ACA compliant health insurance sets the stage for navigating the complex world of healthcare coverage. This comprehensive guide dives deep into the specifics of these plans, outlining everything from their key characteristics to enrollment procedures and cost structures. Understanding these plans is crucial for making informed decisions about your health and well-being.
We’ll explore the different types of ACA compliant plans, highlighting the differences between Bronze, Silver, Gold, and Platinum plans. A detailed table will illustrate the key features and costs associated with each. We’ll also cover the essential health services covered, preventive care, mental health provisions, and the crucial process of finding and enrolling in a plan on healthcare.gov.
Defining ACA Compliant Health Insurance

The Affordable Care Act (ACA) significantly reshaped the US health insurance landscape. A key component of this reform is the requirement for health insurance plans to meet specific criteria to be considered “ACA compliant.” Understanding these plans is crucial for consumers seeking coverage.ACA compliant health insurance plans are designed to ensure essential health benefits are offered to all enrollees.
These plans must adhere to minimum standards for coverage and affordability, aiming to make health insurance accessible to a wider range of individuals.
Key Characteristics of ACA Compliant Plans
ACA compliant plans differ from other plans in several key aspects. They are required to cover essential health benefits, including preventive services, hospitalization, maternity care, and emergency care. Furthermore, these plans cannot impose lifetime or annual limits on coverage. Crucially, they are designed to prevent discrimination based on pre-existing conditions.
Types of ACA Compliant Plans
Several types of ACA compliant plans are available, categorized by the level of coverage and cost. The most common types are Bronze, Silver, Gold, and Platinum plans. These plans offer varying degrees of coverage and out-of-pocket costs, allowing individuals to choose the plan that best suits their needs and budget.
Comparing Bronze, Silver, Gold, and Platinum Plans
The differences between these plan types lie primarily in their cost and the level of coverage they offer. Bronze plans generally have the lowest premiums but also the lowest level of coverage. Conversely, Platinum plans offer the highest level of coverage and often have higher premiums. Silver and Gold plans fall between these two extremes.
Plan Type Comparison Table
| Plan Type | Cost | Coverage | Out-of-Pocket Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bronze | Lowest Premium | Lowest Level of Coverage | Potentially lower out-of-pocket maximum, but still can be a significant amount |
| Silver | Mid-range Premium | Mid-range Level of Coverage | Mid-range out-of-pocket maximum, generally a reasonable amount |
| Gold | Higher Premium | Higher Level of Coverage | Higher out-of-pocket maximum, but also offers more comprehensive coverage |
| Platinum | Highest Premium | Highest Level of Coverage | Highest out-of-pocket maximum, but with the greatest degree of protection against high medical costs |
Note: Costs and coverage levels vary by location and specific plan. Always review the details of individual plans to ensure they meet your needs.
Navigating ACA compliant health insurance can be tricky, but it’s crucial for affordable coverage. If you’re wondering if you have a broken bone, do i have a broken bone is a good starting point to understand the symptoms and when you should seek professional medical attention. Regardless of your injury, knowing your insurance options and coverage is essential for making informed decisions, and ACA compliant plans can help you access necessary care.
Coverage and Benefits
Understanding your ACA-compliant health insurance plan’s coverage is crucial for making informed decisions about your healthcare. This section delves into the specifics of what’s covered, the essential health benefits required, and common preventative services. It also addresses the important aspect of mental health coverage.Essential health services are a cornerstone of ACA-compliant plans. These plans are designed to provide comprehensive coverage for a wide range of medical needs, ensuring access to care for a variety of conditions.
This crucial aspect is a significant advancement in healthcare accessibility.
Essential Health Benefits Required by the ACA
The Affordable Care Act (ACA) mandates specific essential health benefits (EHBs) that all qualifying health insurance plans must cover. These EHBs are designed to ensure comprehensive healthcare access for all Americans. Examples of EHBs include preventive services, hospitalization, maternity care, and emergency services.
Specific Benefits and Exclusions of ACA Plans
The specific benefits and exclusions of ACA-compliant plans can vary. While the essential health benefits are standardized, the details of coverage within those categories can differ between plans. Factors like plan type (e.g., PPO, HMO) and the specific insurance provider can affect the level of coverage. It’s crucial to carefully review the plan documents to understand the specific details and limitations of the coverage.
Essential Health Services Covered
ACA-compliant plans must cover a range of essential health services. These include preventive services, mental health care, and chronic disease management. This comprehensive coverage is a significant step toward ensuring access to essential healthcare services.
Preventive Services Covered
ACA plans are required to cover preventive services without cost-sharing. This means preventive screenings, vaccinations, and counseling for various health conditions are typically covered. This is a critical aspect of maintaining good health. Examples include:
- Well-woman visits
- Well-child visits
- Cancer screenings
- Vaccinations
- Chronic disease management
Mental Health Coverage Requirements
Mental health coverage is a significant component of ACA-compliant plans. These plans must cover mental health services at parity with physical health services. This means mental health services, such as therapy and counseling, are covered at the same level as physical healthcare services.
Summary Table of Preventive Services
| Service Category | Examples |
|---|---|
| Preventive Care | Annual check-ups, cancer screenings, vaccinations, cholesterol screenings, blood pressure screenings, and diabetes screenings. |
| Mental Health | Therapy, counseling, and psychiatric services. |
| Dental | Preventive dental care, such as cleanings and check-ups. (Coverage may vary). |
| Vision | Eye exams and glasses/contacts. (Coverage may vary). |
Marketplace and Enrollment
Navigating the Affordable Care Act (ACA) marketplace can feel overwhelming, but understanding the process is key to securing affordable health insurance. This section details the steps involved in finding and enrolling in an ACA-compliant plan, highlighting crucial deadlines and resources available to consumers. The ACA marketplace is designed to make health insurance more accessible, but knowing the specifics can save you time and potential issues.The ACA marketplace, often referred to as the health insurance exchange, provides a platform for individuals and families to compare and choose health insurance plans.
This centralized system allows for a more streamlined process, helping individuals find plans that meet their specific needs and budgets.
Finding ACA Compliant Plans
The healthcare.gov website is the primary platform for finding and enrolling in ACA-compliant plans. It provides a comprehensive database of available plans, allowing users to compare coverage options based on factors like location, family size, and health needs. Other resources, such as state-based marketplaces and independent insurance agents, can also assist individuals in finding suitable plans.
Enrollment Deadlines and Special Enrollment Periods
The ACA establishes specific enrollment periods, commonly referred to as open enrollment, during which individuals can sign up for health insurance plans. These periods typically run from November to December, offering a window for individuals to secure coverage for the following year. In addition to the standard open enrollment period, special enrollment periods (SEPs) are available for certain life events.
These include, but are not limited to, changes in employment status, marriage, or the birth of a child. Understanding these deadlines and eligibility criteria is crucial to ensuring timely enrollment.
Step-by-Step Enrollment Guide
The enrollment process generally involves these steps:
- Visit the healthcare.gov website or your state’s marketplace.
- Provide personal information, such as your name, address, date of birth, and contact details.
- Specify your household members’ details to determine eligibility for family coverage.
- Review available plans based on your location and needs. Compare premium costs, coverage details, and network providers.
- Select a plan that meets your requirements and complete the enrollment application.
- Verify the information submitted and submit the application.
- Obtain confirmation of enrollment and plan details.
Understanding Your Health Insurance Plan
Thoroughly reviewing the details of your chosen health insurance plan is essential. Understand the coverage offered, including preventive care services, hospitalization benefits, and out-of-pocket expenses. This includes examining the provider network to ensure access to doctors and hospitals you prefer. A clear understanding of your plan’s provisions helps you make informed decisions about your healthcare. Understanding your plan’s deductibles, co-pays, and co-insurance percentages is crucial for effective financial planning.
This information helps you estimate the total cost of care and plan accordingly.
Cost and Premium Structure: Aca Compliant Health Insurance
Understanding the cost of ACA-compliant health insurance plans is crucial for making informed decisions. Premiums, deductibles, and other cost-sharing mechanisms are key components of the total cost, and their calculation methods can vary significantly between plans. This section delves into how these elements are determined and how they affect the overall expense.Premium rates are influenced by several factors, making it important to understand these variables.
These factors can vary considerably based on location, age, and family size. Understanding how these factors affect premium costs is essential for comparing plans.
Premium Determination
Premiums are calculated using complex algorithms considering various factors. These calculations are based on historical claims data, actuarial models, and projected future healthcare costs. The resulting premium is then adjusted for factors such as the geographic location of the insured, age, and family size.
Factors Influencing Premium Costs
Several factors directly impact the premium cost of an ACA-compliant health insurance plan. These factors play a significant role in determining the overall price.
- Location: Healthcare costs vary geographically. Areas with higher medical expenses, specialist availability, and demand for specific services tend to have higher premiums. For example, a plan in a major metropolitan area might have a higher premium than a plan in a rural area due to greater healthcare utilization and higher costs of care.
- Age: Generally, younger individuals have lower premiums than older individuals because they are expected to have fewer healthcare needs. As individuals age, their healthcare needs and associated costs are often higher, resulting in a corresponding increase in premiums.
- Family Size: Larger families often have higher premiums because they typically incur more healthcare costs than smaller families. The number of dependents and their respective needs contribute to the premium calculation.
Cost-Sharing Mechanisms
Cost-sharing mechanisms, such as deductibles, co-pays, and co-insurance, are essential components of health insurance plans. These mechanisms help control costs and manage the financial burden of healthcare services.
Finding affordable ACA compliant health insurance can be a real headache, but it’s crucial for your well-being. One surprisingly beneficial way to potentially boost your health and potentially lower healthcare costs in the long run is through regular sauna use. Studies show that the effects of regular sauna use can include improved circulation and detoxification. Ultimately, prioritizing your health through preventative measures like consistent sauna sessions can complement your ACA compliant health insurance strategy.
- Deductible: The amount an individual must pay out-of-pocket for covered healthcare services before the insurance company starts paying. A higher deductible generally translates to lower premiums.
- Co-pay: A fixed amount paid for specific healthcare services, such as a doctor’s visit or prescription medication. Co-pays help reduce the financial burden of routine care.
- Co-insurance: A percentage of the cost of a covered healthcare service that the insured is responsible for after the deductible has been met. This portion is shared between the insured and the insurance company.
Comparison of Cost-Sharing Among Plans
Different plans often have different cost-sharing arrangements. The choice of plan depends on the individual’s needs and budget. The total cost of the plan should be carefully considered.
- Bronze Plans: Typically offer the lowest premiums but require a higher out-of-pocket expense. This plan type often has a higher deductible, co-pay, and co-insurance rate.
- Silver Plans: Offer a moderate balance between premium costs and out-of-pocket expenses. This plan type has a moderate deductible, co-pay, and co-insurance rate.
- Gold Plans: Generally have higher premiums but lower out-of-pocket expenses. This plan type often has a lower deductible, co-pay, and co-insurance rate.
- Platinum Plans: Have the highest premiums but offer the lowest out-of-pocket costs. This plan type often has the lowest deductible, co-pay, and co-insurance rate.
Calculating Total Plan Cost
To calculate the total cost of a plan, consider the premium, deductible, co-pay, and co-insurance. A comprehensive understanding of these factors is essential for evaluating different plans.
Total Plan Cost = Premium + Estimated Out-of-Pocket Expenses (Deductible + Co-pay + Co-insurance)
Navigating ACA-compliant health insurance can be tricky, but it’s crucial for comprehensive coverage. Understanding potential health risks, like those associated with macular degeneration, is also key. For example, learning about the risk factors for macular degeneration can help you make informed decisions about your health and insurance choices. Macular degeneration causes risk factors are varied and complex, but having good insurance is still a critical first step to managing your health.
Ultimately, finding ACA-compliant insurance that fits your needs is important for your overall well-being.
For example, a Bronze plan might have a $5,000 deductible, $20 co-pay for a doctor’s visit, and 20% co-insurance. If the premium is $300 per month, the estimated annual out-of-pocket cost for a year could be $6,000 (estimated). This example demonstrates how a lower premium can lead to higher out-of-pocket costs, making a complete cost analysis critical.
Understanding Exclusions and Limitations
Navigating the world of health insurance can feel like a maze, especially when trying to decipher the fine print. Knowing what’s covered and what’s not is crucial for making informed decisions about your healthcare. This section delves into the common exclusions and limitations in ACA-compliant plans, providing clarity on pre-existing conditions and coverage denials.Understanding the nuances of coverage is essential to avoid surprises down the road.
By knowing the potential limitations of your plan, you can proactively plan for healthcare needs and avoid unnecessary financial burdens. A health insurance broker can be invaluable in interpreting these complexities.
Common Exclusions and Limitations
Many ACA-compliant plans have limitations on certain types of services. This section Artikels some of the most frequent exclusions and limitations.
- Preventive care is generally covered, but specific preventative services may have limitations, such as certain screenings or vaccinations. Check your plan documents for details.
- Mental health services are generally covered, but there may be limitations on the frequency or duration of therapy sessions or the types of providers accepted.
- Prescription drugs may have limitations on the types of medications covered, the amount of coverage per prescription, or the required co-pays. A formulary (a list of covered drugs) is typically available on the insurance provider’s website.
- Out-of-network care often carries higher costs and reduced coverage compared to in-network providers.
- Alternative medicine, such as acupuncture or chiropractic care, might not be fully covered or may require pre-authorization.
Pre-Existing Conditions and the ACA
The Affordable Care Act (ACA) prohibits insurance companies from denying coverage or charging higher premiums based on pre-existing conditions. This protection is a critical component of the ACA’s aim to ensure everyone has access to affordable healthcare.
- Coverage Requirements: Insurance providers cannot deny coverage or increase premiums due to pre-existing conditions for individuals who obtain coverage during the open enrollment period. Those enrolled outside this period, while still protected, may face specific limitations that vary by plan.
- Specific Considerations: While coverage is generally guaranteed, there might be some exceptions. For example, certain services may require pre-authorization or have waiting periods. This varies between providers and plans.
Appealing Coverage Denials
If a claim is denied, understanding the appeals process is essential. Most plans have a structured appeals procedure.
- Understanding the Process: Review the plan documents for specific appeal procedures. Typically, this involves providing supporting documentation and contacting the insurance provider’s customer service department. A timeline is usually included for resolution.
- Seeking Assistance: Consider contacting a health insurance broker or a consumer advocate for guidance if needed. They can provide assistance in navigating the appeal process.
Examples of Coverage Limitations, Aca compliant health insurance
Specific situations can lead to coverage limitations.
- Out-of-pocket maximums: Most plans have an out-of-pocket maximum, beyond which the insurer will cover 100% of your medical expenses. After reaching this limit, you will not be responsible for any further costs. Be aware of these limits and how they affect your overall costs.
- Pre-authorization requirements: Some services, such as certain surgeries or procedures, may require pre-authorization. Failure to obtain pre-authorization can lead to the denial of the claim.
- Limited coverage for experimental treatments: Experimental or investigational treatments may not be fully covered, or coverage may be limited to specific conditions. Be sure to understand your plan’s coverage for these types of treatments.
Role of a Health Insurance Broker
A health insurance broker can help clarify complex coverage details. They act as an intermediary, assisting in understanding the specific coverage of a plan, and can provide tailored recommendations.
- Expert Guidance: A broker can explain the nuances of different plans, ensuring you choose one that meets your individual healthcare needs and budget.
- Negotiation and Assistance: Brokers can often negotiate better terms and assist with appealing coverage denials, which can potentially reduce your out-of-pocket expenses.
Accessing and Using ACA Compliant Plans
Navigating your ACA compliant health insurance plan can seem daunting, but it doesn’t have to be. This section will detail how to access healthcare services, file claims, use your plan’s online tools, and find network providers. Understanding these processes will empower you to effectively utilize your coverage and receive the care you need.
Accessing Healthcare Services
Your ACA compliant plan provides access to a network of healthcare providers. Finding a doctor within your plan’s network is crucial to ensure your care is covered at the agreed-upon rate. In most cases, you can locate a provider through your plan’s website or app. You’ll need to know your plan’s name and the provider’s specialty or location to efficiently search.
Finding a provider outside your network will likely require higher out-of-pocket costs.
Filing Claims
The claim filing process varies slightly depending on your plan. Some plans allow for online claim submission, while others may require paper forms. You can usually find detailed instructions on your plan’s website or in your member handbook. Review the specific requirements carefully to avoid delays or denials. Commonly, the process involves gathering necessary information, completing the claim form, and submitting it electronically or by mail.
Always keep copies of submitted claims for your records.
Using the Plan’s Website or App
Your plan’s website or mobile app serves as a centralized hub for managing your account. It provides a convenient way to view your benefits, track claims, make payments, and communicate with customer service representatives. These platforms often offer detailed explanations of your coverage, allowing you to quickly understand what is and isn’t covered. Many apps allow you to track your healthcare spending, manage your medical records, and securely communicate with your healthcare providers.
The website also typically contains important information such as a glossary of terms.
Claim Filing Process Flowchart
This flowchart Artikels the typical claim filing process:
Start | V Gather necessary information (patient details, provider information, dates of service) | V Access claim form online or through member portal | V Complete the claim form accurately | V Submit claim electronically or via mail | V Track claim status online | V Review receipt and explanation of benefits (EOB) | V If needed, contact the plan for clarification | V End
Locating a Network Provider
Finding a network provider is straightforward with many ACA compliant plans. The plan’s website or app usually features a searchable database of providers.
You can typically filter results by location, specialty, and other criteria. A user-friendly interface helps locate providers who accept your plan. The plan’s website may also provide a map-based search function. Using this tool, you can find a provider near your home or work. Contacting your plan’s customer service team is another option if you have any issues.
Recent Updates and Changes
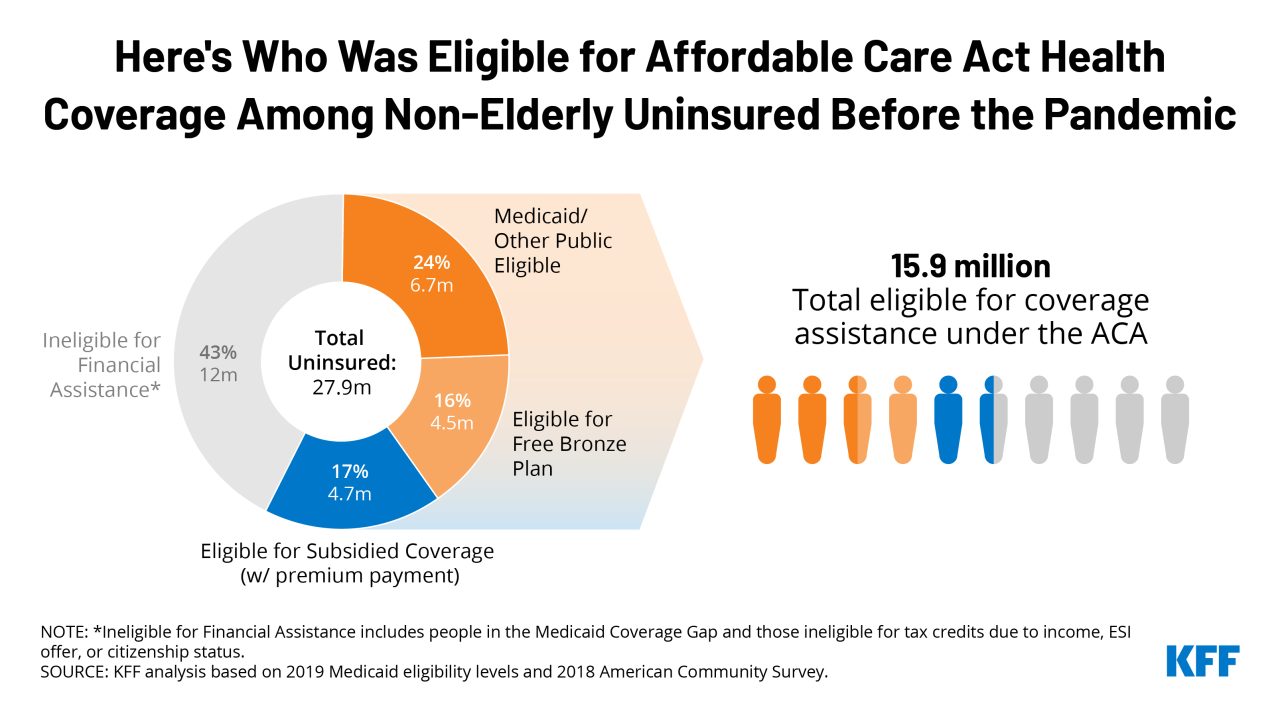
Navigating the Affordable Care Act (ACA) marketplace can feel like a maze, especially when considering the constant evolution of regulations and guidelines. Recent updates and changes to ACA compliant plans have implications for coverage, costs, and enrollment, impacting different groups of people in various ways. Understanding these shifts is crucial for making informed decisions about health insurance.
Recent years have witnessed several key adjustments in the ACA landscape, impacting both the structure of the plans and the ways individuals access them. These adjustments range from modifications to premium subsidies to new regulations regarding essential health benefits. The goal is often to improve access and affordability, but these changes can also create challenges for those navigating the system.
Impact on Coverage and Costs
Recent updates have influenced both the types of coverage offered and the associated costs. For instance, some plans have expanded their offerings of mental health and substance abuse services, a significant development for individuals and families seeking comprehensive care. At the same time, changes in premium subsidies have led to varying levels of affordability depending on individual circumstances and location.
A recent example is the adjustment of cost-sharing reductions (CSR), which influences the amount of financial assistance available to those with moderate incomes.
Impact on Different Groups of People
These changes affect various groups differently. Low-income individuals and families, who often rely heavily on subsidies to afford coverage, may experience varying levels of impact based on the specific modifications to subsidy programs. Similarly, young adults, who are frequently a key demographic for the ACA marketplace, might experience shifts in the affordability and availability of plans. Changes to the essential health benefits requirements could also affect the types of care accessible to certain populations, for example, individuals with specific pre-existing conditions.
New Regulations and Guidelines
Several new regulations and guidelines have emerged concerning ACA plans. For example, there are updated requirements for insurance companies regarding the types of preventative services that must be covered. These adjustments often reflect ongoing efforts to improve the overall quality and accessibility of healthcare services. Furthermore, there might be new guidelines regarding the use of telehealth services, which have become increasingly prevalent in recent years.
Staying Informed
Staying abreast of the latest ACA changes is crucial for making informed choices about health insurance. Several resources can help you navigate this process. The official ACA website provides comprehensive information on current regulations and guidelines. Also, reputable news sources and consumer advocacy groups frequently report on significant developments. Furthermore, healthcare advisors and insurance agents can offer personalized guidance.
These resources help you stay updated and empowered in making informed decisions about your health insurance needs.
Conclusive Thoughts
In conclusion, navigating ACA compliant health insurance can seem daunting, but with a clear understanding of the different plan types, coverage options, and enrollment procedures, it becomes more manageable. We’ve provided a comprehensive overview of the key aspects, empowering you to make informed choices about your health insurance. Remember to always consult with a healthcare professional or broker for personalized advice.