Pain on top of foot can be debilitating, interfering with daily activities and causing significant discomfort. This comprehensive guide explores the multifaceted nature of this common ailment, delving into the underlying causes, anatomical structures, and potential injuries. We’ll cover everything from stress fractures and sprains to non-traumatic conditions like bursitis and arthritis, equipping you with the knowledge to understand your pain and take appropriate action.
We’ll examine the intricate anatomy of the foot’s top, highlighting the bones, ligaments, tendons, and nerves that contribute to its function. This anatomical understanding is crucial in recognizing the potential sources of pain. Furthermore, we’ll analyze common foot injuries, exploring their symptoms, treatment options, and preventative measures. We’ll also consider non-injury-related pain, addressing conditions like nerve entrapment and arthritis.
This in-depth look will equip you with a better understanding of the potential causes and associated symptoms.
Causes of Pain on Top of Foot
A persistent ache or sharp pain on the top of your foot can be a frustrating and often debilitating experience. This discomfort can stem from a variety of underlying issues, ranging from common overuse injuries to more complex medical conditions. Understanding the potential causes is crucial for seeking appropriate medical attention and initiating an effective treatment plan.This discussion delves into the various medical conditions that can lead to pain on the top of the foot.
By examining the symptoms, mechanisms, and specific conditions, we can gain a better understanding of this often-misunderstood pain.
Potential Medical Conditions Causing Top-of-Foot Pain
A variety of medical conditions can cause pain on the top of the foot. Pinpointing the exact cause is crucial for effective treatment. Differentiating between common and less common causes, along with their unique symptoms and underlying mechanisms, allows for a more targeted approach to diagnosis.
| Condition | Symptoms | Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| Metatarsalgia | Pain, burning, or numbness in the ball of the foot, often worse with weight-bearing. May include swelling, redness, and tenderness. | Overuse, high-impact activities, or ill-fitting shoes can cause stress fractures or inflammation of the metatarsal bones. The pressure on the metatarsal heads leads to pain. |
| Sesamoiditis | Pain in the ball of the foot, often beneath the big toe, characterized by tenderness and swelling around the sesamoid bones. May worsen with movement. | Overuse, improper footwear, or abnormal foot mechanics can result in inflammation and irritation of the sesamoid bones, causing pain. |
| Stress Fracture | Pain that is often gradual, worsening with activity and relieved with rest. May be accompanied by swelling and tenderness. | Repeated stress on the metatarsal bones, often from overuse or improper form during exercise, can lead to tiny cracks or breaks in the bone. |
| Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome | Burning, tingling, and numbness in the top of the foot, often radiating to the toes. May also include pain and swelling. | Compression of the tibial nerve within the tarsal tunnel can lead to inflammation and nerve irritation, causing the associated symptoms. |
| Neuroma | Burning, tingling, or numbness in the top of the foot, often accompanied by pain that worsens at night or with pressure. | Nerve entrapment or irritation can lead to the formation of a benign tumor (neuroma) that compresses surrounding nerves, causing pain and other symptoms. |
| Arthritis | Pain, stiffness, and swelling in the top of the foot, often accompanied by decreased range of motion. Pain may be worse in the morning. | Inflammation of the joints in the foot, common in conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or osteoarthritis, can cause pain and stiffness. |
| Ingrown Toenail | Pain, redness, swelling, and tenderness around the affected toenail. May include pus or infection. | When a toenail grows into the surrounding skin, it can cause irritation, infection, and pain. |
| Plantar Fasciitis | Pain in the heel and arch, radiating to the top of the foot, often worse in the morning or after periods of rest. | Inflammation of the plantar fascia, the thick band of tissue that runs along the bottom of the foot, can cause pain that radiates to the top of the foot. |
Importance of Professional Diagnosis
Accurate diagnosis is critical for effective treatment of top-of-foot pain. A healthcare professional, such as a podiatrist or orthopedist, can conduct a thorough physical examination, assess medical history, and potentially order imaging tests (X-rays, MRIs) to determine the underlying cause. This individualized approach is essential to ensure the most appropriate and successful treatment plan.
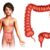
Anatomy of the Foot (Top View)
Understanding the intricate structure of the foot’s top surface is crucial for comprehending potential pain sources. The top of the foot, though seemingly simple, is a complex interplay of bones, ligaments, tendons, and nerves, all working in concert to provide stability and mobility. Damage to any of these components can lead to discomfort and dysfunction.The top of the foot houses several key anatomical structures, each playing a specific role in the foot’s overall function.
These structures are susceptible to various injuries, some more common than others. Recognizing the potential causes and mechanisms of injury can significantly aid in effective diagnosis and treatment.
Bones of the Foot
The bones of the foot’s dorsal (top) aspect contribute to its overall architecture and support. The main bones include the metatarsals, which form the arch of the foot, and the phalanges, which are the bones of the toes. These bones, along with the tarsal bones (not directly on the top surface, but crucial to the foot’s structure), provide a framework for weight distribution and movement.
They are connected by joints and are crucial for the foot’s ability to bear weight and propel the body forward.
Ligaments of the Foot
Ligaments are fibrous tissues that connect bones to bones, providing stability and preventing excessive movement. Several ligaments span the top of the foot, contributing to its structural integrity. These include the dorsal metatarsal ligaments, which support the arch of the foot, and the interosseous ligaments, which connect the metatarsals. Damage to these ligaments can lead to instability and pain.
Tendons of the Foot
Tendons connect muscles to bones, facilitating movement. Tendons on the top of the foot, though not as prominent as those on the sole, are crucial for foot function. These include the extensor tendons, which extend the toes. These tendons are vital for proper toe extension, and their dysfunction can lead to difficulties in walking and running.
Nerves of the Foot
Nerves provide sensory input and control motor functions. Sensory nerves on the top of the foot transmit signals about touch, pressure, and temperature. Motor nerves control the muscles involved in movement. Damage to these nerves can result in numbness, tingling, or loss of function in the toes and foot.
Diagram of the Foot’s Top Surface
[Imagine a detailed, labeled diagram here. The diagram would show the metatarsals, phalanges, dorsal ligaments, extensor tendons, and relevant nerves. It would clearly indicate the locations of each structure and their relationships to one another. Labeling would be essential for understanding the roles of each component.]
Possible Injuries to the Top of the Foot
A variety of injuries can affect the structures of the foot’s dorsal surface. These injuries can range from minor sprains to more severe fractures or nerve damage.
- Sprains: Sprains are common injuries that involve stretching or tearing of ligaments. They often result from sudden twisting or impact forces. Symptoms include pain, swelling, and instability in the foot.
- Fractures: Fractures, or broken bones, can occur in the metatarsals or other bones on the top of the foot, often from direct trauma. Symptoms typically include severe pain, swelling, and bruising.
- Tendinitis: Tendinitis is inflammation of a tendon, often caused by overuse or repetitive stress. This can lead to pain, tenderness, and swelling in the affected area.
- Nerve Entrapment: Nerves can become compressed or trapped, leading to numbness, tingling, or pain. This can occur due to structural abnormalities or external pressure.
- Skin Abrasions/Lacerations: Direct trauma to the top of the foot can cause cuts or scrapes to the skin.
Common Foot Injuries
Experiencing pain on the top of your foot can be debilitating, hindering your daily activities. Understanding the common causes behind this discomfort is crucial for effective self-care and seeking appropriate medical attention. This section delves into the most frequent foot injuries leading to pain in this area, outlining their symptoms, treatment approaches, and key differences.Knowing the various types of injuries that affect the top of the foot allows for quicker and more accurate diagnoses, which can lead to a faster recovery.
Prompt and appropriate treatment is essential to prevent long-term complications and ensure a full return to normal activities.
Stress Fractures
Stress fractures are tiny cracks in the bone, often resulting from repetitive stress and overuse. They are a common cause of pain on the top of the foot, particularly in athletes or individuals engaging in high-impact activities. Symptoms typically include pain that worsens with activity, swelling, and tenderness in the affected area. The pain might be localized or radiate outwards.
Rest and immobilization are crucial for healing, along with gradual return to activity as tolerated. In severe cases, casting or bracing might be necessary. Examples of activities that can lead to stress fractures include running, jumping, and dancing.
Sprains
Sprains occur when ligaments, the tissues connecting bones, are stretched or torn. A sprain on the top of the foot can result from a sudden twist, fall, or impact. Symptoms include pain, swelling, bruising, and instability in the affected area. The severity of a sprain can vary, with mild sprains often resolving with rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE).
More severe sprains may require physical therapy and possibly bracing or taping. A specific example of a sprain could be an ankle inversion injury that extends to the top of the foot, leading to a sprain of the ligaments there.
Tendinitis
Tendinitis involves inflammation of the tendons, the fibrous cords connecting muscles to bones. Top-of-foot tendinitis can result from overuse, improper footwear, or repetitive movements. Symptoms typically include pain and tenderness along the affected tendon, particularly with movement. Stiffness, especially in the morning, can also be a symptom. Treatment often involves rest, ice, and anti-inflammatory medications.
Physical therapy exercises can help to strengthen the surrounding muscles and improve flexibility. Examples include repetitive movements in sports like tennis or activities that require prolonged standing or walking.
Comparison of Common Foot Injuries
| Injury | Cause | Symptoms | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stress Fracture | Repetitive stress, overuse | Pain worsening with activity, swelling, tenderness | Rest, immobilization, gradual return to activity, potentially casting/bracing |
| Sprain | Sudden twist, fall, impact | Pain, swelling, bruising, instability | RICE (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation), physical therapy, bracing/taping (depending on severity) |
| Tendinitis | Overuse, improper footwear, repetitive movements | Pain and tenderness along the tendon, stiffness | Rest, ice, anti-inflammatory medication, physical therapy |
Non-Injury Related Pain

Sometimes, pain on the top of your foot isn’t caused by a sudden injury. Various underlying conditions can contribute to this discomfort, often requiring a different approach to diagnosis and treatment than a typical sprain or fracture. Understanding these non-traumatic causes can help you pinpoint the source of your pain and seek appropriate medical attention.
Non-Traumatic Causes of Top Foot Pain
Non-traumatic causes of top foot pain include a range of conditions, such as bursitis, arthritis, and nerve entrapment. Each condition presents unique symptoms and requires a tailored approach to treatment.
Bursitis
Bursitis involves inflammation of the bursae, small fluid-filled sacs that cushion the joints. On the top of the foot, bursitis often arises from repetitive stress or pressure. Symptoms typically include pain, tenderness, and swelling around the affected area. The pain might be aggravated by activities that increase pressure on the top of the foot, such as walking or wearing tight shoes.
Mild cases might respond to rest, ice, and over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications. More severe cases may necessitate corticosteroid injections or physical therapy.
Arthritis
Arthritis encompasses a group of conditions that cause inflammation in the joints. Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis can affect the joints of the foot, leading to pain and stiffness. Symptoms may vary depending on the type of arthritis but generally include pain, swelling, and reduced range of motion in the affected joint. Pain may worsen with activity and improve with rest.
Treatment approaches often include medications to manage pain and inflammation, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications to reduce stress on the joints.
Nerve Entrapment
Nerve entrapment occurs when a nerve is compressed or pinched. This can happen anywhere in the body, including the foot. On the top of the foot, nerve entrapment can cause pain, numbness, or tingling, often described as a shooting or burning sensation. Symptoms can be localized to the area of the entrapment or radiate to other parts of the foot.
That nagging pain on top of my foot has been driving me crazy lately. I’ve tried everything from icing to new running shoes, but nothing seems to be helping. I was researching different remedies when I stumbled upon an interesting article about which type of mouthwash works best for oral health. While it seems completely unrelated, maybe there’s a connection I’m missing?
Back to the foot pain, anyone have any other ideas?
The pain might worsen with specific movements or activities. Diagnosis often involves nerve conduction studies to pinpoint the affected nerve. Treatment may include physical therapy, splinting, or in some cases, surgery to alleviate the pressure on the nerve.
Comparison of Symptoms and Treatment Approaches
While all these conditions can cause pain on the top of the foot, their specific symptoms and treatment approaches differ. Bursitis typically presents with localized pain and swelling, often exacerbated by pressure. Arthritis may cause pain and stiffness that worsen with activity. Nerve entrapment, on the other hand, might manifest as numbness or tingling sensations, potentially radiating from the affected area.
Treatment for each condition is tailored to the specific diagnosis, considering factors like the severity and duration of symptoms.
Table of Non-Injury Pain Conditions
| Condition | Symptoms | Possible Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Bursitis | Pain, tenderness, swelling around the affected area, pain aggravated by activities increasing pressure on the top of the foot. | Rest, ice, over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications, corticosteroid injections, physical therapy. |
| Arthritis | Pain, swelling, reduced range of motion in the affected joint, pain worsening with activity and improving with rest. | Medications to manage pain and inflammation, physical therapy, lifestyle modifications to reduce stress on the joints. |
| Nerve Entrapment | Pain, numbness, tingling (shooting or burning sensation), localized or radiating pain, worsening with specific movements or activities. | Physical therapy, splinting, surgery (in some cases) to alleviate pressure on the nerve, nerve conduction studies for diagnosis. |
Risk Factors
Pain on the top of the foot can stem from a variety of factors, and understanding these risk factors can help in preventing or managing the condition. These factors can be categorized into biomechanical, lifestyle, and medical conditions, each playing a unique role in increasing the likelihood of experiencing this discomfort. Knowing these factors empowers individuals to take proactive steps to reduce their risk.Understanding the interplay between these risk factors and the development of pain on the top of the foot is crucial for effective prevention and treatment.
Different individuals may have varying combinations of risk factors, which can influence the severity and persistence of the pain.
Biomechanical Risk Factors
Factors related to the structure and function of the foot and lower limb contribute significantly to the development of pain on the top of the foot. Improper foot mechanics, such as flat feet or high arches, can alter the distribution of forces across the foot, increasing stress on the structures on the top. This can lead to inflammation and pain in the tendons, ligaments, and bones.
- Overpronation or Supination: Abnormal foot rolling inward (pronation) or outward (supination) during walking or running can alter the natural shock absorption mechanism, increasing pressure on the top of the foot. This can lead to irritation of the tissues and subsequent pain. For example, runners with excessive pronation often experience pain on the top of the foot due to the excessive inward rolling of the foot, which can stretch or strain the tissues on the top.
- Foot Posture: Individuals with existing foot conditions, such as flat feet or high arches, may experience increased pressure on the top of the foot. The abnormal alignment of the foot’s structure can put undue strain on the tissues, potentially leading to pain.
- Muscle Imbalances: Weak or tight muscles in the lower leg, such as the anterior tibialis, can affect the stability and alignment of the foot. These imbalances can contribute to the development of pain on the top of the foot, particularly during activities that place stress on the foot.
Lifestyle Risk Factors
Lifestyle choices play a significant role in the development of pain on the top of the foot. Certain activities and habits can increase the stress on the foot, leading to irritation and pain.
- Overuse: Engaging in activities that repeatedly stress the top of the foot, such as running, jumping, or prolonged standing, can lead to overuse injuries. This is particularly true for individuals who increase their activity levels too quickly or without proper preparation. For example, a sudden increase in running mileage without adequate training can cause pain on the top of the foot due to repetitive stress on the tissues.
- Poor Footwear: Wearing shoes that do not provide adequate support or cushioning for the foot can contribute to the development of pain on the top of the foot. Shoes with inadequate arch support or poor cushioning can place extra stress on the foot, increasing the risk of injury. Ill-fitting shoes can also cause rubbing or pressure on the top of the foot, leading to discomfort and pain.
- Obesity: Excess weight places increased stress on the feet, potentially leading to pain on the top of the foot. The extra pressure can cause inflammation and irritation of the tissues.
Underlying Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions can increase the risk of experiencing pain on the top of the foot. These conditions may affect the blood flow, nerve function, or overall health of the foot.
That nagging pain on top of my foot has been driving me crazy lately. It’s definitely not fun, and I’ve been trying to figure out what’s causing it. Sometimes, similar aches can be connected to other issues, like right upper quadrant pain, which can be a sign of various things. For more on that, check out this informative article about right upper quadrant pain.
While I’m not a doctor, it’s still important to consider potential underlying causes when dealing with persistent foot pain. I’m hoping to get to the bottom of this soon!
- Neurological Disorders: Conditions affecting nerve function, such as neuropathy, can lead to pain or numbness on the top of the foot. The compromised nerve function can cause abnormal sensations or pain, which can be localized to the top of the foot.
- Rheumatological Conditions: Some forms of arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis, can cause inflammation and pain in the foot’s joints, potentially leading to pain on the top of the foot. The inflammation can cause swelling, stiffness, and discomfort in the foot, potentially affecting the top portion.
- Vascular Disorders: Conditions affecting blood flow, such as peripheral artery disease, can reduce blood supply to the foot. This can lead to pain, numbness, and other symptoms in the foot, including the top portion.
Home Remedies and Self-Care: Pain On Top Of Foot
Taking care of foot pain at home can be a significant step in managing discomfort and promoting healing. Simple, at-home remedies and self-care practices can often provide relief from mild to moderate pain on the top of the foot. Understanding the various options available and how to implement them effectively is crucial for a successful home treatment plan.
Effective Exercises and Stretches
Gentle exercises and stretches can help improve flexibility, reduce tension, and promote blood flow to the affected area. Regular stretching can increase the range of motion in the foot and ankle, potentially easing pain and discomfort. Simple stretches, like dorsiflexion and plantar flexion exercises, can help alleviate tightness in the foot muscles. These exercises should be performed gradually and with proper form to avoid further injury.
Listen to your body and stop if you experience any sharp or increased pain.
Lifestyle Modifications
Certain lifestyle modifications can complement home remedies and exercises to manage foot pain effectively. Maintaining a healthy weight can significantly reduce stress on the feet, while proper footwear selection is essential. Wearing supportive shoes with adequate cushioning can help absorb impact and prevent further irritation. Avoiding prolonged standing or walking sessions can also help alleviate discomfort.
Home Remedies for Pain on the Top of the Foot
Various home remedies can provide temporary relief from mild to moderate pain on the top of the foot. These remedies, while not a substitute for professional medical advice, can be used in conjunction with other treatments. Here’s a summary of some common remedies, along with their potential benefits and limitations:
- Cold Compress: Applying a cold compress to the affected area can help reduce inflammation and swelling. This can provide temporary relief from pain, especially in the initial stages of injury or inflammation. However, applying ice for extended periods can lead to tissue damage, so it’s crucial to use caution and avoid frostbite.
- Rest: Resting the affected foot is vital to allow the tissues to heal and recover. Avoid activities that aggravate the pain, and elevate the foot to promote blood circulation and reduce swelling. Prolonged rest can lead to muscle stiffness if not combined with gentle exercises and stretching.
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), like ibuprofen or naproxen, can help reduce pain and inflammation. However, these medications should be used cautiously, following the recommended dosage and potential side effects.
- Foot Pads and Cushioning: Using specialized insoles or foot pads can help cushion the foot and reduce pressure on the affected area. This can provide comfort and alleviate pain during activities like walking or standing. The effectiveness of foot pads depends on the specific type and the individual’s foot structure.
- Gentle Massage: Gentle massage to the affected area can improve blood circulation and reduce muscle tension. However, avoid applying pressure to painful areas or massaging if the pain is severe. Proper massage techniques can help promote relaxation and alleviate discomfort.
Important Considerations
It’s essential to remember that these home remedies are not a substitute for professional medical advice. If the pain persists, worsens, or is accompanied by other symptoms, it’s crucial to consult a doctor or podiatrist. Self-treating can sometimes mask underlying conditions, so proper diagnosis and treatment are necessary to prevent potential complications.
When to Seek Professional Help
Foot pain on the top of the foot, while often manageable at home, can sometimes signal a more serious underlying issue. Ignoring persistent or worsening pain can delay proper diagnosis and treatment, potentially leading to long-term complications. Understanding when to seek professional medical attention is crucial for a swift and effective recovery.
Signs Requiring Immediate Medical Attention
Persistent, severe pain on the top of the foot, accompanied by other concerning symptoms, necessitates immediate medical attention. This includes situations where pain is significantly interfering with daily activities or if the pain is accompanied by other alarming symptoms.
That throbbing pain on top of my foot has been driving me crazy lately. It’s definitely not fun, especially when I’m trying to get through my day. Sometimes, it’s a simple case of stubbing my toe, but other times, it could be a more serious issue. It’s important to be mindful of how we’re moving around the house, even in the kitchen.
For instance, I’ve had a few close calls with knife injuries in the kitchen, like when I was slicing tomatoes, and had to take a look at my kitchen safety habits. Thankfully, I’ve found some helpful tips on avoiding kitchen accidents, like cuts in the kitchen , which is a great resource. Now, back to the pain on top of my foot.
I’m off to see a doctor to get to the bottom of this.
- Severe pain that is not relieved by over-the-counter pain medication.
- Swelling that rapidly increases in size, particularly if accompanied by redness or warmth.
- Inability to bear weight on the affected foot.
- Deformity or unusual shape of the affected area.
- Numbness or tingling in the toes or foot.
- Skin discoloration, such as bluish or purplish tones.
- A sudden onset of pain after an injury, such as a fall or impact.
- Visible signs of infection, like pus or open wounds.
Red Flags Indicating Professional Care
Certain red flags should prompt immediate consultation with a healthcare professional. These conditions might suggest more serious underlying medical issues that require prompt evaluation.
- Symptoms that worsen over time despite home care measures.
- Pain that is accompanied by fever, chills, or other systemic symptoms.
- Pain that radiates to other parts of the leg or body.
- Symptoms of blood clots, such as swelling, warmth, redness, and pain in the leg or foot.
- Sudden, severe pain that is accompanied by weakness or numbness in the foot or leg.
- History of diabetes, circulatory problems, or other underlying health conditions.
- Inability to control or manage pain effectively with rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE).
When to Schedule an Appointment
If pain on the top of the foot persists for more than a few days, despite home remedies, or if you notice any of the aforementioned red flags, it’s important to schedule an appointment with a podiatrist or other qualified healthcare professional. A prompt diagnosis and treatment plan can prevent further complications and promote a faster recovery.
Different Types of Footwear
Footwear plays a significant role in the health and comfort of our feet. The type of shoe we choose can dramatically impact the distribution of pressure and stress across the foot, potentially exacerbating or alleviating existing pain, particularly on the top of the foot. Understanding how different shoe types affect the foot’s structure and mechanics is crucial for anyone experiencing pain in this area.Choosing the right footwear is often a balance between personal preference and the need to support foot health.
A well-fitting and supportive shoe can protect the foot from injury and reduce pain, while poorly fitting shoes can lead to discomfort and potential long-term problems.
Footwear and Top-of-Foot Pain
Different shoe types exert varying degrees of pressure on the top of the foot. High heels, for example, can cause an unnatural shift in weight distribution, placing undue stress on the front and top of the foot. Conversely, shoes with adequate cushioning and arch support can help to distribute pressure more evenly and alleviate pain.
Comparison of Shoe Types and Their Potential Impact
| Shoe Type | Impact on Foot Pain | Features |
|---|---|---|
| High Heels | Can exacerbate pain on top of the foot due to the unnatural shift in weight distribution, often leading to increased pressure on the ball and top of the foot. | Characterized by a raised heel, often with a narrow toe box, and a pointed or stiletto design. |
| Flat Shoes (e.g., ballet flats, sandals) | Can potentially cause pain if the shoe lacks adequate arch support, leading to excessive pressure on the ball and top of the foot. Some flat shoes with poor support can cause a similar shift in weight distribution as high heels, causing pain. | Typically have no heel or a very low heel. |
| Running Shoes | Generally good for shock absorption, which can help to alleviate pain on the top of the foot, especially during impact activities. However, some running shoes may not provide adequate support for individuals with specific foot conditions. | Designed with features like cushioned midsoles, shock-absorbing soles, and supportive uppers. Often have a wider toe box than other shoe types. |
| Boots (e.g., work boots, ankle boots) | Depending on the style and construction, boots can exert significant pressure on the top of the foot, especially if they are stiff or lack sufficient cushioning. | Typically constructed with thicker materials, potentially creating a more rigid shoe structure. |
| Dress Shoes | If lacking proper cushioning and arch support, dress shoes can cause pressure on the top of the foot, especially in individuals with existing foot conditions. | Typically made with leather or other stiff materials, and sometimes with a narrow toe box. |
| Sandals | Sandals, particularly those without straps or adequate support, can contribute to pain on the top of the foot due to insufficient support and a lack of containment. This can result in foot instability. | Offer little support for the foot. |
Choosing Footwear for Pain Relief, Pain on top of foot
When selecting footwear, consider the following factors:
- Proper Arch Support: Shoes with good arch support help maintain the natural alignment of the foot, reducing pressure on the top of the foot. This is particularly important for individuals with flat feet or high arches.
- Cushioning: Adequate cushioning in the midsole and heel absorbs impact and reduces pressure on the top of the foot, minimizing discomfort during activities.
- Width and Toe Box: A wide toe box allows the toes to spread naturally, preventing pressure on the top of the foot. A narrow toe box can lead to bunions and other foot problems.
- Material: Materials like leather or breathable fabrics can contribute to foot comfort and prevent excessive sweating, which can lead to foot problems.
Final Review
In conclusion, understanding pain on top of foot involves considering a wide range of potential causes, from common injuries to underlying medical conditions. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview of the anatomy, common injuries, and non-injury-related pain, equipping you with the knowledge to identify the possible cause of your pain. Remember, if your pain is severe, persistent, or accompanied by swelling or inability to bear weight, seek professional medical advice immediately.
Knowing when to seek professional help is crucial for effective management and recovery. By understanding the various factors involved, you can take proactive steps to address the pain and improve your overall foot health.