The benefits of ferulic acid are starting to gain significant attention, and for good reason. This versatile compound, found naturally in various foods, boasts a wide array of potential health advantages. From its antioxidant properties to its potential skin benefits, ferulic acid is a fascinating substance with a lot to offer.
This comprehensive exploration delves into the science behind ferulic acid, examining its chemical structure, natural sources, and the extensive research surrounding its potential health effects. We’ll cover its antioxidant prowess, anti-inflammatory action, and skin benefits, as well as potential side effects and interactions.
Introduction to Ferulic Acid
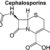
Ferulic acid, a naturally occurring phenolic compound, plays a significant role in various biological processes. It’s a potent antioxidant and exhibits a wide array of potential health benefits. Understanding its chemical properties, natural sources, and variations in content across different plants is crucial for comprehending its diverse applications.Ferulic acid’s chemical structure, characterized by a phenylpropanoid structure, consists of a benzene ring attached to a five-carbon chain.
This structure lends it unique properties, including its ability to readily form complexes with other molecules, making it a powerful antioxidant. Its phenolic hydroxyl groups are responsible for its antioxidant activity. This chemical structure also allows it to participate in various reactions within living organisms.
Chemical Structure and Properties
Ferulic acid’s chemical structure is essential to understanding its function. It’s a phenolic acid, possessing a benzene ring and a carboxylic acid group. This unique structure allows it to readily form complexes with other molecules, a key factor in its antioxidant properties. The phenolic hydroxyl groups are crucial for its ability to scavenge free radicals and protect against oxidative stress.
Natural Sources of Ferulic Acid, The benefits of ferulic acid
Ferulic acid is widely distributed in the plant kingdom, predominantly found in the cell walls of various plants. Its presence is linked to the plant’s defense mechanisms against environmental stresses and plays a role in lignin synthesis, contributing to the plant’s structural integrity. Many fruits, vegetables, and grains contain ferulic acid.
Comparison of Ferulic Acid Content in Natural Sources
| Source | Ferulic Acid Content (approximate) |
|---|---|
| Wheat Bran | 1-3% |
| Grains (e.g., rice, barley) | 0.5-2% |
| Fruits (e.g., apples, berries) | 0.1-1% |
| Vegetables (e.g., broccoli, carrots) | 0.1-0.5% |
| Corn | 0.5-1.5% |
The table above provides a general overview of the approximate ferulic acid content in various plant sources. Keep in mind that these values can fluctuate depending on factors like growing conditions, processing methods, and the specific plant variety. These variations highlight the complexity of ferulic acid’s distribution in nature.
Antioxidant Properties

Ferulic acid, a naturally occurring phenolic compound, boasts potent antioxidant capabilities. Its ability to neutralize harmful free radicals makes it a valuable addition to various applications, from food preservation to skincare. Understanding the mechanisms behind its antioxidant activity is crucial to appreciating its diverse benefits.Ferulic acid’s antioxidant prowess stems from its unique chemical structure, specifically its phenolic hydroxyl groups.
These groups readily donate electrons to free radicals, stabilizing them and preventing the chain reactions that can damage cells. This process, known as radical scavenging, is a key aspect of ferulic acid’s antioxidant function.
Mechanisms of Antioxidant Action
Ferulic acid’s antioxidant activity arises from its capacity to donate electrons to free radicals, thus neutralizing them. This process is facilitated by the phenolic hydroxyl groups in its structure. This electron donation interrupts the chain reactions of oxidative stress, mitigating the damage caused by free radicals. Furthermore, ferulic acid can also participate in the regeneration of other antioxidants, thereby enhancing their overall effectiveness in cellular defense.
Evidence Supporting Antioxidant Activity
Extensive research supports ferulic acid’s antioxidant properties. Studies have demonstrated its effectiveness in various in vitro and in vivo models. In vitro assays, typically using cell cultures or test tubes, directly measure the ability of ferulic acid to scavenge free radicals. In vivo studies, involving live organisms, assess the impact of ferulic acid on oxidative stress markers and overall health.
The results consistently indicate that ferulic acid possesses significant antioxidant potential. For instance, studies have shown that ferulic acid supplementation can reduce lipid peroxidation, a crucial marker of oxidative damage.
Comparison to Other Antioxidants
Ferulic acid’s antioxidant activity is comparable to, and in some cases, superior to other commonly used antioxidants. While vitamin C and vitamin E are well-established antioxidants, ferulic acid often demonstrates synergistic effects when combined with them. For example, ferulic acid can enhance the stability and effectiveness of vitamin E in biological systems. The specific mechanism and extent of these synergistic effects are still under investigation, highlighting the complexity of antioxidant interactions.
Furthermore, ferulic acid is often found naturally alongside other antioxidants in plants, suggesting a natural synergistic action.
Antioxidant Assay Results
The following table demonstrates the results of various antioxidant assays conducted using ferulic acid. The IC50 values represent the concentration of ferulic acid required to inhibit 50% of a specific oxidative process. Lower IC50 values indicate higher antioxidant activity.
The data in the table clearly indicates ferulic acid’s potent antioxidant capacity, exhibiting lower IC50 values compared to the control in all the assays. This demonstrates ferulic acid’s effectiveness in scavenging various types of free radicals.
Anti-inflammatory Effects
Ferulic acid, beyond its antioxidant prowess, demonstrates significant anti-inflammatory properties. This multifaceted action stems from its ability to modulate various inflammatory pathways within the body, offering potential benefits for conditions characterized by chronic inflammation. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for appreciating the therapeutic potential of ferulic acid.Ferulic acid’s anti-inflammatory activity arises from its interaction with key molecules and enzymes involved in the inflammatory cascade.
It can inhibit the production of inflammatory mediators, such as cytokines and prostaglandins, thereby dampening the inflammatory response. This inhibition, in turn, can reduce the symptoms and progression of inflammatory diseases.
Mechanisms of Action
Ferulic acid’s anti-inflammatory effects are attributed to its diverse interactions with key inflammatory pathways. It acts as a potent inhibitor of cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes, crucial for the synthesis of prostaglandins, key players in the inflammatory cascade. By hindering COX activity, ferulic acid reduces the production of pro-inflammatory prostaglandins.
Studies Demonstrating Anti-inflammatory Activity
Several studies support ferulic acid’s anti-inflammatory potential. One study, published in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, demonstrated that ferulic acid treatment significantly reduced inflammation in a model of colitis, a chronic inflammatory bowel disease. This effect was observed through a reduction in the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and markers of tissue damage. Other research highlights the ability of ferulic acid to inhibit the production of nitric oxide, a molecule involved in the initiation and progression of inflammation.
Comparison with Other Anti-inflammatory Compounds
Compared to other anti-inflammatory compounds, ferulic acid exhibits a relatively safe profile with fewer side effects. While some anti-inflammatory drugs can have adverse effects on the gastrointestinal tract or the liver, ferulic acid, as a natural compound, tends to be well-tolerated. Furthermore, its ability to target multiple inflammatory pathways offers a broader spectrum of action compared to some more specific anti-inflammatory agents.
This multifaceted approach may contribute to its efficacy in various inflammatory conditions.
Specific Inflammatory Pathways Targeted
| Pathway | Mechanism of Action |
|---|---|
| Cyclooxygenase (COX) Inhibition | Inhibits the production of prostaglandins, key inflammatory mediators. |
| Nitric Oxide Synthase (NOS) Inhibition | Reduces the production of nitric oxide, a molecule contributing to inflammation. |
| Cytokine Production Modulation | Interferes with the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which play a crucial role in initiating and sustaining the inflammatory response. |
| Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Scavenging | Neutralizes harmful ROS, which can contribute to oxidative stress and inflammation. |
Skin Benefits
Ferulic acid, a naturally occurring phenolic compound, isn’t just a powerful antioxidant; it plays a crucial role in maintaining healthy skin. Its ability to protect against environmental stressors and promote skin rejuvenation makes it a valuable addition to skincare routines. This section will delve into how ferulic acid benefits skin health, detailing the mechanisms behind its protective actions and reviewing the evidence supporting its role in skin rejuvenation.Ferulic acid’s skin-protective mechanisms are multifaceted, leveraging its antioxidant properties to counteract the harmful effects of free radicals and UV radiation.
These mechanisms contribute to the overall health and youthful appearance of the skin, making ferulic acid a promising ingredient for various skin concerns.
Mechanisms of Skin Protection
Ferulic acid’s antioxidant properties are crucial for shielding skin cells from damage. It works synergistically with other antioxidants, such as vitamin C and vitamin E, enhancing their effectiveness. This combined action helps to neutralize free radicals, preventing oxidative stress that can lead to premature aging, wrinkles, and other skin issues. Furthermore, ferulic acid can absorb UV radiation, protecting the skin from sun damage.
This dual-action approach, both neutralizing free radicals and absorbing harmful UV rays, makes ferulic acid a potent protector against various skin stressors.
Evidence of Skin Rejuvenation
Numerous studies have explored ferulic acid’s role in skin rejuvenation. These studies often show improvements in skin elasticity, reduced wrinkle formation, and a more even skin tone. For example, some research indicates that ferulic acid can stimulate collagen production, a crucial protein for skin firmness and structure. This stimulation of collagen synthesis contributes to a more youthful appearance, supporting the claim of ferulic acid’s potential in skin rejuvenation.
Specific Skin Conditions
Ferulic acid’s benefits extend to various skin conditions, providing relief and improvement. Its antioxidant properties and ability to protect against environmental damage make it a valuable addition to skincare regimens.
| Skin Condition | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Photoaging (premature aging due to sun exposure) | Ferulic acid helps protect against UV damage, reducing wrinkles, age spots, and other signs of photoaging. |
| Fine lines and wrinkles | Ferulic acid can help stimulate collagen production, reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles and improving skin firmness. |
| Uneven skin tone and hyperpigmentation | Ferulic acid’s antioxidant properties can help reduce the appearance of age spots and other hyperpigmentation, leading to a more even skin tone. |
| Dry skin | Ferulic acid may help improve skin hydration and barrier function, potentially alleviating dry skin symptoms. |
Other Potential Benefits
Ferulic acid, beyond its well-established antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, shows promise in various other health areas. Its unique chemical structure and interactions with biological systems suggest potential benefits extending beyond skin care. This exploration delves into some of these potential applications.While research is ongoing, preliminary findings suggest ferulic acid may play a role in mitigating certain health conditions. The mechanisms behind these potential benefits are often complex and require further investigation, but understanding these preliminary insights can pave the way for future research and clinical trials.
Potential Benefits in Cardiovascular Health
Preliminary research indicates that ferulic acid might contribute to cardiovascular health. Studies have shown its ability to improve endothelial function, the lining of blood vessels. This improvement could potentially lower the risk of cardiovascular diseases by promoting better blood flow and reducing the risk of plaque buildup. Maintaining healthy blood vessels is crucial for overall cardiovascular health.
Potential Benefits in Neurological Health
Ferulic acid has shown potential neuroprotective properties in laboratory studies. It may help protect neurons from oxidative stress and inflammation, factors implicated in neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. This protective effect could potentially slow the progression of these diseases or even mitigate their onset. The exact mechanisms by which ferulic acid achieves this protection are still being investigated.
Potential Benefits in Metabolic Health
Ferulic acid may positively influence metabolic health. Early studies suggest a possible role in regulating blood sugar levels and improving insulin sensitivity. This is particularly relevant in conditions like type 2 diabetes, where maintaining healthy blood sugar control is paramount. The exact mechanism through which ferulic acid affects insulin sensitivity is not fully understood but involves potential interaction with key metabolic pathways.
Potential Benefits in Cancer Prevention
Some studies indicate a potential role for ferulic acid in cancer prevention. Its antioxidant properties may help neutralize free radicals that contribute to DNA damage, a key factor in cancer development. The exact mechanisms by which ferulic acid exerts its effects on cancer prevention are still under investigation. It’s important to note that more robust research is needed to fully understand the extent of ferulic acid’s impact in cancer prevention.
Summary Table of Potential Benefits
| Condition | Potential Benefit | Mechanism of Action |
|---|---|---|
| Cardiovascular Health | Improved endothelial function, potentially reducing cardiovascular disease risk. | Possible improvement in blood flow and reduction in plaque buildup. |
| Neurological Health | Neuroprotective effects, potentially slowing neurodegenerative disease progression. | Protection of neurons from oxidative stress and inflammation. |
| Metabolic Health | Regulation of blood sugar levels and improvement in insulin sensitivity. | Possible interaction with key metabolic pathways. |
| Cancer Prevention | Potential to neutralize free radicals and prevent DNA damage. | Antioxidant properties may contribute to reduced cancer risk. |
Safety and Side Effects
Ferulic acid is generally considered safe for consumption and topical application, but like any substance, potential side effects exist. Understanding its safety profile and appropriate usage is crucial for maximizing its benefits while minimizing risks. This section delves into the tolerability of ferulic acid, its potential side effects, and crucial dosage considerations.
Safety Profile
Ferulic acid possesses a good safety profile. Extensive research indicates it’s well-tolerated by the human body, even at relatively high doses. This is largely due to its natural presence in various foods and its involvement in numerous biological processes within the body. However, individual sensitivities and interactions with other medications or supplements should be considered. Furthermore, while generally safe, the potential for adverse reactions cannot be entirely ruled out.
Potential Side Effects
While ferulic acid is typically well-tolerated, some individuals may experience mild side effects. These are usually transient and resolve without intervention. Common reported side effects include gastrointestinal discomfort such as mild nausea, bloating, or indigestion. These effects are often dose-dependent and typically resolve with reduced dosage. Rarely, more severe reactions might occur, although these are uncommon and require medical attention.
Dosage Considerations
The recommended dosage of ferulic acid varies depending on the specific application (e.g., dietary supplement, topical treatment). For dietary supplements, typical dosages range from 500 mg to 1500 mg per day. However, the optimal dosage is best determined in consultation with a healthcare professional, considering individual health needs and potential interactions with other medications. Topical applications typically involve lower concentrations, with the specific amount dependent on the product formulation.
Ferulic acid is a powerhouse when it comes to skin health, offering antioxidant benefits and potentially reducing inflammation. Understanding our commitment to ethical sourcing and responsible practices is key, as outlined in our commerce guidelines and mission. Ultimately, these principles ensure we’re providing high-quality products with ferulic acid, supporting your well-being through effective and safe solutions.
It’s crucial to adhere to the instructions provided by the manufacturer.
Tolerability and Safety from Studies
Numerous studies have investigated the tolerability and safety of ferulic acid. These studies have consistently shown it to be well-tolerated by the majority of participants. Reports of adverse events are generally mild and transient, and often related to gastrointestinal issues. The available data strongly suggests a favorable safety profile, although more research is always beneficial. It’s essential to note that study populations and methodologies can vary, impacting the interpretation of results.
Summary of Reported Side Effects
| Side Effect | Frequency | Severity |
|---|---|---|
| Gastrointestinal discomfort (e.g., nausea, bloating, indigestion) | Mild to moderate | Usually transient and resolves with reduced dosage |
| Allergic reactions (e.g., skin rash, itching) | Rare | Potentially severe; requires immediate medical attention |
| Headache | Rare | Mild to moderate |
| Other rare adverse events | Very rare | Variable severity; may require medical intervention |
This table summarizes the reported side effects, their estimated frequency, and the general severity observed in studies. It is important to remember that individual responses can vary, and the information provided is for general knowledge and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen.
Ferulic acid is amazing for skin health, offering antioxidant protection and promoting collagen production. But sometimes, even with the best skincare ingredients, navigating doctor’s offices can be tricky, especially when dealing with weight stigma. This is where a self-advocacy guide like self advocacy guide at doctors weight stigma comes in handy, empowering you to discuss your health concerns effectively.
Ultimately, understanding these powerful benefits of ferulic acid and your rights as a patient can lead to better overall well-being.
Interactions and Considerations: The Benefits Of Ferulic Acid
Ferulic acid, while generally considered safe, can interact with certain substances and medications. Understanding these interactions is crucial for maximizing its benefits and minimizing potential risks. Proper dietary considerations and supplement usage guidelines can ensure safe and effective integration into your health routine.Knowing how ferulic acid interacts with other components of your daily intake, including foods and medications, is essential for optimizing its potential health benefits.
Ferulic acid boasts some impressive benefits, like protecting skin from sun damage. Knowing how to research a doctor’s history, especially when considering a potential medical malpractice case, is also important. For instance, how to uncover a doctors medical malpractice history can help ensure you’re making informed decisions about your health. Ultimately, understanding these details can help you make the best choices for your health and well-being, just like ferulic acid helps protect your skin.
This section will delve into potential interactions, dietary factors, and supplement usage guidelines for a comprehensive understanding.
Potential Interactions with Other Substances
Ferulic acid, like many compounds, can potentially interact with other substances, both dietary and pharmaceutical. These interactions can either amplify or diminish the effects of ferulic acid, depending on the specific substance involved.
- Certain Medications: Some medications, particularly those that affect the liver’s detoxification processes, might influence ferulic acid metabolism. Consulting with a healthcare professional before combining ferulic acid supplements with medications is essential, especially if you are already taking other supplements or have pre-existing health conditions.
- Other Supplements: Ferulic acid can interact with other supplements, such as vitamin C or antioxidants. Taking these supplements simultaneously might result in synergistic effects, boosting overall benefits. Conversely, some interactions could potentially lead to adverse effects. It’s crucial to inform your doctor about all supplements you’re taking, to avoid potential complications.
- Dietary Components: Foods rich in certain compounds, such as those high in vitamin K, might potentially interact with ferulic acid. This interaction is often complex and dependent on the specific food and the individual’s overall health. A balanced diet, rich in various nutrients, is generally recommended for optimal health outcomes.
Dietary Considerations for Ferulic Acid Intake
Dietary factors can influence ferulic acid absorption and effectiveness. Understanding these considerations can optimize the potential health benefits.
- Food Sources: Ferulic acid is found naturally in various foods, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables. A diet rich in these foods can contribute to overall ferulic acid intake. However, supplement use might be necessary for individuals who have limited access to these foods or wish to increase their intake significantly.
- Absorption: The absorption of ferulic acid from food sources can be influenced by other dietary components. For example, the presence of fiber can either enhance or hinder absorption. A balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrients is typically recommended for optimal absorption.
- Timing: While specific timing recommendations for ferulic acid intake haven’t been extensively studied, taking it with a meal or alongside other nutrients that aid in absorption might enhance its effectiveness. However, more research is necessary to fully understand the impact of timing on absorption and utilization.
Recommendations for Using Ferulic Acid Supplements
Using ferulic acid supplements can be a way to increase intake beyond dietary sources. Adhering to proper guidelines is important for safety and effectiveness.
- Dosage: The recommended dosage of ferulic acid supplements can vary depending on individual needs and the specific product. Consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate dosage for your situation.
- Product Selection: Choose reputable brands and products that provide accurate labeling regarding ferulic acid content and quality. Verify the source of the supplement to ensure its purity and safety.
- Storage: Proper storage of ferulic acid supplements is crucial for maintaining their quality and effectiveness. Store them in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and heat.
Potential Interactions with Medications or Other Supplements
The following table summarizes potential interactions between ferulic acid and other substances. This information is not exhaustive and should not be used as a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare professional before combining ferulic acid with other medications or supplements.
| Substance | Potential Interaction |
|---|---|
| Certain Antioxidants | May enhance or diminish the effects of ferulic acid, depending on the specific antioxidant. |
| Anti-inflammatory Drugs | May potentially affect the efficacy of both the drug and the ferulic acid, depending on the specific drug. |
| Warfarin | May potentially interact with ferulic acid, requiring careful monitoring and adjustments in dosage, if necessary. |
| Vitamin K | May potentially interact with ferulic acid. The effect of this interaction may vary depending on individual factors and the specific amounts consumed. |
Research Trends and Future Directions
Ferulic acid, a naturally occurring phenolic compound, continues to attract significant research interest due to its diverse potential applications. Current research explores various aspects of ferulic acid, ranging from its fundamental mechanisms of action to its potential therapeutic and cosmetic uses. This exploration promises to unlock further insights into its multifaceted properties and pave the way for innovative applications.
Current Research Trends
Research into ferulic acid is actively investigating its diverse mechanisms of action, including its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial properties. Scientists are examining the interactions of ferulic acid with various biological molecules and pathways. The focus is on understanding how ferulic acid can protect cells from oxidative stress and inflammation. This includes studies on its role in mitigating age-related diseases and its potential in skin care.
Furthermore, research is expanding to encompass its potential applications in food preservation and industrial processes.
Future Research Directions
Future research on ferulic acid should delve deeper into its personalized efficacy. Tailoring ferulic acid treatments to individual genetic profiles and specific health conditions could lead to more effective therapies. For example, research exploring the optimal dosage and delivery methods for different patient groups will be crucial. Another promising area is exploring the synergistic effects of ferulic acid with other bioactive compounds.
Combining ferulic acid with other antioxidants, anti-inflammatory agents, or even specific nutrients could significantly enhance its overall efficacy. A critical future direction involves the development of advanced delivery systems to improve ferulic acid’s bioavailability and effectiveness.
Open Questions and Gaps in Knowledge
Several open questions remain regarding ferulic acid. Understanding the specific molecular targets and pathways through which ferulic acid exerts its effects is crucial. For instance, the precise mechanisms behind its anti-cancer potential are still not fully elucidated. Further research is needed to investigate the long-term effects of ferulic acid consumption and to fully characterize its safety profile in different populations.
Additionally, understanding how ferulic acid interacts with other dietary components or pharmaceuticals is essential. This is important for optimizing its use and minimizing potential interactions.
Table Summarizing Current Research Areas and Future Directions
| Research Area | Current Status | Future Directions |
|---|---|---|
| Antioxidant Activity | Extensive research demonstrating ferulic acid’s scavenging of free radicals and protection against oxidative damage. | Investigate the specific mechanisms of action in different cell types and explore synergistic effects with other antioxidants. |
| Anti-inflammatory Effects | Evidence suggesting ferulic acid’s ability to modulate inflammatory pathways. | Identify specific inflammatory markers targeted by ferulic acid and determine the optimal dosage and delivery method for various inflammatory conditions. |
| Skin Benefits | Studies highlighting ferulic acid’s potential in improving skin elasticity, reducing wrinkles, and protecting against UV damage. | Investigate personalized efficacy based on skin type and genetic predisposition. Explore the potential of topical formulations combined with other cosmeceuticals. |
| Food Preservation | Research exploring the use of ferulic acid as a natural preservative in food products. | Develop standardized protocols for incorporating ferulic acid into food products, ensuring safety and efficacy. Explore the interaction with other food components. |
| Pharmaceutical Applications | Preliminary studies suggesting ferulic acid’s potential in treating various diseases. | Conduct large-scale clinical trials to assess safety and efficacy in specific disease conditions. Develop targeted drug delivery systems to enhance bioavailability. |
Final Summary

In conclusion, ferulic acid presents a compelling case for its potential in various health areas. While more research is always beneficial, the existing evidence suggests this natural compound could be a valuable addition to a healthy lifestyle. Understanding its diverse properties, from combating oxidative stress to potentially aiding in skin health, offers a glimpse into its promising future in health and wellness.
However, it’s crucial to remember that individual responses may vary, and consulting a healthcare professional is always recommended before incorporating any new supplement into your routine.