Ocd and adhd co occurrence and diagnosis – OCD and ADHD co-occurrence and diagnosis sets the stage for understanding the complex interplay of these conditions. This exploration delves into the shared symptoms, diagnostic hurdles, and the profound impact on daily life for those affected. We’ll examine the unique challenges of diagnosing and treating these disorders when they present together, exploring various treatment approaches and shedding light on current research and future directions.
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) and Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) are both common mental health conditions, but their co-occurrence presents unique diagnostic and treatment complexities. Understanding the overlap in symptoms, the potential for misdiagnosis, and the impact on daily functioning is crucial for effective support and intervention.
Introduction to OCD and ADHD Co-occurrence
Understanding the overlapping symptoms and challenges of Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) and Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment. Both conditions can significantly impact daily life, and their co-occurrence can create a complex interplay of symptoms that may mask or exacerbate individual difficulties. This exploration delves into the core features of OCD and ADHD, highlighting their common ground and the implications of their shared presence.OCD is characterized by intrusive thoughts (obsessions) and repetitive behaviors or mental acts (compulsions) aimed at reducing anxiety.
These obsessions can range from fears of contamination to concerns about symmetry or order, while compulsions can involve excessive handwashing, checking, or arranging objects. ADHD, on the other hand, presents with persistent patterns of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. These characteristics manifest in difficulties focusing, organizing tasks, controlling impulses, and managing time effectively.The co-occurrence of these conditions is a significant area of study in mental health.
The overlap in symptoms can lead to diagnostic challenges and complicate treatment strategies. Recognizing the specific ways these disorders interact is vital to tailoring interventions and maximizing positive outcomes.
Common Symptoms of OCD
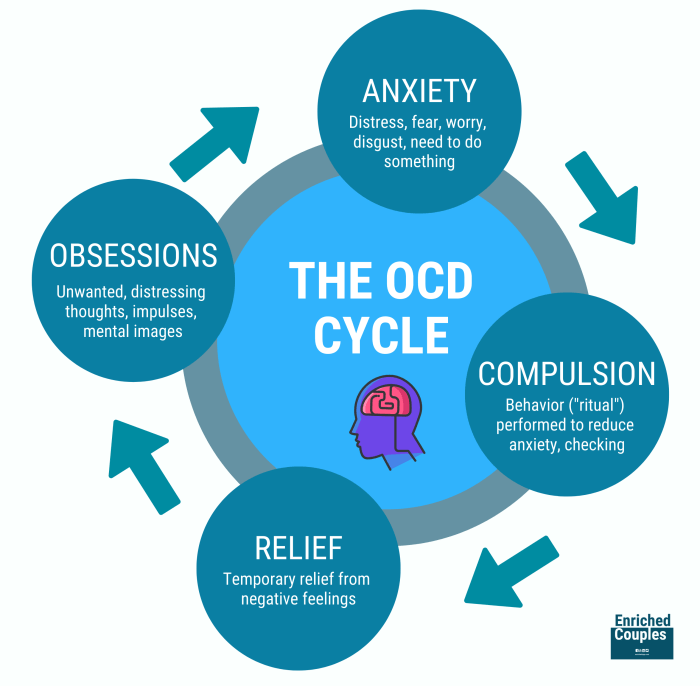
OCD is characterized by recurrent, intrusive thoughts or images (obsessions) that cause significant anxiety or distress. These obsessions are often accompanied by repetitive behaviors or mental acts (compulsions) that the individual feels driven to perform to reduce anxiety. Examples include excessive handwashing, checking locks repeatedly, or arranging objects in a specific order. These rituals are often time-consuming and interfere with daily life, causing significant distress.
Common Symptoms of ADHD
ADHD is marked by persistent patterns of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. Individuals with ADHD may struggle with focusing on tasks, organizing their thoughts, and controlling impulsive behaviors. Hyperactivity can manifest as fidgeting, restlessness, or excessive talking, while impulsivity can lead to interrupting others or making hasty decisions. These symptoms can significantly impair academic, social, and occupational functioning.
Potential Symptom Overlaps
The interplay between OCD and ADHD can be complex. Certain symptoms might appear similar or overlap, making accurate diagnosis challenging.
| Symptom | OCD Presentation | ADHD Presentation |
|---|---|---|
| Inattention | Difficulty focusing on tasks related to obsessions, like maintaining attention on a specific order. | Difficulty focusing on tasks, easily distracted, losing track of thoughts or activities. |
| Repetitive Behaviors | Compulsions, like repeatedly checking a door, are performed to reduce anxiety from obsessions. | Repetitive behaviors may stem from impulsivity or difficulty inhibiting actions. For instance, someone might repeatedly engage in a task without completing it. |
| Impulsivity | Acting on an obsession without considering the consequences. | Impulsive behaviors unrelated to anxiety, such as interrupting conversations or making rash decisions. |
| Organization Issues | Difficulty organizing thoughts or objects related to the obsession. | Difficulty organizing tasks, materials, or belongings, leading to disorganization. |
Diagnostic Challenges
Navigating the complexities of mental health often involves intricate diagnostic puzzles. When conditions like Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) and Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) co-occur, the diagnostic process becomes even more challenging. Overlapping symptoms can obscure the distinct characteristics of each condition, leading to misdiagnosis or delayed intervention. Precise identification is crucial for tailoring effective treatment strategies that address both conditions’ unique needs.The interplay of OCD and ADHD symptoms can mask the presence of either condition.
It’s fascinating how conditions like OCD and ADHD can sometimes occur together, making diagnosis a bit trickier. Sometimes, physical pain, like hip pain from various injuries and conditions, can also mimic symptoms of mental health issues. Understanding the nuances of these co-occurring conditions is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment, especially when considering factors like the potential for overlapping symptoms.
If you’re experiencing hip pain, exploring potential causes like those outlined in this informative article on injuries and conditions causing hip pain is a good first step. Ultimately, a thorough evaluation by a qualified healthcare professional remains essential for a proper diagnosis of OCD and ADHD co-occurrence.
Individuals with both disorders may exhibit behaviors that are seemingly characteristic of only one condition, making it difficult to pinpoint the specific contributing factors. For instance, someone with both OCD and ADHD might experience impulsivity that could be misattributed solely to ADHD. Conversely, repetitive behaviors associated with OCD could be mistaken for symptoms of a different condition. A nuanced understanding of each disorder’s distinct features is essential for accurate diagnosis.
Difficulties in Differentiating Symptoms
Distinguishing between the symptoms of OCD and ADHD is often problematic when they coexist. For example, both conditions can manifest with restlessness, difficulty focusing, and repetitive behaviors. Someone with both disorders might exhibit restlessness associated with ADHD and compulsive behaviors related to OCD, leading to a confusing presentation. The key is to recognize patterns and nuances that differentiate these conditions.
A detailed evaluation of symptom severity, frequency, and impact on daily functioning can help to separate the overlap and pinpoint the underlying factors.
Importance of a Thorough Diagnostic Process
A comprehensive diagnostic approach is vital for accurately identifying co-occurring OCD and ADHD. A detailed patient history plays a critical role. This involves exploring the individual’s experiences, including the onset and progression of symptoms, their impact on daily life, and any potential contributing factors such as family history. Crucially, the history must be carefully examined to identify patterns that indicate the presence of both conditions.A thorough psychological evaluation is equally important.
This evaluation should include assessments of cognitive functions, emotional regulation, and behavioral patterns. For example, assessing for obsessions and compulsions characteristic of OCD, while simultaneously identifying symptoms like inattention and hyperactivity indicative of ADHD, can aid in the correct diagnosis. Standardized assessment tools are helpful for objectively measuring symptom severity and providing valuable data for the diagnostic process.
Comparing Diagnostic Criteria
| Characteristic | OCD | ADHD |
|---|---|---|
| Obsessions | Repetitive, intrusive thoughts or impulses | Not typically present |
| Compulsions | Repetitive behaviors or mental acts to reduce anxiety | Not typically present |
| Inattention | May exhibit some inattention but not a core symptom | Significant difficulty focusing, easily distracted |
| Hyperactivity | May exhibit restlessness but not a core symptom | Excessive energy, fidgeting, impulsivity |
| Repetitive Behaviors | Repetitive, ritualistic actions driven by obsessions | Repetitive actions might be present but not as a response to intrusive thoughts |
This table provides a general comparison. The specific diagnostic criteria and symptoms can vary greatly between individuals. A qualified mental health professional is essential to properly assess each case and establish a comprehensive diagnosis.
Impact on Functioning
The co-occurrence of OCD and ADHD significantly impacts daily functioning and overall well-being. These conditions, while distinct, often interact and exacerbate each other’s challenges, making everyday tasks and relationships more difficult to manage. This complex interplay necessitates a nuanced understanding of how symptoms affect different areas of life, from work and social interactions to personal relationships.The simultaneous presence of both OCD and ADHD symptoms creates a cascade of difficulties.
The intrusive thoughts and compulsive behaviors of OCD can be overwhelming, while the impulsivity and inattention of ADHD can disrupt efforts to manage these symptoms effectively. This often results in a cycle of frustration, low self-esteem, and reduced quality of life.
Impact on Work Performance
The combination of obsessive-compulsive tendencies and attention-deficit/hyperactivity symptoms can significantly impair work performance. Individuals may struggle with sustained attention to tasks, leading to errors and missed deadlines. Compulsions, such as excessive checking or cleaning, can consume significant time, impacting productivity. Furthermore, the impulsivity associated with ADHD can manifest as difficulty with organizational skills, leading to missed appointments, disorganized paperwork, and poor time management.
These factors can result in missed opportunities, negative evaluations, and ultimately, career setbacks.
Impact on Relationships
The complexities of OCD and ADHD can strain relationships with family, friends, and partners. Individuals with OCD may experience difficulty maintaining healthy boundaries, leading to conflicts and misunderstandings. Their intense focus on perceived flaws or imperfections can cause friction and affect communication. ADHD symptoms, such as impulsivity and emotional dysregulation, can contribute to relationship problems, as individuals may struggle with managing their emotions appropriately or anticipating the consequences of their actions.
These issues can lead to conflicts, misunderstandings, and feelings of isolation.
Impact on Social Interactions
Social interactions can be challenging for individuals with co-occurring OCD and ADHD. OCD-related anxieties about social situations, such as fear of contamination or making mistakes, can lead to social avoidance and isolation. ADHD symptoms, such as impulsivity and difficulty with social cues, can make it hard to navigate social situations effectively. These individuals may struggle with maintaining appropriate conversation flow, interrupting others, or misinterpreting social cues, leading to awkward or uncomfortable interactions.
They might also feel overwhelmed by social demands and desire to withdraw.
Impact on Daily Life
Daily life activities, such as household chores, errands, and personal care, can become significant struggles. The compulsive behaviors of OCD, such as repetitive cleaning or checking, can consume excessive time and energy, leaving little time for other essential tasks. The impulsivity and distractibility associated with ADHD can lead to difficulty organizing and completing daily tasks, further compounding the challenges.
This can result in a cycle of procrastination, unfinished tasks, and feelings of inadequacy.
Impact on Overall Well-being, Ocd and adhd co occurrence and diagnosis
The co-occurrence of OCD and ADHD can significantly affect an individual’s overall well-being. The constant internal struggle with intrusive thoughts, compulsive behaviors, and attention-deficit symptoms can lead to anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem. These individuals may experience a reduced sense of control over their lives and struggle to engage in activities they enjoy. The stress and frustration associated with these conditions can negatively impact physical health as well.
| Area of Life | Impact of Co-occurring OCD and ADHD |
|---|---|
| Work | Difficulty with sustained attention, errors, missed deadlines, poor organization, productivity issues, potential career setbacks. |
| Relationships | Difficulty maintaining boundaries, conflicts, misunderstandings, emotional dysregulation, impulsivity-related problems, social avoidance. |
| Social Interactions | Social anxiety, social avoidance, difficulty with social cues, awkward interactions, feeling overwhelmed by social demands. |
| Daily Life | Procrastination, unfinished tasks, difficulty with organization and completion of tasks, time management issues, feelings of inadequacy. |
| Overall Well-being | Anxiety, depression, low self-esteem, reduced sense of control, negative impact on physical health. |
Treatment Approaches
Treating co-occurring OCD and ADHD requires a multifaceted approach tailored to the individual’s specific needs and symptom severity. A comprehensive treatment plan often combines medication management with evidence-based therapies, focusing on addressing both disorders simultaneously. This approach is crucial as neglecting either condition can hinder progress and potentially worsen symptoms.Effective treatment strategies recognize the interplay between the two conditions, understanding how ADHD can exacerbate OCD symptoms and vice versa.
For example, impulsivity associated with ADHD can lead to compulsive behaviors in an attempt to manage anxiety, while OCD-related ruminations and rituals can disrupt attention and focus, characteristic of ADHD. Therefore, a targeted and holistic approach is paramount to fostering lasting improvements in daily functioning and well-being.
Evidence-Based Treatment Approaches
A range of evidence-based therapies and medications have proven effective in managing co-occurring OCD and ADHD. These include, but are not limited to, cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), medication, and other psychosocial interventions. The efficacy of any specific treatment is often dependent on individual factors, including symptom severity, co-morbidities, and personal preferences. Careful consideration and ongoing evaluation of the treatment plan are essential for optimal outcomes.
Medication Management
Pharmacotherapy plays a crucial role in managing both OCD and ADHD symptoms. Stimulant medications are commonly prescribed for ADHD, helping to improve focus, attention, and impulse control. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are often used to treat OCD, targeting the neurochemical imbalances implicated in obsessive-compulsive behaviors. The selection of specific medications and dosages will vary depending on the individual’s response to treatment and the presence of any other medical conditions.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) Techniques
CBT is a cornerstone of treatment for OCD and ADHD. Specific CBT techniques can be adapted to address the co-occurrence of these conditions. Techniques like exposure and response prevention (ERP) are particularly useful for OCD, helping individuals confront feared situations and resist compulsive behaviors. For ADHD, CBT can focus on developing organizational strategies, time management skills, and coping mechanisms for impulsivity and hyperactivity.
A comprehensive CBT approach addresses both the emotional and behavioral aspects of these conditions. It helps individuals develop healthier thought patterns and coping mechanisms to manage symptoms effectively.
Multidisciplinary Approach
A multidisciplinary approach involving collaboration between psychiatrists, psychologists, and other healthcare professionals is highly recommended for individuals with co-occurring OCD and ADHD. This collaborative approach ensures comprehensive care, enabling tailored treatment plans that address both the mental health needs and potential co-occurring conditions. Collaboration facilitates open communication, shared decision-making, and a unified approach to support the individual’s overall well-being.
Comparison of Therapeutic Modalities
| Therapeutic Modality | Focus for OCD | Focus for ADHD | Potential Strengths | Potential Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) | Exposure and response prevention (ERP) to challenge obsessions and reduce compulsive behaviors. | Developing organizational skills, time management techniques, and coping strategies for impulsivity and hyperactivity. | Evidence-based, helps develop coping mechanisms, addresses both behavioral and cognitive aspects. | May require significant effort and commitment from the individual, and effectiveness can vary depending on individual factors. |
| Medication (e.g., SSRIs, stimulants) | Targeting neurochemical imbalances associated with OCD. | Improving focus, attention, and impulse control. | Can provide rapid symptom relief for many individuals. | Potential side effects, need for careful monitoring and dosage adjustments, and may not address underlying thought patterns. |
| Family Therapy | Supporting family understanding and management of OCD symptoms. | Educating family members about ADHD symptoms and behaviors. | Provides a support system for the individual and family, fostering a supportive environment. | May not be suitable for all families, and may require significant commitment from family members. |
Case Studies
Understanding the co-occurrence of OCD and ADHD requires looking at real-life examples. These cases illustrate the complexities of these conditions and highlight the importance of individualized treatment approaches. While each case is unique, they offer valuable insights into the challenges and potential outcomes of these intertwined disorders.
A Hypothetical Case Study
A 12-year-old named Alex presents with a range of symptoms suggesting both OCD and ADHD. Alex experiences intrusive thoughts about germs and contamination, leading to compulsive handwashing rituals that interfere with daily life. He struggles with impulsivity, difficulty focusing in school, and organization problems. His symptoms have been progressively worsening over the past two years. This case illustrates the frequent overlapping nature of OCD and ADHD symptoms, making diagnosis challenging.
Challenges Faced by Alex
Alex faces significant challenges in multiple areas. His obsessive-compulsive behaviors, such as excessive handwashing, consume significant time and energy, disrupting his schoolwork and social activities. His ADHD symptoms exacerbate these difficulties, causing distractions and impulsivity that contribute to mistakes and frustration. Furthermore, the stigma associated with mental health conditions may lead to social isolation and emotional distress.
The co-occurrence of OCD and ADHD can create a vicious cycle, where one condition exacerbates the other.
Understanding the co-occurrence of OCD and ADHD in diagnosis can be tricky, often overlapping with other conditions. Sometimes, symptoms can mimic other issues, like delirium, which can significantly impact accurate diagnosis. For a deeper understanding of delirium and its potential impact on mental health evaluations, check out this helpful resource: delirium what you should know. Ultimately, recognizing these potential overlaps is key to getting the right support for OCD and ADHD.
Treatment Approach for Alex
A comprehensive treatment plan tailored to Alex’s specific needs is essential. This plan should integrate evidence-based therapies, including Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) for OCD, focusing on challenging the distorted thoughts and reducing compulsive behaviors. Simultaneously, strategies for ADHD management, such as medication and organizational techniques, are crucial to improving focus and reducing impulsivity. The therapy for OCD would be specifically adapted to account for the impulsivity often associated with ADHD.
This involves careful consideration of the individual’s emotional and behavioral needs, acknowledging the co-existing conditions and adjusting the approach accordingly.
Potential Outcomes and Long-Term Impact
Successful treatment can significantly improve Alex’s quality of life. By addressing both the OCD and ADHD components, the treatment aims to reduce the intensity of his symptoms and help him develop coping mechanisms. With appropriate support and consistent engagement in therapy, Alex can develop strategies to manage his symptoms and improve his functioning in school, at home, and socially.
This could involve teaching him to prioritize tasks, use organizational tools, and manage his impulses. Long-term, this can lead to increased self-esteem, better relationships, and improved academic performance.
Summary Table
| Symptom | Diagnosis | Treatment Plan |
|---|---|---|
| Intrusive thoughts about germs and contamination | OCD | CBT for OCD, focusing on thought challenges and reducing compulsive behaviors |
| Difficulty focusing, impulsivity, organization problems | ADHD | Medication, organizational techniques, and strategies to manage impulsivity |
| Excessive handwashing | OCD | CBT, exposure and response prevention techniques to address the compulsive behavior. |
| Distraction and frustration | ADHD | Medication, organizational tools, and stress reduction techniques. |
Research and Future Directions
The co-occurrence of Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) and Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) presents a complex challenge for researchers and clinicians alike. Understanding the interplay of these conditions is crucial for developing more effective diagnostic and treatment strategies. Current research offers valuable insights, but significant gaps remain, necessitating further investigation.Research into the underlying mechanisms and potential shared genetic or environmental factors contributing to the co-occurrence of OCD and ADHD is still ongoing.
This understanding is crucial for developing targeted treatments and interventions that address the specific needs of individuals with both conditions.
Current Research Findings on the Co-occurrence of OCD and ADHD
Studies consistently show a higher prevalence of ADHD among individuals with OCD compared to the general population. This suggests a significant link between the two conditions, possibly involving overlapping neurobiological pathways or shared environmental risk factors. Further research is needed to clarify the nature of this association.
Figuring out if OCD and ADHD are co-occurring can be tricky, and diagnosis often involves a careful evaluation. It’s a bit like trying to figure out why a cast might smell – sometimes it’s a straightforward issue, other times, a more complex problem is at play, requiring a specialist. For instance, if you’re concerned about a smelly cast, you should definitely check out this helpful guide on what can I do about a smelly cast – and similar complexities can arise when dealing with overlapping mental health conditions.
Ultimately, understanding the potential interplay between these conditions is key for effective treatment and support.
Gaps in Knowledge and Areas Needing Further Investigation
A significant gap in current research lies in the precise neurobiological underpinnings of the co-occurrence of OCD and ADHD. While some studies suggest potential shared neural circuits, a more detailed understanding of the specific brain regions and neurotransmitters involved is lacking. Further investigation is required to determine the degree of overlap and unique contributions of each disorder. Similarly, the role of specific environmental factors, such as early childhood adversity or specific parenting styles, needs further investigation in the context of co-occurring OCD and ADHD.
Potential Future Research Directions
Future research should focus on longitudinal studies that track individuals with both OCD and ADHD from childhood to adulthood. This will allow researchers to investigate the developmental trajectories of the conditions, potential symptom fluctuations, and the impact on long-term functioning. Further investigation into the effectiveness of combined treatment approaches is warranted, given the potential for synergistic effects.
Developing New Treatments and Interventions
A crucial area for future research is the development of targeted interventions for individuals with both OCD and ADHD. This might involve exploring novel therapies that address both conditions simultaneously, or modifying existing treatments to enhance their efficacy in this population. Consideration should be given to developing personalized treatment plans based on the specific symptom profiles and individual needs of each patient.
Table of Current Research Findings on Treatment Effectiveness
| Treatment Approach | Effectiveness (Summary) | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) for OCD | Generally effective in reducing OCD symptoms. | May not be sufficient for individuals with comorbid ADHD, requiring modifications or combined approaches. |
| Stimulant medication for ADHD | Often effective in managing ADHD symptoms. | May not address OCD symptoms directly and could potentially exacerbate certain OCD traits. |
| Combination Therapy (CBT + Medication) | Potentially more effective than single-modality approaches, particularly in addressing both conditions simultaneously. | Requires careful monitoring and tailored treatment plans. |
Note: The effectiveness of treatments can vary significantly depending on individual factors and treatment fidelity.
Public Awareness and Education: Ocd And Adhd Co Occurrence And Diagnosis
Raising awareness about the co-occurrence of OCD and ADHD is crucial for early intervention and improved quality of life for affected individuals. Ignorance often leads to misdiagnosis or delayed treatment, potentially exacerbating the symptoms and hindering effective management. Education plays a pivotal role in dispelling myths, promoting understanding, and fostering a supportive environment for those living with these conditions.Increased public awareness fosters a greater sensitivity and understanding towards the challenges faced by individuals struggling with these conditions.
This understanding, in turn, leads to a more compassionate and inclusive society where individuals feel empowered to seek help and support.
Strategies for Increasing Public Awareness
Public awareness campaigns can utilize various channels, including social media, community events, and collaborations with healthcare professionals. These campaigns should employ clear, concise messaging that emphasizes the co-occurrence of OCD and ADHD, emphasizing the importance of accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
Importance of Education and Support
Education empowers individuals and families with the knowledge needed to navigate the complexities of these conditions. Understanding the symptoms, challenges, and treatment options is paramount for fostering resilience and well-being. Support networks provide a platform for shared experiences, offering practical advice and emotional comfort to those affected.
Resources and Support Networks
A wide range of resources can contribute to raising awareness and understanding of OCD and ADHD co-occurrence. These resources include educational websites, support groups, and collaborations with schools, workplaces, and community organizations. Accessible information is key to empowering individuals and families to seek help and navigate the challenges together.
Suggested Resources
| Organization/Resource | Focus/Description |
|---|---|
| The International OCD Foundation (IOCF) | Provides information, support, and resources on OCD, including co-occurring conditions. |
| CHADD (Children and Adults with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder) | Offers support, education, and advocacy for individuals with ADHD and related conditions. |
| National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI) | Provides a broad range of mental health resources, including information on co-occurring disorders and support networks. |
| Local mental health clinics and hospitals | Offer diagnosis, treatment, and support services tailored to specific needs and communities. |
| Online support groups and forums | Provide platforms for sharing experiences, seeking advice, and connecting with others facing similar challenges. |
Concluding Remarks
In conclusion, OCD and ADHD co-occurrence demands a thorough and nuanced approach to diagnosis and treatment. The intricate interplay of symptoms necessitates a multidisciplinary team, including clinicians and therapists specializing in both conditions. Continued research is essential to refine diagnostic tools, develop more effective treatments, and ultimately improve the lives of those navigating this challenging co-occurrence. By increasing public awareness and providing access to support resources, we can pave the way for better outcomes and improved quality of life.