HIV symptoms in men can vary greatly, from initial infection to later stages. Early detection is crucial for effective treatment and management. This guide explores the common and less common symptoms, differentiating them from other conditions, and emphasizing the importance of seeking medical attention.
Understanding the progression of HIV, from acute infection to chronic stages, is vital for recognizing potential symptoms. This overview provides a comprehensive look at the diverse ways HIV manifests in men, highlighting the importance of recognizing both common and less prevalent signs.
Introduction to HIV Symptoms in Men
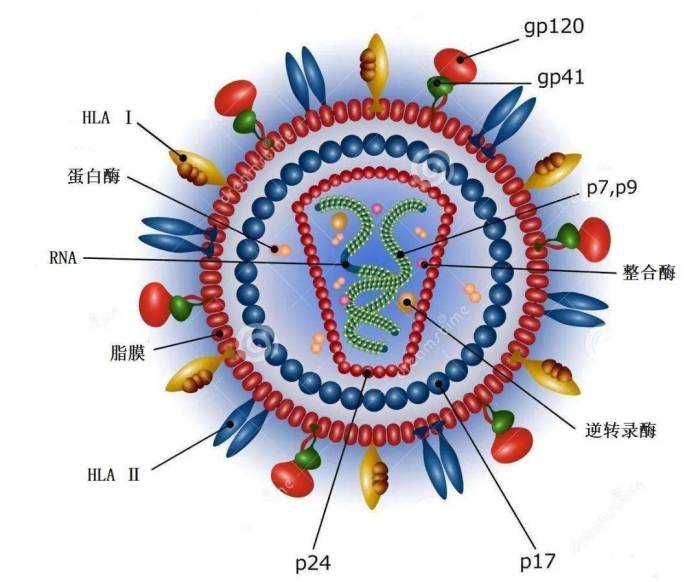
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) is a virus that attacks the body’s immune system, specifically the CD4 cells, which are crucial for fighting off infections. Over time, if left untreated, HIV can weaken the immune system significantly, leading to Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS). Understanding the symptoms of HIV is critical for early diagnosis and treatment, which can dramatically improve the quality of life and prevent the progression to AIDS.Early detection is paramount in managing HIV.
Early intervention allows for timely medical intervention, enabling individuals to maintain a healthier immune system and reduce the risk of opportunistic infections. Prompt treatment also significantly lowers the chance of transmitting the virus to others. Delaying treatment can result in a gradual decline in immune function, leading to serious health complications.
Common Misconceptions about HIV Transmission and Symptoms
Many misconceptions surround HIV transmission and symptoms. One common misconception is that HIV is only transmitted through sexual contact. While sexual contact is a primary mode of transmission, HIV can also be spread through sharing needles, syringes, or other drug paraphernalia, and from mother to child during pregnancy, childbirth, or breastfeeding. It’s crucial to understand that HIV is not transmitted through casual contact, such as sharing utensils or using the same restroom.
Furthermore, HIV symptoms can vary greatly among individuals and may not always be noticeable immediately after infection. Some individuals may experience flu-like symptoms shortly after infection, but many others remain asymptomatic for years, making early detection crucial.
Typical Progression of HIV in Men
The progression of HIV in men, like in individuals of other genders, is generally characterized by stages. The initial stage often involves flu-like symptoms, but many individuals remain asymptomatic for an extended period. Without treatment, the virus progressively damages the immune system, increasing the risk of developing opportunistic infections. As the immune system weakens, individuals become more vulnerable to illnesses that a healthy immune system would easily fight off.
- Acute HIV Infection: This initial phase typically occurs within a few weeks of infection and often resembles a flu-like illness. Symptoms might include fever, fatigue, sore throat, muscle aches, headache, rash, and swollen lymph nodes. This phase is characterized by a high viral load, meaning a large amount of the virus circulating in the body. Many people do not realize they are infected during this phase because symptoms can be mild or mistaken for other illnesses.
- Chronic HIV Infection (Clinical Latency): This is often a long phase, sometimes lasting for many years, where the virus continues to replicate, but the immune system is still relatively intact. Without treatment, the immune system gradually weakens. Individuals may not experience any noticeable symptoms during this phase. Regular testing and medical monitoring are crucial during this stage to detect any potential complications.
- AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome): This is the most advanced stage of HIV infection. The immune system is severely compromised, making individuals highly susceptible to opportunistic infections and cancers. The specific symptoms of AIDS can vary greatly and depend on the opportunistic infections that develop. The severity of AIDS can differ significantly between individuals due to factors like the timing of diagnosis and treatment initiation.
Factors Influencing HIV Progression
Several factors influence the progression of HIV, including the individual’s overall health, the level of viral load, and the access to timely medical care. Genetic factors and the presence of other health conditions can also play a role. Consistent use of antiretroviral therapy (ART) is crucial in managing HIV and slowing its progression to AIDS.
Common Symptoms in Men
Understanding the symptoms of HIV in men is crucial for early detection and effective treatment. Early diagnosis allows for prompt intervention, potentially preventing further complications and improving overall health outcomes. This section details the common symptoms experienced by men across the various stages of HIV infection.The symptoms of HIV infection can vary greatly from person to person, and some individuals may not experience any noticeable symptoms during the early stages.
Understanding HIV symptoms in men can be crucial for early detection. While some symptoms like fatigue and fever are common, it’s important to note that certain rarer conditions, like carcinoid cancer, what is carcinoid cancer , can sometimes mimic HIV symptoms. So, if you’re experiencing unusual symptoms, it’s always best to consult a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment options.
This makes regular testing and awareness of potential signs essential. It’s important to remember that these symptoms can also be indicative of other conditions, and a proper diagnosis requires consultation with a healthcare professional.
Acute HIV Infection Symptoms
Acute HIV infection, typically occurring within 2-4 weeks of infection, often presents with flu-like symptoms. This initial phase can be easily mistaken for other viral illnesses, leading to delayed diagnosis.
- Fever: A persistent elevated temperature is a common symptom.
- Sore throat: A painful and often persistent sore throat is another frequent complaint.
- Muscle aches and pains: Widespread muscle aches and joint pain are characteristic of this phase.
- Rash: A skin rash, sometimes accompanied by itching, can be present.
- Headache: Frequent and persistent headaches are often reported.
- Fatigue: General feelings of tiredness and weakness are also common.
- Swollen lymph nodes: Swollen glands, particularly in the neck and groin, are frequently observed.
Chronic HIV Infection (Latency Period) Symptoms, Hiv symptoms in men
The chronic stage, also known as the latency period, is characterized by a period of relative inactivity of the virus. During this phase, individuals may not experience any noticeable symptoms. However, some individuals may experience mild symptoms, which can be easily overlooked.
- Fatigue: Persistent fatigue and lack of energy are common complaints.
- Weight loss: Unintentional weight loss is a potential symptom.
- Night sweats: Occasional or frequent night sweats can occur.
- Headaches: Recurring headaches may be a sign.
- Swollen lymph nodes: Swollen glands, especially in the neck, armpits, or groin, may persist.
- Mouth sores: Oral sores or thrush (a fungal infection) are also possible symptoms.
Comparison with Other Conditions
It’s crucial to distinguish HIV symptoms from those of other, less serious, conditions. The symptoms of acute HIV infection, for example, can mimic the symptoms of influenza or other viral illnesses. This necessitates seeking medical advice for proper diagnosis.
Symptoms by Stage
| Stage | Symptom | Description | Severity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Early (Acute) | Fever | Sustained elevated body temperature | Moderate to High |
| Early (Acute) | Sore throat | Persistent and painful throat irritation | Moderate |
| Early (Acute) | Muscle aches | Widespread pain and discomfort in muscles | Moderate to High |
| Chronic (Latency) | Fatigue | Persistent tiredness and lack of energy | Moderate |
| Chronic (Latency) | Weight loss | Unintentional and unexplained weight reduction | Moderate |
| Chronic (Latency) | Night sweats | Excessive sweating during sleep | Mild to Moderate |
Less Common Symptoms in Men: Hiv Symptoms In Men

While the more common symptoms of HIV infection in men, like fever, fatigue, and swollen lymph nodes, can be indicative of the virus, a range of less frequent but potentially significant symptoms exist. These less common symptoms might be easily overlooked or misattributed to other conditions, leading to delayed diagnosis and treatment. Understanding these less frequent symptoms is crucial for early detection and intervention.
Less Frequent but Potentially Significant Symptoms
Some men experience symptoms that are less common or less pronounced than the typical indicators of HIV. These symptoms can vary significantly in presentation and severity, and can sometimes be mistaken for other illnesses. This variability can make diagnosis challenging, and early detection is crucial for effective treatment and management.
Examples of Uncommon Symptoms
Some men may experience persistent skin rashes, mouth sores, or neurological issues. These can manifest as numbness, tingling, or weakness in the limbs, or as cognitive changes. Persistent or unusual gastrointestinal problems, such as chronic diarrhea or abdominal pain, might also occur. Less commonly, men might report unexplained weight loss, even when maintaining a healthy diet and exercise routine.
Potential Causes for Less Common Symptoms
The underlying causes for these less common symptoms are multifaceted. The immune system’s weakened state due to HIV infection can make individuals more susceptible to opportunistic infections. These infections can manifest in a variety of ways, including skin rashes, oral sores, and gastrointestinal distress. Additionally, certain medications used to treat HIV can have side effects that mimic some of these less common symptoms.
It’s essential to consider the interplay of HIV infection, opportunistic infections, and medication side effects when evaluating these symptoms.
Table of Less Common Symptoms
| Symptom | Description | Potential Cause | Importance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Persistent Skin Rash | A rash that doesn’t clear up, or appears in unusual patterns or locations. | Opportunistic infections, medication side effects. | May indicate an underlying issue needing investigation. |
| Persistent Oral Sores | Mouth ulcers that don’t heal within a reasonable timeframe. | Opportunistic infections, oral thrush, medication side effects. | Important as a potential sign of weakened immune function. |
| Neurological Issues (Numbness, Tingling, Weakness) | Sensory or motor impairments that affect the limbs or other parts of the body. | Opportunistic infections affecting the nervous system, medication side effects. | Requires immediate medical evaluation due to potential serious implications. |
| Chronic Diarrhea or Abdominal Pain | Persistent loose stools or ongoing stomach discomfort. | Opportunistic infections affecting the gastrointestinal tract, medication side effects. | Can indicate a significant health problem and should be evaluated. |
| Unexplained Weight Loss | Significant weight loss despite maintaining a healthy diet and activity level. | Opportunistic infections, HIV itself, side effects of medications. | Important indicator of underlying health problems and should be evaluated. |
Symptoms of Opportunistic Infections
HIV weakens the immune system, making individuals susceptible to infections that wouldn’t normally cause problems. These opportunistic infections (OIs) can manifest in various ways, and their symptoms can sometimes overlap with common HIV symptoms, making diagnosis challenging. Recognizing the specific symptoms of OIs is crucial for prompt treatment and improved outcomes.
Opportunistic Infections in Men
Opportunistic infections (OIs) are infections that take advantage of a weakened immune system, like the one caused by HIV. These infections can affect various parts of the body and present with a range of symptoms. Distinguishing these symptoms from general HIV symptoms is essential for accurate diagnosis and timely intervention.
Common Opportunistic Infections in Men
Several infections frequently affect men with HIV. Early detection and treatment are vital for preventing severe complications.
| Infection | Symptom | Description | Typical Progression |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP) | Cough, shortness of breath, fever | A fungal infection of the lungs, often presenting with a dry cough that worsens over time, shortness of breath, and fever. Early symptoms might be subtle. | Can progress rapidly, leading to severe respiratory distress if left untreated. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial. |
| Tuberculosis (TB) | Persistent cough, fever, night sweats, weight loss | A bacterial infection that primarily affects the lungs. Symptoms can include a persistent cough, often with blood, fever, night sweats, and significant weight loss. | TB can progress to involve other organs if not treated promptly. The symptoms may be subtle initially, making early detection difficult. |
| Candidiasis (Yeast Infection) | Oral thrush, vaginal or penile sores, fever | A fungal infection caused by the Candida yeast. Oral thrush manifests as white patches in the mouth. Penile or vaginal sores may be present, along with fever. | Oral thrush can be a persistent symptom, while penile or vaginal sores may be intermittent and associated with other symptoms like pain or discharge. |
| Cytomegalovirus (CMV) | Eye problems, gastrointestinal issues, fatigue | A viral infection that can cause a range of problems, including eye problems (retinitis), gastrointestinal issues (diarrhea, abdominal pain), and significant fatigue. | CMV can progress to cause significant vision loss or other serious complications if not treated promptly. Early detection is crucial. |
| Kaposi’s sarcoma (KS) | Skin lesions, sores, lumps | A cancer that commonly presents as purplish or reddish skin lesions, sores, or lumps, often appearing on the skin, mouth, or other areas. | KS can progress to involve other organs and tissues. Early diagnosis and treatment are vital for managing its spread. |
Differentiating Opportunistic Infection Symptoms from Common HIV Symptoms
While some symptoms, like fever and fatigue, can overlap between common HIV symptoms and opportunistic infections, careful attention to the specific location and nature of the symptoms is essential. For example, persistent cough with blood is more indicative of TB than general HIV symptoms. A thorough medical evaluation, including a physical exam and appropriate testing, is critical for accurate diagnosis.
Early intervention and treatment for OIs can prevent severe health complications.
Symptom Progression and Severity
HIV infection’s impact varies significantly from person to person. The severity and progression of symptoms are influenced by several factors, making it crucial to understand how these elements intertwine. Monitoring symptom progression is essential for timely medical intervention and effective management.Understanding the spectrum of symptom presentation and how it relates to the different stages of HIV infection is vital for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
This dynamic interplay between symptoms, infection stage, and individual factors allows for a personalized approach to care.
Variations in Symptom Severity
The severity of HIV symptoms can differ considerably among individuals. Some individuals experience mild symptoms, while others experience more pronounced or debilitating ones. This difference in symptom presentation is due to a combination of genetic predispositions, lifestyle choices, and the overall health status before infection.
Correlation with HIV Infection Stage
The progression of HIV symptoms generally aligns with the stages of HIV infection. The initial phase, often characterized by flu-like symptoms, can progress to a period with no noticeable symptoms (asymptomatic phase). As the infection progresses to AIDS, more severe symptoms and opportunistic infections become more frequent and severe. This correlation underscores the importance of regular testing and monitoring to identify the stage of infection.
Factors Influencing Symptom Progression
Several factors can influence the progression and severity of HIV symptoms. These factors include:
- Individual immune response: The body’s ability to fight off the infection varies greatly. Some individuals have a stronger immune response, potentially delaying the onset of more severe symptoms.
- Lifestyle factors: Healthy habits like a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management can contribute to a stronger immune system and potentially mitigate symptom severity. Conversely, unhealthy lifestyle choices can weaken the immune system, leading to faster progression and more severe symptoms.
- Access to healthcare: Early diagnosis and prompt treatment can significantly slow the progression of HIV and reduce the severity of symptoms. Limited access to healthcare can lead to more severe and prolonged symptoms.
- Concurrent health conditions: Existing health issues, such as diabetes or other chronic illnesses, can exacerbate the effects of HIV, resulting in more severe symptoms and a faster progression.
Monitoring Symptom Progression
Regular monitoring of symptoms is crucial for effective management of HIV. This monitoring should include:
- Regular check-ups: Visits with a healthcare provider for routine check-ups, blood tests, and other diagnostic procedures are essential to assess overall health and detect any changes in symptom presentation or progression.
- Symptom journaling: Keeping a detailed record of symptoms, including their frequency, duration, and intensity, helps track any patterns and alerts the healthcare provider to potential issues.
- Reporting any changes: Immediately informing a healthcare provider of any new or worsening symptoms is crucial for timely intervention.
Examples of Varying Severity
The following are illustrative examples, showcasing the variability in symptom presentation across individuals:
- Individual A: Experienced mild, flu-like symptoms initially, followed by a period with no noticeable symptoms for several years. Maintained a healthy lifestyle and regular check-ups. Symptoms progressed slowly and were well-managed with treatment.
- Individual B: Developed severe, debilitating symptoms shortly after infection due to underlying health conditions and limited access to healthcare. Symptoms progressed rapidly, leading to more severe complications.
- Individual C: Maintained a healthy lifestyle and received early diagnosis and treatment. Symptoms were minimal, and progression was slow. This individual experienced minimal or no debilitating symptoms due to early intervention and a strong immune response.
Importance of Seeking Medical Attention
Knowing the signs of HIV is crucial, but understanding the vital role of prompt medical attention is equally important. Early detection and treatment are fundamental to managing the virus and preventing severe health complications. Ignoring potential symptoms can have serious consequences, so understanding the urgency of seeking help is paramount.Early intervention is key to controlling the progression of HIV and improving overall health outcomes.
A delayed diagnosis can lead to more advanced stages of the disease, making treatment more challenging and potentially increasing the risk of opportunistic infections. Seeking medical attention promptly empowers individuals to take proactive steps towards managing their health and well-being.
Understanding HIV symptoms in men is crucial for early detection and treatment. While many people associate autumn with cozy sweaters and pumpkin spice lattes, it’s also a fantastic time to boost brain health with the abundance of fall produce. Eating foods rich in antioxidants, like those found in fall produce for brain health , can contribute to cognitive function.
Ultimately, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, is key to overall well-being, including managing potential HIV symptoms in men.
Criticality of Immediate Medical Attention
Prompt medical attention is essential when experiencing potential HIV symptoms. Delaying treatment can allow the virus to replicate and damage the immune system, leading to a more complex and potentially life-threatening situation. Early diagnosis allows for the initiation of antiretroviral therapy (ART), which significantly reduces viral load and improves immune function.
Actions to Take When Experiencing Concerning Symptoms
It’s vital to take proactive steps if you suspect you may have HIV. This involves contacting your healthcare provider immediately for proper evaluation. Sharing a detailed medical history, including sexual history and any recent exposure to potentially infectious individuals, is crucial for accurate diagnosis.
- Schedule a consultation with a doctor as soon as possible.
- Provide a comprehensive medical history, including details of recent sexual encounters or potential exposures.
- Follow the doctor’s instructions regarding testing and treatment options.
- Adhere to prescribed medications and attend follow-up appointments diligently.
Importance of Early Diagnosis and Treatment
Early diagnosis and treatment are critical for managing HIV. Early initiation of antiretroviral therapy (ART) can effectively suppress the virus, reducing the risk of transmission and preventing severe health complications. Furthermore, early treatment helps maintain a healthy immune system, reducing the risk of opportunistic infections. A person with a suppressed viral load is much less likely to transmit the virus to others.
Understanding HIV symptoms in men is crucial for early detection. While some symptoms, like fatigue and fever, are common, others can be subtle. It’s essential to remember that some people may not experience any symptoms at all. If you’re concerned about possible HIV symptoms, consulting a doctor is important. For those exploring alternative remedies, understanding the potential side effects, dosage, and storage of supplements like krill, is vital, as detailed in this helpful guide: krill uses side effects dosage storage.
Ultimately, responsible health choices are key in managing your well-being and ensuring you get the right information and care.
How Timely Intervention Improves Outcomes
Timely intervention in HIV cases has a profound impact on long-term health. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly reduce the risk of AIDS-related illnesses and improve the overall quality of life. By controlling the viral load, the immune system is strengthened, leading to a better response to other health concerns. This early intervention also allows for early detection of opportunistic infections, which are treatable if identified in their early stages.
Flowchart of Steps to Take When Experiencing Symptoms
The following flowchart Artikels the steps to take when experiencing potential HIV symptoms. This structured approach ensures that appropriate medical care is sought in a timely manner.
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Recognize Symptoms: Note any concerning symptoms. |
| 2 | Seek Immediate Medical Attention: Contact your healthcare provider or a local clinic. |
| 3 | Follow Doctor’s Instructions: Complete any necessary tests and follow the prescribed treatment plan. |
| 4 | Maintain Regular Follow-ups: Adhere to follow-up appointments and medication schedules. |
Differentiating HIV Symptoms from Other Conditions
Recognizing HIV symptoms can be challenging, as some overlap with other common illnesses and sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Accurately distinguishing between HIV symptoms and those of other conditions is crucial for prompt diagnosis and treatment. This section delves into the key differences, providing examples and highlighting the importance of seeking medical advice.
Comparing HIV Symptoms to Symptoms of Common Illnesses
Many symptoms associated with HIV, such as fever, fatigue, and muscle aches, can also be present in various common illnesses like the flu, a cold, or even the common strain of the flu. However, the duration and pattern of symptoms can provide clues. HIV symptoms often persist or recur over time, while common illnesses typically resolve within a few weeks.
This distinction is not always straightforward, and it is essential to consider the individual’s overall health history and risk factors when evaluating symptoms.
Differentiating HIV Symptoms from Symptoms of Other STIs
Certain symptoms, like sores, discharge, or pain during urination, can be present in both HIV and other STIs. Gonorrhea, chlamydia, and herpes are examples of STIs that can exhibit similar symptoms. The crucial distinction lies in the comprehensive evaluation of the individual’s health history, including sexual practices, recent exposure to potential pathogens, and a thorough physical examination. Accurate diagnosis requires a combination of clinical assessment and laboratory testing.
Examples of Similar Symptoms and Their Distinctions
Fatigue, a common HIV symptom, can also be a symptom of various conditions. For instance, chronic fatigue syndrome or even severe anemia can cause fatigue. The distinguishing factor lies in the accompanying symptoms, medical history, and the results of relevant tests. A comprehensive assessment, including a detailed history and physical examination, can aid in differentiating these conditions.
Similarly, skin rashes can be a symptom of HIV or other infections, or even a reaction to medications. The context of the rash, along with other symptoms and the patient’s medical history, assists in proper diagnosis. The presence of other symptoms, such as fever, night sweats, or swollen lymph nodes, can provide valuable clues in the context of HIV.
Importance of Seeking Medical Advice for Accurate Diagnosis
It is vital to remember that self-diagnosis is unreliable and potentially harmful. The presence of any unusual or persistent symptoms, especially if they are related to sexual activity, should prompt a visit to a healthcare professional. A healthcare provider can conduct a thorough assessment, order appropriate tests, and provide accurate information about the individual’s health status.
Table Contrasting HIV Symptoms with Symptoms of Common Illnesses
| Condition | Symptom | Distinguishing Feature | Diagnostic Approach |
|---|---|---|---|
| HIV | Fever | Persistent or recurrent fever, often accompanied by other symptoms like fatigue and swollen lymph nodes. | Detailed medical history, physical examination, blood tests (e.g., HIV antibody test), and tests for opportunistic infections. |
| Flu | Fever | Typically resolves within a week; often accompanied by sore throat, body aches, and congestion. | Detailed medical history, physical examination, and observation of symptom duration. |
| Mononucleosis | Fatigue | Associated with sore throat, swollen lymph nodes, and a general feeling of malaise. Often follows an acute infection. | Detailed medical history, physical examination, blood tests (e.g., Monospot test). |
| Chronic Fatigue Syndrome | Fatigue | Persistent and debilitating fatigue, often lasting for months or years, with other associated symptoms. | Detailed medical history, physical examination, and exclusion of other potential causes of fatigue. |
Impact on Daily Life
Living with HIV can significantly impact daily activities and overall lifestyle. The range of symptoms experienced, from mild to severe, can affect various aspects of a person’s life, including their ability to work, socialize, and maintain personal relationships. Understanding these impacts is crucial for developing effective coping strategies and support systems.
Impact on Work and Productivity
The symptoms of HIV can range from fatigue and weakness to more severe conditions like opportunistic infections. These can directly impact a person’s ability to concentrate, maintain focus, and perform their job duties. Reduced productivity and potential absences from work are common consequences. Some individuals may experience discrimination or stigma in the workplace due to their HIV status, further complicating their ability to maintain employment.
Impact on Social Interactions and Relationships
HIV symptoms can affect social interactions in a variety of ways. Fatigue, pain, and other physical symptoms can make it difficult to engage in social activities. Fear of judgment or discrimination from others can lead to social isolation. It’s important to recognize that these challenges can also strain relationships with friends and family. Open communication and understanding are crucial for maintaining healthy connections.
Impact on Personal Well-being
HIV can significantly affect a person’s mental and emotional well-being. Anxiety, depression, and feelings of isolation can be common responses to the diagnosis and the challenges associated with living with the condition. The need for medical appointments, medication management, and lifestyle adjustments can also add to stress and emotional burden. Seeking support from mental health professionals and supportive communities is crucial for managing these emotional challenges.
Potential Impacts on Daily Life
- Reduced energy levels and fatigue: This can make it difficult to perform daily tasks and engage in social activities. For example, someone who previously enjoyed long walks might now find themselves exhausted after a short one.
- Difficulty concentrating and remembering things: Cognitive impairment can impact work performance and daily tasks, such as remembering appointments or completing household chores. Someone might struggle to follow a recipe or complete a project at work.
- Pain and discomfort: Various symptoms, such as joint pain, headaches, or nausea, can interfere with daily activities and lead to discomfort. This can make simple tasks like getting dressed or working out difficult.
- Opportunistic infections: Serious complications from opportunistic infections can severely impact daily life, requiring extensive medical care and hospitalization. These infections can significantly disrupt routine and daily functioning, impacting social interactions and employment.
- Financial strain: The cost of medical care, medications, and lifestyle adjustments associated with HIV can create financial strain. This can further affect a person’s ability to manage their daily needs.
- Social isolation and stigma: Fear of judgment or discrimination can lead to social isolation and negatively impact relationships with family, friends, and colleagues. This can create emotional distress and feelings of loneliness.
Importance of Support Systems
Having a strong support system is essential for individuals living with HIV. This includes family, friends, support groups, and healthcare professionals. Support systems can provide emotional, practical, and informational assistance. They can help individuals cope with the challenges of living with HIV and maintain a positive outlook. The presence of a strong support network is vital for improving overall quality of life.
Medical Resources and Support
Navigating an HIV diagnosis can be overwhelming, but remember you’re not alone. Access to reliable medical resources and supportive communities is crucial for managing the condition effectively and improving your overall well-being. Understanding the available help can ease anxieties and empower you to take control of your health journey.
Reliable Medical Resources for HIV Information
Accurate and up-to-date information is essential for making informed decisions about your health. Reputable organizations provide comprehensive resources covering various aspects of HIV, including prevention, treatment, and support. Consult these resources for credible information:
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): A leading US public health agency, the CDC offers a wealth of information on HIV, including statistics, prevention strategies, and treatment guidelines. Their website provides detailed information on symptoms, testing, and treatment options.
- The National Institutes of Health (NIH): The NIH, comprising various institutes, conducts extensive research on HIV and AIDS. Their resources cover research findings, clinical trials, and treatment protocols, offering in-depth knowledge for individuals and healthcare providers.
- The World Health Organization (WHO): A global organization, the WHO provides international guidelines and recommendations on HIV prevention, diagnosis, and treatment. Their data and resources offer a global perspective on the epidemic.
- The AIDS.gov website: A US government resource offering a central hub for HIV information, treatment guidelines, and support services. It’s a user-friendly platform with readily accessible information.
Support Groups and Organizations for Individuals with HIV
Connecting with others who share similar experiences can significantly impact your journey with HIV. Support groups and organizations offer a sense of community and practical assistance.
- Local support groups: Many communities have support groups specifically for people living with HIV. These groups provide a safe space for sharing experiences, providing emotional support, and offering practical advice. Joining a local group can lead to a stronger sense of community and belonging.
- National organizations: Organizations like the Positive Women’s Network and The Body Positive provide national support for individuals affected by HIV. They offer resources, advocacy, and educational programs. These organizations can offer vital support and connect you with others facing similar challenges.
- Online forums and communities: Online platforms provide a virtual space for individuals with HIV to connect, share experiences, and gain support from others. Online communities can be particularly valuable for those who may have limited access to in-person support groups.
Importance of Accessing Comprehensive Care
Comprehensive care is crucial for managing HIV effectively and improving overall health. This encompasses medical, social, and psychological aspects.
- Medical care: Consistent medical care, including regular checkups, laboratory tests, and treatment adherence, is essential for managing HIV and preventing opportunistic infections. This involves working closely with healthcare providers to develop a treatment plan tailored to individual needs.
- Social support: HIV can affect various aspects of daily life, including social relationships and employment. Seeking social support from family, friends, and support groups can help cope with emotional challenges.
- Mental health support: Living with HIV can have a significant impact on mental health. Mental health professionals can provide counseling, therapy, and support to address any mental health concerns that may arise. Seeking mental health services is crucial for maintaining overall well-being.
Organizations Offering Support for HIV
Various organizations dedicate themselves to supporting individuals with HIV and their families.
- The National Alliance of State and Territorial AIDS Directors (NASTAD): NASTAD plays a key role in coordinating HIV/AIDS programs at the state and local levels. This organization fosters collaboration and support for those affected by HIV.
- The AIDS Healthcare Foundation (AHF): A global organization dedicated to fighting HIV/AIDS, AHF offers various services, including treatment, prevention programs, and support for individuals affected by HIV.
- The Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria: A global organization dedicated to funding and implementing programs to combat HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis, and malaria. Their work focuses on improving access to treatment and prevention efforts worldwide.
Final Conclusion
Recognizing HIV symptoms in men is crucial for early intervention and better health outcomes. This exploration of the diverse ways HIV manifests, from common to less frequent symptoms, emphasizes the importance of open communication with healthcare providers. Remember, early diagnosis is key to effective treatment and management. By understanding the signs and symptoms, men can take proactive steps towards their well-being.