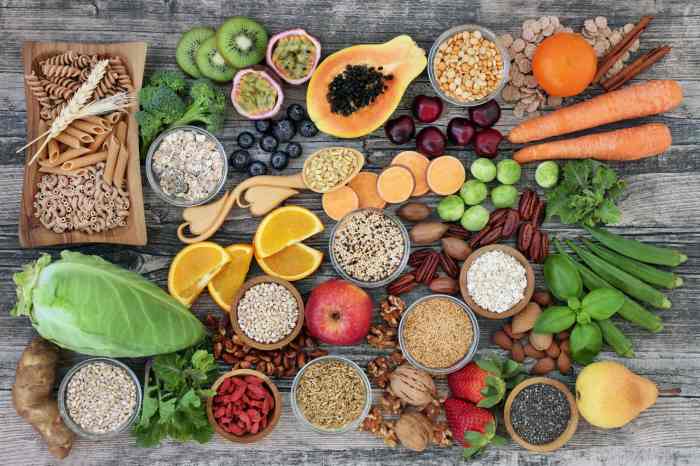
Foods with more omega 3 than sardines – Foods with more omega-3 than sardines is a deep dive into the world of healthy fats. We’ll explore a wealth of alternatives to sardines, highlighting foods packed with these essential nutrients. From nuts and seeds to surprising plant-based options, discover the delicious and diverse ways to boost your omega-3 intake beyond the familiar.
Omega-3 fatty acids are crucial for a variety of bodily functions, from brain health to heart health. This exploration delves into the specific types of omega-3s, their sources, and how they compare nutritionally. We’ll examine various foods and their omega-3 content, alongside other vital nutrients, providing you with a comprehensive guide to enriching your diet with these powerful fats.
Introduction to Omega-3 Rich Foods

Omega-3 fatty acids are essential nutrients our bodies need but cannot produce on their own. They play a crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being, impacting everything from brain function to heart health. Incorporating foods rich in omega-3s into your diet is vital for optimal health outcomes. These polyunsaturated fats are important components of cell membranes and are involved in numerous bodily processes.Consuming sufficient amounts of omega-3s has been linked to a reduced risk of chronic diseases, including heart disease, stroke, and certain mental health conditions.
The specific benefits and mechanisms of action vary slightly depending on the type of omega-3. Understanding the different types and their sources is key to maximizing the health benefits derived from omega-3 consumption.
Types of Omega-3s and Their Sources
Omega-3 fatty acids are categorized into three main types: ALA (alpha-linolenic acid), EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid), and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid). While ALA is considered an essential fatty acid, our bodies can convert it to EPA and DHA, although this conversion rate is often inefficient. EPA and DHA are typically found in animal-based foods and are considered more readily available for direct use by the body.
Comparing Omega-3 Types and Their Benefits
| Omega-3 Type | Sources | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| ALA (alpha-linolenic acid) | Flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts, and some leafy green vegetables | ALA is an essential fatty acid that plays a vital role in maintaining cell membrane structure and function. It may also contribute to reducing inflammation and supporting heart health. |
| EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) | Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, tuna, herring), krill, and algae | EPA is linked to various health benefits, including reducing blood clotting, lowering triglycerides, and supporting heart health. Studies suggest it may also contribute to reducing inflammation and improving brain function. |
| DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) | Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, tuna, herring), krill, algae, and some fortified foods | DHA is a crucial component of brain tissue and plays a vital role in brain development and function, especially in infants and children. It also supports eye health and may contribute to cognitive function in adults. Furthermore, DHA is implicated in maintaining healthy cell membranes. |
Importance of Omega-3s in a Healthy Diet
A diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids is essential for optimal health. The diverse range of benefits, from supporting heart health to cognitive function, highlights the importance of incorporating omega-3-rich foods into a balanced diet.
Identifying Alternatives to Sardines

Sardines, while a fantastic source of omega-3s, might not be everyone’s cup of tea. Fortunately, a plethora of other delicious and nutritious foods offer similar benefits. This exploration delves into several omega-3-rich alternatives, highlighting their nutritional profiles and preparation methods to broaden your choices.A balanced diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids is crucial for overall health. These essential fats play a vital role in maintaining heart health, brain function, and reducing inflammation.
Beyond sardines, numerous other food sources can contribute to your omega-3 intake, each with unique characteristics and nutritional advantages.
Omega-3 Rich Fish Alternatives
A variety of fish offer excellent omega-3 content. Choosing alternatives to sardines opens up a world of culinary possibilities. Salmon, mackerel, tuna, and trout all provide healthy fats, and their flavors are diverse, making them appealing for various dishes.
- Salmon: Known for its rich, pink flesh, salmon is a powerhouse of omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA and DHA. These are crucial for brain health and reducing inflammation. Salmon is a versatile ingredient, suitable for grilling, baking, or pan-frying. Its high protein content also contributes to satiety and muscle maintenance. Wild-caught salmon is often preferred for its lower contamination levels compared to farmed varieties.
The nutritional value of salmon is significant, making it a good alternative to sardines, especially for those seeking a more familiar taste profile.
- Mackerel: This oily fish is packed with omega-3s and other essential nutrients like vitamin D and B vitamins. Mackerel is a good source of protein and offers a slightly stronger, more robust flavor than salmon. It’s best prepared by grilling or baking, allowing the natural flavors to shine through.
- Tuna: Tuna is a popular choice for its quick cooking time and high protein content. Different tuna varieties contain varying amounts of omega-3s. White tuna, for example, has a lower fat content than some other tuna species. Tuna can be prepared in various ways, including salads, sandwiches, or sushi.
- Trout: Trout is a freshwater fish with a mild flavor, making it suitable for various culinary preparations. It’s rich in omega-3 fatty acids, offering a balanced nutrition profile. Trout is often grilled, pan-fried, or baked, and its delicate flavor makes it a delightful addition to many meals.
Plant-Based Omega-3 Sources
Beyond fish, several plant-based foods provide valuable omega-3s. These alternatives offer a unique nutritional profile compared to fish-based sources.
- Chia Seeds: These tiny seeds are incredibly nutrient-dense, boasting a significant amount of ALA, an omega-3 fatty acid. Chia seeds can be incorporated into smoothies, yogurt, or added to baked goods. They are a good source of fiber and other essential nutrients.
- Flax Seeds: Similar to chia seeds, flax seeds are an excellent source of ALA, a type of omega-3 fatty acid. They are commonly ground and used in baking, sprinkled on salads, or added to yogurt.
- Hemp Seeds: These seeds are a complete protein source, containing all nine essential amino acids, alongside a good dose of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. Hemp seeds can be eaten whole or ground into a powder, and they add a nutty flavor to various dishes.
Nutritional Comparison Table
| Food | Omega-3 Content (per serving) | Other Nutrients | Preparation Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sardines (3 oz) | ~1.5 grams | Vitamin D, Calcium, Iron, B Vitamins | Baking, grilling, or canned |
| Salmon (3 oz) | ~1.6 grams | Vitamin D, Protein, Selenium | Baking, grilling, pan-frying |
| Mackerel (3 oz) | ~1.8 grams | Vitamin D, B Vitamins, Iron | Grilling, baking, pan-frying |
| Tuna (3 oz) | ~0.5-1 gram (depending on type) | Protein, Vitamin B12 | Salads, sandwiches, sushi |
| Trout (3 oz) | ~1.2 grams | Vitamin D, Protein, Selenium | Grilling, pan-frying, baking |
| Chia Seeds (1 tbsp) | ~2 grams ALA | Fiber, Protein, Antioxidants | Smoothies, yogurt, baked goods |
| Flax Seeds (1 tbsp) | ~2 grams ALA | Fiber, Magnesium, Lignans | Ground, sprinkled on salads, baked goods |
| Hemp Seeds (1 tbsp) | ~1 gram omega-3s | Protein, Iron, Magnesium | Eaten whole, ground, added to dishes |
Exploring Specific Omega-3 Food Groups
Beyond the familiar fishy delights, a wealth of plant-based and other sources offer omega-3s. These diverse options cater to various dietary preferences and needs, making it easier than ever to incorporate these essential fatty acids into your daily routine. Understanding these diverse food groups can help you create a balanced and comprehensive approach to omega-3 intake.This exploration delves into the different food groups containing omega-3s, highlighting specific examples, preparation methods, and their respective omega-3 content.
This detailed overview empowers you to make informed choices and incorporate these beneficial nutrients into your diet effectively.
While sardines are a fantastic source of omega-3s, did you know some other foods pack an even bigger punch? Flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts are all excellent choices, offering a potent dose of omega-3 fatty acids. Understanding these healthy alternatives is crucial, especially when considering potential liver health concerns, like the warning signs of a dying liver. This article can help you recognize early symptoms.
Ultimately, incorporating a variety of omega-3 rich foods into your diet is a smart move for overall health.
Plant-Based Sources of Omega-3s
Plant-based foods, while not containing the same type of omega-3s as fatty fish, provide significant amounts of ALA (alpha-linolenic acid), a precursor that the body can convert into EPA and DHA, though the conversion rate is not always optimal. This conversion process is influenced by factors such as overall diet and health status. Incorporating a variety of plant-based omega-3 sources can still contribute to overall health benefits.
- Flaxseeds and Flaxseed Oil: These tiny seeds are nutritional powerhouses. Ground flaxseeds can be sprinkled on cereals, yogurt, or smoothies. Flaxseed oil is a versatile addition to salads or dressings. Cold-pressing flaxseed oil is often the best method for preserving its nutrients.
- Chia Seeds: These tiny seeds are a great source of fiber and omega-3s. Chia seeds can be added to yogurt, oatmeal, or mixed into smoothies for a boost of nutrients. Preparation is straightforward, simply adding them to your preferred food or beverage.
- Hemp Seeds: These seeds offer a complete protein profile and are a good source of omega-3s, along with other essential nutrients. Hemp seeds can be eaten as a snack, sprinkled on salads, or blended into smoothies. Their nutty flavor complements many dishes.
- Walnuts: These nutritious nuts are a good source of omega-3s, fiber, and antioxidants. Walnuts can be eaten as a snack, added to salads, or used in baking. They can also be used to add flavor and texture to various recipes.
Other Omega-3 Rich Foods
A variety of other foods offer omega-3s. These often come with their own specific preparation methods, impacting their nutritional value. This section highlights these options.
While sardines are packed with omega-3s, did you know some other foods boast even higher levels? For example, flaxseeds and chia seeds are nutritional powerhouses in this area. Understanding the importance of omega-3 fatty acids for overall health is key, and if you’re interested in learning more about the potential connection between diet and PMDD, exploring PMDD facts and statistics might be helpful.
Ultimately, incorporating a variety of omega-3 rich foods into your diet is a great way to support your well-being.
- Seaweed (e.g., kelp, wakame): A common ingredient in Asian cuisine, seaweed provides a good source of omega-3s. Seaweed can be eaten raw, added to soups, or used as a wrap. Seaweed often benefits from simple cooking methods, like steaming, to maintain its nutrients.
- Edamame: These young soybeans are a delicious and nutritious snack. Steaming or boiling edamame is a common preparation method. This allows for easy consumption and highlights the natural flavor of the soybeans.
- Algae: Certain types of algae, such as spirulina and chlorella, are excellent sources of omega-3s. Algae can be added to smoothies or taken as a supplement in powder form. Their versatility allows them to be integrated into many different recipes.
Omega-3 Food Group Comparison
This table summarizes the omega-3 content (approximate values) per serving for various food groups.
| Food Group | Specific Foods | Omega-3 Content (per serving) | Preparation Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plant-Based | Flaxseeds, Chia Seeds, Hemp Seeds, Walnuts | Varying amounts, dependent on serving size | Sprinkling, adding to smoothies, incorporating into dishes |
| Other | Seaweed, Edamame, Algae | Varying amounts, dependent on serving size | Steaming, boiling, raw consumption, adding to recipes |
Comparing Omega-3 Content Across Foods: Foods With More Omega 3 Than Sardines
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential for human health, playing crucial roles in brain function, heart health, and overall well-being. While sardines are a well-known source, many other foods offer comparable or even superior amounts of these beneficial fats. Understanding the diverse range of omega-3-rich foods allows for a more personalized and effective approach to incorporating these nutrients into a balanced diet.This comparison delves into the omega-3 content of various foods, considering factors like the type of omega-3, the quantity per serving, and important considerations for maximizing nutritional value.
This deeper understanding empowers individuals to make informed choices and optimize their omega-3 intake.
Omega-3 Content Comparison Table
The table below presents a concise comparison of omega-3 content across different foods. Keep in mind that values can vary based on preparation methods and specific growing conditions.
| Food | Omega-3 Type | Content (mg/serving) | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sardines (3 oz) | EPA, DHA | 1000-1500 mg | Excellent source of EPA and DHA, crucial for heart health and brain function. Choose wild-caught for optimal nutritional value. |
| Salmon (3 oz) | EPA, DHA | 600-1000 mg | Another excellent source of EPA and DHA. Wild-caught salmon generally has a higher omega-3 content than farmed. |
| Chia Seeds (1 tbsp) | ALA | 2500-3000 mg | Rich in ALA, a type of omega-3 that the body can convert to EPA and DHA, but this conversion rate is not always optimal. |
| Flax Seeds (1 tbsp) | ALA | 2000-2500 mg | Similar to chia seeds, flaxseeds are a good source of ALA. Be mindful of proper storage and grinding to maximize nutrient absorption. |
| Tuna (3 oz) | EPA, DHA | 200-500 mg | A decent source of omega-3s, but lower content than sardines or salmon. Mercury levels should be considered. |
| Walnuts (1 oz) | ALA | 2500-3000 mg | A good source of ALA, adding variety to omega-3 intake. |
| Edamame (1 cup) | ALA | 100-200 mg | A plant-based option, although ALA content is lower compared to seeds. |
Factors Influencing Omega-3 Content
Several factors influence the omega-3 content of foods. Species variations play a significant role. For example, wild-caught fish often contain higher levels of EPA and DHA compared to farmed fish. Growing conditions, such as the diet of the animal or the type of plant, also impact the omega-3 content of the food. Processing methods can also affect the amount of omega-3s preserved in the final product.
Dietary Considerations and Practical Applications
Making omega-3s a regular part of your diet doesn’t have to feel like a chore. With a little planning and creativity, you can easily incorporate these beneficial fats into your meals, enhancing your overall health and well-being. The key is to view them as part of a delicious and varied diet, not as a separate, difficult task.Integrating omega-3 rich foods seamlessly into a balanced diet is about mindful choices and strategic planning.
Consider the frequency of consumption and the portion sizes for each food source to achieve a healthy balance. Understanding how these foods interact with other nutrients in your meals can help you make informed decisions.
Incorporating Omega-3s into a Balanced Diet
A balanced diet is crucial for optimal health, and omega-3 fatty acids are vital components. To maximize the benefits, consider incorporating a variety of omega-3 sources into your meals throughout the week. This will provide a comprehensive range of essential nutrients and ensure your body receives the complete spectrum of health benefits.
- Prioritize Variety: Don’t rely solely on one or two sources. A diverse intake ensures you obtain the complete range of omega-3 types, each with its unique benefits. Different foods provide different ratios of EPA and DHA, so a mix is best.
- Gradual Integration: Start slowly, adding omega-3-rich foods to your current diet gradually. This will allow your body to adjust and help prevent potential digestive issues.
- Consider Timing: Eating omega-3 rich foods alongside meals containing healthy fats can enhance their absorption and utilization by the body. This is because the fats in your food can help your body absorb the omega-3s more efficiently.
Preparation Methods to Maximize Omega-3 Content
Careful preparation can significantly impact the omega-3 content of certain foods. Understanding these methods is key to maximizing your nutritional intake.
While sardines are packed with omega-3s, did you know some other foods offer even higher amounts? For instance, flaxseeds and chia seeds are excellent sources, and certain types of fish like mackerel and salmon often top the charts. Considering the potential role of omega-3s in overall health, including their potential anti-inflammatory properties, exploring natural treatment options for pancreatitis pain might be beneficial.
For example, natural treatment for pancreatitis pain can be a good starting point for understanding potential approaches. Ultimately, a balanced diet rich in omega-3-rich foods like these can be a powerful part of a healthy lifestyle.
- Cooking Methods: Steaming, baking, or grilling are generally better choices than frying for preserving omega-3s. Avoid high heat, as it can degrade some of these valuable fats. Grilling at medium temperatures and baking in moderate oven temperatures can minimize the loss of omega-3s.
- Portion Control: Even with healthy preparation methods, overconsumption can lead to unnecessary calories. Pay attention to portion sizes to manage calorie intake while still enjoying the nutritional benefits of these foods.
- Minimizing Additives: When preparing omega-3-rich foods, try to avoid adding excessive amounts of salt, sugar, or unhealthy fats. These additives can significantly diminish the nutritional value of the food and may negate some of the benefits of the omega-3s.
Importance of Variety in Omega-3 Food Sources
Different omega-3 sources provide varying types and amounts of these essential fats. A diverse intake is crucial for obtaining the full range of benefits.
- Complementary Benefits: Each food source offers unique benefits. Combining various foods ensures you get a wide spectrum of essential nutrients, further enhancing your health.
- Nutrient Synergy: Different omega-3 sources often contain other essential nutrients, such as vitamins and minerals. This combination creates synergistic effects, where the combined nutrients work together to enhance health benefits.
Recipe Ideas Featuring Omega-3 Rich Foods, Foods with more omega 3 than sardines
Here are a few ideas to inspire you to incorporate omega-3s into your meals:
- Salmon with Roasted Vegetables: Salmon is rich in omega-3s. Roast colorful vegetables like broccoli, carrots, and bell peppers alongside it for a complete and healthy meal. Season with herbs and spices for added flavor.
- Chia Seed Pudding: Chia seeds are an excellent source of omega-3s. Make a delicious and nutritious pudding by combining chia seeds with milk (dairy or non-dairy), fruit, and a touch of sweetener. This is a great breakfast or snack option.
- Tuna Salad Lettuce Wraps: Tuna is a good source of omega-3s. Prepare a light tuna salad with Greek yogurt or plain non-dairy yogurt and add some chopped celery and onion. Serve in crisp lettuce cups for a refreshing and healthy meal.
Food Safety and Sustainability
Choosing omega-3 rich foods is a great way to boost your health, but it’s crucial to consider both the safety and sustainability of your choices. This involves understanding how food is produced, processed, and handled to ensure quality and minimize harm to the environment. Knowing the sources and practices behind your food choices is vital for making informed and responsible decisions.Safe and sustainable omega-3 sources are essential for long-term health and environmental well-being.
Responsible consumption goes beyond simply selecting foods high in omega-3s; it also requires awareness of the entire process, from farm to table. Understanding how different production methods affect both human health and the environment is vital.
Importance of Food Safety
Proper handling and preparation of omega-3 rich foods are crucial for preventing foodborne illnesses. Contamination can occur at any stage of the supply chain, from farm to processing facility to your kitchen. This necessitates adherence to stringent safety protocols throughout the food production process. Consumers should also practice safe food handling techniques at home to minimize risks.
Choosing Sustainable Options
A key aspect of responsible omega-3 consumption is choosing sustainably harvested or farmed options. Overfishing depletes fish populations and disrupts marine ecosystems. Sustainable fishing practices, like those involving selective fishing methods and quotas, are essential to maintain healthy fish populations and ocean biodiversity. Aquaculture, while offering a potential alternative, should be evaluated based on its environmental impact, including water quality and waste management practices.
Certifications like MSC (Marine Stewardship Council) can help consumers identify sustainably sourced seafood.
Environmental Impact of Different Food Sources
The environmental footprint of omega-3 food sources varies significantly. For example, wild-caught fish, while often rich in omega-3s, can have a high carbon footprint due to the energy consumption of fishing vessels. Aquaculture can also have environmental consequences if not managed responsibly, potentially leading to water pollution and habitat destruction. Plant-based omega-3 sources, like flaxseed and chia seeds, generally have a lower environmental impact compared to many animal-based sources.
Ensuring Freshness and Quality
Freshness and quality are paramount when consuming omega-3 rich foods. Proper storage methods are essential to maintain the nutritional value and prevent spoilage. Refrigeration is typically recommended for most perishable omega-3 sources, while some, like certain nuts and seeds, can be stored at room temperature in airtight containers. Checking for signs of spoilage, such as off odors or unusual textures, is crucial before consumption.
Closing Summary
This journey through omega-3-rich foods beyond sardines has revealed a plethora of options for boosting your intake. Beyond the familiar fish, we’ve explored a diverse range of foods, each offering unique nutritional benefits. Understanding the different types of omega-3s and their sources is key to creating a balanced diet. Remember to consider factors like sustainability and preparation methods when making your choices.
The variety of options allows you to discover new culinary delights while nourishing your body with essential nutrients.