Living with low platelets what you need to know. This guide delves into the complexities of low platelet counts, offering a comprehensive understanding of their impact on daily life. From understanding the role of platelets in blood clotting to navigating treatment options and lifestyle adjustments, this resource aims to empower you with the knowledge you need to effectively manage and live with this condition.
We’ll explore the causes, diagnosis, and various treatment options available. We’ll also address important lifestyle considerations and potential complications, equipping you with the tools to make informed decisions about your health. By the end, you’ll have a clearer picture of how to effectively manage your condition.
Understanding Low Platelet Counts
Low platelet counts, also known as thrombocytopenia, can be a serious health concern. Platelets, tiny blood cells, are crucial for blood clotting. When their numbers are too low, the body’s ability to stop bleeding is compromised, leading to various complications. This section will delve into the intricacies of low platelet counts, exploring their causes, symptoms, and potential treatments.Platelets play a vital role in the body’s natural clotting mechanisms.
They clump together at the site of an injury to form a plug, effectively sealing the wound and preventing excessive blood loss. A healthy range of platelets is essential for maintaining the body’s overall integrity and preventing bleeding.
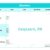
Normal Platelet Ranges
The normal range of platelets in healthy adults typically falls between 150,000 and 450,000 platelets per microliter of blood. Values outside this range may indicate a problem that needs medical attention. Significant deviations from this normal range can increase the risk of spontaneous bleeding, bruising, and other complications.
Consequences of Low Platelet Counts
When platelet counts are significantly lower than the normal range, the body’s ability to clot blood effectively is impaired. This can lead to an increased risk of bleeding from minor cuts, spontaneous bruising, and even internal bleeding. In severe cases, even minor injuries can cause substantial blood loss, necessitating immediate medical intervention.
Symptoms of Thrombocytopenia
Symptoms of low platelet counts can vary depending on the severity of the condition. Common symptoms include easy bruising, prolonged bleeding from cuts, nosebleeds, bleeding gums, and petechiae (tiny red or purple spots on the skin). Internal bleeding, though less common, can also occur and manifest as abdominal pain, back pain, or headaches. It is crucial to note that some individuals may not experience any noticeable symptoms at all, especially with mild reductions in platelet counts.
Types of Low Platelet Disorders
Low platelet disorders can be broadly categorized into several types, each with its own unique characteristics. Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) is an autoimmune disorder where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks platelets. Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) is a rare condition triggered by exposure to heparin, an anticoagulant medication. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) is a more severe condition characterized by the formation of blood clots within small blood vessels.
These disorders have varying causes and require different treatment approaches.
Causes of Low Platelet Counts
Various factors can contribute to low platelet counts. Infections, such as viral infections or bacterial sepsis, can sometimes lead to a reduction in platelet production. Certain medications, including some chemotherapy drugs, can also suppress platelet production. Autoimmune diseases, such as lupus or rheumatoid arthritis, can sometimes trigger the destruction of platelets. In some cases, the underlying cause remains unknown.
Table of Low Platelet Disorders
| Disorder | Common Symptoms | Potential Causes | Treatment Approaches |
|---|---|---|---|
| Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP) | Easy bruising, petechiae, prolonged bleeding | Autoimmune response | Corticosteroids, intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), splenectomy |
| Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia (HIT) | Low platelet count, blood clots | Exposure to heparin | Discontinuation of heparin, alternative anticoagulants |
| Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (TTP) | Neurological symptoms, kidney problems | Deficiency in ADAMTS13 enzyme | Plasma exchange, medications |
| Medication-Induced Thrombocytopenia | Low platelet count, bleeding | Certain medications (e.g., chemotherapy drugs) | Discontinuation of the medication, supportive care |
Diagnosis and Testing
Low platelet counts, or thrombocytopenia, require careful diagnosis to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment. This process often involves a series of tests and a thorough medical history review. Understanding the diagnostic steps can empower individuals to actively participate in their care.Accurate diagnosis of low platelet counts is crucial to effectively manage the condition. Incorrect diagnosis can lead to delayed or inappropriate treatment, potentially causing complications.
Early and accurate diagnosis allows for timely intervention and prevents potential serious health risks.
Blood Tests for Platelet Counts
A crucial aspect of diagnosing low platelet counts is the use of blood tests. These tests provide essential information about the number and health of platelets in the blood.
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): A CBC is a fundamental blood test that provides a comprehensive overview of various blood components, including platelets. The CBC measures the number of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. This test is essential for identifying a broad range of potential health problems, including low platelet counts.
- Platelet Count: This specific test directly measures the number of platelets present in a blood sample. It’s often performed in conjunction with a CBC to confirm and quantify the low platelet count. A low platelet count, as determined by this test, often triggers further investigation into the underlying cause.
- Peripheral Blood Smear: This microscopic examination of a blood sample allows for detailed visualization of blood cells, including platelets. It can help determine the size, shape, and other characteristics of platelets, providing valuable clues about the potential cause of thrombocytopenia. This detailed examination aids in identifying any abnormalities or irregularities in the platelet morphology.
Step-by-Step Procedure for a CBC and Platelet Count
The process for a complete blood count (CBC) and platelet count test typically involves these steps:
- Blood Collection: A blood sample is collected from a vein, usually in the arm, using a sterile needle. The collected blood is then carefully transferred to a test tube.
- Laboratory Analysis: The blood sample is sent to a laboratory for analysis. Specialized laboratory equipment and trained technicians perform the required tests to determine the platelet count and other blood cell counts.
- Result Interpretation: The laboratory reports the results, which include the platelet count along with other relevant blood parameters. A healthcare professional will interpret these results in the context of the patient’s medical history and symptoms.
Importance of Medical History
A thorough medical history plays a critical role in diagnosing low platelet counts. Information about past illnesses, medications, and family history can provide crucial clues about the underlying cause. For instance, a patient with a history of autoimmune diseases might be more likely to have immune-mediated thrombocytopenia.
Potential Complications of Undiagnosed Low Platelet Counts
Undiagnosed or inadequately managed low platelet counts can lead to various complications. An increased risk of bleeding, ranging from minor bruising to severe internal bleeding, is a significant concern. Delayed diagnosis can also hinder effective treatment, potentially leading to more severe consequences.
Comparison of Diagnostic Tests
| Test | Accuracy | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Complete Blood Count (CBC) | High | Provides a broad overview of blood cell counts, including platelets. Useful for initial screening. |
| Platelet Count | High | Directly measures platelet count, confirming the presence of thrombocytopenia. |
| Peripheral Blood Smear | Moderate to High | Microscopic examination of blood cells, providing detailed information about platelet morphology and aiding in identifying potential causes. |
Treatment Options
Navigating low platelet counts can feel overwhelming. Fortunately, various treatment approaches exist, aiming to increase platelet production or prevent further decline. Understanding these options, alongside potential side effects and monitoring strategies, is crucial for effective management.Treatment for low platelets hinges significantly on identifying the underlying cause. Different causes necessitate different treatment plans, and some cases may require a combination of approaches.
Living with low platelets can be tricky, and understanding the nuances is key. While a healthy diet is important, discovering how a high protein fat breakfast can impact your overall health, like potentially reducing your A1C levels, is also beneficial. Check out this great resource on high protein fat breakfast can reduce a1c for more information.
Ultimately, managing low platelets involves a holistic approach, considering your dietary choices alongside other lifestyle factors.
Monitoring platelet counts and adjusting the treatment plan as needed is essential to ensure the best possible outcome.
Common Treatment Approaches
Treatment strategies for low platelet counts often involve addressing the root cause. If the low platelet count is due to an underlying medical condition, treating that condition is paramount. This might involve medications, lifestyle changes, or even surgical interventions. If the cause is medication-related, switching to a different medication or adjusting the dosage can be beneficial. Supportive care, including blood transfusions or platelet transfusions, may be necessary to manage symptoms and prevent complications.
Potential Medications Affecting Platelet Counts
Certain medications can impact platelet production or function. For instance, some chemotherapy drugs and anti-inflammatory medications can lower platelet counts. Similarly, some herbal supplements may also interact with platelet function. It is crucial to discuss all medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, with a healthcare provider to assess potential effects on platelet counts.
Role of Supportive Care
Supportive care plays a vital role in managing low platelet counts. This can include blood transfusions or platelet transfusions to increase the platelet count quickly, especially when the count is dangerously low. Monitoring for signs of bleeding, such as easy bruising or prolonged bleeding from cuts, is critical. Maintaining a healthy diet and avoiding activities that could increase the risk of injury is also part of supportive care.
Importance of Monitoring Platelet Counts During Treatment
Regular monitoring of platelet counts is essential during treatment. This allows healthcare providers to track the effectiveness of the treatment plan and make necessary adjustments. Changes in platelet counts can indicate the need for dosage adjustments or alternative treatment strategies. Furthermore, monitoring platelet counts helps detect any potential complications or side effects that may arise from treatment.
Living with low platelets can be tricky, and understanding the underlying factors is key. One important aspect to consider is the partial pressure of oxygen, or PaO2, which can be affected by various conditions. Knowing your partial pressure of oyxgen pa02 levels can help your doctor assess your overall health and determine the best course of action for managing your low platelet count.
Ultimately, a comprehensive approach is crucial for effectively living with low platelets.
Comparison of Treatment Options Based on Underlying Cause
The best treatment option depends heavily on the underlying cause of the low platelet count. For example, if the cause is an autoimmune condition, immunosuppressive medications may be necessary. If the cause is a viral infection, supportive care and monitoring are often sufficient. If the cause is medication-induced, discontinuing or modifying the medication may be the solution.
Treatment Options Table
| Treatment Option | Potential Side Effects | Underlying Cause Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Medication Adjustments (e.g., changing or reducing dosage) | Possible worsening of underlying condition, emergence of new side effects | Medication-induced thrombocytopenia, certain medical conditions |
| Immunosuppressive Medications | Increased risk of infection, other immune system issues | Autoimmune conditions causing low platelets |
| Blood/Platelet Transfusions | Reactions to the transfusion, infection risk | Severe thrombocytopenia requiring rapid intervention |
| Treating Underlying Condition | Side effects associated with the specific treatment for the underlying condition | Infections, autoimmune diseases, cancers |
Lifestyle Considerations
Living with low platelets requires careful attention to lifestyle choices. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is crucial for supporting platelet production and reducing the risk of complications. A balanced approach encompassing diet, exercise, and stress management plays a vital role in overall well-being and platelet health.Adopting a healthy lifestyle is not just about feeling better; it’s a proactive measure to support your body’s natural healing processes.
This includes focusing on nutritious foods, incorporating regular physical activity, and finding healthy ways to manage stress. By making these conscious choices, you can actively participate in your health journey and improve your overall quality of life.
Living with low platelets can be tricky, and understanding the potential impact on your overall health is key. One aspect often overlooked is how dietary choices, like artificial sweeteners, might affect your kidneys. Researching the effects of these sweeteners on kidney health is important, as artificial sweeteners effects on the kidneys could potentially influence your body’s ability to manage platelets.
Ultimately, knowing what you can and can’t consume is part of responsible management when dealing with low platelets.
Importance of a Healthy Diet
A well-balanced diet rich in essential nutrients is fundamental for optimal platelet production. Nutrients like iron, vitamin B12, and folate are critical for the formation of healthy blood cells, including platelets. Choosing the right foods can significantly impact platelet counts and overall health.
Foods Rich in Nutrients Supporting Platelet Production
A variety of foods contribute to healthy platelet counts. Leafy green vegetables like spinach and kale are excellent sources of folate, a crucial nutrient for red blood cell and platelet production. Lean meats, poultry, and fish provide iron, essential for hemoglobin production and indirectly supporting platelet function. Eggs and dairy products are rich in vitamin B12, which is vital for cell growth and division.
Furthermore, fruits like berries and citrus fruits offer antioxidants, which can protect cells from damage. These examples demonstrate the importance of a diverse and nutrient-rich diet.
Impact of Exercise on Platelet Counts
Regular exercise can positively influence platelet counts. Moderate-intensity aerobic activities, such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling, can promote overall cardiovascular health, potentially supporting platelet production. However, strenuous exercise or activities that increase the risk of injury should be approached cautiously to avoid bleeding complications.
Avoiding Activities that Increase Bleeding Risk
Individuals with low platelet counts need to be mindful of activities that could increase the risk of bleeding. Avoiding contact sports, activities involving strenuous physical exertion, and potentially risky or harmful behaviors is essential to prevent injury and potential complications. This is particularly important for those with significantly reduced platelet counts.
Stress Management Techniques
Chronic stress can negatively impact various bodily functions, potentially affecting platelet counts. Implementing stress-reducing techniques such as yoga, meditation, deep breathing exercises, or spending time in nature can promote overall well-being and contribute to maintaining stable platelet levels. Finding healthy ways to manage stress is an integral part of overall health management.
Dietary Recommendations for Individuals with Low Platelets
| Nutrient | Food Sources | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Iron | Red meat, poultry, fish, beans, lentils, spinach | Essential for hemoglobin production, indirectly supporting platelet function. |
| Folate | Leafy green vegetables, citrus fruits, beans, lentils | Crucial for red blood cell and platelet production. |
| Vitamin B12 | Meat, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy products | Vital for cell growth and division, including platelet production. |
| Vitamin C | Citrus fruits, berries, peppers | Supports iron absorption and overall immune function. |
| Protein | Lean meats, poultry, fish, beans, lentils, eggs | Essential for cell repair and growth, including platelets. |
Monitoring and Management
Living with a low platelet count requires proactive monitoring and management to prevent complications. Regular check-ups and understanding potential warning signs are crucial for maintaining good health and well-being. This section will delve into the importance of ongoing care and how to stay informed about your condition.Ongoing monitoring is key to preventing serious complications and ensuring that any issues are addressed promptly.
This proactive approach allows for early intervention and helps to maintain a healthy platelet count.
Importance of Regular Check-ups
Regular check-ups with your doctor are essential for individuals with low platelets. These appointments allow your doctor to assess your overall health, monitor your platelet count, and adjust your treatment plan as needed. Consistent monitoring allows your healthcare team to catch any developing problems early, enabling prompt intervention. They can also evaluate the effectiveness of current treatments and make adjustments as necessary.
Monitoring Platelet Counts at Home
While you cannot directly measure your platelet count at home, you can actively participate in monitoring your general well-being. This includes noting any unusual symptoms, like easy bruising, or increased bleeding. It’s vital to communicate these observations to your doctor during appointments. This helps them understand the nuances of your condition and allows for more informed decisions about treatment and management.
Situations Requiring Immediate Medical Attention
Certain situations warrant immediate medical attention. These include significant bleeding, such as prolonged bleeding from cuts or injuries, or signs of internal bleeding, like severe abdominal pain or persistent vomiting of blood. Headaches that are unusually severe or accompanied by vision changes, or any sign of neurological distress should also be immediately addressed. Always prioritize seeking immediate medical care in these circumstances.
Signs and Symptoms to Watch Out For
Recognizing potential complications is crucial for timely intervention. Look out for excessive bruising, unexplained bleeding from nose or gums, heavy menstrual bleeding in women, or blood in urine or stool. Any signs of infection, such as fever, chills, or fatigue, should also be reported. Recognizing these symptoms early enables prompt treatment and prevents potential complications.
- Excessive bruising: This can manifest as easy bruising, even with minor impacts.
- Unexplained bleeding: This includes prolonged bleeding from cuts, nosebleeds, or bleeding gums.
- Blood in urine or stool: These signs can indicate internal bleeding and need immediate medical attention.
- Severe headache: Especially if accompanied by vision changes or neurological symptoms.
- Signs of infection: Such as fever, chills, or fatigue.
- Abdominal pain: Severe or persistent pain may indicate internal bleeding.
- Persistent vomiting of blood: A clear indication of internal bleeding that requires urgent medical care.
Essential Steps for Managing Low Platelets
Effective management of low platelets involves a multi-faceted approach. Adhering to your treatment plan, taking medications as prescribed, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle are essential components. Avoiding activities that could increase the risk of injury or bleeding, such as contact sports, are also vital. Maintaining open communication with your healthcare team is crucial for tailoring your care to your specific needs.
- Adhere to your treatment plan: This includes taking medications as prescribed and attending all scheduled appointments.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle: This includes a balanced diet, regular exercise (within safe limits), and adequate rest.
- Avoid activities that could increase the risk of injury or bleeding: Contact sports or activities with a high risk of falls should be avoided.
- Maintain open communication with your healthcare team: Regularly discussing your symptoms and concerns with your doctor is essential.
- Report any changes in your health: Promptly reporting any new symptoms or concerns to your doctor is critical.
Potential Complications and Warning Signs
Recognizing potential complications and their associated warning signs can be crucial for timely intervention. The table below provides a summary of potential complications and their early indicators.
| Potential Complications | Warning Signs |
|---|---|
| Internal Bleeding | Severe abdominal pain, persistent vomiting of blood, blood in urine or stool, unusual bruising |
| Infection | Fever, chills, fatigue, increased pain or tenderness in an area |
| Thrombocytopenia-induced purpura (ITP) | Unexplained bruising, prolonged bleeding, bleeding from the gums, nosebleeds, blood in the urine or stool |
| Bleeding Disorders | Excessive bruising, prolonged bleeding from minor cuts or injuries |
Potential Complications
Living with a low platelet count can introduce a range of potential complications. Understanding these risks is crucial for proactive management and ensuring optimal health. While treatments aim to restore platelet levels, the underlying cause and the treatments themselves can sometimes lead to unforeseen challenges. This section delves into the potential difficulties associated with low platelets, emphasizing the importance of open communication with healthcare providers.
Risks Associated with Bleeding
Low platelet counts significantly increase the risk of bleeding, both internally and externally. This heightened susceptibility to bleeding can manifest in various ways, from minor bruising to severe internal hemorrhages. Individuals with low platelet counts should be vigilant about any signs of unusual bleeding, such as prolonged bleeding from cuts, easy bruising, or unexplained nosebleeds.
Potential Complications from Treatments
Certain treatments for low platelet counts can have associated risks. For instance, some medications used to stimulate platelet production may cause side effects like fever, nausea, or headache. Blood transfusions, while vital in some cases, carry the risk of adverse reactions, such as allergic responses or infections. Careful monitoring and prompt management of any side effects are essential.
Complications Specific to Underlying Causes, Living with low platelets what you need to know
The specific underlying cause of thrombocytopenia can influence the potential complications. For example, if the cause is an autoimmune disorder, the complications might include other autoimmune conditions or organ damage. If the cause is a medication, discontinuation of the medication might resolve the issue, but there could be repercussions. Infections, if present, may lead to further complications.
Understanding the root cause is paramount for targeted and effective management.
Situations Requiring Immediate Medical Intervention
Certain situations demand immediate medical attention. Severe bleeding, such as internal bleeding or significant blood loss, requires immediate intervention. Similarly, any signs of an allergic reaction to medication or blood transfusions should be addressed immediately. A sudden and significant drop in platelet counts may indicate a critical condition requiring immediate medical attention. Recognizing these warning signs is crucial for seeking prompt medical help.
Table of Potential Complications and Associated Risks
| Potential Complication | Associated Risk |
|---|---|
| Excessive bleeding | Internal or external bleeding, potentially life-threatening |
| Side effects from medication | Nausea, fever, allergic reactions, or other adverse events |
| Blood transfusions | Allergic reactions, infections, or other complications |
| Complications from underlying causes | Organ damage, other autoimmune conditions, or infection, depending on the specific cause |
| Sudden and significant drop in platelet counts | Critical condition requiring immediate medical attention |
Living with Low Platelets
Living with a low platelet count, or thrombocytopenia, can be challenging, but with proper management and a proactive approach, it’s possible to lead a fulfilling life. This section focuses on practical strategies for adapting daily activities, managing potential risks, and maintaining a positive outlook. Understanding the psychological impact of this chronic condition is also crucial for overall well-being.Living with low platelets requires careful consideration of daily activities and potential risks.
Maintaining a safe environment and adjusting lifestyle choices are essential for minimizing bleeding complications. This includes being mindful of activities that could increase the risk of injury.
Adapting Daily Activities
Careful planning and adjustments to daily routines are key to managing the risks associated with low platelets. This involves understanding which activities might increase the risk of bleeding and modifying them accordingly.
- Avoiding High-Impact Activities: Activities that involve a high risk of falls or collisions, such as contact sports (football, hockey), vigorous exercise like running or jumping, and activities that require forceful movements should be approached cautiously or avoided altogether.
- Modifying Physical Activities: For activities like walking or swimming, consider using appropriate safety measures. Avoid walking or running on uneven surfaces. Use assistive devices if necessary and wear appropriate protective gear like knee and elbow pads for certain activities.
- Protecting Skin: Be cautious about activities that could cause skin abrasions or cuts. Use protective clothing, avoid sharp objects, and apply pressure to any cuts or bruises for an extended period.
Precautions During Physical Activities
Taking proactive measures to minimize the risk of injury is crucial for maintaining safety.
- Soft Surfaces: Choose surfaces that are soft and less likely to cause injury, such as grass or a gym floor with padding.
- Avoiding Rough Play: Limit activities involving rough play or contact with others, particularly when engaging in sports or recreational activities.
- Proper Equipment: Use appropriate safety equipment, such as helmets, pads, or braces, when engaging in activities that carry a higher risk of injury.
Psychological Impact of a Chronic Condition
Living with a chronic condition like low platelets can have a significant psychological impact. Coping mechanisms and support systems are vital to maintain emotional well-being.
- Managing Stress: Develop strategies to manage stress, such as relaxation techniques, mindfulness, or engaging in activities that promote relaxation and reduce anxiety.
- Seeking Support: Don’t hesitate to seek support from mental health professionals, support groups, or family and friends.
- Maintaining a Positive Outlook: Focus on positive aspects of life and cultivate a sense of optimism.
Maintaining a Positive Outlook
A positive outlook is crucial for managing the emotional challenges associated with living with a chronic condition.
- Focus on Strengths: Identify and celebrate personal strengths and accomplishments.
- Building a Support System: Connect with friends, family, or support groups to share experiences and provide mutual encouragement.
- Practicing Self-Care: Engage in activities that promote relaxation and well-being, such as hobbies, meditation, or spending time in nature.
Support Groups and Resources
Connecting with others facing similar challenges can provide valuable support and encouragement.
- Online Forums: Online support groups and forums can connect individuals with low platelets with others who share similar experiences.
- Support Groups: Local support groups can provide opportunities for in-person connection and support.
- Healthcare Professionals: Healthcare professionals can provide guidance and resources for accessing support systems.
Helpful Tips for Daily Living
This table Artikels practical strategies for managing daily activities and minimizing risks associated with low platelets.
| Activity | Tips for Managing Risks |
|---|---|
| Household Chores | Avoid tasks involving sharp objects or heavy lifting. Use protective gear where needed. |
| Outdoor Activities | Choose soft surfaces for walking and playing. Avoid rough play or activities that could cause falls. |
| Exercise | Choose activities with low impact. Use proper equipment and clothing. |
| Travel | Plan ahead and inform transportation providers of the condition. Carry emergency supplies. |
Closing Summary: Living With Low Platelets What You Need To Know
In conclusion, living with low platelets requires a multifaceted approach. Understanding the condition, seeking proper diagnosis, and adhering to a treatment plan are crucial steps. By adopting healthy lifestyle choices and seeking support when needed, you can significantly improve your quality of life. Remember, proactive management and open communication with your healthcare provider are key to navigating this condition successfully.