Mpox clade 1 US case: Understanding this emerging health concern requires a thorough exploration of its characteristics, transmission, and impact. This post delves into the specifics of this mpox clade, including its geographic distribution within the US and the unique epidemiological trends observed.
The case presents a unique opportunity to analyze the effectiveness of public health responses and preventative measures, along with the clinical presentation and diagnostic approaches. This comprehensive analysis will consider the potential impact on various communities, the treatment options available, and future research directions.
Introduction to mpox Clade 1 US Case
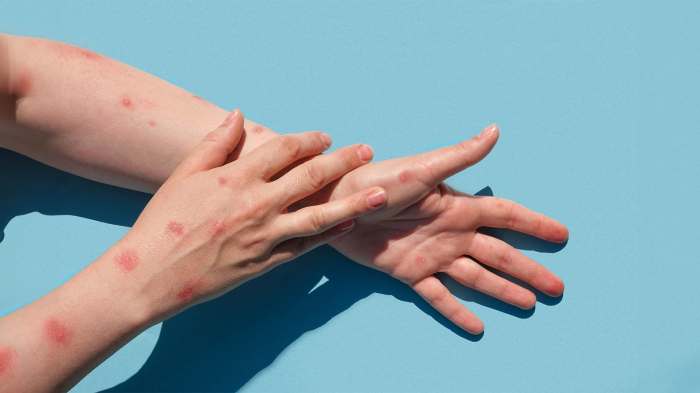
The recent emergence of monkeypox clade 1 cases in the US necessitates a deeper understanding of this specific variant. Understanding its characteristics, geographic spread, and historical context within US outbreaks is crucial for effective public health responses. This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of clade 1, highlighting its key features and comparisons to other clades.This analysis aims to contextualize mpox clade 1 cases within the broader US mpox outbreak, drawing on available data and insights to illuminate its unique features.
The recent US case of mpox clade 1 has sparked some interesting discussions, particularly regarding potential transmission methods. While not directly related, the cardiopulmonary bypass machine used for surgery cardiopulmonary bypass machine used for surgery raises questions about potential contamination risks in medical settings. This highlights the need for rigorous infection control measures in the face of emerging infectious diseases like mpox clade 1.
It explores the geographical distribution of these cases, their clinical presentation, and places them in the historical context of mpox outbreaks in the US.
Mpox Clade 1 Summary
Mpox clade 1 is one of the several lineages (clades) of the monkeypox virus. These clades are categorized based on genetic similarities and differences in the virus’s DNA sequence. Understanding these genetic variations is critical for tracking the spread and evolution of the virus.
Geographic Distribution of Mpox Clade 1 Cases in the US
The geographic distribution of mpox clade 1 cases in the US exhibits patterns. Initial outbreaks were concentrated in specific regions, potentially due to localized transmission clusters or initial points of introduction. Further analysis is needed to fully understand the factors contributing to the observed geographic spread.
Characteristics of Mpox Clade 1 Infections in the US
The clinical characteristics of mpox clade 1 infections in the US are largely consistent with those observed in other clades. Symptoms, such as fever, rash, and swollen lymph nodes, are generally similar across different clades. However, variations in the severity and duration of these symptoms may exist. Detailed case reports are essential for a deeper understanding of the disease presentation associated with clade 1 in the US.
Historical Context of Mpox Outbreaks in the US
Historically, mpox outbreaks in the US have been sporadic and often linked to imported cases. The current outbreak, however, has shown a different dynamic, with a broader geographic spread and a higher number of cases. Understanding past outbreaks provides valuable context for responding to the present situation and developing effective preventative measures.
Comparison of Mpox Clade 1 with Other Clades
| Characteristic | Mpox Clade 1 | Other Clades (e.g., Clade 3) |
|---|---|---|
| Genetic Sequence | Specific genetic makeup; potentially unique characteristics. | Different genetic makeup, possibly influencing transmission or clinical presentation. |
| Geographic Distribution (US) | Specific regions of the US. | Potentially different or overlapping regions. |
| Clinical Presentation | Similar to other clades, but potentially nuanced variations in severity. | Generally similar symptoms, but potential differences in severity. |
| Transmission Dynamics | May exhibit distinct patterns in transmission. | Transmission patterns may differ, requiring separate analysis. |
This table provides a concise overview of the differences and similarities between mpox clade 1 and other clades, focusing on critical aspects like genetic makeup, geographical spread, clinical presentation, and transmission dynamics.
Transmission and Epidemiology
Mpox, particularly Clade 1, continues to present unique transmission dynamics and epidemiological patterns in the US. Understanding these aspects is crucial for effective public health interventions and containment strategies. Detailed analysis of transmission routes, case demographics, and symptom profiles aids in tailoring appropriate preventative measures and resource allocation.
Transmission Modes
The primary mode of transmission for mpox, including Clade 1, involves close contact with an infected person or contaminated materials. This includes direct contact with skin lesions, respiratory droplets produced during prolonged, close contact, and contact with contaminated objects like bedding or clothing. Indirect transmission, through contact with contaminated surfaces, is also a potential route, though less frequent than direct contact.
Understanding these various avenues of transmission is vital for public health messaging and the development of preventive guidelines.
Reported Cases: Statistical Overview
Reported cases of mpox Clade 1 in the US demonstrate a notable pattern in terms of age and demographics. Data suggest that the majority of cases are in younger adults, though transmission across different demographics is observed. Specific age ranges and proportions will vary and are subject to ongoing reporting and analysis. The exact numbers of reported cases and specific demographics are continually updated and can be found in public health agency reports.
The recent Mpox clade 1 US case has understandably raised some health concerns. While it’s important to stay informed about this, it’s also worth remembering that various treatments for digestive issues exist. For example, some people find pepto bismol for ibs helpful pepto bismol for ibs , though individual results may vary. Ultimately, the best approach to managing any health concern is to consult a medical professional.
Hopefully, more information about this Mpox clade 1 US case will become available soon.
Symptoms of Mpox Clade 1
Mpox Clade 1, like other clades, presents a spectrum of symptoms. Common symptoms include skin lesions, often developing into fluid-filled vesicles, along with fever, headache, muscle aches, and fatigue. The severity and duration of symptoms can vary considerably between individuals. The appearance of skin lesions can vary, including characteristic pox-like lesions that progress through different stages of development.
Comparison with Other Clades (if applicable)
While comprehensive comparative data between mpox Clade 1 and other clades in the US is still emerging, early indications suggest similarities in the transmission patterns and symptom presentation. However, variations in the severity of the illness, the rate of transmission, and the overall impact on public health may emerge as more data become available. It’s essential to emphasize that continued surveillance and comparison are vital to understanding the unique characteristics of each clade and their impact on public health.
Epidemiological Trends of Mpox Clade 1 in the US
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Reporting Period | Data are dynamic and subject to continuous updates. |
| Transmission Dynamics | Primarily through close contact, with potential for indirect transmission via contaminated materials. |
| Demographic Trends | Majority of cases are observed in younger adults, although this may vary over time. |
| Symptom Profiles | Typical mpox symptoms, including skin lesions, fever, and fatigue. |
| Severity Comparison | Severity appears comparable to other clades, requiring ongoing observation. |
Public Health Response and Prevention
The emergence of mpox clade 1 cases in the US necessitated a swift and comprehensive public health response. Understanding the specific measures implemented and the preventative strategies advised is crucial for mitigating further spread and ensuring public safety. This approach involves not only identifying and isolating infected individuals but also educating the public about preventive measures.The public health response to mpox clade 1 in the US involved a multifaceted approach.
Strategies focused on contact tracing, testing, and providing comprehensive information to the public. This proactive response aims to curb transmission and reduce the overall burden of the disease.
Public Health Measures Implemented
The US response to mpox clade 1 cases involved a coordinated effort among various public health agencies. This coordinated effort included rapid case identification, contact tracing, and public health interventions. These measures aimed to break chains of transmission and prevent further spread.
- Case Identification and Surveillance: Public health officials implemented robust systems for identifying and tracking mpox cases. This involved collaboration between local, state, and federal health agencies to quickly identify and isolate infected individuals, thus enabling effective contact tracing. This early detection was crucial in managing the outbreak effectively.
- Contact Tracing and Isolation: Thorough contact tracing was employed to identify individuals who had been in close contact with confirmed cases. This was done to limit further spread of the virus and reduce the risk of infection in the community. This practice proved to be an effective measure in controlling the spread.
- Testing and Diagnostics: Reliable and accessible testing for mpox was crucial to confirm cases and monitor the outbreak. The availability of accurate testing facilitated the identification of individuals with the infection and enabled targeted interventions.
Preventative Measures Advised
Public health officials emphasized several preventative measures to mitigate the spread of mpox clade 1. These measures focused on reducing transmission risk and promoting public health.
- Hygiene Practices: Adherence to good hygiene practices, such as frequent handwashing and avoiding contact with contaminated materials, was critical. This basic measure helped limit the transmission of the virus, as it often spread through physical contact with contaminated surfaces or infected individuals.
- Avoiding Close Contact: Public health officials strongly advised individuals to avoid close contact with people who may have the infection. This included minimizing physical interaction with potential sources of infection to prevent the virus from spreading.
- Safe Handling of Materials: Instructions on safe handling of potentially contaminated materials, such as bedding or clothing, were provided to the public. These guidelines were intended to reduce the risk of exposure to the virus through indirect contact.
Comparison of Preventative Measures Across US Regions
The implementation of preventative measures varied slightly across different US regions due to variations in population density, community resources, and healthcare infrastructure. Some regions may have had more robust resources available for public health campaigns or access to testing.
- Regional Variations: While the core preventative measures remained consistent, specific implementation strategies might have varied. For example, awareness campaigns might have focused on specific community needs and vulnerabilities.
- Resource Allocation: The availability of resources and public health infrastructure influenced the level of preventative measures implemented in different regions. Regions with more substantial resources were often better equipped to offer robust public education campaigns.
Resources for Public Education
Numerous resources were available for public education about mpox clade 1. These resources provided valuable information and guidance on prevention and safety measures.
- CDC Website: The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) website served as a central resource for reliable information on mpox, including preventive measures and updated guidelines.
- Local Health Departments: Local health departments provided localized information and guidance, tailored to specific communities. This included regional details and targeted outreach to specific populations.
- Social Media Platforms: Public health agencies utilized social media platforms to disseminate timely information and updates, ensuring wide reach and quick dissemination of crucial information.
Public Health Agencies Involved
A coordinated response from various public health agencies was crucial in addressing the mpox clade 1 outbreak.
| Agency | Role |
|---|---|
| Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) | Oversight, coordination, and resource provision |
| State Health Departments | Implementation of local strategies, contact tracing |
| Local Health Departments | Community outreach, testing, and monitoring |
| World Health Organization (WHO) | Global coordination and support |
Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis
Monkeypox, particularly Clade 1, presents a spectrum of clinical manifestations, from mild to severe. Understanding the typical presentation and diagnostic approaches is crucial for effective case management and public health interventions. Accurate and timely diagnosis allows for prompt isolation, contact tracing, and the provision of appropriate treatment.
Typical Clinical Presentation of Clade 1
The clinical presentation of mpox Clade 1 often follows a recognizable pattern, though individual experiences can vary. Initial symptoms typically include fever, headache, muscle aches, backache, swollen lymph nodes, and fatigue. These prodromal symptoms often precede the characteristic skin lesions by a few days. The development of the rash is a key feature.
Diagnostic Methods for Clade 1
Several methods are used to diagnose mpox, including Clade 1. Laboratory confirmation is essential for accurate identification. These methods typically involve analyzing samples, such as skin lesions or swabs, to detect the presence of the monkeypox virus. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing is a common and highly sensitive technique. Immunofluorescence assays (IFAs) can also be used, though they may not be as widely available or as sensitive as PCR.
Additionally, microscopy, where specialized stains are used to view the virus under a microscope, can be used, but it is generally less sensitive than PCR.
Diagnostic Timelines
The diagnostic timelines for mpox Clade 1 and other clades are not significantly different. Typical laboratory turnaround times for PCR testing range from a few hours to a couple of days. The timeline is affected by factors such as the volume of samples being processed, the laboratory’s capacity, and the testing method.
Typical Skin Lesions, Mpox clade 1 us case
Skin lesions are a hallmark of mpox infection. They typically begin as macules (flat, discolored spots), which progress to papules (small, solid bumps), vesicles (fluid-filled blisters), and pustules (pus-filled blisters). These lesions can evolve over several days, often changing color from reddish to brownish to black. Lesions may be located on the face, extremities, palms, soles, and genitals.
The distribution and appearance of the lesions can provide valuable clues to clinicians in distinguishing mpox from other diseases. For example, a patient presenting with extensive lesions on the face and extremities, along with systemic symptoms, would raise suspicion for mpox.
Differential Diagnosis
| Disease | Key Features | Distinguishing Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Smallpox | Historically, a highly contagious disease characterized by a distinct rash. | While the rash may share some similarities, the clinical history, laboratory testing, and the presence of characteristic skin lesions can differentiate it from mpox. |
| Chickenpox | Highly contagious disease characterized by itchy rash with small, fluid-filled blisters. | Chickenpox typically involves a more widespread rash, often appearing in successive crops, and is typically less severe than mpox. |
| Eczema herpeticum | Severe skin infection caused by herpes simplex virus. | Eczema herpeticum is characterized by vesicular lesions that are often localized and associated with pre-existing eczema. A thorough medical history and viral culture can differentiate the conditions. |
| Herpes zoster | Shingles caused by the varicella-zoster virus. | Herpes zoster typically presents as a painful rash that follows a dermatomal distribution, while mpox can manifest in various locations. |
| Other viral exanthems | Various viral infections causing skin rashes. | The specific symptoms and distribution of lesions, along with the patient’s history, can assist in differentiating from other viral exanthems. |
Impact on Communities and Societal Implications: Mpox Clade 1 Us Case
The emergence of mpox clade 1 cases in the US necessitates a comprehensive understanding of its potential impact on various communities and societal structures. This includes examining the disproportionate effects on marginalized groups, the economic ramifications, and the psychological toll on those affected. Recognizing these factors is crucial for developing effective public health responses and preventative measures.Understanding the societal impact of mpox clade 1 requires acknowledging the potential for stigma, discrimination, and social isolation.
The disease’s transmission dynamics and potential for severe illness can lead to anxieties and fear within communities, impacting social interactions and economic activities.
Potential Impact on Different Communities
The impact of mpox clade 1 will likely vary across different communities in the US due to existing health disparities. Communities with limited access to healthcare, higher rates of poverty, or pre-existing health conditions may be disproportionately affected. This includes racial and ethnic minorities, individuals experiencing homelessness, and those in marginalized socioeconomic groups. Historical and ongoing systemic inequalities can exacerbate existing vulnerabilities and complicate the response to outbreaks.
Social and Economic Implications
The spread of mpox clade 1 can have significant social and economic consequences. School closures, business disruptions, and restrictions on social gatherings can disrupt daily life and negatively impact the economy. The need for increased healthcare resources and workforce demands further compounds the economic burden. Reduced productivity and lost wages among infected individuals and their caretakers will also impact the economy.
The social implications extend to potential stigma and discrimination against affected individuals and communities.
So, the recent US case of mpox clade 1 is definitely raising some eyebrows. While we’re still learning about this virus, it’s worth exploring other ways to boost our immune systems. Did you know that eating two dates a day for health benefits could be a surprisingly effective way to support overall well-being? two dates a day for health benefits are packed with nutrients, and maintaining a healthy immune response might be key in helping our bodies fight off infections, including mpox clade 1, which is something to keep in mind.
Let’s stay informed and proactive about our health.
Psychological Impact on Affected Individuals
The diagnosis and experience of mpox clade 1 can have a substantial psychological impact on individuals. The physical discomfort, isolation, and fear associated with the disease can lead to anxiety, depression, and other mental health challenges. The experience of stigma and discrimination can further exacerbate these issues. Support systems and mental health resources are critical for affected individuals and their families.
Disparities in Access to Healthcare
Existing health disparities may lead to unequal access to healthcare for mpox clade 1. Individuals in marginalized communities may face barriers to testing, treatment, and supportive care due to factors such as lack of insurance, transportation issues, language barriers, and mistrust of the healthcare system. Addressing these disparities is essential to ensure equitable access to care and prevent further health inequities.
Potential Social Consequences of Mpox Clade 1
| Social Consequence | Description |
|---|---|
| Stigma and Discrimination | Negative attitudes and behaviors towards individuals with mpox clade 1, leading to social isolation and marginalization. |
| Economic Disruption | Potential for reduced productivity, lost wages, and economic instability for infected individuals and their families. |
| Social Isolation | Fear of transmission and social distancing measures leading to reduced social interactions and community engagement. |
| Strain on Healthcare Resources | Increased demand for testing, treatment, and healthcare services, potentially leading to shortages and delays in care. |
| Disruption of Daily Life | School closures, business disruptions, and restrictions on social gatherings impacting daily routines and activities. |
Treatment and Management
Currently, there’s no specific antiviral treatment for mpox. Management focuses on supportive care to alleviate symptoms and prevent complications. While research continues, available interventions aim to reduce transmission risk and provide comfort to affected individuals. This includes addressing pain, fever, and other discomfort through readily accessible measures.
Available Treatment Options
The current approach to managing mpox clade 1 involves a multi-faceted strategy focused on supportive care. This strategy recognizes that while no specific antiviral treatment exists, various interventions can significantly improve the patient experience and reduce the duration and severity of symptoms.
Supportive Care Strategies
Supportive care is crucial in managing mpox clade 1. It encompasses a range of measures aimed at alleviating symptoms and promoting overall well-being. These strategies include providing pain relief, fever reduction, hydration, and rest. Proper nutrition is also important, and clinicians often advise patients to maintain a balanced diet to support their immune response.
Role of Antiviral Medications
While no antiviral medications are specifically licensed for mpox, some existing drugs are being explored in clinical trials for their potential to treat the infection. Ongoing research is crucial to determine the efficacy and safety of these treatments. The selection of any potential treatment is dependent on the specific patient’s condition and is part of a broader strategy.
Examples of Successful Treatment Strategies
Successful mpox clade 1 treatment strategies generally involve a combination of supportive care measures. This includes managing pain and fever, ensuring adequate hydration, and providing rest. Early intervention and access to quality medical care are essential components of successful outcomes. Specific strategies may vary based on the severity of the infection and individual patient responses.
Treatment Protocols for Mpox Clade 1
| Treatment Phase | Intervention | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Early Infection (within first week) | Supportive care (pain relief, fever reduction, hydration) | Focus on alleviating symptoms, promoting comfort, and preventing dehydration. |
| Moderate Infection (week 2-3) | Continued supportive care, monitoring for complications, potentially exploring investigational therapies in clinical trials (with ethical oversight) | Maintaining hydration and comfort, while carefully considering the potential benefits and risks of any experimental therapies. |
| Late Infection (after week 3) | Continued supportive care, monitoring for resolution of symptoms, ongoing clinical assessment | Support healing and recovery, ensuring the infection resolves without significant complications. |
Future Research and Prevention Strategies
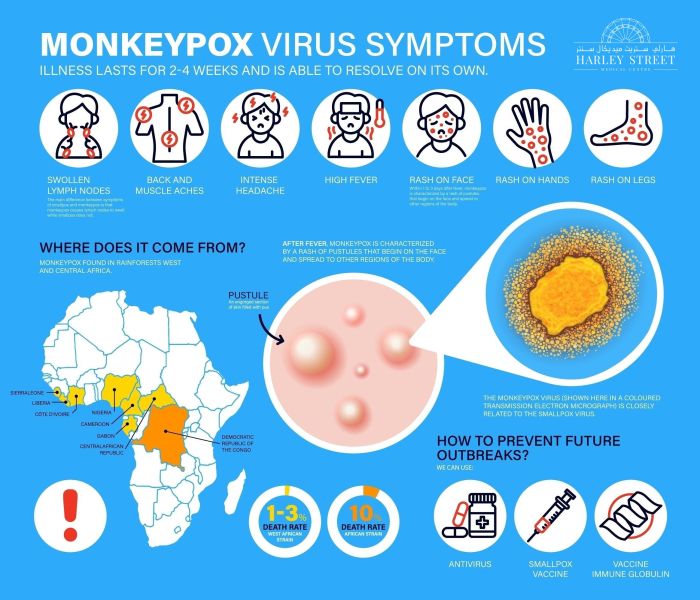
The ongoing mpox clade 1 outbreak necessitates a proactive approach to future prevention and research. Understanding the intricacies of this virus, its transmission dynamics, and potential long-term effects is crucial for developing effective strategies. This requires a multi-faceted approach encompassing laboratory research, epidemiological studies, and community engagement.Future research must address critical gaps in our knowledge, including the factors influencing transmission patterns, the effectiveness of various preventative measures, and the long-term health consequences for affected individuals.
This knowledge will be critical for developing tailored prevention strategies and mitigating the impact of future outbreaks.
Key Areas for Future Research
Understanding the long-term effects of mpox clade 1 infection is paramount. Studies should investigate the potential for long-term sequelae, including neurological complications, cardiovascular issues, and dermatological problems. The impact of pre-existing health conditions on disease severity and outcomes needs to be explored further. Detailed analysis of the genetic characteristics of mpox clade 1 viruses will aid in understanding the virus’s evolution and potential for future mutations.
This knowledge can help predict the virus’s behavior and tailor interventions.
Potential Preventative Strategies
A multi-pronged approach to preventative measures is essential. Enhanced public health messaging emphasizing safe sexual practices and hygiene measures remains critical. Development of a safe and effective vaccine tailored to mpox clade 1 is a high priority. Improved surveillance systems, particularly in areas with high population density, can provide early warning systems for potential outbreaks. Addressing socioeconomic factors contributing to vulnerability to infection is equally important.
This may include community-based interventions focused on promoting hygiene and providing resources to vulnerable populations.
Potential Long-Term Effects
The long-term effects of mpox clade 1 infection are still being studied. Early reports suggest that in some cases, individuals may experience persistent skin lesions or scarring. The potential for long-term neurological, cardiovascular, or psychological complications requires further investigation. The long-term effects are not fully understood and warrant further research.
Global Surveillance and Response Strategies
Global collaboration in surveillance and response is essential to prevent future outbreaks. This includes the development of standardized reporting protocols, the establishment of robust laboratory networks, and the implementation of early warning systems. Sharing data and best practices across countries is critical for a coordinated global response. International collaborations and data-sharing agreements are necessary to monitor emerging trends and proactively respond to outbreaks.
Possible Prevention Strategies
| Prevention Strategy | Description | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Improved Surveillance | Enhanced monitoring of mpox cases, including geographic distribution, transmission patterns, and clinical characteristics. | High; early detection allows for swift intervention and containment. |
| Public Health Campaigns | Disseminating information about mpox transmission, prevention, and treatment to the public. | Medium; effective in promoting awareness and behavioral changes. |
| Vaccination Programs | Implementing a vaccine program targeting high-risk populations and communities. | High; vaccines can reduce the risk of infection and severity of disease. |
| Improved Hygiene Practices | Promoting hygiene measures, such as handwashing and avoiding contact with contaminated surfaces. | High; these practices are generally effective in preventing infection. |
| Enhanced Laboratory Capacity | Improving laboratory diagnostic capabilities to facilitate rapid identification of mpox cases. | High; quick diagnosis enables timely treatment and containment. |
Wrap-Up
In conclusion, the mpox clade 1 US case underscores the importance of ongoing vigilance and proactive public health measures. This analysis provides a detailed understanding of the various aspects surrounding this emerging health concern, and highlights the need for continued research and international collaboration to mitigate future outbreaks. By learning from this experience, we can better prepare for and respond to similar challenges in the future.