How long can you stay in a sauna? This question delves into the fascinating world of sauna use, exploring optimal session durations for various benefits and safety considerations. Understanding the relationship between time in the sauna, your body’s response, and potential risks is crucial for a safe and enjoyable experience.
Factors like age, fitness level, and underlying health conditions significantly impact how long you can safely stay in a sauna. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of recommended session durations, highlighting the importance of proper hydration and safety measures. Different sauna types also play a role in the duration guidelines. We’ll cover traditional saunas and infrared saunas, examining their unique characteristics.
Session Duration Limits

Sauna sessions offer numerous health benefits, but proper duration is crucial for safety and effectiveness. Overexposure can lead to adverse effects, while insufficient time may not fully realize the therapeutic potential. Understanding the optimal session duration for various individuals and sauna types is essential for maximizing the positive impact and minimizing risks.Sauna sessions are a powerful tool for relaxation, detoxification, and even pain relief.
However, maintaining a safe and effective experience hinges on understanding the optimal duration tailored to individual needs. This involves recognizing the limits of time spent in the sauna and the connection between time and core temperature elevation. It’s vital to understand how different sauna types, such as infrared saunas, can influence the duration and safety precautions.
Typical Session Durations
Sauna sessions should be tailored to individual tolerance and health conditions. A general guideline is to start with shorter sessions and gradually increase duration as tolerance improves. This allows for a safer and more enjoyable experience. The following considerations apply to various scenarios.
Recommended Maximum Session Times
Different demographics and health conditions require adjustments to maximum session durations. Elderly individuals, those with cardiovascular issues, or pregnant women should consult with their doctor before using a sauna. Generally, individuals with underlying health conditions should start with shorter sessions and gradually increase duration as tolerated. This cautious approach minimizes potential risks.
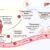
Relationship Between Session Length and Core Body Temperature Increase
The duration of a sauna session directly correlates with the increase in core body temperature. Longer sessions lead to higher core temperatures, which can impact cardiovascular health if not managed properly. Careful monitoring of time spent in the sauna is essential to avoid overheating. A rapid rise in body temperature, if not managed properly, can cause discomfort or even medical issues.
Comparison of Session Durations for Different Sauna Types
| Sauna Type | Typical Session Duration (minutes) | Recommended Max Duration (minutes) | Health Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional | 15-30 | 20-30 | Risk of dehydration, heart issues. Traditional saunas generate heat through heated stones and air, leading to potential for faster core temperature increases, especially in prolonged sessions. Careful monitoring is crucial. |
| Infrared | 10-20 | 15-20 | Increased heat intensity, potential for burns. Infrared saunas utilize infrared rays to heat the body directly, potentially leading to faster temperature elevation. Higher intensity necessitates shorter session durations. |
Factors Affecting Duration
Sauna sessions, while offering numerous health benefits, must be approached cautiously. Individual factors significantly influence how long a person can safely stay in a sauna. Understanding these factors is crucial for maximizing the benefits and minimizing risks.Individual variations in physiology, physical fitness, hydration, and pre-existing health conditions all impact the safe duration of a sauna session. A tailored approach to sauna use, considering these individual variables, is essential to prevent adverse effects.
Wondering how long you can comfortably stay in a sauna? It really depends on your tolerance and overall health. However, it’s crucial to remember that prolonged sauna sessions can be a risk factor for certain health conditions, potentially increasing your chances of experiencing issues like IBS, or even more concerning, colon cancer. For a deeper dive into understanding the subtle but important differences between irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and colon cancer, check out this helpful resource: ibs vs colon cancer.
Always listen to your body and don’t push yourself too hard; a shorter, less intense session might be more beneficial in the long run.
Physical Fitness Levels
Physical fitness significantly impacts tolerance to heat. Individuals with higher levels of cardiovascular fitness generally have a greater capacity to withstand the elevated temperatures and increased heart rate associated with sauna use. This is because their cardiovascular systems are more efficient at regulating body temperature. Conversely, those with lower fitness levels may experience adverse reactions at lower temperatures and durations.
They might experience dizziness, nausea, or other symptoms sooner. Proper warm-up and cool-down periods are especially important for individuals with lower fitness levels to help acclimate to the heat and recover effectively.
Hydration Levels
Adequate hydration is vital for safe sauna use. Sweating during a sauna session leads to fluid loss. Insufficient hydration before or during a sauna session can exacerbate dehydration, potentially leading to dizziness, lightheadedness, and even heat stroke. Maintaining proper hydration before, during, and after a sauna session is crucial for minimizing these risks. Drink plenty of water throughout the session, and replenish fluids afterward.
Pre-existing Health Conditions
Pre-existing health conditions can significantly impact the safe duration of a sauna session. Conditions such as heart disease, high blood pressure, and certain respiratory issues may make prolonged exposure to heat more risky. Consult with a healthcare professional before using a sauna if you have any pre-existing health conditions. They can provide personalized guidance on safe sauna use based on your specific medical history.
This is particularly crucial for those with pre-existing conditions, as they may need to adjust the duration and frequency of their sauna sessions to prevent potential complications.
Age and Recommended Sauna Time
Sauna use can be safe and beneficial for individuals of all ages, but it’s important to consider the age-related physiological changes that can impact tolerance. The following table Artikels the recommended maximum durations for different age groups, emphasizing the importance of adjusting sessions based on individual tolerance and health status.
So, how long can you comfortably stay in a sauna? It really depends on your tolerance, but generally, you should aim for sessions of 10-20 minutes at a time. While you’re sweating it out, remember that a healthy diet, including plenty of nutritious foods like nuts, can significantly impact your overall well-being. For a deeper dive into the nutritional benefits of nuts, check out this informative article on are nuts good for you.
After all, a balanced approach to both your sauna time and your diet is key to feeling your best. Too long in the sauna and you might risk overheating, so don’t overdo it!
| Age Group | Recommended Max Duration (minutes) | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| 18-30 | 25-35 | Generally healthy, good fitness levels |
| 31-50 | 20-30 | Potential for health concerns |
| 51+ | 15-25 | Higher risk of health issues |
Safety Measures & Procedures
Sauna sessions can be incredibly beneficial for relaxation and well-being, but safety is paramount. Proper precautions and awareness of potential risks are crucial for a safe and enjoyable experience. This section Artikels essential safety measures to ensure a healthy and secure sauna session.
Essential Safety Measures for Extended Sessions
Extended sauna sessions, while potentially beneficial, demand heightened vigilance. Strict adherence to safety guidelines is vital to avoid complications. These guidelines encompass various aspects, from hydration to monitoring vital signs, ensuring a safe and effective sauna experience.
Importance of Hydration
Adequate hydration is essential before, during, and after a sauna session. The body loses significant amounts of water through sweating during a sauna session, which can lead to dehydration if not replenished. Maintaining proper hydration prevents heat stroke, dizziness, and other potential complications. Drinking plenty of water before entering the sauna, during the session (with caution), and after is critical for maintaining bodily functions and overall well-being.
Monitoring Vital Signs During a Session
Regular monitoring of vital signs is important for identifying potential issues early. A key aspect of this is recognizing changes in heart rate and blood pressure. If you experience significant changes in these vital signs during a session, you should immediately exit the sauna. Furthermore, observe your body’s signals. If you feel lightheaded, dizzy, or experience chest pain, leave the sauna immediately.
Signs Indicating Potential Health Risks
Recognizing potential health risks is vital for a safe sauna experience. These signs can vary, from mild discomfort to more serious symptoms. Pay close attention to your body and immediately exit the sauna if you experience any of these signs:
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Headache or nausea
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat
- Muscle cramps or weakness
- Shortness of breath
- Skin rash or flushing
- Fainting or loss of consciousness
Procedure for Exiting the Sauna Safely
Exiting the sauna safely is crucial for preventing potential injuries or complications. A gradual transition from the hot sauna environment to a cooler environment is essential. Slowly step out of the sauna and into a cool room or area, allowing your body to adjust to the temperature change. Avoid abrupt changes in temperature, which can lead to shock.
Wondering how long you can comfortably stay in a sauna? Well, it really depends on your individual tolerance, but generally, sessions shouldn’t exceed 15-20 minutes at a time. Interestingly, similar to the effects of heat on the body, some people experience digestive issues like those related to irritable bowel syndrome. Understanding the nuances of conditions like facts about irritable bowel syndrome can help you adjust your sauna time accordingly.
Longer sessions might not be the best idea if you’re prone to such sensitivities. It’s always a good idea to start with shorter periods and gradually increase your sauna time as needed.
Preventing Overheating
Preventing overheating during a sauna session is crucial. The risk of overheating increases with longer durations and higher temperatures. Start with shorter sessions and gradually increase the duration as your body adapts. Monitoring your body’s response is essential. If you feel overly hot, uncomfortable, or experience any of the warning signs, exit the sauna immediately.
Furthermore, listen to your body and take breaks when needed.
Sauna Etiquette and Culture: How Long Can You Stay In A Sauna
Stepping into a sauna is more than just a heat therapy; it’s a cultural experience steeped in tradition and etiquette. Respect for the space and the practice is paramount. Understanding the nuances of sauna etiquette ensures a pleasant and harmonious experience for everyone. Different cultures have evolved unique traditions and customs surrounding the sauna, each contributing to its rich tapestry.Sauna etiquette is a blend of unspoken rules and deeply ingrained customs.
These practices, often passed down through generations, are designed to create a welcoming and respectful atmosphere within the sauna. From the initial entry to the final exit, every action is imbued with a sense of mindful consideration for the other individuals sharing the space.
Common Sauna Etiquette Rules
Sauna etiquette is crucial for maintaining a positive and comfortable atmosphere for all users. These rules are not rigid regulations but rather guidelines aimed at promoting respect and ensuring a harmonious experience for everyone. These rules are important for both public and private saunas.
- Stay Hydrated: Maintaining adequate hydration is essential for both safety and comfort during sauna sessions. Dehydration can lead to various health issues, so ensuring you drink enough water before, during, and after your sauna session is vital.
- Monitor Your Body: Pay close attention to your body’s signals. If you experience discomfort, dizziness, or any other unusual symptoms, leave the sauna immediately. Recognizing your physical limitations is crucial for a safe and enjoyable experience.
- Never Force Yourself: Pushing your body beyond its limits can lead to serious health problems. Listen to your body and avoid exceeding your physical capabilities. This crucial practice prevents potential harm.
Proper Sauna Behavior
Proper sauna behavior demonstrates respect for the environment and the other sauna users. These examples showcase appropriate conduct.
- Respect Personal Space: Maintain a respectful distance from others in the sauna. Avoid crowding or making unnecessary physical contact.
- Cleanliness: Maintain the cleanliness of the sauna by properly disposing of waste and wiping down your equipment after use.
- Quiet Conduct: Keep the volume of conversations low, particularly during periods of relaxation. Avoid loud music or boisterous behavior.
Cultural Significance of Sauna
The sauna holds significant cultural meaning in various societies. It is often intertwined with social gatherings, relaxation, and community bonding.
- Finnish Sauna: The Finnish sauna is deeply ingrained in Finnish culture, representing a sense of community and relaxation. It is often used for social gatherings and communal experiences.
- Russian Banya: The Russian banya, a type of sauna, is a central part of Russian culture, used for both physical and spiritual well-being. It’s a social space for relaxation and socializing.
- Nordic Countries: In Nordic countries, the sauna is an essential part of everyday life, offering a unique opportunity for relaxation, social interaction, and stress relief.
Historical Evolution of Sauna Practices
The sauna’s history spans centuries, evolving from simple to sophisticated structures. Understanding this evolution offers a deeper appreciation for the practice.
- Ancient Origins: Sauna practices trace their roots back to ancient times, with early forms likely evolving from communal bathing rituals.
- Modern Adaptations: The sauna has evolved over time, adapting to modern lifestyles and preferences, while retaining its core principles.
- Global Adoption: The sauna’s popularity has spread globally, with various cultures adapting and integrating it into their own traditions.
Common Sauna Rules for Public and Private Use, How long can you stay in a sauna
These rules apply to both public and private sauna facilities, ensuring a respectful and enjoyable experience for all.
- Stay hydrated
- Monitor your body
- Never force yourself
- Respect personal space
- Maintain cleanliness
- Keep conversations low
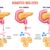
Health Benefits and Risks
Saunas have become a popular wellness practice, offering a range of potential benefits for physical and mental well-being. However, like any activity, extended sauna sessions carry potential risks. Understanding these benefits and risks, along with the nuances of different sauna types, is crucial for responsible and safe use.This section will delve into the positive impacts of sauna use, the risks associated with prolonged sessions, and how these factors differ across various sauna types.
We will also explore potential dangers related to dehydration and high blood pressure, highlighting the importance of mindful sauna practices.
Potential Health Benefits of Sauna Use
Saunas offer a variety of potential health benefits, often stemming from the heat’s effect on the body. These include improved cardiovascular health, reduced muscle soreness, and even potential stress reduction. The heat promotes blood flow, which can help relax muscles and potentially lower blood pressure in some individuals. Some studies suggest that regular sauna use may contribute to better sleep quality and improved immune function.
Risks Associated with Extended Sauna Sessions
Prolonged sauna sessions can pose risks to individuals with certain pre-existing conditions or those who are not accustomed to the heat. Extended exposure to high temperatures can lead to dehydration, heat exhaustion, and even heat stroke, especially if not adequately hydrated before, during, and after the session. Individuals with heart conditions, high blood pressure, or other health concerns should consult their physician before using a sauna, particularly for extended periods.
Comparison of Sauna Types and Their Potential Risks
Different sauna types, including traditional Finnish saunas, infrared saunas, and steam rooms, differ in the way they produce heat and the intensity of the experience. Finnish saunas, known for their high temperatures and dry heat, may pose a greater risk of dehydration if not properly managed. Infrared saunas, using infrared heat, may be gentler on the body, but still require caution.
Steam rooms, with their moist environment, may be more forgiving for those with respiratory issues but also present a risk of overheating. Ultimately, each type requires individual consideration of tolerance and pre-existing conditions.
Risks of Dehydration
Dehydration is a significant risk during sauna use. The high temperatures cause the body to sweat profusely, leading to fluid loss. If not replenished, this can lead to dizziness, weakness, and in severe cases, heat stroke. It’s crucial to drink plenty of water before, during, and after a sauna session to counter the effects of dehydration. Maintaining hydration is a key aspect of safe sauna use.
Risks of High Blood Pressure
Individuals with high blood pressure should be cautious when using a sauna. The sudden increase in body temperature can cause a temporary rise in blood pressure, which could be dangerous for those with pre-existing conditions. Consult with a doctor before using a sauna if you have high blood pressure or any other cardiovascular concerns. This risk highlights the importance of personalized sauna use, especially for those with health conditions.
Final Wrap-Up
In conclusion, safe sauna use hinges on understanding individual factors and adhering to recommended session durations. Prioritizing hydration, monitoring your body, and recognizing potential risks are paramount. Remember, a safe and enjoyable sauna experience is achievable by respecting your body’s limitations and following the guidelines Artikeld in this article. Whether you’re a seasoned sauna enthusiast or a newcomer, this guide equips you with the knowledge to make informed decisions.