How to get rid of nausea? This comprehensive guide explores various approaches, from simple home remedies to medical interventions. We’ll delve into the causes, ranging from common food poisoning to pregnancy-related discomfort, and examine the physiological mechanisms behind each. Whether you’re battling a sudden bout of nausea or seeking preventive measures, this guide offers practical advice and actionable steps to help you feel better.
The journey to conquering nausea often involves understanding its root cause. Identifying the source empowers you to target the specific trigger and implement the most effective solution. This guide is designed to be your personal navigator through the maze of nausea, equipping you with knowledge and solutions.
Identifying Causes of Nausea
Nausea, a sensation of discomfort in the stomach often accompanied by the urge to vomit, can stem from a multitude of factors. Understanding these underlying causes is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment. This section explores common triggers, examining the physiological mechanisms behind each and highlighting the nuances in symptom presentation.Identifying the root cause of nausea is essential for determining the appropriate course of action.
Different triggers elicit distinct physiological responses, leading to varied symptom profiles. This understanding allows for better self-assessment and, importantly, enables prompt consultation with a healthcare professional when necessary.
Common Causes of Nausea
Understanding the varied origins of nausea is key to effective management. A range of factors, from dietary indiscretions to physiological changes, can trigger this unpleasant sensation. This section details several common causes, outlining their respective physiological mechanisms and characteristic symptom profiles.
- Food Poisoning: Food poisoning, often caused by consuming contaminated food or water, results in an acute inflammatory response in the gastrointestinal tract. This response is typically triggered by toxins produced by bacteria, viruses, or parasites. Symptoms manifest quickly, often within hours of ingestion, due to the body’s attempt to expel the harmful substances.
- Motion Sickness: Motion sickness, a common experience during travel, arises from conflicting sensory information received by the brain. The inner ear, responsible for balance, detects movement, while the eyes perceive a different reality. This mismatch leads to a cascade of physiological responses, including nausea and vomiting. The duration and severity of symptoms often correlate with the duration and intensity of the motion.
- Pregnancy: Morning sickness, a common experience during pregnancy, is attributed to hormonal fluctuations. The surge in hormones, particularly human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), triggers nausea and vomiting, often most pronounced during the first trimester. These hormonal changes can impact the digestive system, leading to reduced stomach emptying rates and increased sensitivity to stimuli.
- Medications: Many medications have nausea as a potential side effect. The physiological mechanisms vary depending on the specific drug. Some medications directly irritate the stomach lining, while others impact the central nervous system, leading to nausea and vomiting. The intensity of the nausea varies considerably between individuals and depends on the specific medication.
- Anxiety and Stress: The body’s stress response, often triggered by psychological distress, can lead to nausea. The release of stress hormones like cortisol can disrupt normal digestive processes and lead to nausea and other related symptoms. This connection underscores the importance of managing stress and anxiety for overall well-being.
Symptom Comparison of Nausea Triggers
This table provides a comparative overview of symptoms, duration, and severity associated with different causes of nausea. This structured view helps in differentiating between potential triggers.
| Cause | Symptoms | Duration | Severity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food Poisoning | Nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps, diarrhea, fever, headache | Typically hours to a few days | Moderate to severe, depending on the contaminant |
| Motion Sickness | Nausea, vomiting, dizziness, headache, sweating, pallor | Usually resolves within hours, can be intermittent | Mild to moderate, often resolves with rest |
| Pregnancy | Nausea, vomiting, fatigue, food aversions, heightened sensitivity to smells | Can persist throughout pregnancy, often most severe in first trimester | Can range from mild discomfort to severe episodes requiring medical attention |
| Medications | Nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, abdominal discomfort | Variable, dependent on medication and dosage | Mild to severe, often dose-dependent |
| Anxiety and Stress | Nausea, dizziness, headache, sweating, palpitations | Variable, dependent on stressor and individual response | Mild to moderate, often accompanied by other symptoms of anxiety |
Home Remedies for Nausea: How To Get Rid Of Nausea
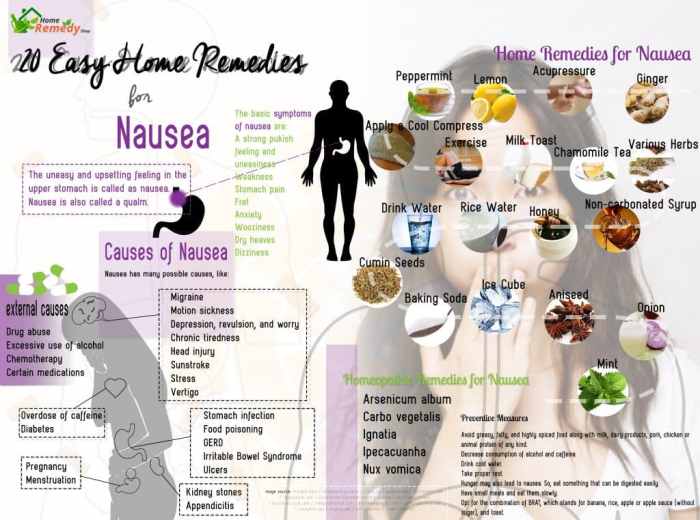
Nausea, that queasy feeling in your stomach, can be incredibly disruptive. While over-the-counter medications are readily available, sometimes you’d prefer a more natural approach. Fortunately, many home remedies offer relief from nausea, often with fewer potential side effects. This exploration will delve into several common home remedies, highlighting their potential effectiveness and safety.These natural approaches can provide soothing relief from nausea.
However, it’s crucial to remember that these remedies may not be effective for everyone and shouldn’t replace medical advice. If nausea is persistent or severe, consult a healthcare professional immediately.
Common Natural Remedies for Nausea
Natural remedies for nausea often utilize easily accessible ingredients. These approaches aim to soothe the stomach and alleviate the unpleasant sensation of nausea.
Ginger
Ginger has a long history of use in traditional medicine for its anti-nausea properties. Gingerol, a compound in ginger, is believed to help regulate stomach motility and reduce nausea-inducing signals. Studies have shown ginger can be effective in treating nausea associated with morning sickness and motion sickness.
Preparation:
- Ginger Tea: Steep 1-2 teaspoons of grated or sliced fresh ginger in hot water for 5-10 minutes. Strain and drink as needed.
- Ginger Ale: Many brands of ginger ale contain ginger extract, providing a readily available and palatable option.
Potential Benefits: Ginger is generally considered safe, but individuals with certain medical conditions (like stomach ulcers) should use caution. It can reduce nausea and vomiting, and may help with motion sickness.
Peppermint Tea
Peppermint tea is another popular home remedy for nausea. Peppermint oil has a calming effect on the digestive system, and the menthol in peppermint may help to relax the stomach muscles.
Preparation: Steep 1-2 tea bags or 1-2 teaspoons of dried peppermint leaves in hot water for 5-10 minutes. Strain and drink warm.
Potential Benefits: Peppermint tea is generally safe, but avoid it if you have gallbladder issues or heartburn. It can help relieve nausea by soothing the digestive tract and potentially reducing muscle spasms.
Brisk Walking
Walking can help settle your stomach, particularly if the nausea is associated with motion sickness or anxiety.
Dealing with nausea can be a real drag, right? One potential solution to explore is magnesium, specifically looking at the different forms like magnesium l-threonate vs magnesium citrate. Choosing the right type might make a difference in how your body responds. For example, some studies suggest that magnesium l-threonate may be more effective for nausea relief compared to magnesium citrate, though further research is needed to confirm this.
You can dive deeper into the pros and cons of each type by checking out this helpful comparison: magnesium l threonate vs magnesium citrate. Ultimately, figuring out what works best for you in terms of nausea relief is a personal journey, so keep experimenting and see what helps!
Preparation: Take a brisk walk for 15-20 minutes.
Potential Benefits: Walking is a low-impact exercise and a generally safe approach to nausea relief, especially if it’s due to anxiety. It helps improve blood circulation and can stimulate the release of endorphins, which have mood-boosting effects that may indirectly help with nausea.
Acupressure Wrist Bands
Acupressure bands stimulate pressure points on the wrists, believed to help regulate nausea signals.
Preparation: Apply pressure to the designated points on the wrist using an acupressure wrist band or similar device.
Potential Benefits: Acupressure bands are generally safe and non-invasive. They can help with nausea and vomiting, but their effectiveness may vary among individuals.
BRAT Diet
A BRAT diet (bananas, rice, applesauce, toast) can be beneficial for soothing an upset stomach. The bland nature of these foods may help reduce irritation and promote healing.
Preparation: Consume small portions of bananas, rice, applesauce, and toast. The consistency of these foods is often gentle on the stomach.
Potential Benefits: A BRAT diet is generally safe. It’s a soothing diet that can help alleviate nausea by providing bland, easily digestible foods.
Table of Home Remedies for Nausea
| Remedy | Ingredients | Preparation | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ginger | Fresh ginger root | Steep grated or sliced ginger in hot water. | Reduces nausea and vomiting, may help with motion sickness. |
| Peppermint Tea | Dried peppermint leaves or tea bags | Steep leaves or tea bags in hot water. | Soothes digestive tract, may reduce muscle spasms. |
| Brisk Walking | None (physical activity) | Take a brisk walk for 15-20 minutes. | Improves blood circulation, releases endorphins. |
| Acupressure Wrist Bands | Acupressure wrist bands | Apply pressure to designated points on the wrist. | May help regulate nausea signals. |
| BRAT Diet | Bananas, rice, applesauce, toast | Consume small portions of these foods. | Provides bland, easily digestible foods. |
Over-the-Counter Medications
Over-the-counter (OTC) medications can be a helpful part of managing nausea, especially for mild to moderate cases. They often provide quick relief and are readily available without a prescription. However, it’s crucial to understand how these medications work, their potential side effects, and the appropriate dosage to avoid complications. Always consult a healthcare professional before taking any new medication, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are pregnant or breastfeeding.
Common Over-the-Counter Medications for Nausea
Many over-the-counter medications can effectively address nausea. These medications work through different mechanisms to target the underlying causes of nausea, such as histamine or dopamine receptors. Understanding the specific mechanism of action for each medication can help you choose the most suitable option for your situation.
Table of Over-the-Counter Medications for Nausea
| Medication | Active Ingredient | Dosage | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dramamine | Dimenhydrinate | 25-50 mg every 4-6 hours as needed, up to 400 mg per day. | Drowsiness, dizziness, dry mouth, blurred vision, constipation, difficulty urinating, nervousness, confusion, or allergic reactions. |
| Bonine | Meclizine | 25 mg twice daily or as directed by your doctor. | Drowsiness, dizziness, dry mouth, headache, and constipation. May also cause allergic reactions. |
| Dramamine Junior Strength | Dimenhydrinate | 12.5 mg every 4-6 hours as needed, up to 200 mg per day. (Important: Consult a physician or pharmacist for the correct dosage, as this can vary depending on the patient’s age.) | Similar to Dramamine, but potential side effects are likely to be less pronounced in children due to lower dosage. |
| Gravol | Dimenhydrinate | 50 mg every 4-6 hours as needed, up to 400 mg per day. | Similar to Dramamine, including drowsiness, dizziness, dry mouth, blurred vision, constipation, difficulty urinating, nervousness, confusion, or allergic reactions. |
| Bonine | Meclizine | 25 mg twice daily or as directed by your doctor. | Drowsiness, dizziness, dry mouth, headache, and constipation. May also cause allergic reactions. |
Mechanism of Action
The medications listed above typically work by targeting the vestibular system in the inner ear, which is responsible for balance and spatial orientation. They also impact receptors in the brain that regulate nausea. Dimenhydrinate, for instance, acts as an antihistamine and anticholinergic, while meclizine primarily affects histamine receptors. Understanding these mechanisms can help you choose the most appropriate medication for your specific needs.
Dealing with nausea can be tough, especially if it’s persistent. Sometimes, nausea can be a symptom of something more serious, like stage 1 non small cell lung cancer, which requires immediate medical attention. Finding ways to manage nausea in these cases often involves a combination of lifestyle adjustments, medications, and, importantly, consulting with a healthcare professional. For more information on stage 1 non small cell lung cancer and its potential symptoms, check out this resource: stage 1 non small cell lung cancer.
Regardless of the cause, finding effective nausea relief strategies is key to improving your overall well-being.
Dosage Recommendations
Dosage recommendations vary depending on the specific medication and the individual. Always follow the instructions on the medication label or consult your physician or pharmacist. It is important to adhere to the recommended dosage to maximize efficacy and minimize the risk of adverse effects. For example, exceeding the recommended dosage of Dramamine could lead to increased drowsiness or other side effects.
Overuse of any medication can also contribute to tolerance or resistance.
Potential Side Effects
Potential side effects vary among the medications. Some common side effects include drowsiness, dizziness, dry mouth, and constipation. The severity and likelihood of these side effects can differ based on individual factors and medication. For example, individuals with pre-existing conditions may experience more pronounced side effects, while some individuals might be more sensitive to certain medications than others.
It’s important to be aware of these potential side effects and to contact a doctor if you experience any concerning symptoms.
Medical Treatments for Persistent Nausea
Persistent nausea that doesn’t respond to home remedies or over-the-counter medications warrants medical attention. It could be a symptom of a more serious underlying condition requiring professional diagnosis and treatment. Seeking medical help is crucial for identifying the root cause and preventing potential complications.Understanding the underlying cause is key to effective treatment. Medical professionals utilize various diagnostic tools and treatments tailored to the specific cause of the nausea.
Proper diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve quality of life and prevent further complications.
When Medical Attention is Necessary
Nausea that lasts for more than a few days, is severe, or is accompanied by other symptoms such as fever, abdominal pain, weight loss, or blood in vomit or stool, requires immediate medical attention. These symptoms may indicate a more serious condition, necessitating prompt evaluation and treatment. Likewise, persistent nausea that interferes with daily activities, such as eating, sleeping, or working, should prompt a visit to a healthcare provider.
Common Medical Treatments for Severe or Persistent Nausea, How to get rid of nausea
Various medical treatments are available for severe or persistent nausea, depending on the underlying cause. These treatments range from medications to therapies. Prescription antiemetics (medications that help control nausea and vomiting) are often used to alleviate symptoms. Dietary modifications and lifestyle adjustments may also be recommended.
Role of Different Medical Professionals
Primary care physicians often initially assess and manage nausea. However, more specialized medical professionals, such as gastroenterologists, may be consulted depending on the suspected cause. Gastroenterologists specialize in the digestive system and can provide specialized care for conditions like inflammatory bowel disease, ulcers, or gallbladder issues, which often present with nausea. Other specialists, like oncologists, may also be involved in cases where nausea is related to cancer treatment.
Trying to shake off nausea can be tricky, but sometimes a simple change in your breathing pattern can help. Deep, controlled breathing exercises, like the ones found in this article on breathing exercises to lower blood pressure , can actually calm your system and ease those queasy feelings. Focus on slow, steady inhalations and exhalations to help regulate your body and potentially banish that nausea.
Diagnostic Process Overview
The diagnostic process for persistent nausea involves a thorough evaluation of the patient’s medical history, current symptoms, and physical examination. A detailed history helps identify potential contributing factors and relevant medical conditions. A physical examination helps rule out any visible abnormalities or potential causes of discomfort. Further diagnostic tests may be ordered based on the initial evaluation.
Medical Tests for Diagnosing Nausea
| Nausea Cause | Treatment | Possible Medical Professionals |
|---|---|---|
| Gastroenteritis | Antidiarrheal medications, fluid replacement, rest, and supportive care. Depending on the severity, hospitalization might be necessary. | Primary care physician, gastroenterologist |
| Morning Sickness | Anti-nausea medications, such as vitamin B6 or acupressure bands. Dietary changes and rest are also often recommended. | Primary care physician, obstetrician-gynecologist |
| Medication Side Effects | Adjusting medication dosage, switching to a different medication, or using anti-nausea medications. | Primary care physician, pharmacist |
| Food Poisoning | Fluid replacement, rest, and supportive care. Antibiotics might be necessary in severe cases. | Primary care physician, infectious disease specialist |
| Migraines | Over-the-counter pain relievers, prescription medications to prevent migraines. Relaxation techniques and lifestyle changes might be recommended. | Primary care physician, neurologist |
| Pregnancy | Anti-nausea medications, dietary changes, and rest. | Obstetrician-gynecologist |
Lifestyle Changes to Prevent Nausea
Nausea can be a debilitating experience, impacting daily life and overall well-being. While addressing the underlying cause is crucial, incorporating certain lifestyle adjustments can significantly reduce the frequency and intensity of nausea episodes. These changes focus on supporting the body’s natural mechanisms for managing discomfort and promoting overall health.Understanding how our bodies react to various factors, such as diet, stress, and hydration, is key to effectively preventing nausea.
By making conscious choices in these areas, we can create a more supportive environment for our bodies to maintain a healthy state and effectively manage potential triggers.
Hydration
Adequate hydration is essential for numerous bodily functions, including digestion and nutrient absorption. Dehydration can exacerbate nausea, making it more difficult for the body to process and eliminate unwanted substances. Maintaining proper fluid intake supports overall bodily functions and aids in preventing nausea. The body relies on water to transport nutrients, regulate temperature, and eliminate waste products, all of which contribute to digestive health and reduce the likelihood of nausea.
Stress Reduction
Stress is a significant factor in many health issues, including nausea. Chronic stress can negatively impact the digestive system, leading to various symptoms, including nausea. Implementing stress-reduction techniques can create a more balanced internal environment, which supports overall health and reduces the risk of nausea. Stress management strategies can include mindfulness practices, regular exercise, and sufficient sleep.
Chronic stress can alter the body’s physiological responses, leading to decreased immunity, increased inflammation, and potentially affecting the digestive system, all of which contribute to nausea.
Balanced Diet
A balanced diet rich in nutrient-dense foods can significantly influence nausea prevention. Eating regular, smaller meals rather than large, infrequent meals can help manage blood sugar levels, promoting a stable environment for digestion and reducing the likelihood of nausea. Avoiding trigger foods, such as spicy or fatty foods, can also help prevent nausea episodes. Poor nutrition, whether due to deficiencies or overconsumption of certain foods, can lead to digestive upset and contribute to nausea.
Regular Exercise
Regular physical activity promotes overall well-being and can positively influence the digestive system. Moderate exercise can aid in digestion, improve blood circulation, and potentially reduce the risk of nausea. Physical activity stimulates the body’s natural processes and promotes overall health. Inactivity can lead to digestive stagnation and contribute to various health issues, including nausea.
Table of Lifestyle Changes and Benefits
| Lifestyle Change | Benefit | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Hydration | Reduces the risk of dehydration-related nausea, supports digestion, and promotes overall bodily functions. | Maintaining adequate water intake is crucial for optimal bodily functions, including nutrient absorption, waste removal, and temperature regulation. Dehydration can lead to digestive issues and exacerbate nausea. |
| Stress Reduction | Reduces the likelihood of stress-induced nausea by promoting a more balanced internal environment. | Chronic stress can negatively impact the digestive system, leading to nausea and other symptoms. Stress reduction techniques, such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises, can help create a more supportive environment for digestion and overall health. |
| Balanced Diet | Improves digestive health, stabilizes blood sugar levels, and minimizes the risk of nausea-inducing foods. | A balanced diet with nutrient-dense foods promotes optimal digestive function and helps maintain stable blood sugar levels. Avoiding trigger foods, such as spicy or fatty foods, can also reduce the likelihood of nausea episodes. |
| Regular Exercise | Promotes overall well-being, improves digestion, and potentially reduces the risk of nausea. | Moderate exercise can aid in digestion, improve blood circulation, and potentially reduce nausea-inducing factors. Inactivity can lead to digestive stagnation, contributing to various health issues, including nausea. |
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
Nausea, while often manageable with home remedies and over-the-counter medications, can sometimes signal a serious underlying condition. Understanding when to seek immediate medical attention is crucial for ensuring a swift and effective response to potentially life-threatening situations. Knowing the warning signs and acting promptly can significantly improve outcomes.Recognizing the severity of nausea is essential. Mild nausea can often be treated at home, but certain symptoms require immediate medical evaluation.
Delaying treatment for serious conditions can have detrimental consequences, ranging from discomfort to potentially life-threatening complications.
Identifying Severe Symptoms
Nausea is often a symptom of a variety of issues, ranging from mild indigestion to serious medical emergencies. Understanding the context surrounding the nausea is vital to determining the appropriate course of action. Severe nausea can be accompanied by other alarming symptoms, necessitating immediate medical attention.
Red Flags Requiring Immediate Medical Attention
Certain symptoms strongly suggest a need for immediate medical intervention. These “red flags” signal the possibility of serious conditions that require prompt medical evaluation. Delaying treatment could have significant consequences.
- Severe, persistent abdominal pain that worsens over time.
- Nausea accompanied by high fever (101°F or higher) and/or stiff neck.
- Nausea accompanied by rapid pulse or difficulty breathing.
- Nausea with severe headache, especially if accompanied by stiff neck, double vision, or loss of consciousness.
- Nausea associated with significant blood in vomit or stool.
- Nausea accompanied by numbness or weakness in an extremity.
- Nausea that follows a head injury, even if the injury seems minor.
- Nausea accompanied by jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes).
- Nausea during pregnancy with vaginal bleeding or severe abdominal pain.
- Nausea that does not improve after 24 hours of home remedies and over-the-counter medication.
Potential Consequences of Delaying Treatment
Delaying treatment for severe nausea can have serious consequences. The potential complications can range from discomfort to life-threatening situations, depending on the underlying cause. Immediate medical attention is critical to prevent further deterioration.
- Dehydration: Prolonged nausea and vomiting can lead to significant fluid loss, potentially causing electrolyte imbalances and organ damage. This is particularly concerning for infants, children, and older adults.
- Internal bleeding: Severe nausea accompanied by blood in vomit or stool may indicate internal bleeding, which requires immediate medical intervention to prevent complications.
- Gastrointestinal infections: Untreated infections can lead to severe complications, including dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, and sepsis. Prompt treatment is crucial to avoid these potential outcomes.
- Appendicitis: Delaying treatment for appendicitis can lead to a ruptured appendix, a life-threatening condition requiring immediate surgery.
- Heart attack or stroke: Some types of nausea are associated with cardiovascular conditions. Delaying treatment for these conditions can have devastating consequences. The potential for serious complications emphasizes the urgency of seeking immediate medical attention when experiencing such symptoms.
Steps to Take in a Medical Emergency
When dealing with a medical emergency involving nausea, immediate action is paramount. Following the steps below can help ensure appropriate care and prevent further complications.
- Call emergency services (911 or equivalent): In the case of a medical emergency, contacting emergency services immediately is critical. Providing accurate information to dispatchers is vital for prompt and effective response.
- Stay calm and provide details: Remain calm and provide emergency personnel with accurate information regarding the symptoms and circumstances surrounding the nausea.
- Follow instructions from emergency personnel: Follow the instructions given by emergency personnel, including any necessary steps to take before their arrival.
- Monitor the individual’s condition: Continue to monitor the individual’s condition until medical help arrives. If the individual’s condition deteriorates, call emergency services again.
Last Word

In conclusion, dealing with nausea can involve a multifaceted approach. Understanding the underlying cause is key to selecting the appropriate remedy. From readily available home remedies to over-the-counter medications and, when necessary, medical treatments, this guide provides a range of options. Ultimately, the best approach depends on the individual situation, severity, and duration of the nausea. Remember to listen to your body and seek professional medical advice when necessary.