area, is a common approach. In cases where the abnormal cells are extensive, a mastectomy, the removal of the entire breast, might be considered.
In cases where the abnormal cells are extensive, a mastectomy, the removal of the entire breast, might be considered. Minimally invasive techniques are also employed whenever possible. These procedures aim to minimize scarring and recovery time, enhancing the patient’s well-being and quality of life.
Role of Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy is frequently used in conjunction with or as an alternative to surgery for stage zero breast cancer. High-energy beams are targeted to destroy the abnormal cells, particularly in areas where surgery may not be fully effective. The precise dosage and duration of radiation therapy are determined based on factors such as the size and location of the DCIS.
The goal is to eliminate any remaining cancerous cells and minimize the risk of recurrence.
Role of Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is not typically used for stage zero breast cancer. Since the cancer is confined to the milk ducts, it hasn’t spread to other parts of the body, making chemotherapy unnecessary. The use of chemotherapy is reserved for cases where the cancer has spread to other tissues or organs.
Importance of Individualized Treatment Plans
Every patient with stage zero breast cancer is unique. Treatment decisions should be tailored to the individual’s specific circumstances. Factors such as the size and location of the DCIS, the patient’s overall health, and personal preferences should all be considered when creating a treatment plan. This individualized approach ensures the most effective and least invasive treatment option for each patient.
Treatment Options Summary
| Treatment Type | Success Rate | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Lumpectomy | High, typically over 95% | Mild to moderate pain, swelling, bruising, and temporary discomfort. |
| Mastectomy | High, typically over 95% | More significant pain, swelling, scarring, potential for long-term physical effects, and potential psychological impact. |
| Radiation Therapy | High, typically over 90% | Fatigue, skin irritation (redness, dryness, or peeling), temporary discomfort in the treated area, potential for long-term complications. |
| Chemotherapy | Not typically used | Significant side effects, including nausea, hair loss, fatigue, and potential long-term health issues. |
Prognosis and Long-Term Outcomes of Stage Zero Breast Cancer

Stage zero breast cancer, also known as ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), is characterized by abnormal cells confined to the milk ducts. While the cancer cells haven’t spread to surrounding tissues, their presence necessitates careful monitoring and management. The prognosis for stage zero breast cancer is generally excellent, with a high likelihood of successful treatment and long-term remission.
However, individual outcomes can vary depending on several factors.The prognosis for stage zero breast cancer is typically positive, as the cancer is contained within the milk ducts. This containment significantly impacts the likelihood of successful treatment and long-term survival. Early detection and prompt treatment are crucial for managing the disease effectively and minimizing the risk of complications.
Typical Prognosis
Stage zero breast cancer, being a localized condition, usually responds well to treatment. The likelihood of successful treatment and long-term remission is high, with most patients experiencing no recurrence of the disease. However, individual outcomes can vary based on factors such as the size and characteristics of the lesion, as well as the patient’s overall health. Close monitoring and follow-up care are essential for managing any potential risks.
Factors Influencing Prognosis
Several factors can potentially influence the prognosis for stage zero breast cancer. Understanding these factors can help patients and healthcare providers make informed decisions regarding treatment and management.
| Prognostic Factor | Description | Impact on Survival |
|---|---|---|
| Tumor size | The dimensions of the abnormal area within the milk duct. | Larger tumors may be associated with a slightly increased risk of recurrence. |
| Histological grade | The degree of cellular abnormality and aggressiveness. | Higher grade tumors are more likely to require more aggressive treatment strategies. |
| Presence of microcalcifications | Tiny deposits of calcium in the breast tissue, often visible on mammograms. | The presence of microcalcifications can be an indicator of the cancer’s characteristics, potentially influencing treatment decisions. |
| Patient age | Age of the patient at diagnosis. | Generally, no significant impact on survival rates for stage zero breast cancer. |
| Patient’s overall health | The patient’s general health condition prior to diagnosis. | Underlying health conditions can sometimes impact the patient’s response to treatment and overall prognosis. |
Long-Term Implications
Long-term implications for patients with stage zero breast cancer are generally favorable. The primary concern is the potential for the cancer to progress to invasive breast cancer if not managed appropriately. Regular follow-up appointments, including mammograms and clinical breast exams, are essential to detect any changes or recurrence. The risk of recurrence is significantly lower compared to more advanced stages of breast cancer.
Statistics on Long-Term Survival
Data on long-term survival rates for stage zero breast cancer patients show very high rates of survival. Extensive research indicates that with appropriate treatment and ongoing monitoring, the vast majority of patients experience no recurrence or progression to invasive breast cancer. The specific survival rates are influenced by the aforementioned factors and are best discussed with a healthcare provider.
Risk Factors and Prevention Strategies
Understanding the factors that increase the likelihood of developing stage zero breast cancer, and the lifestyle choices that can mitigate those risks, is crucial for proactive health management. While stage zero breast cancer is often considered a non-invasive condition, early detection and preventive measures remain important. Proactive steps can help reduce the overall risk, even if not eliminating it entirely.While the exact causes of stage zero breast cancer are not always fully understood, research has identified several contributing factors and strategies to reduce the chance of developing this condition.
Identifying Risk Factors
Stage zero breast cancer, also known as ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), can be influenced by a combination of genetic and lifestyle factors. Identifying these risk factors is crucial for understanding the potential triggers and implementing preventive strategies. A thorough understanding of these elements allows individuals to make informed choices about their health and well-being.
Lifestyle Choices for Reduced Risk
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is vital for minimizing the risk of developing stage zero breast cancer. These choices directly impact overall health and can significantly reduce the chances of developing this type of breast cancer. Implementing healthy lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a balanced diet and engaging in regular physical activity, are crucial steps toward reducing the risk of various health problems, including breast cancer.
- Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Maintaining a healthy weight through balanced nutrition and regular exercise is crucial. Obesity is a known risk factor for various cancers, including breast cancer. Weight management plays a vital role in reducing the risk of developing this type of breast cancer.
- Regular Physical Activity: Regular physical activity, such as brisk walking, jogging, swimming, or cycling, can contribute significantly to reducing the risk of breast cancer. Exercise plays a critical role in overall health, including reducing the risk of developing this type of breast cancer.
- Balanced Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can have a positive impact on overall health and reduce the risk of developing breast cancer. Consuming a variety of nutrient-rich foods supports a healthy body, potentially reducing the risk of various cancers, including this one.
- Limiting Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol consumption is linked to an increased risk of various cancers, including breast cancer. Moderation in alcohol intake is crucial for reducing the risk of developing this type of cancer.
Preventive Measures to Minimize Risk
Implementing preventive measures, in addition to lifestyle choices, can contribute to lowering the risk of developing stage zero breast cancer. Beyond lifestyle modifications, certain preventive measures can help reduce the chance of developing this type of breast cancer.
- Breastfeeding: Breastfeeding has been linked to a lower risk of breast cancer, and this is attributed to the hormonal changes that occur during breastfeeding. Breastfeeding has a wide range of health benefits, including potentially reducing the risk of developing breast cancer.
- Regular Breast Exams: Regular breast self-exams and clinical breast exams can help in early detection, which is critical in managing the condition effectively. Regular breast exams are vital in identifying any abnormalities at an early stage, which is crucial for effective management.
- Genetic Counseling: Individuals with a strong family history of breast cancer should consider genetic counseling to assess their risk and explore potential preventive options. Genetic counseling plays a vital role in identifying potential genetic predispositions to various diseases, including breast cancer, and allows individuals to make informed decisions about their health.
Role of Genetic Factors
Genetic predisposition plays a significant role in the development of stage zero breast cancer. Inherited genetic mutations, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, increase the risk of developing this type of cancer. These genetic mutations can be a significant factor in increasing the risk of developing this type of breast cancer. Genetic factors contribute significantly to the development of various cancers, and in some cases, can significantly increase the likelihood of developing this type of breast cancer.
Risk Factors and Prevention Strategies Comparison
| Risk Factor | Description | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Obesity | Excess body weight increases the risk of various cancers, including breast cancer. | Maintain a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise. |
| Alcohol Consumption | Excessive alcohol consumption is linked to an increased risk of various cancers, including breast cancer. | Limit alcohol consumption or abstain from it entirely. |
| Family History | A strong family history of breast cancer increases the risk. | Consult with a genetic counselor to assess risk and explore preventive options. |
| Lack of Physical Activity | Sedentary lifestyles increase the risk of developing various health issues, including breast cancer. | Engage in regular physical activity. |
| Poor Diet | A diet lacking in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains may increase the risk. | Consume a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. |
Support and Resources for Patients and Families: Breast Cancer Staging Stage Zero
Navigating a breast cancer diagnosis, even at the seemingly less aggressive stage zero, can be overwhelming. Beyond the medical treatments, emotional and practical support are crucial for a positive outcome. This section explores the vital support systems available to patients and their families, empowering them to face this challenge together.Facing a stage zero breast cancer diagnosis can trigger a range of emotions, from anxiety and fear to uncertainty and hope.
Having access to strong support networks and resources can make a significant difference in the patient’s journey. Understanding the available resources and utilizing them effectively can provide comfort, guidance, and a sense of community.
Support Groups and Organizations
Numerous organizations offer valuable support for patients and families dealing with stage zero breast cancer. These groups provide a safe space to share experiences, learn from others, and receive emotional support from those who understand the challenges. They also often offer educational workshops and resources.
- The American Cancer Society (ACS) provides comprehensive support groups, educational materials, and a helpline. They offer personalized support tailored to different needs and circumstances, fostering a sense of community.
- The National Breast Cancer Foundation (NBCF) offers resources, including support groups, information on coping mechanisms, and emotional support services.
- Look for local support groups through hospitals, community centers, or online forums. These local groups often offer personalized support, enabling individuals to connect with others facing similar situations in their immediate surroundings.
Emotional and Psychological Support
The emotional toll of a breast cancer diagnosis can be significant. Professional counseling and support groups play a crucial role in helping patients cope with anxiety, fear, and other emotional challenges.
- Therapists and counselors specializing in cancer care can offer personalized guidance and strategies to manage emotional distress. This tailored approach can help individuals navigate the complexities of the diagnosis and treatment process effectively.
- Support groups offer a safe space to share experiences, receive emotional support, and connect with others who understand the challenges. This shared experience can provide a sense of community and validation.
- Online forums and support communities can connect individuals with others who are going through similar experiences. The anonymity of these platforms can provide comfort and a sense of belonging.
Patient Education and Empowerment
Understanding the diagnosis and treatment options is essential for empowering patients to take an active role in their care.
- Patient education materials, workshops, and seminars provided by medical professionals, cancer organizations, and support groups can equip individuals with the knowledge necessary to make informed decisions about their treatment and care.
- Empowering patients through knowledge fosters a sense of control and agency. This active participation can significantly impact their emotional well-being and treatment outcomes.
- By actively participating in their care, patients feel more empowered and better equipped to navigate the complexities of their treatment journey.
Resources for Stage Zero Breast Cancer Patients and Families
This list provides valuable resources for patients and families dealing with stage zero breast cancer.
| Organization | Website | Helpline |
|---|---|---|
| American Cancer Society | cancer.org | 1-800-227-2345 |
| National Breast Cancer Foundation | nbcf.org | (Information on website) |
| [Example Local Support Group] | [Website Address] | [Phone Number] |
Final Wrap-Up
In conclusion, understanding breast cancer staging stage zero is vital for early detection and effective treatment. The early intervention strategies, combined with individualized treatment plans, contribute to improved outcomes. By recognizing the characteristics, diagnosis methods, and treatment options, individuals and healthcare providers can proactively address this critical stage of breast cancer. Proactive measures and a supportive environment are crucial for positive outcomes.










