Rash that moves to different parts of the body sets the stage for this exploration of a perplexing medical phenomenon. We’ll delve into the various characteristics of this migrating rash, from its color and shape to its patterns of movement. Understanding the potential causes, from allergies to infections, is crucial, and we’ll explore diagnostic considerations and the importance of a thorough medical history.
This comprehensive look at the topic will include potential causes, detailed diagnostic procedures, effective management strategies, and preventative measures. We’ll also present illustrative examples to highlight the diverse presentations of this condition, offering a richer understanding of this often-confusing medical issue.
Defining the Rash
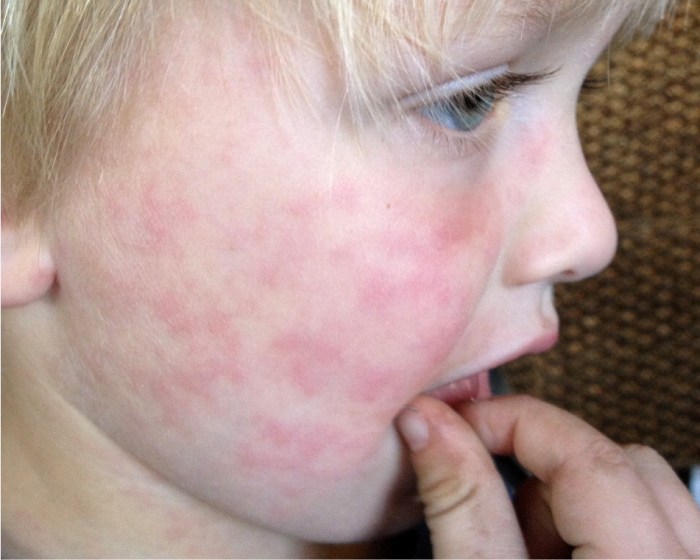
Migratory rashes, characterized by their unpredictable movement across different parts of the body, can be a perplexing health concern. These rashes often present a diagnostic challenge, as their seemingly random patterns can make pinpointing the underlying cause difficult. Understanding the various characteristics, including color, shape, and patterns of movement, is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.A migratory rash isn’t a single entity; it’s a symptom that can indicate a variety of conditions.
The key is recognizing the consistent and recurring patterns in its presentation, which helps in distinguishing it from other skin conditions. Careful observation of the rash’s evolution, including its location, shape, and any accompanying symptoms, is essential.
Rash Characteristics
The appearance of a migratory rash can vary significantly, making it crucial to document all observed details. Color can range from subtle pink to intense red, purple, or even brown. Shapes can be anything from small, circular lesions to larger, irregular patches. Size can also fluctuate, from a few millimeters to several centimeters in diameter. Texture may be smooth, rough, bumpy, or even blistered.
Careful observation of these details can provide valuable information for a diagnosis.
Rash Movement Patterns
Migratory rashes can exhibit various movement patterns, adding to the complexity of diagnosis. These patterns can include spreading, where the rash gradually expands over time; cyclical, where the rash appears, disappears, and reappears in a regular or irregular sequence on different parts of the body; or appearing in a particular sequence, such as starting on the trunk and moving to the extremities.
Recording the specific order of rash appearance can be an important diagnostic clue.
Comparison of Migratory Rash Types
| Rash Type | Color | Shape | Size | Texture | Movement Pattern | Potential Causes ||—|—|—|—|—|—|—|| Erythema migrans (Lyme disease) | Initially red, then expanding | Usually circular | Can vary from 5-50 cm | Smooth, often with central clearing | Spreading, often with a characteristic “bull’s-eye” pattern | Lyme disease bacteria || Pityriasis rosea | Pink or salmon-colored | Oval or round | Can vary in size | Smooth, scaly | Typically starts with a herald patch, followed by a widespread rash that spreads outwards | Unknown, likely viral || Drug eruptions | Variable, depending on the drug | Can be maculopapular, urticarial, or other patterns | Can range from small spots to large plaques | Smooth, itchy, or bumpy | Spreading, appearing in response to medication exposure | Adverse reactions to medication || Henoch-Schönlein purpura (HSP) | Palpable purpura (raised, purplish spots) | Can be maculopapular, or form larger plaques | Usually small, but can coalesce | Can be smooth or slightly raised | Usually appears on the buttocks, legs, and lower extremities; often accompanied by other symptoms | Immune system response, often triggered by an infection |This table provides a basic comparison.
A definitive diagnosis requires a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional, considering individual patient history, symptoms, and physical examination findings. Remember, this table is not exhaustive and should not be used for self-diagnosis.
Potential Causes
A rash that moves around the body can be a perplexing symptom, and pinpointing the cause often requires careful consideration of various factors. The unpredictable nature of its migration can make diagnosis challenging, but understanding potential underlying conditions can help healthcare professionals and individuals alike navigate this often-confusing situation. Many factors can contribute to this, ranging from allergic reactions to infections, and each presents with a unique set of characteristics.Migratory rashes can stem from a complex interplay of factors, and the pattern of their movement can offer valuable clues about the underlying cause.
The speed at which the rash spreads, the accompanying symptoms, and the specific areas affected can all help narrow down the possibilities.
Underlying Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions can present with a migratory rash as a symptom. These conditions often involve the immune system’s response to various triggers, leading to inflammation and skin reactions that shift locations. Examples include lupus, dermatomyositis, and vasculitis. Lupus, for instance, can manifest with a variety of symptoms, including joint pain, fatigue, and a butterfly-shaped rash on the face.
Dermatomyositis typically involves muscle weakness and a rash on the face, upper eyelids, and knuckles. Vasculitis, involving inflammation of the blood vessels, can present with rashes that appear and disappear in various areas of the body. These conditions often require specialized medical evaluation to differentiate them from other causes.
Allergic Reactions
Allergic reactions are another potential cause of a migratory rash. Contact dermatitis, an allergic reaction to substances that come into contact with the skin, is a common example. Exposure to certain materials, such as jewelry, latex, or cosmetics, can trigger a rash that moves to areas of repeated contact. Food allergies can also manifest as a rash that migrates across the body, with the rash often appearing near areas of ingestion or contact with the allergen.
Urticaria (hives) is a common allergic reaction characterized by raised, itchy welts that can appear anywhere on the body and often disappear within a few hours. The rash often appears in a distinctive, often itchy, pattern.
Infections, Rash that moves to different parts of the body
Infections, both bacterial and viral, can cause migratory rashes. Bacterial infections, such as scarlet fever, can present with a characteristic rash that spreads across the body. Viral infections, such as roseola, can cause a rash that appears and disappears in various locations. Measles, for example, presents with a characteristic rash that begins on the face and spreads downwards.
Ever noticed a rash that seems to hop around your body? It’s definitely a cause for concern, and while some rashes are harmless, others could signal underlying issues. Sometimes, a rash moving to different parts of the body can be a symptom of a more serious problem, potentially even cancer. Understanding the possible causes is crucial, and if you’re worried, a visit to the doctor is a must.
One diagnostic tool used to detect potential cancer is a bone scan, which helps evaluate if the cancer has spread to the bones. Learning more about what a bone scan for cancer entails can be helpful in understanding this process. what is a bone scan for cancer. Regardless of the results, it’s always best to get a professional opinion if you experience a rash that moves around.
The timing of the rash’s appearance in relation to other symptoms, such as fever or fatigue, can provide important diagnostic clues.
Comparison of Symptoms
The following table summarizes the potential causes of migratory rashes, highlighting common symptoms, typical rash locations, and potential underlying conditions.
| Potential Cause | Symptoms | Typical Rash Locations |
|---|---|---|
| Lupus | Joint pain, fatigue, butterfly-shaped rash on face, fever | Face (butterfly pattern), other areas |
| Allergic Reactions (e.g., Contact Dermatitis) | Itching, redness, swelling, rash at contact site | Areas of contact with allergen |
| Bacterial Infections (e.g., Scarlet Fever) | Fever, sore throat, headache, rash | Typically starts on the trunk and spreads to extremities |
| Viral Infections (e.g., Roseola) | High fever, rash | Often starts on the trunk and spreads to other areas |
Diagnostic Considerations
Migratory rashes, with their unpredictable movement across the body, pose a diagnostic challenge. A thorough understanding of the patient’s medical history, coupled with a careful physical examination and potentially, diagnostic testing, is crucial for pinpointing the underlying cause. Accurate diagnosis is paramount to initiating the appropriate treatment and preventing potential complications.
Importance of Medical History
A detailed medical history is essential in evaluating a migratory rash. The history should encompass all relevant factors, including recent illnesses, medications, exposures to allergens or irritants, and any underlying medical conditions. For instance, a patient with a history of Lyme disease might exhibit a rash with a characteristic migratory pattern. Similarly, recent travel or exposure to specific animals or environments could provide valuable clues.
A complete medication list, including over-the-counter drugs, is also vital.
Steps in Diagnosing a Migratory Rash
Diagnosing a rash with a migratory pattern involves a systematic approach. First, the doctor will typically obtain a detailed medical history, focusing on the rash’s progression, including its location, timing, and any associated symptoms. Next, a physical examination will be performed to assess the rash’s characteristics, such as its appearance, size, and distribution. The doctor may also order diagnostic tests to rule out or confirm suspected conditions.
Ever had a rash that just wouldn’t stay put? It’s frustrating when it pops up in one spot, then mysteriously migrates to another. Sometimes, hidden culprits like sodium intake can be a contributing factor. Cutting back on sodium can be tricky, as it’s often found in unexpected places, and it’s difficult to break old habits. Have you considered how much sodium you consume in your daily diet?
Understanding why it’s so hard to cut back on sodium can help you tackle this issue head-on. Check out this article for more info: why is it so hard to cut back on sodium. Regardless of the reason, persistent moving rashes definitely need medical attention to rule out any serious underlying issues.
Ultimately, the choice of diagnostic tests depends on the specific clinical presentation and the doctor’s assessment of the patient’s condition.
Questions a Doctor Might Ask
Gathering information about the rash’s progression is crucial. A doctor might inquire about the rash’s onset, its spread across the body, the duration of the rash at each location, and any accompanying symptoms like fever, itching, or pain. Specific questions regarding recent exposures to animals, plants, or medications may be asked. Details regarding the rash’s appearance, such as its color, shape, and texture, are also crucial.
The doctor may ask about the patient’s general health, recent illnesses, and current medications.
Significance of Physical Examination
A comprehensive physical examination is vital in assessing the rash’s characteristics. The doctor will carefully examine the rash’s morphology, including its shape, size, color, and distribution. The presence of any accompanying signs, such as swelling, lesions, or blisters, will also be noted. The doctor will also assess the patient’s general condition, looking for any other signs or symptoms that might indicate an underlying systemic illness.
The doctor may also feel lymph nodes for any enlargement, which could suggest an infection.
Diagnostic Tests
The choice of diagnostic tests for a migratory rash depends on the suspected underlying cause. These tests may include blood tests, skin biopsies, and possibly, imaging studies.
| Diagnostic Test | Purpose | Potential Results |
|---|---|---|
| Complete Blood Count (CBC) | Assess for signs of infection or inflammation. | Elevated white blood cell count may indicate infection. |
| Lyme Disease Panel | Detect antibodies against Lyme disease bacteria. | Positive results suggest Lyme disease. |
| Skin Biopsy | Examine skin tissue for cellular abnormalities. | May reveal signs of allergic reactions, infections, or other skin conditions. |
| Allergy Testing | Identify potential allergens triggering the rash. | Positive results indicate a possible allergic reaction. |
| Imaging Studies (e.g., X-rays, CT scans) | Assess for underlying conditions affecting other parts of the body. | May reveal evidence of infections, tumors, or other conditions. |
Management and Treatment
Navigating a migrating rash can be frustrating, but understanding the potential causes and appropriate treatment strategies is crucial for managing discomfort and preventing complications. Effective management often involves a combination of medical interventions and lifestyle adjustments. Different causes require tailored approaches, so a proper diagnosis is paramount.
Common Treatment Strategies
Various treatment strategies address the underlying causes of migrating rashes. These strategies aim to alleviate symptoms, reduce inflammation, and prevent further spread. Topical corticosteroids, for instance, can be effective in reducing inflammation in certain cases. Antihistamines can help manage itching and discomfort, while systemic medications, like immunosuppressants, might be necessary for more severe or chronic conditions.
Role of Medication
Medication plays a significant role in managing the symptoms of a rash that moves. The specific type of medication depends heavily on the diagnosed cause. For example, if the rash is linked to an allergic reaction, antihistamines can be prescribed to alleviate itching and reduce inflammation. If the cause is an infection, antibiotics or antiviral medications might be necessary.
In cases of autoimmune conditions, immunosuppressants can help regulate the immune response, thus reducing the rash’s severity and frequency. Always consult a medical professional for the appropriate medication and dosage.
Importance of Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications can significantly contribute to managing conditions that cause migratory rashes. Avoiding potential triggers, such as certain foods, environmental allergens, or stress, can often lessen the frequency and severity of outbreaks. Maintaining a healthy diet, getting sufficient sleep, and practicing stress-reducing techniques like yoga or meditation can support the body’s natural healing processes and contribute to overall well-being.
For example, someone with a rash linked to food allergies might benefit from keeping a detailed food diary to identify potential triggers.
Self-Care Measures
Implementing self-care measures can complement medical treatment and help manage the symptoms of a migrating rash. These measures include keeping the affected area clean and dry, applying cool compresses to soothe itching, and wearing loose-fitting clothing to prevent irritation. Avoiding scratching is crucial to prevent skin damage and potential secondary infections. Using gentle cleansers and avoiding harsh soaps can help protect the skin’s integrity.
Treatment Options Table
| Rash Type | Potential Causes | Treatment Options | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|---|
| Allergic Reaction Rash | Exposure to allergens (foods, pollen, etc.) | Antihistamines, topical corticosteroids, avoidance of triggers | Generally effective in reducing symptoms, but long-term avoidance is key. |
| Infectious Rash | Viral or bacterial infections | Antibiotics (bacterial), antiviral medications (viral), supportive care | Effectiveness depends on the specific infection and prompt treatment. |
| Autoimmune Rash | Underlying autoimmune disorders | Immunosuppressants, corticosteroids, lifestyle modifications | Can help manage symptoms but may not always eliminate the rash entirely. |
| Drug Reaction Rash | Adverse reaction to medication | Discontinuation of the suspected drug, supportive care | Symptoms usually resolve once the offending drug is stopped. |
Prevention Strategies
Migrating rashes, while often frustrating and concerning, can often be managed effectively through proactive prevention. Understanding the potential triggers and implementing appropriate strategies can significantly reduce the risk of recurrence and the associated discomfort. By focusing on a combination of lifestyle adjustments, environmental modifications, and early intervention, individuals can actively take control of their well-being and minimize the likelihood of these rashes developing.Effective prevention hinges on recognizing the factors that contribute to the rash’s migration.
This involves identifying potential triggers, such as specific foods, environmental allergens, or underlying health conditions. Early diagnosis and appropriate management are crucial in preventing the rash from spreading and causing further complications.
Dietary Changes
Dietary choices play a significant role in overall health and can influence the likelihood of developing a migrating rash. Certain foods and beverages may act as triggers, exacerbating existing sensitivities or contributing to the development of new ones.
- Identifying and avoiding potential allergens is paramount. This might involve keeping a detailed food diary to track potential correlations between specific foods and rash outbreaks. Common allergens include dairy products, certain fruits, nuts, and processed foods. If a specific food is suspected, eliminating it from the diet and monitoring for improvements is a valuable step.
- Maintaining a balanced and nutritious diet is crucial. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can support a healthy immune system, potentially reducing susceptibility to various skin conditions. Conversely, a diet high in processed foods and refined sugars may increase inflammation, potentially contributing to rash development.
Skincare Routines
Maintaining a consistent and appropriate skincare routine can contribute to preventing and managing migrating rashes. Proper hygiene and skin care are critical in preventing infections and further irritation.
Ever noticed a rash that seems to hop around your body? It’s definitely a cause for concern. While a wandering rash could be a sign of various things, sometimes it’s linked to underlying health issues like those related to weight management, such as those addressed in the American Diabetes Association’s BMI weight management guidelines. american diabetes association bmi weight management can offer valuable insights.
Regardless, it’s crucial to consult a doctor to pinpoint the exact cause and get appropriate treatment for any rash that moves around.
- Gentle cleansing is key. Using harsh soaps or excessive scrubbing can irritate the skin and exacerbate existing conditions. Opt for mild, fragrance-free cleansers to avoid further irritation.
- Moisturizing is essential for maintaining skin hydration and preventing dryness. Regular application of a suitable moisturizer can help maintain the skin’s protective barrier, reducing its susceptibility to irritation and potential triggers.
Environmental Modifications
Environmental factors can also contribute to the development and spread of migrating rashes. Identifying and controlling environmental triggers is an important aspect of prevention.
- Managing exposure to irritants, such as certain chemicals or fabrics, can be helpful. Pay close attention to clothing materials, household cleaning products, and potential environmental allergens in the home or workplace.
- Controlling temperature and humidity levels can also minimize skin irritation. Maintaining a comfortable temperature range and proper humidity levels in the home or workplace can contribute to overall skin health and reduce the likelihood of flare-ups.
Importance of Early Diagnosis and Treatment
Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are crucial in preventing the rash from spreading and causing further complications. Prompt intervention can often limit the duration and severity of the rash.
- Seeking medical attention as soon as a rash appears is essential. Early intervention allows for proper diagnosis and targeted treatment, potentially preventing the rash from spreading and causing long-term discomfort.
Comprehensive Prevention Measures
Implementing a multi-faceted approach that encompasses dietary adjustments, skincare practices, and environmental modifications can significantly reduce the risk of developing a migrating rash.
| Category | Preventive Measure |
|---|---|
| Dietary Changes | Identify and avoid potential food allergens, maintain a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables. |
| Skincare Routines | Gentle cleansing with fragrance-free products, consistent moisturizing. |
| Environmental Modifications | Minimize exposure to irritants (chemicals, fabrics), control temperature and humidity. |
Illustrative Examples
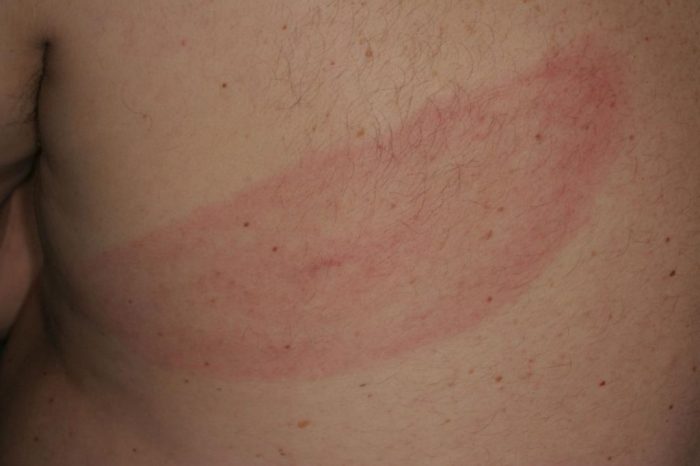
Understanding the journey of a migrating rash requires looking at real-life scenarios. This section provides case studies to illustrate the complexities of this skin condition, showcasing different patterns and progressions. These examples highlight the importance of accurate diagnosis and prompt treatment in managing these types of rashes.
Case Study 1: Migratory Rash with Cyclical Pattern
This case involves a 32-year-old female presenting with a rash that moved in a cyclical pattern across her body. The rash initially appeared on her left arm, then migrated to her chest, abdomen, and finally, her right leg. This cyclical movement repeated over a period of two weeks, with each episode lasting approximately 24-48 hours. The rash was characterized by erythematous macules and papules, accompanied by mild itching.
Diagnostic testing revealed no evidence of systemic infection. The patient reported a history of stress and recent changes in her diet, which may have played a role in the presentation of the rash. Treatment focused on managing the symptoms with topical antihistamines and addressing the underlying potential stressors.
Case Study 2: Sequential Rash Progression
In this case, a 45-year-old male experienced a rash that followed a specific sequence across his body. The rash initially appeared on his face, progressing to his neck, then upper back, and finally, his lower back. The rash was characterized by erythematous plaques with a slightly raised border. A thorough medical history revealed no known allergies or systemic illnesses.
The diagnostic process included ruling out infectious causes and evaluating potential contact dermatitis triggers. Treatment involved identifying and eliminating potential allergens and applying topical corticosteroids to manage the inflammation.
Case Study 3: Rash Progression Over Time
This table details the progression of a rash from its initial appearance to its resolution. The data illustrates how the rash’s location changed over time.
| Day | Rash Location | Rash Description |
|---|---|---|
| Day 1 | Right Forearm | Small, red, slightly raised patches |
| Day 2 | Right Forearm, Left Forearm | Patches spreading, slight itching |
| Day 3 | Right Forearm, Left Forearm, Upper Chest | Rash continues to spread, some areas starting to fade |
| Day 4 | Upper Chest, Upper Back | Rash subsides on the forearms, appears on upper back |
| Day 5 | Upper Back, Abdomen | Rash continues to move downwards, itching subsides |
| Day 6 | Abdomen, Thighs | Rash is almost completely gone, some slight discoloration remains |
| Day 7 | No rash visible | Complete resolution |
These illustrative examples highlight the varied presentations of migratory rashes. Each case emphasizes the importance of a detailed medical history, thorough physical examination, and appropriate diagnostic testing to determine the underlying cause and develop an effective treatment plan.
Final Thoughts: Rash That Moves To Different Parts Of The Body
In conclusion, understanding rashes that move across the body requires a multi-faceted approach. By exploring the various causes, diagnostic steps, and treatment options, we can gain a clearer picture of this often-challenging condition. Remember, early diagnosis and proper medical attention are crucial for effective management and prevention of further complications. This information is not a substitute for professional medical advice.