How to treat bug bites effectively is a crucial skill, especially during warm months and outdoor adventures. This comprehensive guide covers everything from identifying the culprit to employing effective home remedies and knowing when to seek professional help. Learn how to navigate various bug bites, from the annoying itch to potential health concerns.
This guide will delve into the different types of bugs that bite, their identifying characteristics, and the symptoms of their bites. It will provide a clear, step-by-step approach to dealing with these bites, covering immediate actions, home remedies, over-the-counter treatments, and situations requiring medical attention. We’ll also explore preventative measures to keep those pesky bites at bay.
Identifying the Bug
Knowing the culprit behind a pesky bite is crucial for appropriate treatment. Proper identification helps determine the potential severity of the reaction and guides you toward the most effective course of action. This involves recognizing the specific bug, its distinguishing features, and its typical biting habits. Accurate identification can also prevent future bites by allowing you to understand the bug’s environment and behaviors.
Common Biting Insects and Arachnids
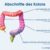
Understanding the types of insects and arachnids that bite humans is essential for swift and effective treatment. Different species have different behaviors and bite characteristics, which may affect the severity of the reaction.
| Bug Name | Image Description | Region | Identifying Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mosquito | A small, winged insect with a slender body and long legs. It typically has a dark-colored abdomen and translucent wings. | Worldwide | Mosquitoes are attracted to warm-blooded animals and often feed on blood. They typically bite during the daytime or early evening. The bite is often itchy and may cause a small, red bump. |
| Black Fly | A small, dark-colored fly with a short body and wings. Its body often appears shiny or metallic. | Temperate and tropical regions | Black flies are known for their painful bites, which can cause significant swelling and itching. They are attracted to moisture and often bite near water sources. The bites usually appear as a red bump. |
| Tick | A small, eight-legged arachnid with a round or oval body. Ticks can vary in color, often ranging from reddish-brown to dark brown or black. | Various regions | Ticks are often found in grassy areas, forests, and wooded regions. They attach themselves to their hosts and feed on their blood. The bite itself is often painless, but a tick may leave a small red bump or mark, sometimes with a visible tick. |
| Spider | A small arachnid with eight legs, a cephalothorax (fused head and chest), and an abdomen. Spider species vary greatly in appearance, color, and size. | Worldwide | Spiders can be found in a variety of habitats. Many spiders inject venom during a bite, causing varying symptoms from mild discomfort to severe reactions. The bite site may show a small puncture wound or mark. |
| Bed Bug | A small, flat insect, typically reddish-brown in color. They are oval-shaped and have a nearly flat body. | Worldwide | Bed bugs are nocturnal and feed on human blood. They are often found in mattresses, bedding, and furniture. The bites usually appear as small, itchy welts or bumps, often in a linear pattern. |
Recognizing the Bite
Identifying the bug responsible for the bite is crucial, but recognizing the bite itself is equally important for proper treatment. Different bug bites exhibit varying symptoms, and understanding these symptoms can help you determine the appropriate course of action. Knowing what to look for will allow you to seek timely and effective treatment, preventing potential complications.
So, you’ve got a pesky bug bite? First, clean the area gently with soap and water. Then, apply a cool compress to reduce swelling. Interestingly, understanding different medical conditions, like the distinctions between diabetes insipidus vs mellitus, diabetes insipidus vs mellitus , can sometimes impact how you react to minor irritations. Finally, if the bite is bothering you significantly, see a doctor.
A doctor can give specific advice based on your individual needs.
Common Symptoms of a Bug Bite
Recognizing the symptoms of a bug bite is essential for effective treatment and preventing potential complications. Typical symptoms include itching, redness, swelling, and pain at the bite site. These reactions can vary depending on the individual and the type of bug.
Examples of Different Bite Marks
Bug bites often manifest in distinct ways. Pinpoint marks, indicating a small, localized puncture, are common. Larger, raised welts, or areas of swelling, can also be present. Sometimes, a red ring or a small blister can form around the puncture site. The size and appearance of the bite can offer clues to the type of insect that caused it.
Comparison of Bug Bite Symptoms
The following table provides a comparative overview of symptoms associated with bites from various insects. Note that individual reactions can vary.
| Insect | Typical Bite Marks | Common Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Mosquito | Small, pinpoint marks, often itchy. | Itching, redness, swelling, sometimes a small blister. |
| Bed Bug | Multiple small, reddish-brown marks, often in a linear pattern. | Itching, redness, swelling, sometimes tiny spots of blood. |
| Spider (e.g., Brown Recluse) | Initially, a small, barely noticeable mark. Later, a necrotic lesion (tissue death) may form. | Pain, redness, swelling, possible blistering, tissue damage. |
| Ant | Small, often painful puncture wounds, may be clustered. | Itching, redness, swelling, pain, possible allergic reactions. |
| Tick | Small, round, often a reddish-brown bump, with a possible attached tick. | Itching, redness, swelling, flu-like symptoms (in some cases), possible infection. |
Immediate Actions: How To Treat Bug Bites
Dealing with a bug bite swiftly and correctly can significantly influence the severity and duration of any discomfort or potential complications. Taking immediate action helps prevent infection and minimize the allergic reaction, if any. Prompt first aid can make a real difference in the healing process.A bite from an insect, whether it’s a bee, mosquito, spider, or other creature, can lead to a variety of reactions.
Some are minor, while others can be more serious. Understanding the immediate steps for managing a bug bite is crucial for ensuring the best possible outcome.
First Aid Procedures
Proper first aid procedures are essential for minimizing the impact of a bug bite. Prompt action reduces the risk of infection and allergic reactions. The first few minutes following a bite are critical.
- Cleaning the Wound: Thorough cleaning is vital to prevent infection. Gently wash the affected area with mild soap and lukewarm water. Use a clean cloth or cotton ball to avoid spreading germs. Avoid harsh scrubbing, which can irritate the skin further. A gentle, circular motion is recommended for cleaning.
- Removing Stingers: If a stinger remains embedded in the skin, carefully remove it using a flat object, like a credit card or a tweezers. Avoid squeezing the stinger, as this can release more venom into the wound. Grasp the stinger with the flat end of the tool and gently pull it straight out.
- Applying a Cold Compress: Applying a cold compress to the bite site can help reduce swelling and pain. A cool, wet cloth or ice pack wrapped in a thin towel can be used. Apply for 10-15 minutes at a time, several times a day. Excessive or prolonged cold application can also cause harm.
- Elevating the Affected Area: If the bite is on a limb, elevating it slightly above the heart can help reduce swelling. This is especially helpful for bites on the lower extremities.
- Monitoring for Allergic Reactions: Pay close attention to any signs of an allergic reaction, such as difficulty breathing, swelling of the face, throat, or tongue, hives, or dizziness. If such reactions occur, seek immediate medical attention. An allergic reaction can manifest in various ways, requiring prompt medical intervention.
Step-by-Step Guide to Cleaning and Caring for a Bug Bite
A systematic approach to cleaning and caring for a bug bite is critical for proper wound healing and minimizing discomfort.
- Assess the Bite: First, carefully examine the bite site. Identify the type of insect or arachnid responsible, if possible. This information can be valuable for treatment and follow-up care. Accurate identification can aid in determining the potential severity of the bite.
- Clean the Wound: Gently wash the bite site with mild soap and lukewarm water. Use a clean cloth or cotton ball to avoid spreading germs.
- Apply a Cold Compress: Wrap an ice pack or a cool, wet cloth in a thin towel and apply it to the bite for 10-15 minutes at a time. This helps to reduce swelling and pain.
- Monitor for Allergic Reactions: Watch for signs of an allergic reaction, such as swelling, hives, difficulty breathing, or dizziness. If any of these symptoms occur, seek immediate medical attention. Allergic reactions can range in severity, from mild discomfort to life-threatening conditions.
- Apply a Protective Barrier: Consider using a thin layer of antibiotic ointment to protect the bite site and prevent infection.
- Elevate the Area (Optional): If the bite is on a limb, elevating it slightly can help reduce swelling.
Home Remedies
So, you’ve identified the bug, recognized the bite, and taken immediate action. Now, let’s explore some common home remedies that might soothe the itch and reduce swelling. These remedies can be a helpful first step before seeking professional medical attention, especially for mild reactions. However, remember that these are just suggestions, and it’s crucial to monitor the bite closely for any signs of worsening symptoms.While many home remedies are generally safe, individual reactions can vary.
If you have any underlying health conditions or are unsure about a particular remedy, it’s best to consult with a healthcare professional before trying it. Some remedies might not be suitable for everyone, particularly those with allergies or sensitivities to certain ingredients.
Common Home Remedies for Bug Bites
A variety of common household items can provide temporary relief from the discomfort of bug bites. By understanding their potential effectiveness and safety, you can make informed choices about which remedies might work best for you.
| Remedy | Ingredients | Preparation | Effectiveness | Safety Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ice | Ice cubes or a cold pack | Apply a cold pack or ice wrapped in a cloth to the bite for 10-15 minutes at a time, several times a day. | Effective in reducing swelling and pain. The cold constricts blood vessels, lessening the inflammation. | Avoid applying ice directly to skin, as this can cause tissue damage. Always use a thin cloth or towel as a barrier. |
| Calamine Lotion | Active ingredient: Zinc oxide | Apply a thin layer of calamine lotion directly to the bite. | Effective in soothing itching and providing a cooling sensation. Zinc oxide can help dry up the blister and lessen inflammation. | Some individuals may be allergic to zinc oxide. Test a small area of skin before applying it to the entire bite. |
| Baking Soda Paste | Baking soda and water | Mix a small amount of baking soda with water to create a paste. Apply the paste to the bite and let it dry. | Baking soda has mild antiseptic properties and can help neutralize acids that may be contributing to the irritation. | Avoid applying baking soda paste to open wounds or sores. It might cause further irritation. |
| Aloe Vera Gel | Aloe vera plant | Extract fresh aloe vera gel from a leaf and apply it directly to the bite. | Known for its soothing and anti-inflammatory properties. It can help reduce itching and swelling. | Some individuals may have allergic reactions to aloe vera. Patch test before applying to a large area. |
| Over-the-counter hydrocortisone cream | Hydrocortisone | Apply a thin layer of cream to the bite as directed on the package. | Can reduce inflammation and itching, especially for more severe reactions. | Follow the dosage instructions carefully. Avoid using for prolonged periods without consulting a doctor. |
It’s important to remember that these remedies are often temporary solutions. If the bite becomes increasingly painful, swollen, or shows signs of infection (such as redness, warmth, pus, or fever), seek medical attention immediately. Prompt medical care can prevent complications and ensure proper treatment.
Over-the-Counter Treatments
Dealing with a bug bite can be irritating and uncomfortable. Fortunately, many over-the-counter (OTC) treatments can help manage the symptoms and promote healing. Understanding the various options and their potential benefits and drawbacks is crucial for choosing the most suitable treatment for your specific needs.Effective management of bug bite symptoms often involves using OTC medications to alleviate itching, reduce swelling, and promote healing.
Different OTC treatments vary in their active ingredients and mechanisms of action, leading to different efficacy and potential side effects. Choosing the right treatment is essential to ensure comfort and prevent complications.
Available OTC Medications
A variety of OTC medications are available to alleviate the discomfort and symptoms associated with bug bites. These include antihistamines, hydrocortisone cream, and topical pain relievers. Each option offers unique benefits, but also carries potential drawbacks.
Dealing with pesky bug bites? First, gently clean the area with mild soap and water. Then, apply a cool compress to soothe the itch. Knowing how many days a week you should exercise is crucial for overall health, but also for how you react to minor irritations like bug bites. For a deeper dive into that, check out this great resource on how many days a week should you exercise.
Finally, consider over-the-counter hydrocortisone cream to help reduce inflammation and itching.
Comparing Antihistamines
Antihistamines work by blocking the effects of histamine, a chemical released by the body in response to an allergic reaction, which often exacerbates itching. Oral antihistamines, like diphenhydramine (Benadryl), are effective in reducing itching and swelling. However, they may cause drowsiness as a side effect. Second-generation antihistamines, like loratadine (Claritin), are generally less sedating but may not be as effective for severe itching.
Dealing with itchy bug bites can be a real drag, but luckily, simple remedies often do the trick. A cool compress and some hydrocortisone cream usually soothe the irritation. However, if the bites are severe or numerous, it’s wise to consider other options. Learning about the prognosis of conditions like metastatic breast cancer, for example, can be emotionally challenging, but also very informative.
Understanding the different treatments and potential outcomes for these types of cancers is key. metastatic breast cancer prognosis Ultimately, remember to keep the bite area clean and avoid scratching, as this can lead to infection. A little TLC goes a long way in getting rid of those pesky bug bites!
Hydrocortisone Creams
Hydrocortisone creams are topical corticosteroids that reduce inflammation and itching. They are particularly useful for localized swelling and redness. The strength of hydrocortisone cream varies, with higher concentrations offering greater anti-inflammatory effects. However, prolonged use of high-strength hydrocortisone cream can lead to skin thinning and other side effects.
Topical Pain Relievers
Topical pain relievers, such as menthol-containing creams or gels, provide temporary relief from itching and pain. Their cooling sensation can offer some soothing effect. However, these creams may not address the underlying inflammation or swelling caused by the bite.
OTC Treatment Comparison Table
| Treatment | Active Ingredient(s) | Benefits | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diphenhydramine (Benadryl) | Diphenhydramine | Effective for itching and swelling; available in various forms (oral, cream). | Drowsiness, dizziness, dry mouth, blurred vision. |
| Loratadine (Claritin) | Loratadine | Effective for itching and swelling; generally less sedating than diphenhydramine. | Headache, fatigue, upset stomach. |
| Hydrocortisone Cream (1%) | Hydrocortisone | Reduces inflammation and itching; suitable for localized reactions. | Skin thinning, skin irritation (with prolonged use), possible allergic reaction. |
| Menthol Cream | Menthol | Provides temporary cooling sensation, relieving itching and pain. | Possible skin irritation in sensitive individuals. |
When to Seek Medical Attention
Knowing when a bug bite warrants medical attention is crucial for preventing complications. Minor bites can often be treated at home, but some bites require immediate medical intervention to avoid serious health consequences. This section Artikels the situations where professional medical help is necessary.While most bug bites are harmless, certain bites can trigger severe allergic reactions or introduce infectious agents.
Prompt medical attention is essential to manage these potentially life-threatening situations.
Severe Allergic Reactions
A severe allergic reaction, or anaphylaxis, is a potentially life-threatening response to an insect bite. Symptoms can appear rapidly and include hives, swelling of the face, lips, or tongue, difficulty breathing, dizziness, or loss of consciousness. A person experiencing these symptoms needs immediate medical help. Early intervention with epinephrine (an auto-injector like an EpiPen) is crucial to reverse the effects of anaphylaxis.
Venomous Insect Bites
Some insects possess venom that can cause significant tissue damage or systemic illness. Bites from venomous insects like spiders, scorpions, or certain wasps and bees necessitate prompt medical evaluation. Symptoms of venom-related complications can range from localized pain and swelling to more serious systemic effects like fever, nausea, and difficulty swallowing.
Signs Requiring Immediate Medical Attention, How to treat bug bites
The following symptoms warrant immediate medical attention:
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing.
- Rapid, weak pulse.
- Swelling of the face, lips, or tongue.
- Severe itching or hives spreading rapidly.
- Persistent, severe pain at the bite site.
- Loss of consciousness.
- Fever and chills, especially after a suspected spider or scorpion bite.
- Signs of infection, such as increasing redness, warmth, swelling, or pus at the bite site.
These symptoms, alone or in combination, signal a need for urgent medical care.
Urgency Levels of Bug Bite Situations
The severity of a bug bite situation can be assessed by the symptoms and the insect involved. This table provides a general guideline for urgency levels:
| Urgency Level | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Immediate | Life-threatening symptoms; requires immediate medical attention (e.g., difficulty breathing, loss of consciousness, severe allergic reaction). | Anaphylactic shock, significant swelling of the airway, severe pain radiating from the bite site. |
| Urgent | Serious symptoms that could lead to complications if not treated promptly (e.g., severe pain, increasing swelling, signs of infection). | Significant swelling in a limb, difficulty swallowing, persistent fever. |
| Routine | Minor symptoms; can be treated at home with home remedies or over-the-counter medications (e.g., mild itching, slight swelling). | Localized itching, small, painless bite marks. |
This table is a general guide, and individual situations may vary. Always consult a healthcare professional if you are unsure about the severity of a bug bite.
Preventing Bug Bites
Staying safe from bug bites is crucial for avoiding the discomfort and potential complications associated with them. Effective prevention involves a multi-faceted approach, combining smart choices with appropriate tools. Understanding the behavior and habits of common biting insects allows you to take proactive steps to minimize your risk.Effective prevention strategies not only reduce the chance of being bitten but also protect you from the potential spread of diseases carried by certain insects.
Insect Repellents
Insect repellents are a cornerstone of bite prevention. Choosing the right repellent and using it correctly significantly impacts effectiveness. The active ingredients in repellents work by creating a barrier that interferes with the insect’s ability to detect and locate you.
- DEET-based repellents are generally considered the most effective, offering broad-spectrum protection against a wide range of insects. The concentration of DEET is important, as higher concentrations offer longer-lasting protection. However, excessive use or prolonged exposure can cause skin irritation or other adverse reactions. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully.
- Picaridin and IR3535 are other common active ingredients with generally good effectiveness and lower reported instances of skin irritation compared to DEET. These repellents are often a good alternative for those sensitive to DEET.
- Natural repellents, such as citronella, lemon eucalyptus, and oil of peppermint, may provide some protection, but their effectiveness is often less than that of chemical repellents. Their use is often suitable for localized protection or in specific situations, but not for extensive outdoor activities.
Protective Clothing
Appropriate clothing plays a significant role in preventing bug bites. Certain fabrics and designs offer a physical barrier against insects.
- Wearing long sleeves and pants, especially in areas with known insect activity, is an effective way to reduce exposed skin. Darker colors, for example, can attract certain insects. Light colors might be preferable.
- Using permethrin-treated clothing is another powerful method. Permethrin is a synthetic insecticide that repels insects and can be applied to clothing. This is particularly helpful for extended outdoor activities. The treatment, however, may need to be reapplied after washing.
- Consider wearing hats or head coverings to protect the head and neck, areas often targeted by insects. The efficacy of these measures depends on the insect species and the environment.
Environmental Considerations
Modifying your surroundings can also contribute to reducing the risk of bug bites.
- Eliminating standing water sources around your home, like stagnant water in flower pots or clogged gutters, reduces breeding grounds for mosquitoes and other insects.
- Inspecting your yard regularly for potential insect breeding sites and promptly addressing any issues can significantly decrease the local insect population. The effectiveness of this depends on how diligently this is carried out.
- Using insect traps or other pest control measures in your yard may reduce the number of insects in your area, but their effectiveness depends on the type of trap and the insect population.
Effectiveness Ratings (Illustrative Table)
This table provides a general overview of effectiveness ratings for various prevention methods. Note that effectiveness can vary based on specific conditions, including insect species, environmental factors, and individual susceptibility.
| Prevention Method | Effectiveness Rating (1-5, 5 being highest) |
|---|---|
| DEET-based repellents (high concentration) | 4 |
| Picaridin or IR3535 repellents | 3 |
| Permethrin-treated clothing | 5 |
| Long sleeves and pants | 3 |
| Eliminating standing water | 4 |
Bug Bite Prevention in Specific Environments
Staying safe from bug bites is crucial, especially when engaging in outdoor activities, camping, or traveling. Different environments present unique risks, requiring tailored preventative measures. Understanding these specifics can significantly reduce the likelihood of unwanted encounters with insects.Effective bug bite prevention hinges on understanding the habits and habitats of the insects most prevalent in a given environment. By anticipating where bugs might be, and what they need to thrive, we can employ targeted strategies to keep them away.
Outdoor Activities
Understanding the time of day and location is key to preventing bug bites during outdoor activities. Early mornings and evenings, when insects are most active, often present the highest risk. Choosing shaded areas and avoiding dense vegetation can also help minimize encounters.
- Apply insect repellent containing DEET, picaridin, or oil of lemon eucalyptus, as directed.
- Wear light-colored clothing that is long-sleeved and long-legged to cover exposed skin.
- Wear hats and socks to protect additional areas.
- Check for ticks after outdoor activities, especially if hiking in wooded areas.
Camping
Camping often brings a higher risk of bug bites due to the proximity to nature and increased time spent outdoors. Taking proactive steps is essential to avoid discomfort and potential health concerns.
- Set up camp away from dense vegetation and standing water, as these areas often attract mosquitoes and other biting insects.
- Use mosquito nets over beds or sleeping areas.
- Hang food and other attractants from trees, away from the ground.
- Apply insect repellent to exposed skin and clothing before going to sleep.
Travel
Travel, particularly to tropical or subtropical regions, can expose individuals to a wider array of biting insects. Adapting to local conditions and adopting specific precautions is crucial.
- Research the local insect population before traveling to a new destination.
- Use insect repellent containing DEET, picaridin, or oil of lemon eucalyptus, as directed.
- Wear protective clothing, including long-sleeved shirts, long pants, and hats.
- Inspect your clothing and body for insects after returning from the outdoor environment.
Prevention Strategies by Environment
| Environment Type | Recommended Prevention Strategies |
|---|---|
| Outdoor Activities | Apply insect repellent, wear protective clothing, choose shaded areas, check for ticks. |
| Camping | Set up camp away from dense vegetation, use mosquito nets, hang food, apply repellent before sleeping. |
| Travel | Research local insects, use insect repellent, wear protective clothing, inspect clothing and body upon return. |
Closing Summary
In conclusion, treating bug bites involves a multi-faceted approach that considers the specific bug, the bite’s symptoms, and the individual’s overall health. By understanding the various types of bites, implementing appropriate first aid, using home remedies, and knowing when to seek professional care, you can effectively manage these common annoyances. This guide equips you with the knowledge to handle bug bites confidently and safely, whether you’re enjoying the outdoors or simply relaxing at home.