What is a DEXA scan? It’s a non-invasive procedure used to assess bone health and body composition. This informative guide dives deep into the details, from the basics to the intricate measurements and interpretations. We’ll explore the different types of DEXA scans, the preparation involved, and how results are analyzed. Get ready to learn everything you need to know about this crucial diagnostic tool.
Understanding the process, from the initial scheduling to the interpretation of results, is key to feeling confident about this procedure. We’ll walk you through each step, providing clear explanations and insights.
Introduction to DEXA Scan
A DEXA scan, short for dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry, is a non-invasive medical imaging technique used to measure bone mineral density (BMD). It’s a safe and highly accurate method for assessing the strength and health of bones, crucial for understanding their risk of fractures. This information is vital for preventative health strategies and treatment planning for various bone-related conditions.DEXA scans work by using two X-ray beams with different energies to differentiate between bone and soft tissue.
This precise measurement allows for a detailed evaluation of bone density, enabling healthcare professionals to identify areas of low bone density, which can indicate osteoporosis or osteopenia, and to monitor the effectiveness of treatment. This technology allows for early detection and intervention, minimizing the risk of serious fractures.
A DEXA scan measures bone density, but it can also provide a detailed body composition analysis. Knowing your body composition is crucial for understanding your overall health and how to achieve your goals. If you’re looking to optimize your weight loss journey, exploring different supplements like green tea extract or protein powders could be helpful. For more information on potential weight loss supplements, check out this helpful resource: what supplements help with weight loss.
Ultimately, a DEXA scan is a powerful tool for personalized health insights, giving you a clear picture of your body’s needs.
DEXA Scan Purpose and Applications, What is a dexa scan
DEXA scans serve a wide range of purposes, extending beyond basic bone density measurement. They are integral in diagnosing, monitoring, and managing various bone-related conditions. By providing a comprehensive picture of bone health, DEXA scans aid in early detection, personalized treatment plans, and risk assessment. They are particularly valuable in identifying individuals at high risk of fractures, facilitating proactive interventions and improving overall health outcomes.
A DEXA scan, or dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry, measures bone density. It’s a pretty straightforward process, but understanding its results can be crucial for overall health. While we’re on the subject of health, did you know that the amount of heavy metals in dark chocolate can vary significantly? For example, you can find out more about the potential heavy metal content in dark chocolate by checking out this informative article on heavy metals dark chocolate.
Ultimately, a DEXA scan helps determine your bone health, which is vital for everything from preventing fractures to just feeling good overall.
Types of Information Provided by a DEXA Scan
A DEXA scan provides critical information about bone health, including bone mineral density (BMD) and bone mineral content (BMC). The results provide a quantitative assessment of bone density, allowing healthcare providers to compare the patient’s bone density to established norms for their age and gender. This comparison is crucial for evaluating the risk of fractures and determining appropriate treatment strategies.
Furthermore, DEXA scans can help assess the effectiveness of therapies designed to improve bone health over time.
Different Types of DEXA Scans and Their Uses
| Scan Type | Purpose | Areas Measured | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Central DEXA Scan | Measures bone mineral density in the spine and hip. | Lumbar spine and hip | Primary screening for osteoporosis, monitoring treatment effectiveness, and evaluating fracture risk. |
| Peripheral DEXA Scan | Measures bone mineral density in the forearm, heel, or finger. | Forearm, heel, or finger | Provides a quick, convenient, and less expensive initial assessment of bone health, particularly suitable for large-scale screening programs and follow-up monitoring of specific populations. |
| Quantitative Computed Tomography (QCT) Scan | Provides detailed 3D images of bone structure. | Specific areas of the body | Used to assess bone structure and microarchitecture, providing valuable information about bone quality beyond simple density measurements. Useful in research and specific clinical situations. |
Procedure and Preparation: What Is A Dexa Scan
Getting a DEXA scan involves a series of steps, from scheduling to post-procedure follow-up. Proper preparation is crucial for accurate results and a smooth experience. Understanding the procedure and necessary preparations can ease any anxieties and ensure the scan is conducted effectively.DEXA scans, or dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry scans, are non-invasive procedures used to measure bone density. A crucial aspect of the process is preparation, which directly impacts the accuracy and reliability of the results.
Following the Artikeld steps and instructions ensures the best possible outcome.
Scheduling and Administrative Procedures
The scheduling process for a DEXA scan typically involves contacting the facility directly to book an appointment. The facility will provide instructions regarding the necessary documentation and any specific requirements. It is important to carefully follow the instructions to avoid delays or complications in the scanning process.
Preparation for the Scan
Accurate DEXA scans depend on proper preparation. Specific clothing restrictions and instructions regarding medication are essential to ensure the scan yields reliable results.
- Clothing Restrictions: Patients are typically asked to remove all metal objects from their bodies, including jewelry, belts, and watches. This ensures that these objects do not interfere with the scan’s accuracy. Comfortable clothing is recommended for the scan. Loose clothing, such as a top without a bra, or a pair of shorts, will likely be required to facilitate the scan process.
- Medication Considerations: Certain medications can affect the accuracy of the scan. Patients should inform their healthcare provider or the DEXA scanning facility about any medications they are taking. This is vital to ensure that the results are not compromised by extraneous factors.
Duration of the Scan
The DEXA scan is generally a quick procedure. The time required for the entire process, from preparation to post-procedure instructions, varies depending on the individual’s circumstances and the specific requirements of the facility.
- Typical Duration: The actual scan itself typically takes only a few minutes. However, the entire process, including preparation, the scan itself, and any follow-up, can take approximately 30 minutes to an hour. This timeframe includes administrative procedures, such as signing forms, and potentially waiting periods.
Summary of Preparation Steps
The table below summarizes the preparation steps and estimated timeframes involved in undergoing a DEXA scan.
| Step | Description | Timeframe | Important Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scheduling | Contacting the facility to book an appointment | Variable, depends on facility availability | Follow facility’s instructions for documentation. |
| Preparation (clothing, medications) | Removing metal objects, following clothing guidelines, and disclosing medication information. | 15-30 minutes | Ensure complete disclosure of all medications. |
| DEXA Scan Procedure | The actual scan process | Few minutes | Remain still during the scan. |
| Post-procedure Instructions | Receiving results and any follow-up instructions | 5-15 minutes | Follow the facility’s instructions for post-procedure care. |
What is Measured
DEXA scans provide a wealth of information beyond just bone density. They offer a comprehensive assessment of skeletal health and overall body composition, crucial for diagnosing and managing various medical conditions. Understanding the different measurements and their significance is key to interpreting the results accurately.DEXA scans excel at quantifying bone mineral density (BMD), a crucial indicator of bone strength.
Beyond BMD, the technology also assesses body composition, distinguishing between fat mass, lean muscle mass, and other important elements. This detailed analysis is invaluable in identifying potential risks and tailoring appropriate interventions.
Bone Mineral Density (BMD) Measurements
Bone mineral density (BMD) is a key parameter in assessing bone health. A higher BMD generally indicates stronger, healthier bones, reducing the risk of fractures. Measuring BMD helps in identifying osteoporosis and osteopenia, conditions characterized by reduced bone density. This is crucial for early interventions and preventative strategies.
Body Composition Analysis
DEXA scans are capable of providing a detailed breakdown of body composition. This analysis differentiates between fat mass, lean muscle mass, and other components like water content. This information is invaluable for understanding overall health and identifying potential imbalances. For example, an individual with a high percentage of body fat might be at a higher risk for various health issues, and the DEXA scan provides this information for appropriate interventions.
Bone Density Measurement Technique
DEXA utilizes dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry. This sophisticated technique employs two different X-ray energies to differentiate between bone mineral and soft tissue. The varying absorption of these energies by different tissues allows the machine to precisely calculate bone density. The lower energy X-rays are absorbed more by soft tissue, while the higher energy X-rays are absorbed more by bone.
The difference in absorption between the two energies is used to calculate the bone mineral content and density at specific locations.
T-scores and Z-scores
T-scores and Z-scores are standardized values used to interpret DEXA scan results. A T-score compares an individual’s BMD to the average BMD of a healthy young adult of the same sex. A Z-score compares an individual’s BMD to the average BMD of individuals in the same age group and sex. These scores help clinicians determine the risk of fractures and the need for interventions.
A T-score of -2.5 or lower indicates osteoporosis, while a T-score between -1 and -2.5 suggests osteopenia. A Z-score below -2 often warrants further investigation to rule out other underlying factors affecting bone density.
A high T-score suggests excellent bone health, while a low T-score indicates a higher risk of fractures. The Z-score helps in identifying if there are any other underlying issues that are contributing to low bone density, which is not usually related to aging.
Results and Interpretation
Decoding your DEXA Scan: Understanding the numbers and what they mean is crucial for effective bone health management. A DEXA scan provides a wealth of information about your bone density, allowing doctors to assess your risk of fractures and monitor the progress of any related conditions. The results are not just a set of numbers; they’re a key to understanding your bone health and developing a personalized strategy for maintaining it.Doctors meticulously analyze these results to paint a clear picture of your bone health.
This analysis goes beyond simply looking at the numbers; it considers your age, gender, and other relevant factors to determine if your bone density is within the healthy range or if it falls below the threshold for concern. This comprehensive approach allows for targeted interventions and personalized treatment plans.
DEXA Scan Result Presentation
DEXA scan results are typically presented in a report that combines numerical data with visual representations, such as graphs and images. The report often includes both a summary of your bone density and detailed information about each measured area. This multifaceted approach ensures a comprehensive evaluation of your bone health.
Interpretation of DEXA Scan Results
Doctors interpret DEXA scan results by comparing your bone mineral density (BMD) to the average BMD for healthy individuals of your age and gender. This comparison is often expressed as a T-score and a Z-score. A T-score compares your BMD to the average BMD of a healthy 30-year-old adult of the same gender, while a Z-score compares your BMD to the average BMD of other people in your age group.
Potential Conditions Detected by DEXA Scans
DEXA scans can detect various conditions that affect bone density, such as osteoporosis, osteopenia, and other bone-related diseases. Osteoporosis, characterized by low bone density and an increased risk of fractures, is a common condition that DEXA scans help diagnose and monitor. Osteopenia, a precursor to osteoporosis, is also detectable and allows for early intervention. Additionally, certain medications or medical conditions can also impact bone density, and DEXA scans play a crucial role in monitoring these effects.
A DEXA scan, or dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry scan, measures bone density. Understanding how different medications, like naloxone and naltrexone, work is also crucial for overall health. For example, learning the similarities and differences between naloxone and naltrexone can be helpful in understanding their specific roles in opioid overdose reversal and addiction treatment. naloxone vs naltrexone similarities and differences.
Ultimately, a DEXA scan provides valuable insights into bone health, which is important for preventing fractures and overall well-being.
Typical DEXA Scan Report Format
A typical DEXA scan report includes the following information:
Example Report:Patient Name: Jane DoeDate of Scan: October 26, 2023Referring Physician: Dr. SmithSummary:T-score: -2.5 at the lumbar spine, -1.8 at the femoral neckZ-score: -1.0 at the lumbar spine, -0.5 at the femoral neckDiagnosis: Osteopenia (lumbar spine), Normal bone density (femoral neck)Measurements:Lumbar Spine BMD: 0.95 g/cm2Femoral Neck BMD: 1.02 g/cm2Total Hip BMD: 0.98 g/cm2Comparison:Results are compared to the average BMD for a 55-year-old female.Recommendations:Lifestyle modifications to increase calcium and vitamin D intake are recommended. Follow-up DEXA scan in 2 years.Conclusion:The patient exhibits osteopenia at the lumbar spine, while bone density at the femoral neck is within the normal range. Monitoring is advised.
Benefits and Risks
DEXA scans provide valuable insights into bone health, enabling early detection and management of osteoporosis and other bone-related conditions. Understanding the advantages and potential drawbacks of this technology is crucial for informed decision-making. Weighing the benefits against the risks empowers individuals to make choices aligned with their specific health needs.DEXA scans, while generally safe, carry potential risks, albeit minimal.
The ionizing radiation exposure, though low, warrants careful consideration. Furthermore, the accuracy of the scan can be affected by various factors, such as the presence of metallic implants or artifacts. Comparing DEXA scans to alternative methods for assessing bone health is vital for understanding their strengths and limitations.
Advantages of DEXA Scans
DEXA scans are highly effective for diagnosing and monitoring bone health, providing precise measurements of bone mineral density (BMD). This precision enables clinicians to detect osteoporosis and other bone-related diseases in their early stages. Early detection allows for timely intervention, which can significantly improve treatment outcomes and reduce the risk of fractures.
Potential Risks of DEXA Scans
The radiation exposure associated with DEXA scans is minimal and generally considered safe for the majority of individuals. However, pregnant women and young children should avoid unnecessary radiation exposure. In individuals with metallic implants, the presence of these implants may influence the accuracy of the DEXA scan.
Comparison with Other Bone Health Assessment Methods
DEXA scans are considered the gold standard for assessing bone mineral density. Other methods, such as quantitative ultrasound (QUS), provide a less detailed assessment of bone health. QUS is often used as a preliminary screening tool due to its lower cost and faster scan time. However, DEXA scans offer superior accuracy and detailed information for diagnosis and monitoring.
Benefits for Specific Populations
DEXA scans offer several advantages across various populations.
- Post-menopausal women: Post-menopausal women are at increased risk of osteoporosis, and DEXA scans can detect bone loss early, allowing for prompt treatment and reducing the risk of fractures.
- Individuals with a family history of osteoporosis: Individuals with a family history of osteoporosis are more susceptible to the disease. DEXA scans can help identify those at high risk and implement preventive strategies.
- Individuals taking medications that can affect bone health: Some medications can lead to bone loss. DEXA scans help monitor bone health in individuals undergoing such treatments. For example, long-term use of corticosteroids can significantly impact bone density.
- Individuals experiencing unexplained bone pain or fractures: DEXA scans can help assess the cause of unexplained bone pain or fractures, helping determine whether osteoporosis is a contributing factor. For example, a sudden, unexplained fracture in an older adult may be a sign of underlying bone loss.
Contraindications and Limitations
DEXA scans are generally safe, but certain factors can influence their interpretation or pose limitations.
- Metallic implants: The presence of metallic implants in the body can affect the accuracy of DEXA scans. Results may be inaccurate or difficult to interpret. Clinicians need to consider the presence of implants and adjust the interpretation of the scan accordingly.
- Body size: For individuals with extremely large or small body sizes, the scan may not always provide a precise measure of bone mineral density.
- Certain medical conditions: Some medical conditions can influence the accuracy of DEXA scans. For example, the presence of large amounts of calcium or other substances can affect the readings. Clinicians must consider these factors to ensure accurate interpretation.
- Patient positioning: Proper patient positioning during the scan is critical for accurate results. Poor positioning can lead to inaccurate measurements.
Alternatives to DEXA Scans
DEXA scans, while the gold standard for bone density assessment, aren’t always the most accessible or suitable option for everyone. Fortunately, several alternative methods exist for evaluating bone health, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Understanding these alternatives can help patients and healthcare providers make informed decisions about the best approach for assessing and managing bone health.Alternative methods for evaluating bone health offer a range of approaches, each with unique advantages and disadvantages.
Some rely on imaging techniques, while others utilize blood tests or clinical assessments. This exploration delves into these options, providing a comparative overview to aid in understanding the various avenues for evaluating bone health.
Quantitative Ultrasound (QUS)
QUS is a non-invasive technique that uses sound waves to measure bone density. It’s a relatively quick and painless procedure, and results are available immediately. The advantages of QUS include its portability and cost-effectiveness compared to DEXA. QUS can be particularly useful in screening large populations or in areas with limited access to DEXA scanners. However, QUS may not be as precise as DEXA in measuring bone density, especially in individuals with complex bone conditions.
The accuracy of QUS can also vary depending on the specific location being assessed and the type of bone.
Peripheral DEXA (pDXA)
pDXA scans measure bone mineral density (BMD) in the peripheral areas, such as the forearm or heel. This technique is often more convenient and less expensive than a full-body DEXA scan. The advantage of pDXA is its portability and lower cost compared to central DEXA. It can be useful for screening and monitoring bone health in specific populations.
However, pDXA measurements might not accurately reflect BMD in the spine or hip, the areas most commonly associated with osteoporosis-related fractures.
Blood Tests
Blood tests, while not directly measuring bone density, can provide valuable information about bone metabolism. Markers like Vitamin D levels, calcium, and parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels can indicate potential risk factors for bone loss. The advantage of blood tests is their ability to identify underlying nutritional deficiencies or hormonal imbalances that may be contributing to bone health issues.
However, these tests alone do not provide a direct measure of bone density, and they may not be sufficient to diagnose osteoporosis or predict fracture risk.
Clinical Assessments
Clinical assessments, which involve a physical examination, medical history review, and risk factor evaluation, can help identify individuals at risk for osteoporosis. These assessments are often the first step in the diagnostic process, and they can be highly effective in identifying individuals who might benefit from further testing, such as DEXA scans. A significant advantage is the relative affordability and accessibility of this method.
However, it is not as precise as DEXA or other imaging techniques, and it may not capture all relevant aspects of bone health.
Comparison Table
| Method | Advantages |
|---|---|
| DEXA Scan | High accuracy, comprehensive assessment of bone density across various sites, reliable for diagnosing osteoporosis. |
| QUS | Non-invasive, quick, portable, cost-effective, suitable for large-scale screening. |
| pDXA | Portable, less expensive than central DEXA, convenient for screening and monitoring. |
| Blood Tests | Identify underlying nutritional deficiencies or hormonal imbalances, can help pinpoint risk factors. |
| Clinical Assessments | Affordable, accessible, identifies individuals at risk for osteoporosis, first step in the diagnostic process. |
Preparing a Visual Guide
Understanding DEXA scans can be easier with visual aids. This section provides a visual representation of the DEXA scan process, highlighting key areas measured, and explaining the underlying technology. Visualizing the procedure and the data interpretation process can significantly improve comprehension and aid in understanding the importance of this crucial diagnostic tool.
DEXA Scan Process Flowchart
The following flowchart illustrates the DEXA scan process, from scheduling to results interpretation. A clear visual representation of the steps involved can facilitate patient understanding and ensure a smooth process.  Description: The flowchart depicts the DEXA scan process from scheduling to result interpretation. Key steps include scheduling the appointment, patient preparation, scan procedure, data analysis, and finally, result interpretation by a healthcare professional. Each step is connected to the next, creating a clear path for the DEXA scan journey.
Description: The flowchart depicts the DEXA scan process from scheduling to result interpretation. Key steps include scheduling the appointment, patient preparation, scan procedure, data analysis, and finally, result interpretation by a healthcare professional. Each step is connected to the next, creating a clear path for the DEXA scan journey.
Areas of the Body Measured
This infographic highlights the different areas of the body measured during a DEXA scan. Visualizing the specific anatomical regions assessed allows for a better comprehension of the scan’s scope and how it provides comprehensive information.  Description: The infographic displays a human body Artikel with highlighted areas specifically measured by the DEXA scan. This includes the spine, hips, and other skeletal regions. Color-coding or shading can be used to emphasize these areas. The diagram should clearly show the different anatomical locations scanned to provide a clear visual representation of the DEXA scan’s function.
Description: The infographic displays a human body Artikel with highlighted areas specifically measured by the DEXA scan. This includes the spine, hips, and other skeletal regions. Color-coding or shading can be used to emphasize these areas. The diagram should clearly show the different anatomical locations scanned to provide a clear visual representation of the DEXA scan’s function.
DEXA Scan Machine and Components
A DEXA scan machine is a sophisticated device that uses X-rays to measure bone density. Understanding the components of the machine is crucial for comprehending the scan process.  Description: The image shows a typical DEXA scan machine. The image should clearly depict the scanner’s main components, including the X-ray source, detectors, and the patient table. The illustration should emphasize the precise positioning of the detectors and X-ray source for accurate measurement. The image should also show the patient table’s adjustable design, highlighting the need for accurate positioning to ensure reliable measurements.
Description: The image shows a typical DEXA scan machine. The image should clearly depict the scanner’s main components, including the X-ray source, detectors, and the patient table. The illustration should emphasize the precise positioning of the detectors and X-ray source for accurate measurement. The image should also show the patient table’s adjustable design, highlighting the need for accurate positioning to ensure reliable measurements.
Bone Mineral Density Measurement
This detailed illustration demonstrates how bone mineral density (BMD) is measured during a DEXA scan. This process involves analyzing X-ray absorption differences in various bone regions.  Description: The illustration depicts the process of measuring bone mineral density (BMD). It showcases how X-rays are transmitted through the body, and how the varying absorption of these X-rays by bone tissue is measured by detectors. The diagram should clearly show the correlation between X-ray absorption, bone density, and the resultant data generated by the machine. The illustration should be labelled to highlight the different phases of the measurement process and provide an understanding of how the information is derived and interpreted. The illustration should also highlight the mathematical models used to calculate bone mineral density from the data collected.
Description: The illustration depicts the process of measuring bone mineral density (BMD). It showcases how X-rays are transmitted through the body, and how the varying absorption of these X-rays by bone tissue is measured by detectors. The diagram should clearly show the correlation between X-ray absorption, bone density, and the resultant data generated by the machine. The illustration should be labelled to highlight the different phases of the measurement process and provide an understanding of how the information is derived and interpreted. The illustration should also highlight the mathematical models used to calculate bone mineral density from the data collected.
Epilogue
In conclusion, a DEXA scan is a valuable tool for evaluating bone density and body composition. This detailed look at the procedure, preparation, measurements, and results empowers you to understand this diagnostic method and its implications. Whether you’re a patient considering the scan or a healthcare professional seeking to learn more, this guide provides a comprehensive overview. Remember, always consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice.
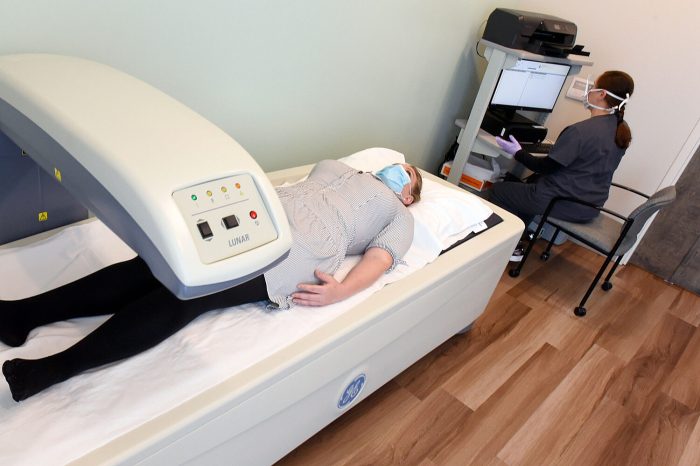









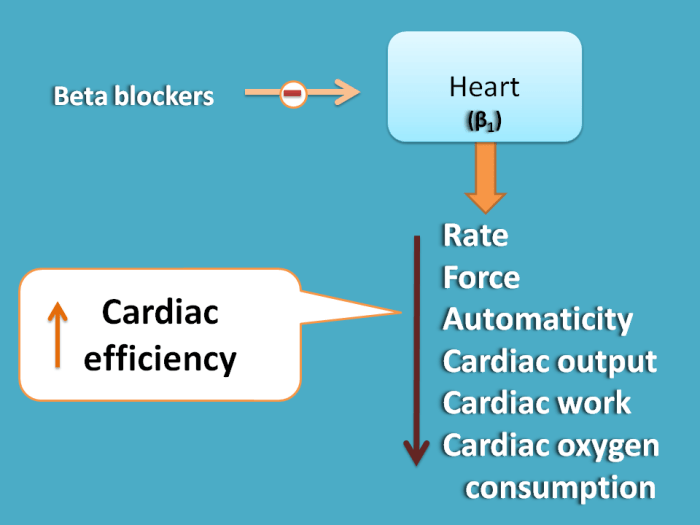

 Diagram Description: A diagram illustrating the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. The diagram depicts the sequential activation of enzymes and hormones, culminating in the production of angiotensin II and aldosterone. The diagram should show the key components like renin, angiotensinogen, angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE), angiotensin II, and aldosterone. It should also visually demonstrate the effects of these hormones on blood vessels and the kidneys.
Diagram Description: A diagram illustrating the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. The diagram depicts the sequential activation of enzymes and hormones, culminating in the production of angiotensin II and aldosterone. The diagram should show the key components like renin, angiotensinogen, angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE), angiotensin II, and aldosterone. It should also visually demonstrate the effects of these hormones on blood vessels and the kidneys. Diagram Description: A diagram showcasing the sympathetic nervous system’s impact on blood vessels. The diagram should depict the pathway of sympathetic nerve impulses, the release of norepinephrine, and the subsequent vasoconstriction of blood vessels. The diagram should highlight the involvement of alpha- and beta-adrenergic receptors in this process.
Diagram Description: A diagram showcasing the sympathetic nervous system’s impact on blood vessels. The diagram should depict the pathway of sympathetic nerve impulses, the release of norepinephrine, and the subsequent vasoconstriction of blood vessels. The diagram should highlight the involvement of alpha- and beta-adrenergic receptors in this process. Diagram Description: A diagram illustrating the mechanism of action of ACE inhibitors. The diagram should visually represent the normal conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, and how ACE inhibitors inhibit this conversion. The diagram should highlight the decreased vasoconstriction and aldosterone release as a result of this inhibition.
Diagram Description: A diagram illustrating the mechanism of action of ACE inhibitors. The diagram should visually represent the normal conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, and how ACE inhibitors inhibit this conversion. The diagram should highlight the decreased vasoconstriction and aldosterone release as a result of this inhibition. Diagram Description: A diagram illustrating the mechanism of action of beta-blockers. The diagram should visually demonstrate the interaction of beta-blockers with beta-adrenergic receptors in the heart and blood vessels. It should illustrate the resultant decrease in heart rate and contractility, and the potential for vasodilation.
Diagram Description: A diagram illustrating the mechanism of action of beta-blockers. The diagram should visually demonstrate the interaction of beta-blockers with beta-adrenergic receptors in the heart and blood vessels. It should illustrate the resultant decrease in heart rate and contractility, and the potential for vasodilation.


 Figure 1: Potential Short-Term Impact on Various Sectors of the Economy. This chart depicts a hypothetical scenario showing a temporary dip in consumer confidence and a possible increase in demand for healthcare-related goods and services. It is important to note that the actual impact will depend on numerous factors and could differ from this example.
Figure 1: Potential Short-Term Impact on Various Sectors of the Economy. This chart depicts a hypothetical scenario showing a temporary dip in consumer confidence and a possible increase in demand for healthcare-related goods and services. It is important to note that the actual impact will depend on numerous factors and could differ from this example.