Bursitis inflammation swelling joints can be a painful condition affecting various parts of the body. This comprehensive guide delves into the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for this often-misunderstood ailment. We’ll explore the different types of bursae, the role of repetitive stress, and the importance of early intervention.
From understanding the underlying mechanisms of bursitis to practical self-care strategies, this article aims to equip you with the knowledge you need to navigate this condition effectively. We’ll cover everything from preventative measures to potential complications, ensuring you’re well-informed about bursitis inflammation swelling joints.
Introduction to Bursitis
Bursitis is a common condition characterized by inflammation of the bursae, small fluid-filled sacs that cushion the joints and facilitate smooth movement. This inflammation can lead to pain, swelling, and reduced mobility in the affected area. Understanding the different types of bursae, their locations, and the causes of inflammation is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment.Bursae are located throughout the body wherever tendons, muscles, or ligaments rub against bones.
They act as shock absorbers, preventing friction and damage during movement. Different types of bursae have specific roles in various joints. Common locations include the shoulder, elbow, knee, and hip.Common causes of bursitis inflammation include overuse, repetitive movements, direct impact, and underlying medical conditions. Overuse injuries are frequently encountered in athletes or individuals performing repetitive tasks, such as painting or typing.
Direct trauma, like a fall or blow to the affected area, can also lead to bursitis. Certain medical conditions, such as gout or rheumatoid arthritis, can increase the risk of bursitis development.Symptoms of bursitis typically include pain, which may be localized or radiating. The pain is often described as aching, throbbing, or sharp, varying in intensity depending on the activity or rest.
Swelling and tenderness around the affected joint are also common. The location and severity of pain can help in determining the type of bursitis.
Types of Bursae and Their Locations
- Subacromial bursa: Located beneath the acromion (part of the shoulder blade) and above the rotator cuff tendons in the shoulder joint. This bursa cushions the rotator cuff tendons during shoulder movement.
- Prepatellar bursa: Located in front of the kneecap. This bursa is crucial for cushioning the skin over the patella during knee flexion and extension.
- Olecranon bursa: Located in the back of the elbow joint, cushioning the olecranon process (the bony prominence of the elbow). This bursa protects the elbow from rubbing against the skin.
- Trochanteric bursa: Located on the outer side of the hip joint, cushioning the tendons and muscles that surround the hip joint.
Common Types of Bursitis
| Type of Bursitis | Location |
|---|---|
| Olecranon bursitis | Back of the elbow |
| Prepatellar bursitis | Front of the knee |
| Subacromial bursitis | Shoulder |
| Trochanteric bursitis | Outer hip |
Causes and Risk Factors
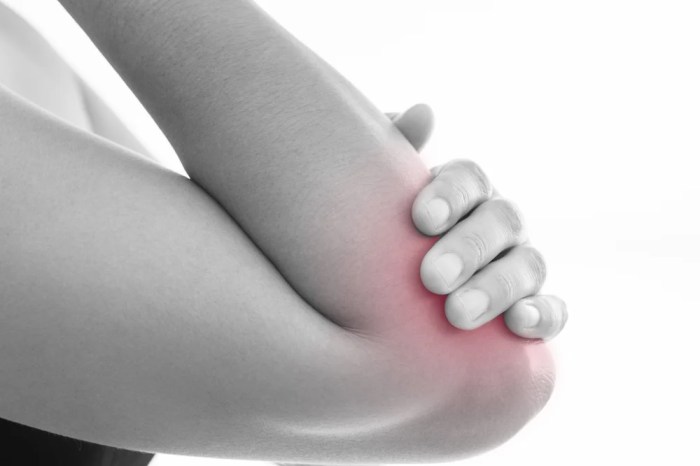
Bursitis, the inflammation of the fluid-filled sacs (bursae) that cushion joints, often arises from a combination of factors. Understanding these causes and risk factors is crucial for prevention and effective management. Identifying contributing elements allows for proactive measures to reduce the likelihood of developing bursitis.
Ugh, dealing with bursitis inflammation and the swelling in my joints is seriously tough. It’s like my body is rebelling against me. Finding relief can be a real challenge, especially when you’re considering things like gaviscon antacid treatment for heartburn for something completely different. But seriously, I’m still focused on figuring out ways to ease the pain and swelling of this frustrating bursitis.
Hopefully, some good natural remedies will help in the end.
Repetitive Stress and Overuse
Repetitive movements and overuse of a particular joint are significant contributors to bursitis. Repeated motions place consistent pressure on the bursa, leading to irritation and inflammation. Think of a factory worker performing the same hand movements all day, or a tennis player repeatedly hitting the ball. These repetitive actions can gradually damage the bursa, leading to bursitis.
Sustained pressure from improper posture or awkward body mechanics can also trigger the condition.
Underlying Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions can increase the risk of bursitis. Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, gout, and certain infections can create an environment conducive to inflammation, increasing the likelihood of bursitis developing. These conditions can directly impact the bursae, making them more susceptible to inflammation. Individuals with these conditions may experience bursitis more frequently or severely than those without.
Occupational and Activity-Related Risk Factors
Certain occupations and activities expose individuals to higher risks of developing bursitis. Jobs requiring repetitive arm movements, such as assembly line work or painting, or activities involving forceful movements, like weightlifting or certain sports, can all contribute to bursitis. This is due to the repeated stress on the bursae, leading to irritation and inflammation. For example, construction workers, plumbers, and painters often report bursitis in the shoulder, elbow, or hip.
Sports like tennis, baseball, and swimming can also put specific joints at risk.
Categorized Risk Factors
| Factor | Description | Preventative Measures |
|---|---|---|
| Repetitive Stress | Repeated motions or sustained pressure on a joint can irritate the bursa, leading to inflammation. | Taking breaks during repetitive tasks, using proper lifting techniques, and adjusting posture can help reduce stress on the affected joint. Employing ergonomic tools and equipment can also be beneficial. |
| Underlying Medical Conditions | Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, gout, or infections can increase the likelihood of bursitis by creating an inflammatory environment. | Managing underlying conditions effectively through appropriate medical care can reduce the risk of bursitis. Individuals with these conditions should consult their doctor for personalized prevention strategies. |
| Occupational/Activity-Related | Certain occupations (e.g., assembly line work) or activities (e.g., weightlifting) can put extra stress on specific joints, increasing the risk of bursitis. | Using proper techniques during work or exercise, taking breaks, and using supportive equipment can help mitigate the risk of bursitis. Ergonomic assessments and adjustments for workspaces can be extremely helpful. |
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Bursitis, an inflammation of the bursae, often presents with characteristic symptoms that can vary in severity. Understanding these symptoms and the diagnostic methods employed by healthcare professionals is crucial for prompt and accurate diagnosis. Proper identification allows for the implementation of appropriate treatment strategies and management plans.
Symptoms of Bursitis
Bursitis is primarily characterized by pain, swelling, and tenderness around the affected joint. These symptoms are often localized to the specific bursa involved. The pain can range from mild discomfort to severe throbbing or shooting pain, depending on the severity of inflammation and the location of the bursa. Swelling is a visible manifestation of fluid accumulation in the bursa, which can also contribute to discomfort and restricted movement.
Dealing with bursitis inflammation and swelling in your joints can be tough. The pain and stiffness can really impact your daily life. Fortunately, there are various treatment options available, including different kinds of prescription and OTC drugs prescription and otc drugs. These medications can help manage the pain and inflammation, allowing you to get back on your feet faster.
Ultimately, proper diagnosis and a tailored treatment plan from a healthcare professional are key to effectively addressing bursitis inflammation and swelling in your joints.
Tenderness is a key symptom, as the affected area is typically sensitive to the touch.
Methods for Diagnosing Bursitis
Accurate diagnosis of bursitis involves a combination of methods, including careful physical examination, patient history, and potentially, imaging techniques. Healthcare professionals will assess the affected area for swelling, tenderness, and range of motion limitations. They will also consider the patient’s medical history and self-reported symptoms.
Role of Medical History and Patient Self-Report
A detailed medical history is vital in the diagnostic process. Factors such as previous injuries, repetitive movements, underlying medical conditions, and medications can all contribute to the development of bursitis. Patient self-report, including the onset, duration, location, and characteristics of the pain, is also critical. This information helps healthcare professionals narrow down the possibilities and identify potential causes.
For example, a history of repetitive overhead activities might suggest bursitis in the shoulder, while a recent fall could point to a hip bursa injury.
Diagnostic Tools and Potential Differential Diagnoses
| Symptom | Severity Level | Diagnostic Tools | Potential Differential Diagnoses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pain | Mild to Severe | Physical Examination (palpation, range of motion assessment), Patient History | Tendinitis, arthritis, fractures, nerve impingement |
| Swelling | Slight to Significant | Physical Examination (visual inspection), Imaging (ultrasound, X-ray) | Cellulitis, gout, infection, other inflammatory conditions |
| Tenderness | Localized | Physical Examination (palpation), Imaging (ultrasound) | Muscle strain, contusion, other localized pain conditions |
| Limited Range of Motion | Mild to Significant | Physical Examination (assessing joint mobility), Imaging (MRI) | Joint sprains, fractures, other joint conditions |
A comprehensive physical examination, incorporating palpation (touching) and assessment of the affected joint’s range of motion, is often the initial step. Imaging techniques, such as X-rays, ultrasound, or MRI, may be used to rule out other conditions or to confirm the presence and extent of bursitis. X-rays are helpful in identifying bony abnormalities or fractures, while ultrasound can visualize soft tissues and assess the fluid collection within the bursa.
MRI is valuable for detailed soft tissue evaluation, but is typically not the first imaging modality utilized.
Treatment and Management: Bursitis Inflammation Swelling Joints
Bursitis, characterized by inflammation of the bursae, can be effectively managed with a combination of conservative and sometimes, medical interventions. Understanding the various treatment approaches is crucial for alleviating pain and restoring function. Early intervention and adherence to the prescribed treatment plan are vital for optimal recovery.
Dealing with bursitis inflammation and swelling in my joints has been a real pain lately. I’ve been researching different remedies, and while trying to figure out what to eat, I stumbled upon this helpful article about whether pregnant women can eat shrimp can pregnant women eat shrimp. Knowing what’s safe to consume during pregnancy is crucial, and it’s a good reminder that even seemingly simple dietary choices can have a larger impact than we realize.
Hopefully, focusing on proper nutrition will help my joint pain subside. Back to the bursitis, I’m now looking into more natural remedies for this joint inflammation.
Conservative Treatment Approaches
Conservative treatments focus on reducing inflammation and pain without surgery. These approaches are often the first line of defense for bursitis management. A key aspect of conservative care is the “RICE” principle: Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation. These methods aim to minimize swelling and pain.
- Rest: Avoiding activities that exacerbate pain is essential. This allows the inflamed bursa to heal. Rest periods can range from a few days to several weeks, depending on the severity of the condition and the individual’s response to treatment.
- Ice: Applying ice packs to the affected area for 15-20 minutes at a time, several times a day, can help reduce swelling and pain. Proper application minimizes the risk of frostbite.
- Compression: Using elastic bandages or wraps can help control swelling and support the affected joint. Compression aids in limiting fluid buildup.
- Elevation: Keeping the affected area elevated above the heart can further reduce swelling by promoting lymphatic drainage. This is particularly helpful for areas like the elbow or knee.
Pain Relievers and Anti-inflammatory Medications
Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or naproxen, can effectively manage mild to moderate pain associated with bursitis. These medications help reduce inflammation and provide pain relief. Prescription-strength anti-inflammatory medications may be necessary for more severe cases. Always consult a healthcare professional before starting any new medication regimen. The decision to use pain relievers should be made in consultation with a doctor.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in restoring joint function and range of motion after bursitis. A physical therapist can design a personalized exercise program to strengthen the muscles surrounding the affected joint and improve flexibility. Exercises gradually increase the range of motion and improve the joint’s stability. Examples include gentle stretching and strengthening exercises tailored to the specific joint involved.
Summary of Treatment Approaches
| Treatment Approach | Effectiveness | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Rest | Generally effective in reducing inflammation and pain, especially when combined with other approaches. | Potential for decreased activity tolerance and muscle weakness if prolonged. |
| Ice | Effective in reducing inflammation and pain, but limited to short-term effects. | Risk of frostbite if applied improperly or for extended periods. |
| Compression | Helpful in controlling swelling and providing support. | Potential for skin irritation if the bandage is too tight or used for too long. |
| Elevation | Promotes lymphatic drainage, reducing swelling. | No significant side effects, but comfort may be affected depending on the position. |
| Pain Relievers (OTC) | Effective for managing mild to moderate pain and inflammation. | Potential for stomach upset, bleeding, or allergic reactions in some individuals. |
| Prescription Anti-inflammatory Medications | More effective for severe cases, but with higher potential side effects. | Increased risk of stomach ulcers, bleeding, or kidney problems. |
| Physical Therapy | Helps restore joint function and range of motion, and improve strength and flexibility. | Potential for muscle soreness during initial sessions, which subsides with time. |
Prevention and Self-Care
Bursitis, while often manageable, can be prevented through proactive measures and self-care strategies. Understanding the contributing factors and adopting healthy habits can significantly reduce the risk of developing or re-experiencing bursitis. This section details key strategies for preventing bursitis and managing symptoms effectively.
Strategies to Prevent Bursitis Inflammation
Preventing bursitis involves addressing the underlying factors that contribute to inflammation of the bursae. Consistent effort in maintaining good posture, proper warm-up and cool-down routines, and appropriate protective measures are crucial for long-term prevention. Avoiding repetitive stress on the affected joints and recognizing warning signs are also vital components of a preventative approach.
Importance of Proper Warm-up and Cool-down Routines
A comprehensive warm-up before physical activity prepares the muscles and joints for the exertion ahead, gradually increasing blood flow and elasticity. This prepares the tissues for the anticipated stress, reducing the risk of injury. A proper cool-down, conversely, gradually reduces the intensity of the activity, allowing the body to recover and prevent stiffness and muscle soreness. This reduces the risk of micro-tears and subsequent inflammation.
For example, before a tennis match, a player might perform dynamic stretches like arm circles and leg swings to warm up, and static stretches like holding a hamstring stretch to cool down.
Significance of Maintaining Good Posture and Proper Body Mechanics
Maintaining good posture and employing proper body mechanics are critical in minimizing stress on joints. Good posture distributes weight evenly, reducing pressure on the bursae. Proper body mechanics during activities like lifting or repetitive movements ensure that the stress is distributed effectively throughout the body. For example, when lifting a heavy object, bending the knees and keeping the back straight minimizes the stress on the lower back, thereby reducing the likelihood of bursitis.
Examples of Protective Equipment
Protective equipment can serve as a crucial barrier against external forces that can trigger or exacerbate bursitis. For example, in sports like tennis or racquetball, wearing appropriate wristbands or braces can help stabilize the wrist and reduce the impact forces on the affected area. In activities that involve repetitive hand movements, using ergonomic tools or gloves can also help prevent bursitis.
Other examples include knee pads for cycling or appropriate footwear for specific sports to reduce the impact on joints.
Effective Use of Ice Packs to Reduce Inflammation
Applying ice packs to the affected area is a common and effective method for reducing inflammation associated with bursitis. Ice constricts blood vessels, decreasing blood flow to the area, and reducing swelling. Applying ice packs in 15-20 minute intervals, several times a day, can provide substantial relief. It is important to wrap the ice pack in a thin cloth to prevent direct skin contact and potential frostbite.
Preventative Measures
- Regular Exercise: Consistent low-impact exercise strengthens muscles around the affected joints, improving support and reducing stress. Examples include swimming, cycling, or walking.
- Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Excess weight puts additional stress on joints, increasing the risk of bursitis. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise helps to reduce this burden.
- Ergonomic Assessments: Analyzing work or hobby-related tasks for ergonomic hazards can identify repetitive movements or postures that increase bursitis risk. Adjustments can be made to improve posture and minimize stress on the affected areas.
- Proper Footwear: Wearing supportive footwear that fits well is essential for maintaining proper foot and ankle alignment, reducing stress on the joints. This is especially important for activities like running or walking.
- Adequate Rest: Allowing sufficient time for rest and recovery between activities is vital to prevent overuse and subsequent inflammation. Rest periods should be taken throughout the day, especially after strenuous activities.
Potential Complications and Prognosis
Bursitis, while often manageable, can lead to various complications if left untreated or improperly managed. Understanding these potential issues and the factors influencing recovery is crucial for effective self-care and seeking appropriate medical attention when needed. Knowing the typical recovery timeline and the potential long-term effects on joint function can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their health.
Potential Complications of Untreated Bursitis
Untreated or poorly managed bursitis can lead to several complications, ranging from persistent pain and stiffness to more severe issues. These complications often arise from the inflammation and potential damage to the bursa and surrounding tissues. Chronic inflammation can result in the formation of adhesions, which are bands of scar tissue that restrict joint movement. If the inflammation becomes severe, it can lead to joint damage, impacting mobility and causing persistent discomfort.
In rare cases, untreated bursitis may result in infection, necessitating prompt medical intervention.
Long-Term Effects on Joint Function and Mobility
Chronic bursitis can significantly impact joint function and mobility. Prolonged inflammation can lead to the gradual thickening and scarring of the bursa, reducing its capacity to cushion the joint. This can lead to persistent pain, stiffness, and a decreased range of motion. The affected joint may become more susceptible to further injury and wear and tear, potentially accelerating the progression of osteoarthritis.
In some cases, individuals may experience chronic pain and limited mobility even after the acute inflammation subsides.
Typical Recovery Timeline for Bursitis, Bursitis inflammation swelling joints
The recovery timeline for bursitis varies greatly depending on the severity of the condition, the individual’s overall health, and the effectiveness of the treatment plan. Mild cases of bursitis may resolve within a few weeks with conservative treatment, while more severe cases may take several months or even longer to fully recover. Factors such as age, activity level, and underlying health conditions can influence the healing process.
Factors Influencing the Prognosis of Bursitis
Several factors influence the prognosis of bursitis. These factors include the severity of the inflammation, the individual’s overall health, the promptness and effectiveness of treatment, and the presence of any underlying conditions. For instance, individuals with pre-existing joint issues or weakened immune systems may experience slower recovery times. The type of bursitis and the location of the affected joint can also impact the prognosis.
Summary of Prognosis
The prognosis for bursitis is generally favorable with appropriate treatment. While recovery times vary, most individuals experience significant improvement with conservative management. However, persistent or severe bursitis can lead to long-term joint issues, impacting function and mobility. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to minimize potential complications and ensure a positive outcome. Prompt medical attention is recommended for individuals experiencing persistent pain, limited mobility, or signs of infection.
Last Point

In conclusion, bursitis inflammation swelling joints, while potentially painful, is often manageable with the right knowledge and approach. By understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and implementing appropriate treatment strategies, individuals can significantly reduce discomfort and improve their overall well-being. Remember that proactive self-care, combined with professional medical guidance, is key to a successful recovery.