How does melatonin work? This fascinating hormone plays a crucial role in regulating our sleep-wake cycle, impacting everything from our mood to our immune system. This exploration delves into the intricate process of melatonin production, its molecular mechanisms, and its profound effects on various bodily functions. We’ll uncover the science behind melatonin’s sleep-promoting capabilities and its wider impact on health.
Melatonin production is tightly linked to our daily light exposure, peaking at night. The suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN), a tiny part of the brain, acts as the master clock, regulating this production. Different age groups experience varying melatonin levels, and these differences impact sleep quality. Understanding the complex interplay of hormones and enzymes is key to grasping how melatonin works.
Melatonin Production and Regulation
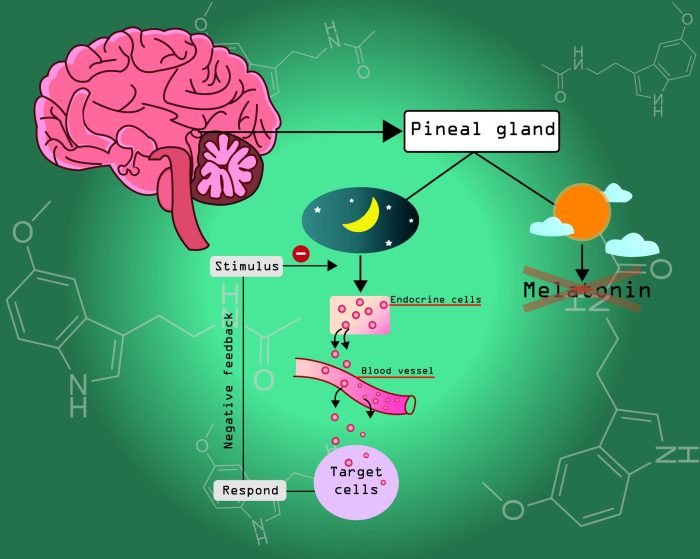
Melatonin, a hormone crucial for regulating the sleep-wake cycle, is produced primarily in the pineal gland. Its production is intricately linked to environmental cues, particularly light exposure, and influenced by various physiological factors. Understanding this intricate process is key to comprehending how melatonin impacts our sleep and overall well-being.The body’s internal clock, largely controlled by the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN), plays a central role in orchestrating melatonin production.
This rhythmic release of melatonin helps synchronize our biological processes with the natural day-night cycle. This delicate balance can be disrupted by factors like shift work, jet lag, and certain medical conditions, leading to sleep disturbances.
Melatonin Synthesis Process
Melatonin synthesis is a multi-step process, beginning with the amino acid tryptophan. This crucial step involves several enzymatic conversions, ultimately culminating in the production of melatonin. The pineal gland, situated deep within the brain, is the primary site of melatonin synthesis.
The conversion of tryptophan to melatonin involves a series of enzymatic reactions, primarily catalyzed by tryptophan hydroxylase and arylalkylamine N-acetyltransferase.
The process is directly impacted by light exposure. Light signals reaching the eyes are transmitted to the SCN, which then regulates the release of hormones like norepinephrine. Norepinephrine, in turn, stimulates the pineal gland to produce melatonin.
Melatonin, a hormone, helps regulate your sleep-wake cycle. It’s often touted for its sleep-promoting effects, but it’s not a magic bullet. Sometimes, you might experience a chest ache when you cough, which could be a sign of something more serious, and seeking medical advice for issues like chest hurts when i cough is always a good idea.
Regardless, understanding how melatonin works in your body is key to managing your sleep and overall health.
Factors Influencing Melatonin Production
Several factors significantly impact the rate and timing of melatonin production. Light exposure is arguably the most influential. Exposure to bright light, particularly in the morning, suppresses melatonin production, while darkness promotes it. The time of day also plays a crucial role, with melatonin levels typically peaking in the late evening and gradually decreasing throughout the night.
Age is another important factor, as melatonin production and secretion patterns change throughout the lifespan.
Role of the Suprachiasmatic Nucleus (SCN)
The SCN, often called the body’s internal clock, acts as the master regulator of the circadian rhythm. It receives light information from the eyes and transmits signals to the pineal gland to adjust melatonin production accordingly. This precise regulation ensures that melatonin levels align with the natural day-night cycle. Disruptions to the SCN’s function can lead to various sleep disorders.
Specific Enzymes and Hormones
Several key enzymes and hormones are involved in melatonin synthesis. Tryptophan hydroxylase, for example, is essential for converting tryptophan to 5-hydroxytryptophan. This intermediate compound is then converted to serotonin, which is further metabolized into melatonin. N-acetyltransferase plays a critical role in the final stages of melatonin synthesis.
Melatonin Production Across Age Groups
The table below highlights how melatonin production varies across different age groups. This variation reflects the developmental changes in the body’s circadian rhythm and hormonal balance.
| Age Group | Production Rate | Influencing Factors | Impact on Sleep |
|---|---|---|---|
| Infancy (0-1 year) | Relatively low, but increasing | Immature circadian rhythm, fluctuating light exposure | Often irregular sleep patterns, potential for feeding difficulties |
| Childhood (2-12 years) | Increasing steadily | Developing circadian rhythm, increasing light exposure | Generally better sleep quality, but still susceptible to sleep disturbances |
| Adolescence (13-18 years) | Peak production during adolescence | Puberty, hormonal changes, irregular sleep schedules | Potential for delayed sleep phase syndrome, sleep deprivation |
| Adulthood (19-65 years) | Stable production | Stable circadian rhythm, but potential for lifestyle factors affecting sleep | Generally good sleep quality, but can be influenced by stress, diet, and exercise |
| Older Adulthood (65+ years) | Decreasing production | Aging circadian rhythm, potential for health conditions | Increased sleep disturbances, potential for sleep disorders |
Melatonin’s Mechanism of Action
Melatonin, a crucial hormone in regulating our circadian rhythm, exerts its effects through a complex interplay of molecular interactions. Its influence extends beyond sleep regulation, affecting various bodily processes. This section delves into the intricate mechanisms by which melatonin interacts with cells, highlighting the diverse receptors involved and the pathways affected.Melatonin’s impact on cells is multifaceted. It acts as a signaling molecule, binding to specific receptors and initiating intracellular cascades that modulate diverse cellular functions.
Understanding these molecular mechanisms provides insight into the wide-ranging physiological effects of this fascinating hormone.
Molecular Mechanisms of Melatonin Action
Melatonin’s primary mode of action involves binding to specific membrane-bound and intracellular receptors. This interaction triggers downstream signaling pathways, influencing cellular activities. The precise mechanisms through which melatonin affects specific cellular processes are still under investigation, but a growing body of research highlights the importance of various cellular pathways.
Receptors Involved in Melatonin’s Effects
Melatonin exerts its effects through a variety of receptors, primarily MT1 and MT2. These receptors are G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), meaning their activation leads to the activation of intracellular signaling pathways. Other receptors and signaling mechanisms may also contribute to melatonin’s diverse actions. The interaction between melatonin and these receptors is critical for the diverse range of physiological responses observed.
Melatonin’s Effects on Bodily Functions
Melatonin’s influence on various bodily functions is substantial. It plays a crucial role in regulating sleep-wake cycles, but its impact extends to influencing antioxidant defenses, regulating immune responses, and potentially influencing cardiovascular health. The effects of melatonin are highly context-dependent, varying based on factors like dosage, time of administration, and the specific cells or tissues involved.
Cellular Pathways Affected by Melatonin
Melatonin affects various cellular pathways, influencing diverse cellular functions. These pathways include those involved in gene expression, cellular growth, apoptosis, and antioxidant protection. Understanding these pathways is essential to comprehend melatonin’s intricate role in maintaining homeostasis and regulating various bodily functions.
| Cell Type | Receptor | Pathway | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pinealocytes | MT1, MT2 | cAMP/PKA, Calcium/Calmodulin | Circadian rhythm regulation, melatonin synthesis |
| Immune cells (e.g., macrophages) | MT1, MT2 | MAPK, NF-κB | Modulation of inflammatory responses, antioxidant protection |
| Cardiovascular cells | MT1, MT2 | Akt/PI3K | Regulation of blood pressure, potentially reducing oxidative stress |
| Brain cells (neurons) | MT1, MT2 | cAMP/PKA, Calcium/Calmodulin | Synaptic plasticity, neuroprotection |
Melatonin’s Role in Sleep
Melatonin, a hormone naturally produced by the pineal gland, plays a crucial role in regulating our sleep-wake cycle. Its influence extends beyond simply signaling sleepiness; it orchestrates a complex interplay of physiological changes that prepare the body for rest and contribute to a restorative night’s sleep. This section delves into how melatonin promotes sleep onset and maintenance, the associated physiological shifts, the relationship between melatonin levels and sleep stages, and the impact on overall sleep quality.Melatonin’s effect on sleep is multifaceted, acting as a crucial signal for the body to transition from wakefulness to sleep.
Melatonin, a hormone, plays a crucial role in regulating our sleep-wake cycle. It’s often touted as a natural sleep aid, but it can also impact other bodily functions. Sometimes, eye pain, like that often associated with various eye conditions, eye pain pain in the eyes , can be linked to sleep disruptions. Understanding how melatonin affects our bodies is key to understanding why it’s so important for overall health and well-being.
And how it might affect those with eye discomfort. In short, melatonin’s impact is multifaceted, and its role in sleep is just one piece of the puzzle.
It works by coordinating various physiological processes to facilitate the sleep stages. The specific mechanisms are not fully understood, but the effects are well-documented and widely recognized within the scientific community.
Melatonin and Sleep Onset
Melatonin’s primary role in sleep is to initiate the sleep process. As darkness falls, melatonin secretion increases, signaling to the body that it’s time to wind down. This gradual increase in melatonin levels prepares the body for sleep by influencing the central nervous system and other biological processes. This preparatory phase allows for the transition into various stages of sleep, ultimately promoting sleep onset.
Melatonin, a hormone, helps regulate your sleep-wake cycle. Sometimes, a persistent, stubborn pimple, like the ones discussed in this article about a big pimple that wont go away , can be a sign of underlying hormonal imbalances. These imbalances can disrupt your sleep patterns, impacting melatonin production. So, a deeper understanding of how melatonin works is key to understanding your overall health, especially when dealing with persistent skin issues.
A steady increase in melatonin levels before bed, triggered by the environmental cues of darkness, creates a favorable internal environment for sleep initiation.
Physiological Changes Associated with Melatonin
Melatonin’s influence on sleep extends beyond simple sleep onset. A cascade of physiological changes occurs as melatonin levels rise. Body temperature typically decreases, heart rate slows, and the respiratory rate generally diminishes. These changes create a more relaxed and conducive environment for sleep. The decrease in core body temperature, for example, is a significant physiological change that is closely linked to the sleep-promoting effects of melatonin.
Melatonin Levels and Sleep Stages
The relationship between melatonin levels and sleep stages is intricate. Melatonin secretion typically peaks in the early hours of the night, corresponding with the transition into deep sleep stages. During these stages, the body repairs and regenerates itself, essential for overall well-being. The correlation between melatonin levels and specific sleep stages is an area of ongoing research, but current findings suggest a strong link.
The presence of melatonin is considered a critical factor for transitioning through the different stages of sleep effectively.
Impact of Melatonin on Sleep Quality, How does melatonin work
Melatonin’s impact on sleep quality is substantial. By facilitating sleep onset and promoting deeper sleep stages, melatonin contributes to a more restorative and rejuvenating night’s sleep. This leads to improved sleep quality, characterized by reduced sleep disturbances and increased feelings of well-being upon waking. Individuals experiencing sleep issues often find that optimizing melatonin levels can improve their sleep quality and overall health.
Effects of Melatonin on Sleep
- Melatonin signals the body to prepare for sleep, initiating the transition from wakefulness.
- Increased melatonin levels are associated with decreased body temperature, heart rate, and respiratory rate.
- Melatonin’s secretion often correlates with the transition into deeper sleep stages.
- Melatonin contributes to a more restorative and rejuvenating night’s sleep, leading to improved sleep quality.
- A consistent melatonin production cycle is crucial for maintaining a healthy sleep-wake cycle.
Melatonin’s Effects on Other Biological Processes: How Does Melatonin Work
Melatonin, a hormone primarily associated with sleep regulation, plays a surprisingly multifaceted role in numerous other bodily functions. Beyond its influence on the sleep-wake cycle, melatonin interacts with various biological pathways, impacting immune responses, antioxidant defenses, and even mood. This exploration delves into melatonin’s broader effects, highlighting its influence on circadian rhythms, immune function, and other vital processes.Melatonin’s influence extends far beyond the realm of sleep.
It acts as a crucial signaling molecule, orchestrating a symphony of biological processes that maintain overall health and well-being. Understanding these interactions offers insights into potential therapeutic applications and the intricate interconnectedness of our internal systems.
Melatonin’s Role in Regulating Circadian Rhythms
Melatonin is a key player in maintaining our internal 24-hour clock, the circadian rhythm. The pineal gland synthesizes melatonin in response to darkness, signaling the body to prepare for sleep. This rhythmic secretion, precisely timed with the day-night cycle, synchronizes various physiological processes, from hormone release to body temperature regulation. Disruptions in melatonin production or secretion can lead to misalignment of the circadian rhythm, potentially impacting sleep quality and overall health.
Melatonin’s Impact on the Immune System
Melatonin’s immunomodulatory effects are increasingly recognized. It influences the production and function of various immune cells, promoting a balanced immune response. This includes supporting the activity of natural killer (NK) cells, a crucial component of the body’s defense mechanisms against pathogens. Furthermore, melatonin’s antioxidant properties contribute to a healthy immune response by protecting immune cells from damage.
Research suggests that melatonin may play a vital role in preventing chronic inflammation and supporting immune function, especially in individuals exposed to oxidative stress.
Melatonin’s Influence on Antioxidant Activity
Melatonin’s antioxidant properties are well-documented. It acts as a potent scavenger of free radicals, protecting cells from oxidative damage. This antioxidant capacity contributes to the preservation of cellular health and integrity. By neutralizing harmful free radicals, melatonin helps maintain the integrity of cellular structures and functions, potentially mitigating age-related decline and preventing cellular damage. Furthermore, melatonin’s antioxidant action can support other cellular processes, enhancing overall well-being.
Melatonin’s Role in Regulating Various Bodily Functions
Melatonin’s influence extends to mood regulation and stress response. Studies suggest that melatonin may help modulate the neurotransmitter systems involved in mood, potentially contributing to a sense of calm and well-being. In the face of stress, melatonin’s antioxidant properties may help mitigate the negative effects of stress hormones on the body, offering potential support for stress management. Its impact on the cardiovascular system and bone health is also an area of ongoing research.
Impact of Melatonin on Various Bodily Functions
| Function | Mechanism | Impact | Potential Benefits/Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Circadian Rhythm Regulation | Pineal gland synthesis in response to darkness | Synchronizes physiological processes, promotes sleep-wake cycle | Improved sleep quality, potential for improved alertness; possible disruption of natural sleep-wake cycle if taken improperly |
| Immune System Modulation | Influences immune cell function, antioxidant protection | Supports immune response, potentially mitigates inflammation | Potential for enhanced immune function, support for healthy inflammatory response; may interact with certain medications |
| Antioxidant Activity | Scavenges free radicals, protects cells | Preserves cellular health, reduces oxidative damage | Protection against cell damage, potential support for age-related decline; potential for interactions with other medications |
| Mood Regulation | Modulates neurotransmitter systems | Potential for improved mood, sense of calm | Potential mood support; interactions with other medications are possible |
| Stress Response | Mitigates negative effects of stress hormones | Potential support for stress management | Potential for stress reduction, support for overall well-being; potential for interactions with other medications |
Melatonin and Health

Melatonin, a naturally occurring hormone, plays a crucial role in regulating our sleep-wake cycle. While the body produces melatonin naturally, supplementation is becoming increasingly popular, particularly for individuals experiencing sleep difficulties. However, it’s important to understand the potential benefits, risks, and responsible use of melatonin. This section delves into the use of melatonin supplements for various health concerns, addressing safety, dosage, and contraindications.Understanding the potential benefits and drawbacks of melatonin supplementation is essential for making informed decisions about its use.
This knowledge allows individuals to approach melatonin use responsibly, potentially alleviating sleep disorders while mitigating potential risks.
Potential Benefits of Melatonin Supplementation for Sleep Disorders
Melatonin supplementation can be a helpful strategy for managing sleep disorders, especially when combined with other sleep hygiene practices. Studies have shown that melatonin can improve sleep onset latency and overall sleep quality in various populations, including individuals with insomnia and jet lag. This is particularly relevant for those experiencing difficulty falling asleep, as melatonin can help regulate the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle.
Potential Risks and Side Effects of Melatonin Use
While generally considered safe, melatonin supplementation can sometimes cause adverse effects. Common side effects include headaches, dizziness, nausea, and daytime drowsiness. Less frequently, more serious side effects such as allergic reactions or interactions with other medications can occur. It’s crucial to be aware of these potential risks and to consult a healthcare professional before starting any supplementation regimen.
Individuals with pre-existing health conditions should be particularly cautious.
Appropriate Dosages and Administration of Melatonin
The recommended dosage of melatonin varies depending on the individual’s needs and the specific condition being addressed. A healthcare professional can provide personalized recommendations based on a comprehensive evaluation of the individual’s medical history and current health status. It’s crucial to follow the prescribed dosage and administration instructions carefully. Generally, dosages range from 0.5mg to 10mg, but it’s crucial to follow a healthcare professional’s guidance.
Melatonin is typically taken orally, either as a capsule, tablet, or liquid, often an hour before bedtime.
Situations Where Melatonin Use May Be Contraindicated
Certain individuals should avoid melatonin supplementation. Those with a history of allergies to melatonin or other components of the supplement should refrain from using it. Furthermore, individuals taking certain medications, such as blood thinners or immunosuppressants, should consult their doctor before using melatonin. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should also discuss the use of melatonin with their healthcare provider.
Summary Table of Melatonin Supplementation
| Benefit | Risk | Dosage | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Improved sleep onset and quality in some individuals, especially those with insomnia or jet lag. | Headaches, dizziness, nausea, daytime drowsiness, potential allergic reactions, and interactions with other medications. | 0.5mg to 10mg, individualized by healthcare professional. | Consult a healthcare professional before use, especially for pre-existing conditions, pregnancy, or breastfeeding. Follow prescribed dosage and administration instructions carefully. |
Melatonin Research and Future Directions
Melatonin’s role in human health extends far beyond its sleep-regulating function. Ongoing research delves into its potential impact on a range of conditions, from cardiovascular health to neurological disorders. Understanding these complex interactions is crucial for developing effective therapeutic strategies. This exploration will examine the current state of melatonin research, highlight future directions, and Artikel areas needing further investigation.Current research suggests that melatonin may play a protective role in various physiological processes, potentially impacting aging and disease progression.
Investigating these interactions will be critical in harnessing melatonin’s potential benefits.
Ongoing Research on Melatonin’s Role in Health Conditions
Research into melatonin’s potential therapeutic applications for diverse health conditions is actively progressing. Studies explore its impact on conditions like diabetes, neurodegenerative diseases, and certain cancers. Preliminary findings often show promising trends, though further rigorous testing is essential. For example, some studies suggest a potential link between melatonin supplementation and improved glucose control in individuals with type 2 diabetes, but more robust clinical trials are needed to confirm these preliminary observations.
Potential Future Directions for Melatonin Research
Future research should focus on understanding the intricate mechanisms through which melatonin influences various physiological processes. This includes identifying specific melatonin receptor subtypes and their roles in different tissues. A deeper understanding of the molecular pathways involved in melatonin’s action will enable the development of more targeted therapies. Researchers are also exploring personalized approaches to melatonin supplementation, considering individual genetic variations and metabolic profiles.
Key Findings in Melatonin Research
Significant progress has been made in understanding melatonin’s effects on various health conditions. Some key findings include:
- Melatonin’s potential protective effects against oxidative stress and inflammation have been demonstrated in several studies.
- Preliminary evidence suggests a possible role for melatonin in improving sleep quality and reducing sleep disturbances in various populations, particularly the elderly.
- Some research suggests that melatonin may exhibit anti-cancer properties in certain cell lines, but further research is required to determine its efficacy in human subjects.
Areas Requiring Further Research
Despite promising findings, further research is crucial in several areas:
- Long-term safety and efficacy of melatonin supplementation in various populations need comprehensive evaluation.
- Understanding the precise mechanisms of melatonin’s action on specific cellular pathways requires detailed investigation.
- Developing standardized methods for melatonin measurement in biological fluids is essential for consistent research.
Open Questions in Melatonin Research
Several critical questions remain unanswered:
- What are the optimal dosages and administration schedules for melatonin supplementation in different health conditions?
- How can melatonin be combined with other therapies to maximize its benefits and minimize adverse effects?
- What are the long-term effects of chronic melatonin use on various physiological systems?
Final Conclusion
In conclusion, melatonin’s impact on our health extends far beyond sleep. From its role in circadian rhythms to its potential antioxidant properties, this hormone influences numerous bodily functions. While supplementation can offer potential benefits for sleep disorders, it’s essential to understand the potential risks and follow appropriate guidelines. Further research is crucial to fully unravel the intricacies of melatonin’s mechanisms and unlock its potential in various health applications.