Colon Cancer Causes Risk Factors Unveiled
Colon cancer causes risk factors are a complex interplay of genetic predispositions, lifestyle choices, environmental exposures, and underlying medical conditions....


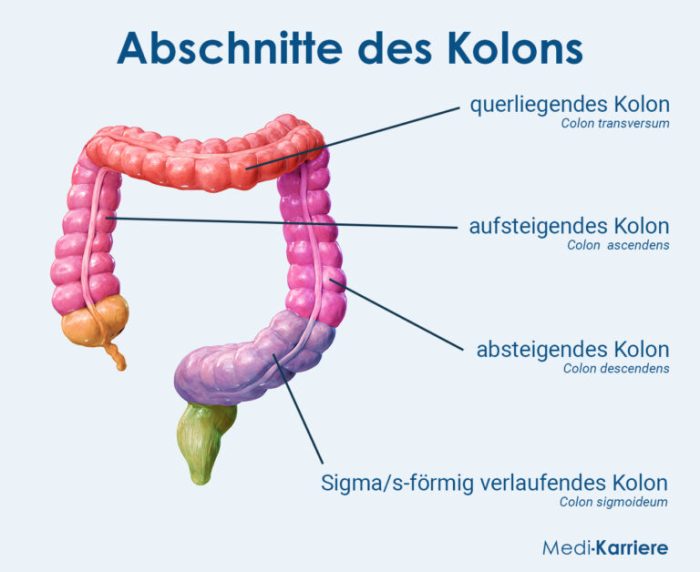



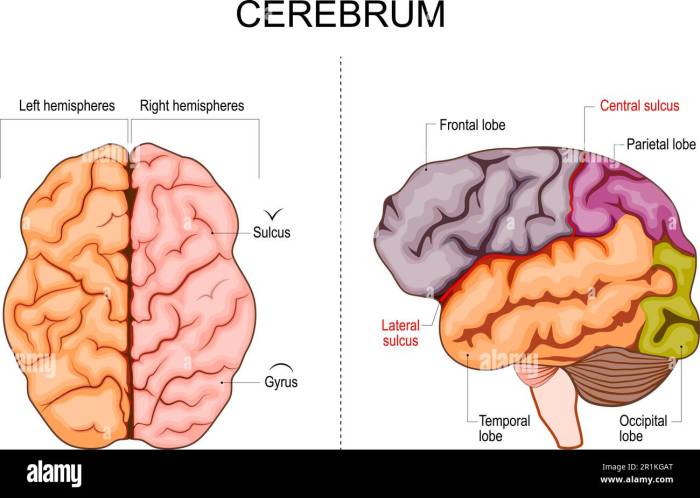

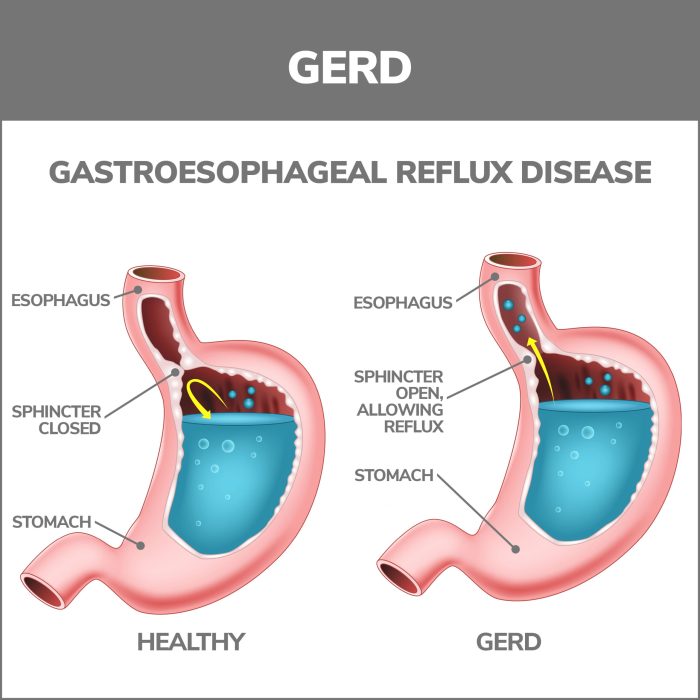
Colon cancer causes risk factors are a complex interplay of genetic predispositions, lifestyle choices, environmental exposures, and underlying medical conditions....
Hyperinflation of the lungs, a condition characterized by an abnormal expansion of the lung airspaces, presents a complex interplay of...
What is brocas aphasia – What is Broca’s aphasia? This neurological condition impacts a person’s ability to produce speech, significantly...
Medication changes after semaglutide can be a complex process, impacting various aspects of a patient’s health. This guide explores potential...
How to reduce a stuffy nose at night? This guide delves into the common causes of nighttime nasal congestion, from...
Phuoc Anne Nguyen PharmD MS BCPS is a highly accomplished pharmacist with extensive experience in [mention a specific area of...
Acute infectious thyroiditis overview: This condition, often caused by bacterial or viral infections, can lead to inflammation and pain in...
Headache in kids when to worry – Headache in kids: when to worry? This is a crucial question for parents,...
Why does COPD cause increased mucus production? This question delves into the complex interplay of inflammation, structural changes, genetics, and...
Achilles tendon rupture non operative treatment – Achilles tendon rupture non-operative treatment explores a conservative approach to healing a torn...