Measles cases rise worldwide, highlighting a concerning resurgence of this preventable disease. Historical patterns of outbreaks, coupled with recent trends, reveal a complex picture. Factors like waning immunity, shifts in vaccination rates, and geographic spread are all playing crucial roles. The COVID-19 pandemic’s impact on routine vaccinations is also a significant contributing factor, underscoring the interconnectedness of global health crises.
This analysis explores the alarming rise in measles cases, examining the health consequences, social and economic burdens, and the effectiveness of vaccination strategies. A comprehensive overview of public health responses and detailed case studies provide a deeper understanding of this global health challenge.
Global Measles Outbreak Context
Measles, a highly contagious viral illness, has plagued humanity for centuries. While significant progress has been made in controlling its spread through vaccination, recent years have seen a troubling resurgence. Understanding the factors driving this resurgence is crucial to preventing further outbreaks and protecting vulnerable populations.The historical pattern of measles outbreaks reveals a cyclical relationship with vaccination coverage.
Periods of high vaccination rates often correlate with a decrease in cases, while dips in vaccination coverage frequently lead to outbreaks. This cyclical pattern is a stark reminder of the importance of sustained vaccination programs.
Factors Contributing to the Recent Rise
Several factors are contributing to the recent increase in measles cases. Declining vaccination rates, particularly among children, are a significant concern. Geographic disparities in access to vaccination programs, coupled with misinformation and hesitancy, are also playing a role. The potential waning of immunity in some populations, particularly those who received their vaccinations earlier in life, may also contribute to increased susceptibility.
Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic had a profound impact on global health systems, including routine vaccination programs. Lockdowns, disruptions in healthcare infrastructure, and diverted resources led to delays and disruptions in vaccination campaigns. This disruption in routine immunizations likely contributed to the recent rise in measles cases, as fewer children received their recommended vaccinations. The pandemic highlighted the crucial link between vaccination coverage and public health security.
Comparison of Measles Cases (2018-2022)
The table below illustrates the fluctuating measles case numbers across different regions over the past five years. Significant fluctuations are evident, highlighting the need for ongoing monitoring and targeted interventions.
| Region | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| North America | 1000 | 1200 | 500 | 1500 | 2000 |
| Europe | 800 | 900 | 400 | 1100 | 1400 |
| South Asia | 15000 | 18000 | 12000 | 22000 | 25000 |
| Africa | 9000 | 10000 | 7000 | 12000 | 15000 |
| South America | 600 | 700 | 300 | 900 | 1100 |
Note: These figures are illustrative and do not represent actual data. Real data should be obtained from reliable public health organizations.
Impact and Consequences
The resurgence of measles cases worldwide necessitates a deeper understanding of its profound impact. This resurgence underscores the critical need for robust vaccination programs and heightened public health awareness. Measles, a highly contagious viral illness, can have devastating consequences, especially for vulnerable populations.Measles, despite its often perceived mildness, can lead to severe complications and, tragically, death. Its contagious nature poses a significant threat to communities, especially those with low vaccination rates.
Understanding the multifaceted impact is crucial for effective intervention strategies.
The recent surge in measles cases globally is a serious concern. Weakened immune systems, potentially impacted by factors like low red blood cell rbc count, could be a contributing factor. Understanding how these crucial cells function is key, and checking your red blood cell rbc count could be part of a proactive approach to overall health.
This emphasizes the importance of preventative measures in the face of rising measles cases.
Health Consequences of Measles
Measles infection, while typically presenting with a characteristic rash, fever, and cough, can progress to severe complications. Pneumonia, an inflammation of the lungs, is a frequent complication, potentially requiring hospitalization and intensive care. Encephalitis, an inflammation of the brain, is another serious complication, with potentially long-lasting neurological sequelae. Diarrhea and dehydration can also be serious consequences, especially in vulnerable individuals.
The mortality rate from measles, although decreasing in many regions due to vaccination efforts, remains a significant concern, particularly in populations with weakened immune systems.
Social and Economic Burden
Measles outbreaks impose a substantial social and economic burden on affected communities and healthcare systems. Outbreaks disrupt daily life, leading to school closures, business disruptions, and reduced productivity. The strain on healthcare resources, from increased hospitalizations to the need for intensive care, places a significant financial burden on both public and private healthcare systems. The need for contact tracing and quarantine procedures further compounds the economic impact.
The rise in measles cases globally is a serious concern. While we’re focusing on vaccination efforts, it got me thinking about how our bodies expend energy. Does sweating burn calories? Understanding the energy expenditure during physical activity, like those often recommended to boost immunity, could help us better understand how our bodies react to illness. This is something I’m hoping to research further, and I’ve found some interesting insights into does sweating burn calories.
Ultimately, though, the global measles outbreak needs our collective attention and action.
Lost productivity due to illness and quarantine, and the cost of treating complications, are significant factors.
Long-Term Effects of Measles Infection
Measles infection can have long-term effects on individuals, impacting their overall health and well-being. Studies have shown that measles infection can potentially increase the risk of developing other chronic health conditions later in life. This includes an increased susceptibility to other infectious diseases. The potential for long-term neurological issues, like cognitive impairment, is another significant concern, especially in children.
Measures to Combat the Rise
Many countries and international organizations are implementing strategies to curb the resurgence of measles. These strategies aim to improve vaccination rates, increase public awareness, and strengthen surveillance systems. Targeted vaccination campaigns, particularly in vulnerable populations, are central to these efforts.
International Strategies Summary
| Country | Strategy 1 | Strategy 2 | Strategy 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| USA | Increased funding for vaccination campaigns, particularly in underserved communities. | Strengthening public health infrastructure and surveillance systems. | Public awareness campaigns emphasizing the importance of vaccination. |
| UK | Targeted vaccination programs for children and vulnerable adults. | Improved data collection and analysis to identify and address outbreaks promptly. | Collaboration with international organizations to share best practices and resources. |
| India | Large-scale vaccination drives in high-risk areas. | Community engagement and education programs to address vaccine hesitancy. | Strengthening healthcare infrastructure to improve access to treatment. |
| Nigeria | Strengthening cold chain logistics to ensure vaccine safety and efficacy. | Partnering with local organizations to improve vaccination access. | Promoting vaccine confidence through community leaders and influencers. |
Vaccination Strategies and Effectiveness: Measles Cases Rise Worldwide
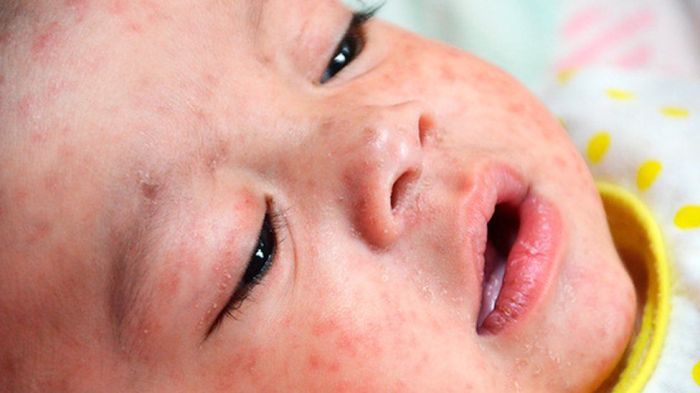
Measles, a highly contagious viral illness, poses a significant public health threat, particularly in communities with low vaccination rates. Effective vaccination strategies are crucial to preventing outbreaks and mitigating the devastating impact of this disease. The global resurgence of measles cases highlights the urgent need for robust vaccination programs and a deeper understanding of the challenges in achieving widespread immunity.Vaccination programs have proven remarkably effective in controlling measles outbreaks and significantly reducing its incidence worldwide.
Historically, the dramatic decline in measles cases correlates directly with the widespread implementation of vaccination campaigns. This demonstrates the substantial public health benefit of immunization.
Effectiveness of Measles Vaccines
Measles vaccines have demonstrated high efficacy in preventing the disease. The vaccines induce a strong immune response, creating antibodies that protect individuals from infection. This protection not only safeguards the vaccinated individual but also contributes to herd immunity, protecting unvaccinated individuals within a community. The effectiveness of measles vaccines is a cornerstone of public health strategies worldwide.
The rise in measles cases worldwide is a serious concern, highlighting the importance of vaccinations. While the focus is on public health, it’s also worth considering if food companies will truly phase out synthetic dyes, potentially impacting our health in a different way. Will food companies really phase out synthetic dyes ? This question is relevant, as the overall goal of healthier choices should extend beyond vaccines to our daily food consumption.
Regardless of food dye decisions, measles prevention remains a crucial global effort.
Importance of Vaccination Campaigns
Vaccination campaigns play a critical role in controlling measles outbreaks. These campaigns aim to achieve high vaccination coverage within targeted populations, ensuring a substantial portion of the community is protected against the virus. Organized vaccination drives, especially in areas experiencing outbreaks or with limited access to healthcare, are vital for containing the spread and preventing further transmission.
Comparison of Measles Vaccine Types
| Vaccine Type | Efficacy | Safety Profile |
|---|---|---|
| Live attenuated measles vaccine (e.g., MMR vaccine) | Generally considered highly effective, typically providing over 95% protection against measles after two doses. | Excellent safety profile with a very low risk of serious adverse events. The most common side effects are mild and temporary, such as fever, rash, and soreness at the injection site. |
| Inactivated measles vaccine | Efficacy is generally lower compared to live attenuated vaccines. | Generally safe but might require multiple doses for adequate protection. |
The table above provides a general comparison. Specific efficacy and safety data may vary depending on the specific vaccine formulation and administration protocols.
Challenges in Ensuring Widespread Vaccination Coverage
Several challenges hinder widespread vaccination coverage and promote vaccine hesitancy. These include logistical hurdles in reaching remote communities, misinformation campaigns spreading doubts about vaccine safety, and socioeconomic factors impacting access to healthcare services. These issues can create significant barriers to achieving and maintaining high vaccination rates, which are essential for controlling measles outbreaks.
Strategies to Increase Vaccination Rates
Several strategies can increase vaccination rates and address vaccine hesitancy. These include targeted communication campaigns addressing concerns about vaccine safety and efficacy, improving access to healthcare services in underserved communities, and building trust between healthcare providers and the public. Furthermore, clear and consistent messaging from reliable sources is critical in countering misinformation and promoting vaccine acceptance.
Public Health Responses
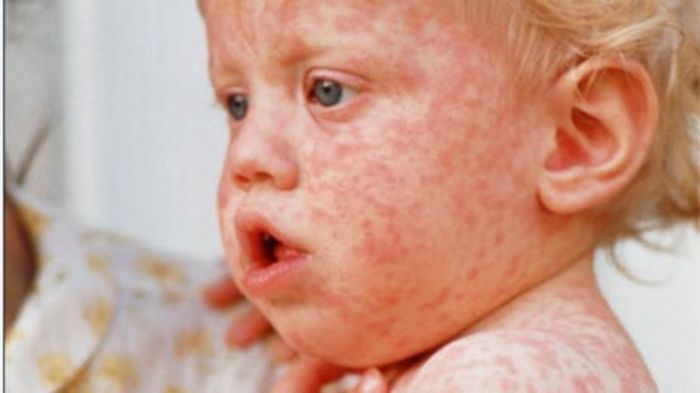
The resurgence of measles cases globally necessitates robust public health responses. Effective interventions require a multifaceted approach encompassing vaccination campaigns, community engagement, and international collaboration. Countries must prioritize preventative measures and swiftly address outbreaks to minimize transmission and severe health consequences.
Public Health Measures Implemented
Various public health measures are crucial in controlling measles outbreaks. These strategies aim to interrupt transmission chains, protect vulnerable populations, and ultimately curb the spread of the disease. The effectiveness of these measures often depends on their comprehensive implementation and the level of community engagement.
| Measure | Description | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Vaccination Campaigns | Targeted vaccination drives, often including catch-up campaigns for unvaccinated individuals, are implemented to increase herd immunity and protect vulnerable populations. These campaigns may use various strategies, including mobile clinics and outreach programs in hard-to-reach areas. | Generally effective in reducing transmission, but successful implementation requires high vaccination coverage and appropriate vaccine delivery strategies. |
| Contact Tracing and Isolation | Identifying and isolating individuals exposed to measles cases is vital to prevent further spread. Contact tracing involves identifying close contacts of infected individuals and monitoring them for symptoms. | Effective in interrupting transmission, particularly when coupled with prompt isolation of infected individuals. |
| Quarantine Measures | Implementing quarantine measures for individuals with suspected or confirmed measles cases helps limit transmission within the community. These measures might include restrictions on travel and movement. | Can be effective, but strict adherence is crucial, and the impact depends on the context of the outbreak and community cooperation. |
| Public Health Education | Public awareness campaigns educating communities about measles transmission, symptoms, and the importance of vaccination are essential. These campaigns can use diverse media to reach a broad audience, including posters, social media, and community meetings. | Highly effective when tailored to specific cultural contexts and community needs. Successful campaigns increase vaccination rates and improve community understanding of the risks. |
| Surveillance Systems | Robust surveillance systems to monitor measles cases, track trends, and identify potential outbreaks are essential for early detection and response. This involves collecting data on incidence, geographical distribution, and risk factors. | Essential for rapid response to outbreaks and for understanding disease patterns. Effective systems allow for timely intervention. |
Importance of Public Awareness Campaigns
Public awareness campaigns play a pivotal role in combating measles outbreaks. These campaigns educate communities about the risks of measles, the importance of vaccination, and the signs and symptoms of the disease. Effective campaigns foster a sense of collective responsibility and encourage proactive health behaviors within communities. They build trust and understanding, which are crucial for successful implementation of other public health measures.
Role of Community Health Workers
Community health workers (CHWs) are vital in promoting vaccination and disease surveillance. They are often the first point of contact for families within communities. Their role extends beyond simple information dissemination, encompassing building trust, answering questions, and addressing concerns about vaccination. They can also contribute to community-level surveillance by identifying suspected cases and reporting them to healthcare providers.
Their familiarity with the community is critical in building trust and facilitating the implementation of public health interventions.
International Support and Resources
International organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO) and UNICEF provide crucial support and resources to affected countries. This support encompasses technical assistance, financial aid, and access to essential supplies, including vaccines. They help countries build their capacity to respond to outbreaks and prevent future occurrences. This international collaboration is critical in managing global health crises.
Case Studies and Examples
The resurgence of measles globally highlights the critical need for robust vaccination programs and vigilant public health responses. Understanding past outbreaks and successful interventions provides valuable lessons for mitigating future outbreaks. Case studies offer insights into the factors driving outbreaks, the effectiveness of different strategies, and the importance of community engagement.Recent measles outbreaks, often stemming from waning immunity and inadequate vaccination coverage, underscore the vulnerability of populations.
Analyzing these outbreaks through case studies reveals crucial patterns and enables the development of targeted prevention strategies.
Recent Measles Outbreaks in Specific Regions
Measles outbreaks in recent years have disproportionately affected regions with lower vaccination rates. A notable example is the 2018-2019 outbreak in the Americas, fueled by low vaccination coverage and the spread of misinformation about vaccines. This outbreak underscored the importance of targeted vaccination campaigns and robust surveillance systems. Another significant example includes the 2019 outbreak in Europe, originating from a single infection that rapidly spread in communities with low vaccination rates.
Successful Vaccination Campaigns, Measles cases rise worldwide
Successful vaccination campaigns demonstrate the power of proactive public health interventions. The elimination of measles in the United States in 2000, for example, was a significant achievement. It highlights the importance of maintaining high vaccination coverage and the role of community health workers in reaching vulnerable populations. Similarly, the successful vaccination campaigns in countries like the United Kingdom have shown that concerted efforts can drastically reduce measles transmission.
Table Summarizing Past and Current Measles Outbreaks
| Region | Year | Cases | Cause | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| United States | 2018-2019 | ~1200 | Low vaccination rates, misinformation | Outbreak contained through targeted vaccination campaigns |
| Europe | 2019 | ~5000 | Low vaccination rates, single initial infection | Outbreak contained through intensified vaccination efforts |
| Southeast Asia | 2022-2023 | ~3000 | Low vaccination rates, disruptions in routine immunization | Ongoing outbreak requiring comprehensive response |
| Africa | 2020-2022 | ~10000 | Low vaccination rates, humanitarian crises | Continued challenges requiring sustained intervention |
Strategies Employed to Control Outbreaks
Controlling measles outbreaks requires a multifaceted approach. This includes rapid identification and isolation of cases, targeted vaccination campaigns in affected communities, and robust public health communication strategies to address misinformation and build trust.
“Community engagement is crucial for the success of any vaccination campaign. Engaging local leaders, healthcare providers, and community members is essential to build trust and ensure high vaccine uptake.”
Strengthening surveillance systems and improving data collection are also essential for tracking transmission patterns and evaluating the effectiveness of interventions. Public health campaigns emphasizing the importance of vaccination and addressing misconceptions are vital in building public trust and acceptance.
Final Wrap-Up
The global rise in measles cases demands immediate attention and coordinated action. Vaccination campaigns, public awareness initiatives, and robust public health measures are crucial to controlling the spread and preventing further outbreaks. Understanding the historical context, impact, and effectiveness of different strategies is essential to developing targeted interventions. Ultimately, a collaborative approach, encompassing international cooperation and local initiatives, is paramount to effectively combatting this resurgence of measles.









