Ear mites in humans are a less common but still concerning issue. This comprehensive guide delves into the world of these tiny parasites, examining their characteristics, prevalence, and the steps to take if you suspect an infestation. We’ll cover everything from causes and symptoms to effective treatment options and preventative measures.
Understanding ear mites in humans involves recognizing their unique characteristics, differentiating them from other ear conditions, and comprehending the factors that can lead to infestation. This guide offers a deep dive into the science behind these parasites, providing readers with actionable information to protect themselves and their families.
Introduction to Ear Mites in Humans
Ear mites, scientifically classified asOtodectes cynotis*, are tiny arachnids that infest the external ear canal. These parasites are common in animals, particularly dogs and cats, but can occasionally affect humans. While rarely a serious health concern in humans, an infestation can be itchy and uncomfortable. Understanding the characteristics, symptoms, and prevalence of these mites in humans is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.Infestations of ear mites in humans, although less common than in animals, can cause significant discomfort.
The mites burrow into the ear canal, leading to irritation and an intense urge to scratch. The symptoms and severity of the infestation can vary from person to person.
Scientific Classification and Characteristics
Ear mites,Otodectes cynotis*, belong to the arachnid class, specifically the order Acari. They are microscopic parasites, typically measuring between 0.3 to 0.5 millimeters in length. Their morphology includes eight legs, a segmented body, and a hard exoskeleton. Their presence in the ear canal is often associated with a specific lifecycle and feeding habits.
Symptoms and Signs of Ear Mite Infestation
A key indicator of an ear mite infestation is intense itching within the ear canal. This itching is often described as persistent and bothersome, particularly at night. Other symptoms can include a waxy or brownish discharge from the ear, which may be accompanied by a foul odor. In some cases, individuals may experience pain or a feeling of fullness in the ear.
Ever wondered about ear mites in humans? They’re a surprisingly common, albeit often overlooked, issue. While less dramatic than some other health concerns, they can be quite irritating. Interestingly, similar to the genetic complexities associated with conditions like four types symptoms waardenburg syndrome , the subtle signs and symptoms can sometimes be confusing. Fortunately, proper diagnosis and treatment are readily available, and ear mites in humans are generally manageable.
These symptoms can mimic other ear conditions, making accurate diagnosis essential.
Prevalence and Geographical Distribution
Ear mite infestations in humans are relatively uncommon, often associated with close contact with pets or other individuals harboring the mites. While not as widespread as some other ear conditions, the mites are found globally, though prevalence may vary based on factors such as hygiene practices, environmental conditions, and the level of pet ownership. The geographical distribution is influenced by factors like the prevalence of pet ownership and human-animal interaction.
For example, areas with higher pet ownership rates might show a slightly higher incidence of human ear mite infestations.
Key Differences Between Human Ear Mites and Other Ear Conditions
| Characteristic | Human Ear Mites | Other Ear Conditions (e.g., Swimmer’s Ear, Foreign Body) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Symptom | Intense itching, often worse at night, accompanied by a possible discharge | Pain, discomfort, fullness, possible discharge (not always itchy), presence of a foreign object |
| Appearance of Discharge | Waxy, brownish, possibly with a foul odor | Clear, yellow, thick, or bloody, depending on the condition |
| Associated Factors | Close contact with pets or other infested individuals | Water exposure, presence of foreign objects, immune deficiencies, or other infections |
| Diagnostic Tests | Microscopic examination of ear discharge | Visual examination, potentially further tests like cultures or imaging |
This table highlights the key differences in symptoms, associated factors, and diagnostic approaches to distinguish human ear mites from other common ear conditions. Accurate diagnosis is essential for appropriate treatment.
Causes and Risk Factors
Ear mites in humans, while less common than in animals, can still be a nuisance and cause discomfort. Understanding the factors contributing to these infestations is crucial for prevention and effective treatment. Different conditions and behaviors can increase the risk of encountering these tiny parasites.The primary cause of human ear mite infestations stems from direct contact with infected individuals or contaminated objects.
This is particularly relevant for close-knit communities or shared living spaces where transmission is more likely. Environmental factors, though not the sole cause, can also play a role.
Factors Contributing to Infestations
Various factors can increase the risk of developing an ear mite infestation. These include close contact with individuals who have the mites, sharing personal items like towels or bedding, and exposure to contaminated environments. Maintaining good hygiene practices can significantly reduce the likelihood of infestation.
Potential Risk Groups
Certain groups of people might be more susceptible to ear mite infestations due to specific lifestyle factors. Children, due to their close interactions with other children, and individuals in communal living situations, such as dorm rooms or refugee shelters, are at higher risk. The prevalence of ear mites in certain communities might also correlate with hygiene practices and environmental factors.
Comparison to Animal Infestations
While the underlying mechanism of infestation is similar, the causes of ear mite infestations in humans differ from those in animals. In animals, environmental factors like exposure to contaminated bedding or contact with other infested animals are major contributors. In humans, the primary source is often direct contact with infected individuals or contaminated objects.
Transmission Mechanisms
Ear mites in humans are typically transmitted through direct contact. This could involve touching the infected individual’s ear, sharing personal items, or even exposure to contaminated objects or environments. The mites themselves are tiny, and they can be easily transferred between people. It’s important to emphasize that good hygiene practices can greatly reduce the risk of transmission.
In rare cases, transmission might occur via indirect means, like sharing towels or bedding.
Diagnosis and Assessment
Identifying ear mites in humans often relies on a combination of clinical observations and diagnostic tests. A thorough understanding of the patient’s symptoms, medical history, and physical examination findings is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. This section will Artikel the common diagnostic procedures, methods to differentiate ear mites from other ear conditions, and the steps involved in a physical examination.
Diagnostic Procedures for Ear Mites
Accurate diagnosis hinges on recognizing the characteristic symptoms and signs of ear mites, differentiating them from other ear problems, and performing a thorough physical examination. Proper identification ensures appropriate treatment and prevents the misdiagnosis of other conditions.
Methods to Distinguish Ear Mites from Other Ear Problems
Ear mites are often confused with other ear conditions. Differentiating ear mites from other issues such as infections (bacterial or fungal), allergies, or foreign bodies requires careful consideration of the patient’s history and physical examination. A key aspect is the presence of intense itching, which is often a prominent feature of ear mite infestations. Other factors like discharge characteristics, and the presence of visible mites or their droppings can also help to distinguish ear mites from other causes.
Physical Examination for Suspected Ear Mites
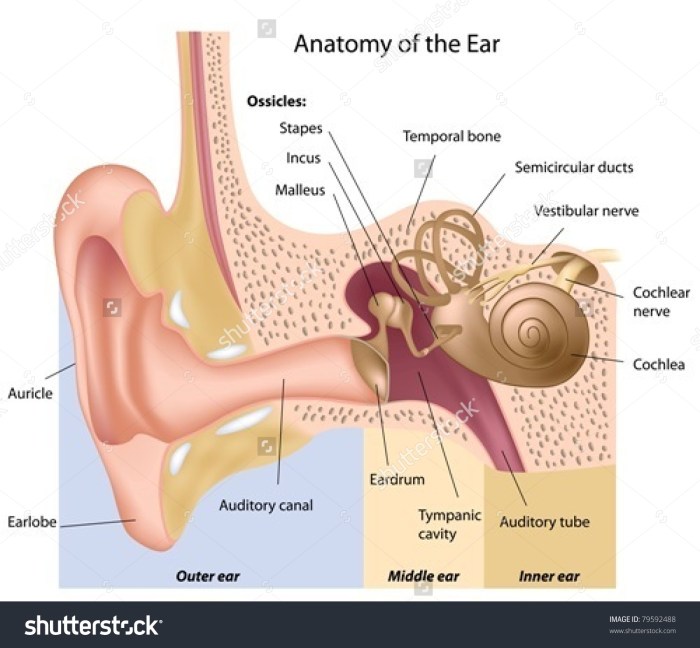
A physical examination is a cornerstone of diagnosing ear mites. The examiner carefully observes the ear canal for signs of inflammation, redness, and the presence of tiny mites or their characteristic debris. The examination should include a visual inspection of the ear canal, paying close attention to the presence of any secretions or debris. Gentle manipulation of the ear canal is important, but should be avoided if the patient reports pain.
This examination is vital for gathering information on the ear canal’s overall health, identifying any abnormalities, and guiding further diagnostic steps.
- Visual Inspection: A careful visual inspection of the ear canal, using an otoscope, is crucial. This allows for the observation of any abnormalities, including inflammation, redness, or the presence of mites, debris, or secretions.
- Otoscopic Examination: The otoscope provides a magnified view of the ear canal. It allows the examiner to identify the presence of tiny mites, their droppings (which appear as small, dark specks), or other signs of infection.
- Collection of Debris for Microscopy: If mites or their debris are suspected, a sample of the debris can be collected and examined under a microscope. This microscopic analysis can confirm the presence of mites, which typically appear as small, eight-legged creatures.
Diagnostic Tools and Typical Results
The following table summarizes common diagnostic tools and their typical results when used to assess for ear mites:
| Diagnostic Tool | Typical Results (Ear Mites Present) | Typical Results (Ear Mites Absent) |
|---|---|---|
| Otoscopic Examination | Presence of small, dark specks (mite droppings), or tiny, eight-legged creatures within the ear canal. Possible inflammation or redness. | Normal ear canal appearance; absence of mites, debris, or inflammation. |
| Microscopic Examination of Debris | Identification of mites or their characteristic parts (e.g., eggs, fecal matter). | Absence of mites or their components in the collected debris. |
Treatment and Management
Ear mite infestations, while often treatable, require a structured approach to ensure complete eradication and prevent recurrence. Proper diagnosis and treatment are crucial to alleviate discomfort and prevent potential complications. The treatment plan should be tailored to the individual patient and their specific needs.Effective management of ear mites involves a combination of topical medications and meticulous cleaning procedures.
This multifaceted strategy targets the mites directly while also addressing the environment where they thrive. The key is to follow the prescribed treatment regimen diligently to maximize its effectiveness.
Common Treatment Approaches
The primary approach to treating ear mites in humans involves the use of topical medications designed to eliminate the mites and any resulting irritation. These medications come in various forms, and the choice often depends on the severity of the infestation and the patient’s specific needs.
Medication Options
Various medications are available to address ear mite infestations. These medications typically contain insecticidal agents that effectively kill the mites.
Ever wondered about ear mites in humans? They’re surprisingly common, causing itchy ears and discomfort. Fortunately, many treatments are available, some of which involve prescription and otc drugs prescription and otc drugs. These medications, either over-the-counter or needing a doctor’s prescription, can effectively target the mites and ease the symptoms. So, if you suspect you have ear mites, it’s always best to consult a medical professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
- Otic Solutions: These solutions are formulated to be applied directly into the ear canal. They contain active ingredients like acaricide to kill mites. A common example is a solution containing a specific acaricide, which is applied as directed. Proper application technique is crucial to ensure the medication reaches all affected areas. For example, if the solution is viscous, it may need to be gently warmed to improve flow.
- Ear Drops: These drops, similar to otic solutions, are applied directly into the ear canal. They contain similar active ingredients and are used to kill mites. A specific example of an ear drop formulation, containing a certain concentration of acaricide, is frequently employed. These drops should be applied as directed, ensuring the entire ear canal is coated. Using a dropper to administer the ear drops ensures precision and reduces the risk of contaminating the solution.
Effectiveness and Potential Side Effects
The effectiveness of treatments for ear mites varies depending on factors like the severity of the infestation and adherence to the prescribed treatment regimen. Most topical treatments are effective when used consistently and as directed.
- Effectiveness: If used properly, topical treatments typically eliminate ear mites within a few days to a week. However, it’s crucial to complete the entire course of treatment, even if the symptoms improve earlier, to prevent re-infestation. For instance, some individuals might notice a reduction in itching within a few days but should still continue treatment to ensure all mites are eliminated.
- Side Effects: Potential side effects of topical medications include mild irritation, itching, or redness in the ear canal. These side effects are generally temporary and resolve with continued treatment or by using a milder formulation. Rarely, more severe reactions can occur. It’s essential to monitor for any unusual reactions and report them to a healthcare professional immediately.
Management Steps and Follow-up Care, Ear mites in humans
Proper management of ear mite infestations includes consistent application of the prescribed medication and diligent follow-up care.
- Adherence to Treatment Regimen: This is paramount to achieving effective treatment. It is crucial to follow the prescribed dosage and frequency of application as directed by a healthcare professional. This includes the number of drops, the duration of treatment, and any necessary precautions.
- Follow-up Appointments: Regular follow-up appointments with a healthcare professional are essential to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and address any concerns or complications. This allows the healthcare professional to assess the condition, adjust the treatment plan if needed, and ensure complete eradication of the mites.
- Cleaning Procedures: In addition to medication, gentle cleaning of the ear canal can help remove debris and facilitate the effectiveness of the treatment. Excessive cleaning, however, should be avoided.
Prevention and Control Measures
Ear mites, while often a nuisance, can be effectively managed with proactive measures. Understanding the factors contributing to their presence and implementing appropriate preventive strategies are key to minimizing the risk of infestation. This section details practical steps to reduce the risk of ear mites and maintain ear health.Preventing ear mite infestations involves a multifaceted approach, encompassing personal hygiene, environmental awareness, and proactive measures within shared living spaces.
By focusing on these aspects, the likelihood of encountering these tiny parasites can be significantly decreased.
Preventive Measures to Reduce Infestation Risk
Personal hygiene plays a crucial role in preventing ear mite infestations. Regular cleaning of the ear canal, while important, should be done gently and avoid deep insertion of cotton swabs or other objects. Excessive cleaning can potentially damage the ear canal, increasing the risk of infection.
Maintaining Ear Hygiene
Regular and gentle ear cleaning is essential to prevent the buildup of debris that can create a conducive environment for ear mites. Use a clean washcloth or cotton ball moistened with a mild, non-irritating solution, such as warm water. Avoid using harsh chemicals or solutions that could irritate the delicate ear canal lining. Towel-dry the ear gently after cleaning.
Ensure you avoid inserting anything into the ear canal beyond the visible part of the ear.
Ever wondered about ear mites in humans? It’s a fascinating, albeit often uncomfortable, topic. Understanding how we approach these situations is crucial, especially when considering the ethical implications involved in handling such cases. This directly connects to our commerce guidelines and mission, commerce guidelines and mission , which emphasizes responsible and ethical practices. Ultimately, educating ourselves and others about ear mites in humans, and the related issues, is a key component of a healthy community.
Environmental Factors in Prevention
Environmental factors can also influence the prevalence of ear mites. Maintaining a clean living environment, especially in shared spaces, can help minimize the risk of infestation. Regular cleaning of bedding, floors, and shared surfaces can help prevent the accumulation of dust and debris, which may harbor mites or their eggs.
Tips for Preventing Ear Mite Infestations in Families or Shared Living Spaces
Shared living spaces, such as dormitories or households with multiple individuals, require extra attention to hygiene and cleanliness. Regular cleaning and disinfection of shared areas, especially bedding, can significantly reduce the risk of infestation.
- Regularly clean and disinfect shared bedding, such as pillows, blankets, and mattresses. This includes vacuuming or sweeping the floor frequently to remove dust mites and debris.
- Enforce good hygiene practices for all members of the household, particularly children. Teach them about the importance of keeping their ears clean and avoiding the use of foreign objects in their ears.
- If an infestation is suspected or confirmed, consult a healthcare professional promptly for appropriate treatment and to prevent the spread within the family or shared living space.
- Regularly inspect pets for ear mites, as they can serve as carriers and spread the infestation to humans. If a pet has ear mites, seek veterinary care immediately.
Complications and Prognosis

Ear mite infestations, while often treatable, can lead to a range of complications if left untreated. Understanding the potential consequences and the prognosis for successful treatment is crucial for managing these infestations effectively. The severity of complications can vary depending on factors such as the individual’s overall health, the extent of the infestation, and the promptness of treatment.The potential complications and long-term consequences of untreated ear mite infestations are multifaceted.
These range from mild discomfort to more serious conditions, highlighting the importance of seeking timely medical attention. Appropriate treatment strategies are crucial for mitigating these complications and ensuring a favorable prognosis.
Potential Complications of Untreated Infestations
Untreated ear mite infestations can cause a range of complications, ranging from mild to severe. The mites themselves can irritate the ear canal, leading to discomfort, itching, and pain. Constant scratching can further damage the delicate skin lining the ear canal, increasing the risk of secondary infections.
- Secondary Infections: A significant concern associated with untreated ear mite infestations is the potential for secondary bacterial or fungal infections. The irritated and compromised skin lining the ear canal becomes a breeding ground for harmful microorganisms, leading to more intense inflammation, pain, and potentially more serious complications.
- Chronic Ear Infections: Persistent scratching and irritation can lead to chronic ear infections. This can involve a prolonged inflammatory response in the ear canal, causing ongoing pain, discomfort, and difficulty hearing.
- Hearing Loss: In severe cases, untreated ear mite infestations can lead to temporary or even permanent hearing loss. The inflammation and potential damage to the eardrum and inner ear structures can impair the transmission of sound waves, impacting hearing function.
- Tinnitus: Persistent irritation and inflammation in the ear canal can cause tinnitus, a condition characterized by a ringing or buzzing sensation in the ears. This can be a persistent and distressing symptom, impacting the individual’s quality of life.
Long-Term Consequences of Untreated Infestations
The long-term consequences of untreated ear mite infestations can be significant and impact the individual’s quality of life. The persistent itching and pain can lead to chronic discomfort and sleep disturbances. Furthermore, the potential for secondary infections and hearing loss can have lasting implications.
- Chronic Itching and Pain: Untreated ear mite infestations can lead to persistent itching and pain, disrupting sleep patterns and overall quality of life. This constant discomfort can be debilitating, impacting the individual’s ability to focus and participate in daily activities.
- Impaired Hearing: Untreated infections can lead to permanent hearing damage, particularly if the infection spreads to the inner ear. This can significantly impact the individual’s ability to communicate and engage in social interactions.
- Psychological Impact: The persistent discomfort and potential hearing loss associated with untreated ear mite infestations can take a toll on the individual’s mental well-being. The emotional distress and anxiety associated with these conditions can negatively affect the individual’s overall health and functioning.
Prognosis with Appropriate Treatment
The prognosis for individuals with ear mite infestations is generally excellent when appropriate treatment is followed. Most cases respond well to the prescribed medications, and the discomfort and complications are typically resolved within a few weeks. The efficacy of treatment can be significantly affected by adherence to the prescribed regimen and the promptness of seeking medical attention.
Comparison of Treatment Approaches
Different treatment approaches for ear mite infestations vary in their effectiveness and potential side effects. A thorough assessment of the individual’s condition and medical history is crucial in determining the most suitable treatment plan.
- Topical Medications: Topical medications, such as ear drops containing acaricide, are often effective in eliminating the mites and reducing inflammation. The effectiveness depends on the individual’s adherence to the prescribed treatment duration and the severity of the infestation.
- Oral Medications: In some cases, oral medications may be necessary, particularly for extensive infestations or individuals with underlying health conditions. The efficacy and potential side effects of oral medications vary, and the decision to use them is made on a case-by-case basis.
Illustrative Case Studies
Ear mite infestations, while often treatable, can vary significantly in presentation and severity. Understanding these variations through case studies provides valuable insights into effective diagnosis, treatment, and potential complications. These examples highlight the importance of prompt attention to ear health and the range of potential outcomes.Successful treatment often relies on accurate diagnosis and adherence to prescribed therapies. The following case studies illustrate different scenarios, from simple infestations to more complex cases requiring specialized intervention.
Successful Treatment of an Ear Mite Infestation
A 10-year-old boy presented with itching and a mild discharge from his right ear. Otoscopic examination revealed small, whitish mites in the ear canal. The patient was prescribed a topical acaricide, a medication specifically designed to kill mites. Following a week of daily application, the itching subsided, and the discharge ceased. A follow-up examination confirmed the successful eradication of the mites.
This case demonstrates a straightforward and effective treatment approach for a typical ear mite infestation.
Importance of Early Diagnosis and Treatment
A 3-year-old girl experienced persistent ear itching for several weeks. Initially, the parents attributed the discomfort to allergies. However, the itching worsened, and a yellowish discharge became apparent. Delayed diagnosis and treatment led to a secondary bacterial infection within the ear canal. The infection required a course of oral antibiotics in addition to topical medications.
Early diagnosis, through prompt otoscopic examination, could have prevented the development of the secondary infection.
Complications of Delayed Treatment
A 25-year-old male experienced a severe earache and intense itching. He neglected the symptoms for two months, believing they were a minor annoyance. By the time he sought medical attention, the ear canal was inflamed and swollen, with significant tissue damage evident. Aural polyps developed in the ear canal. The patient required a more involved treatment plan, including surgical intervention to remove the polyps and address the extensive inflammation.
This case highlights the potential for severe complications, including infection and tissue damage, resulting from delayed treatment of ear mites.
Rare or Unusual Presentation of Ear Mites
A 60-year-old woman presented with a unique presentation of ear mites. In addition to the typical symptoms of itching and discharge, she also experienced an unusual level of dizziness and tinnitus. Otoscopic examination revealed a dense cluster of mites along with some debris. The unusual combination of symptoms suggested a possible underlying neurological involvement. The patient responded well to the standard treatment, but the case underscored the potential for atypical presentations and the importance of considering broader differential diagnoses.
Ear Mites in Humans
Ear mites, tiny arachnids, are a common cause of ear discomfort in humans. While less prevalent than other ear conditions, understanding their characteristics, diagnosis, and treatment is essential for effective management. These parasites, though rarely serious, can lead to significant discomfort if left untreated.
Patient-Friendly Information on Ear Mites
Ear mites, scientifically known asOtodectes cynotis*, are microscopic parasites that primarily affect the external ear canal. They are typically transmitted through close contact with infected animals, such as dogs or cats. While they don’t usually pose a significant health risk to humans, they can cause itching, redness, and a discharge in the ear. Early detection and treatment are crucial for alleviating discomfort and preventing potential complications.
Common Questions and Answers
This table provides concise answers to frequently asked questions about ear mites in humans.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What are ear mites? | Ear mites are tiny parasites that infest the external ear canal. They are typically transmitted from infected animals. |
| What are the symptoms of ear mites? | Symptoms often include intense itching, redness, and a yellowish-brown discharge in the ear canal. Some individuals may also experience pain or a feeling of fullness in the ear. |
| How are ear mites diagnosed? | Diagnosis typically involves an examination of the ear canal by a healthcare professional. The presence of mites or their droppings can be observed using an otoscope. |
| How are ear mites treated? | Treatment usually involves topical medications, such as ear drops containing acaricide, prescribed by a doctor. These medications kill the mites and relieve symptoms. |
| Can ear mites be prevented? | Minimizing contact with infected animals, especially pets, can help prevent the spread of ear mites. Practicing good hygiene and promptly addressing any symptoms can also help prevent complications. |
| Are ear mites contagious? | While less contagious than some other ear infections, ear mites can be transmitted through close contact with infected animals. |
Diagnosis and Treatment Flowchart
This flowchart Artikels the typical steps involved in diagnosing and treating ear mites:
Note: This flowchart is a general guideline and individual cases may vary. Always consult a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and treatment.

FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions about Ear Mites
This section addresses common questions regarding ear mites, providing straightforward answers in an accessible format.
- What are the common symptoms of ear mites in humans? Common symptoms include intense itching, a yellowish-brown discharge, and redness in the ear canal. Some individuals may experience pain or a feeling of fullness in the ear.
- How are ear mites typically diagnosed? A healthcare professional typically examines the ear canal using an otoscope to look for the presence of mites or their droppings. A thorough history of symptoms and contact with animals can also help in diagnosis.
- What is the typical treatment for ear mites? Treatment usually involves the use of topical medications, such as ear drops containing acaricide, prescribed by a healthcare professional. These medications kill the mites and alleviate symptoms.
- What is the prognosis for ear mites? With appropriate treatment, ear mites typically resolve within a few weeks. Prompt treatment is essential to minimize discomfort and prevent complications.
Closing Notes
In conclusion, while ear mites in humans aren’t as prevalent as other ear issues, understanding their lifecycle, symptoms, and treatment is crucial for timely intervention. This guide offers a roadmap to navigate the complexities of ear mite infestations, empowering you to make informed decisions about your health and well-being. Prevention, early detection, and proper treatment are key to managing and overcoming these small but potentially troublesome parasites.