Tranexamic acid for skin is gaining popularity as a potential solution for various skin concerns. This powerful ingredient, often found in topical creams and serums, is gaining traction for its purported ability to reduce redness, control inflammation, and even prevent acne. We’ll explore its mechanism of action, historical context, efficacy, safety, and practical applications, comparing it to other treatments along the way.
Understanding the different formulations, potential side effects, and optimal usage guidelines is crucial for anyone considering incorporating tranexamic acid into their skincare routine. This comprehensive guide aims to equip you with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions about your skin health.
Introduction to Tranexamic Acid for Skin

Tranexamic acid (TXA) is gaining popularity as a powerful tool in dermatology, primarily for its ability to effectively address concerns like hyperpigmentation and redness. It’s a synthetic amino acid derivative that works differently than many other skin-care ingredients, offering a unique approach to improving skin health. This article delves into the specifics of its use in skin care, exploring its mechanism of action, available forms, and historical context.Tranexamic acid’s mechanism of action hinges on its ability to inhibit the breakdown of blood clots.
It achieves this by competing with the activation of plasmin, an enzyme responsible for dissolving fibrin, a crucial component of blood clots. By preventing this breakdown, tranexamic acid can potentially minimize the appearance of inflammation and redness, and may also help reduce the formation of new blood vessels. This principle is often applied to skin conditions where these processes contribute to the symptoms.
Forms of Tranexamic Acid for Skin
Tranexamic acid is available in various forms for topical and systemic use. Topical formulations are most common in skincare applications, including creams, serums, and patches. Oral administration is another option, often prescribed by dermatologists for more extensive treatment, such as addressing severe cases of skin conditions involving inflammation or hyperpigmentation. The chosen form depends on the specific needs and severity of the condition being treated.
Historical Context of Tranexamic Acid in Dermatology
The use of tranexamic acid in dermatology has evolved over time. Initially, it was primarily recognized for its role in controlling bleeding, and its dermatological applications were more niche. However, as research unveiled its positive impact on reducing inflammation and hyperpigmentation, its use in dermatology expanded. Clinical studies provided evidence for its efficacy in treating various skin concerns, solidifying its position as a valuable tool for dermatologists.
Comparison of Topical Tranexamic Acid Formulations
Understanding the different formulations helps in selecting the most appropriate product for individual needs.
| Formulation | Ingredients (Example) | Concentration (Example) | Intended Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cream | Tranexamic acid, humectants (e.g., hyaluronic acid), emollients (e.g., shea butter) | 2% | Moisturizing, reducing inflammation, and promoting skin regeneration. |
| Serum | Tranexamic acid, vitamin C, antioxidants | 5% | Targeting hyperpigmentation, promoting collagen production, and brightening the skin. |
| Patch | Tranexamic acid, hydrocolloid | Variable | Targeting specific areas of hyperpigmentation or inflammation. |
Note that the exact ingredients and concentrations can vary significantly between different products. Always consult with a dermatologist or healthcare professional before using any new skincare product.
Efficacy and Benefits: Tranexamic Acid For Skin
Tranexamic acid (TXA) is gaining traction as a topical treatment for various skin concerns. Its purported benefits extend beyond its traditional role in blood clotting, with emerging evidence suggesting a positive impact on skin inflammation, redness, and even acne. This exploration delves into the scientific backing behind these claims and compares TXA’s effectiveness with other treatments.TXA’s mechanism of action on the skin involves its ability to inhibit the breakdown of collagen and elastin, thus potentially reducing the appearance of wrinkles and scars.
Moreover, it acts as an anti-inflammatory agent, potentially reducing redness and inflammation associated with conditions like rosacea and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. By controlling inflammation, TXA might also play a role in preventing acne outbreaks by minimizing pore clogging and reducing bacterial activity.
Reducing Redness and Inflammation
Tranexamic acid’s anti-inflammatory properties are believed to be a key factor in its effectiveness for treating skin conditions characterized by redness and inflammation. Studies have indicated that TXA can effectively reduce erythema (redness) in various skin conditions, including rosacea. It works by suppressing inflammatory mediators and potentially reducing the dilation of blood vessels, thereby diminishing the appearance of redness.
Controlling Acne
While TXA isn’t a primary acne treatment, its anti-inflammatory properties might help in controlling acne outbreaks. By reducing inflammation, TXA may help minimize the redness and swelling associated with acne lesions, and potentially slow the development of acne scars. However, more research is needed to definitively establish its role in acne treatment compared to other established acne therapies.
Treating Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH), Tranexamic acid for skin
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, or PIH, often follows skin injuries or inflammation. TXA, due to its anti-inflammatory effects, may help prevent and reduce the appearance of PIH by mitigating the inflammatory response that triggers pigment production. While more research is needed to fully understand its role in PIH, some studies show promise in its ability to fade dark spots and even out skin tone.
Comparison with Other Topical Treatments
Comparing TXA to other topical treatments for redness and inflammation, like azelaic acid or niacinamide, reveals that TXA’s mechanism of action differs. Azelaic acid targets bacteria and inflammation, while niacinamide often focuses on improving skin barrier function and reducing redness. TXA’s focus on inhibiting inflammatory mediators may make it a beneficial alternative or a complementary treatment in specific cases, depending on the individual’s skin type and condition.
Summary Table: Tranexamic Acid for Skin
| Feature | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Effectiveness | Potentially reduces redness, inflammation, and PIH. May help control acne. | Limited research on acne treatment efficacy compared to established treatments. May not be suitable for all skin types or conditions. |
| Mechanism of Action | Inhibits inflammatory mediators and potentially reduces blood vessel dilation. | Mechanism of action differs from other topical treatments, requiring further investigation for specific skin concerns. |
| Side Effects | Generally well-tolerated, but potential for mild irritation, dryness, or burning sensations in some individuals. | Potential for skin sensitivity, requiring careful monitoring and potential adjustment of usage. |
| Overall | A promising topical treatment with potential benefits for various skin concerns. | Requires further research to establish optimal use and efficacy in diverse scenarios. |
Safety and Side Effects
Tranexamic acid, while a promising topical treatment for skin concerns, like hyperpigmentation, comes with potential side effects. Understanding these risks is crucial for safe and effective use. This section delves into the possible adverse reactions, safety precautions, and situations where tranexamic acid use might be inappropriate.Topical tranexamic acid, like any other skincare product, can cause reactions in susceptible individuals.
Careful monitoring and adherence to recommended usage guidelines are vital to minimizing potential problems. Understanding the potential side effects empowers you to make informed decisions about your skincare routine.
Potential Side Effects
Potential adverse reactions to topical tranexamic acid can range from mild irritation to more severe allergic responses. Common skin reactions include redness, itching, and a burning sensation. In rare cases, more serious allergic reactions like hives or swelling can occur.
Safety Precautions
Adherence to the recommended usage instructions is paramount. Always start with a low concentration and gradually increase as tolerated. Patch testing before full application is crucial to identify potential sensitivities. Stop use immediately if any adverse reaction develops. Avoid contact with eyes and mucous membranes.
Use sunscreen when applying topical tranexamic acid, as it may increase sun sensitivity in some individuals.
Contraindications and Special Considerations
Individuals with known allergies to tranexamic acid or similar compounds should avoid use. Pre-existing skin conditions, like eczema or rosacea, might require special consideration and a lower concentration or alternative treatment. Consult a dermatologist or healthcare professional before using tranexamic acid, especially if you are pregnant, breastfeeding, or have underlying medical conditions.
Adverse Effect Summary
| Adverse Effect | Frequency | Severity |
|---|---|---|
| Erythema (redness) | Common | Mild |
| Pruritus (itching) | Common | Mild to Moderate |
| Burning sensation | Common | Mild to Moderate |
| Skin irritation | Common | Mild to Moderate |
| Allergic reaction (hives, swelling) | Rare | Moderate to Severe |
| Contact dermatitis | Rare | Moderate to Severe |
Note: This table provides a general overview. Individual responses to tranexamic acid may vary. Consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
Applications and Usage
Tranexamic acid, a powerful ingredient in skincare, offers a targeted approach to reducing the appearance of hyperpigmentation and improving skin texture. Understanding how to incorporate it into your routine is key to maximizing its benefits and minimizing potential side effects. This section will provide practical guidance on application methods, optimal concentrations, and usage frequencies, tailored for different skin types.
Tranexamic acid is a skincare game-changer, helping to fade dark spots and even skin tone. But when you’re considering treatments like this, understanding your healthcare coverage is crucial. For example, knowing your Minimum Essential Coverage (MEC) is vital to ensure you’re getting the most out of your skincare routine without unnecessary financial stress. What is Minimum Essential Coverage and Why Does It Matter?
This knowledge can help you determine if your coverage includes the cost of tranexamic acid treatments or if you need additional coverage. Ultimately, knowing your coverage empowers you to make informed decisions about your skincare journey.
Incorporating Tranexamic Acid into Your Routine
Tranexamic acid is typically formulated as a topical serum or cream. It’s crucial to integrate it into your existing skincare regimen, applying it at the appropriate time to ensure maximum effectiveness and to avoid any negative interactions with other products. Consider placing it in your routine after cleansing and toning, but before moisturizing. This order allows the serum to fully absorb and work its magic on the skin.
Application Methods and Concentrations
The appropriate application method and concentration depend largely on your skin type and the specific product you are using. Generally, a pea-sized amount of serum or a thin layer of cream is sufficient for most applications. For sensitive skin, a lower concentration product may be recommended. Products often come with specific instructions for usage, and it’s crucial to adhere to these recommendations for optimal results.
Optimal Duration and Frequency of Use
The optimal duration and frequency of tranexamic acid use vary based on individual needs and product formulations. Some studies suggest visible improvements in hyperpigmentation can be seen after several weeks of consistent use, with a noticeable reduction in redness or dark spots. However, results may vary, and it’s essential to be patient and consistent. It’s often recommended to use tranexamic acid for at least 8 weeks for optimal results.
If you do not see improvement, consulting a dermatologist is advised.
Step-by-Step Guide for Using Tranexamic Acid
- Cleanse your face: Gently cleanse your skin with a mild cleanser to remove dirt, makeup, and impurities. This prepares the skin for the subsequent application.
- Apply toner (optional): A toner can help to balance the skin’s pH and further prepare it for the tranexamic acid.
- Apply Tranexamic Acid: Using a clean fingertip or a cotton swab, gently apply a pea-sized amount of the tranexamic acid serum or a thin layer of cream to the affected areas of your skin.
- Allow to absorb: Allow the tranexamic acid to absorb completely into your skin before applying any other skincare products, such as moisturizers or sunscreen.
- Follow with moisturizer: Apply a moisturizer to seal in the tranexamic acid and provide additional hydration.
- Sunscreen: Applying sunscreen is crucial, as tranexamic acid can increase the skin’s sensitivity to UV rays. Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher.
Formulation and Ingredients
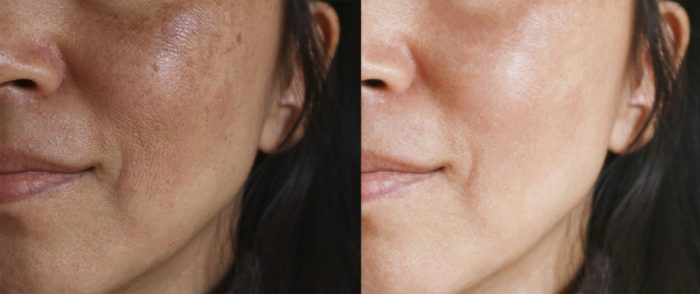
Tranexamic acid, while effective on its own, often performs better when combined with other ingredients in skincare products. This synergistic approach enhances its efficacy and safety, leading to improved results for the user. Understanding the supporting ingredients is crucial for selecting a product that meets individual needs and skin types.Formulations designed for tranexamic acid often include a blend of ingredients beyond the active component, carefully selected to optimize its effectiveness and minimize potential side effects.
The choice of these supporting ingredients is influenced by the intended effect, whether it’s targeting hyperpigmentation, moisturizing the skin, or protecting it from environmental stressors.
Tranexamic acid is a skincare ingredient that’s gaining popularity for its potential to reduce redness and improve skin tone. But, like any skincare product, understanding its effectiveness and potential downsides is key. To get a better understanding of how environmental factors can impact your skin health, check out this insightful article on whether air purifiers actually help with dust: Do Air Purifiers Help With Dust?
A Deep Dive. A cleaner environment might contribute to healthier skin, and understanding the role of environmental factors can be crucial when considering treatments like tranexamic acid.
Common Ingredients and Their Roles
Formulations frequently incorporate ingredients that enhance the benefits of tranexamic acid. These additions contribute to improved product texture, absorption, and overall skin health.
- Moisturizers: Ingredients like hyaluronic acid, glycerin, and ceramides are commonly included to maintain skin hydration. Hydrated skin is less prone to irritation, a potential side effect of some active ingredients, and tranexamic acid is no exception. Proper hydration supports the skin’s natural barrier function, enhancing the efficacy of tranexamic acid.
- Antioxidants: Vitamins C and E, along with other antioxidants, protect the skin from free radical damage. Free radicals can contribute to premature aging and skin discoloration, which tranexamic acid is designed to address. Combining tranexamic acid with antioxidants creates a comprehensive approach to skin health, potentially minimizing the risk of future damage.
- Skin-Lightening Agents: In some products, ingredients like vitamin C or kojic acid are included to further enhance skin lightening effects. The combination of tranexamic acid and these agents can potentially reduce hyperpigmentation more effectively than either ingredient alone. It’s important to note that the inclusion of these agents may increase the potential for skin sensitivity in some individuals.
- Emollients: Ingredients like shea butter, cocoa butter, and oils like jojoba or argan oil are often used to soften and smooth the skin. They help to create a more comfortable and user-friendly experience while enhancing the overall efficacy of the product by improving product spreadability and absorption.
- Sunscreen Agents: It is crucial to include broad-spectrum sunscreens in any skincare regimen containing tranexamic acid, regardless of the presence of other ingredients. Tranexamic acid is not a sunscreen and does not protect against UV damage. Exposure to the sun can lead to further skin damage and negate the benefits of tranexamic acid.
Potential Interactions
Careful consideration must be given to potential interactions between tranexamic acid and other ingredients. Some ingredients may enhance or diminish the efficacy of tranexamic acid, while others may increase the risk of skin irritation.
For example, certain ingredients, like vitamin C, can potentially increase skin sensitivity. Therefore, products containing both tranexamic acid and vitamin C might require a gradual introduction to the skin. Conversely, ingredients like hyaluronic acid can enhance the absorption of tranexamic acid, leading to improved results.
Ingredient Summary Table
The following table provides a concise overview of common ingredients found in tranexamic acid skincare products, categorized by their function.
Tranexamic acid is a popular ingredient for skin, often used to reduce redness and even out skin tone. But, did you know that some foods can influence estrogen levels in the body? Understanding the role of estrogen in your overall health is key, and exploring foods that may impact your estrogen levels, like those discussed in the Foods with Estrogen Eat or Avoid?
article, could be a helpful piece of the puzzle for those seeking to optimize their skin health through diet and lifestyle choices. Ultimately, tranexamic acid for skin can be a powerful tool, but a holistic approach to skincare, including mindful dietary choices, is often more effective in the long run.
| Category | Ingredient Examples | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Moisturizers | Hyaluronic Acid, Glycerin, Ceramides | Maintain skin hydration, support skin barrier function |
| Antioxidants | Vitamin C, Vitamin E, Niacinamide | Protect skin from free radical damage |
| Skin Lightening | Vitamin C, Kojic Acid, Arbutin | Reduce hyperpigmentation |
| Emollients | Shea Butter, Cocoa Butter, Jojoba Oil | Soften and smooth the skin, improve product spreadability |
| Sunscreen | Zinc Oxide, Titanium Dioxide | Protect against UV damage |
Comparison with Other Treatments
Tranexamic acid is gaining popularity as a skin-lightening and anti-inflammatory agent, but how does it stack up against other popular skincare ingredients? This section delves into comparisons with vitamin C, niacinamide, and arbutin, highlighting their unique benefits, drawbacks, and potential synergistic effects when used together.Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each treatment allows for more informed choices and potentially better results.
A thorough comparison also helps in determining the most suitable approach for specific skin concerns.
Tranexamic Acid vs. Vitamin C
Vitamin C, a potent antioxidant, is widely recognized for its brightening and collagen-boosting properties. Tranexamic acid, on the other hand, primarily focuses on reducing redness and inflammation, and preventing further damage to the skin barrier.Vitamin C excels at reducing hyperpigmentation by inhibiting tyrosinase activity, the enzyme responsible for melanin production. However, its efficacy in reducing redness is limited compared to tranexamic acid.
Tranexamic acid’s anti-inflammatory properties can effectively target existing redness and prevent future breakouts.A potential synergy arises when combining these two ingredients. Vitamin C’s antioxidant properties can protect the skin from environmental damage, while tranexamic acid can further reduce inflammation and promote a healthier complexion.
Tranexamic Acid vs. Niacinamide
Niacinamide, a form of vitamin B3, is known for its broad-spectrum benefits, including reducing redness, improving skin barrier function, and controlling oil production. Tranexamic acid, while also addressing redness, focuses on preventing blood vessel leakage and reducing inflammation, particularly related to post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.Niacinamide is particularly effective in improving skin texture and reducing the appearance of pores. Tranexamic acid, however, is more directly targeted at post-inflammatory responses.
A potential synergistic effect is seen in combining both ingredients, with niacinamide improving skin barrier function, potentially enhancing the absorption and effectiveness of tranexamic acid.
Tranexamic Acid vs. Arbutin
Arbutin, a natural skin-lightening agent, works by inhibiting melanin production. Tranexamic acid, on the other hand, addresses inflammation and subsequent hyperpigmentation resulting from skin damage or irritation.Arbutin’s effectiveness in reducing existing hyperpigmentation is well-established. Tranexamic acid, however, addresses the root cause of inflammation, potentially preventing future hyperpigmentation. The combination can be beneficial as arbutin tackles existing discoloration while tranexamic acid minimizes the occurrence of new inflammation-related spots.
Comparison Table
| Treatment | Primary Mechanism | Benefits | Drawbacks | Synergy Potential |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tranexamic Acid | Inhibits blood vessel leakage, reduces inflammation | Reduces redness, post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, improves skin barrier | May not be as effective in treating deep-seated hyperpigmentation | High with vitamin C, niacinamide for comprehensive skin health |
| Vitamin C | Inhibits melanin production, antioxidant | Brightens skin, boosts collagen production, protects against free radicals | May cause slight irritation in sensitive skin | High with tranexamic acid for antioxidant protection and inflammation reduction |
| Niacinamide | Improves skin barrier function, controls oil production, reduces redness | Reduces redness, improves skin texture, controls oil | May not be as effective as tranexamic acid for specific inflammatory conditions | High with tranexamic acid for comprehensive skin health and barrier improvement |
| Arbutin | Inhibits melanin production | Reduces hyperpigmentation | Can be less effective in treating inflammatory-related hyperpigmentation | High with tranexamic acid for addressing both inflammation and hyperpigmentation |
Research and Future Directions
Tranexamic acid’s promise for skin rejuvenation continues to be explored through ongoing research. While initial studies show promising results in reducing hyperpigmentation and improving skin texture, the field is still developing. Understanding the mechanisms of action and optimizing formulations are key to unlocking tranexamic acid’s full potential. Future directions will likely focus on tailored treatments and personalized approaches.
Ongoing Research Summary
Current research investigating tranexamic acid for skin applications is multifaceted. Studies are examining its efficacy in various skin conditions, including melasma, acne scars, and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. Researchers are also looking into optimal application methods, such as topical creams, serums, and even in-office treatments, to maximize penetration and effectiveness. The mechanisms behind tranexamic acid’s action on melanogenesis and collagen synthesis are also being investigated.
These studies are crucial for establishing the safety and efficacy of tranexamic acid as a standalone treatment or as part of a combination therapy.
Potential Future Research Areas
Future research will likely focus on personalized treatment approaches. This includes identifying specific genetic or environmental factors that influence the efficacy of tranexamic acid on different skin types and individuals. Furthermore, the development of targeted delivery systems for tranexamic acid will be crucial for improving its penetration into the skin and reducing side effects. Research into combination therapies with other active ingredients, such as vitamin C or retinoids, could also unlock synergistic benefits and improve treatment outcomes.
The development of non-invasive techniques for delivering tranexamic acid, such as microneedling or ultrasound-assisted topical application, is also a promising area for investigation.
Limitations of Current Research
A significant limitation of current research is the relatively short duration of many clinical trials. Longer-term studies are needed to fully assess the long-term safety and efficacy of tranexamic acid for skin use. Another area requiring further investigation is the potential interaction of tranexamic acid with other skincare products. Furthermore, the variability in skin types and responses needs to be carefully considered in future studies.
A deeper understanding of the molecular mechanisms through which tranexamic acid exerts its effects on the skin will be essential for improving treatment outcomes.
Timeline of Key Milestones
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 2010s | Initial clinical trials focusing on topical application in various skin conditions begin. |
| 2015-2020 | Increasing number of publications emerge, showcasing the potential of tranexamic acid in reducing hyperpigmentation. Studies begin to explore different delivery methods. |
| 2020-present | Research continues to investigate optimal concentrations, combination therapies, and personalized approaches. Focus shifts towards understanding the molecular mechanisms and long-term effects. |
Closure
In conclusion, tranexamic acid shows promise as a powerful tool in skincare, offering potential benefits for various skin concerns. However, its use should be approached cautiously, considering potential side effects and individual sensitivities. By understanding its mechanism of action, efficacy, and safety precautions, you can potentially harness its benefits for healthier, more radiant skin. Further research and clinical trials will continue to shed light on its full potential in the dermatological realm.