Treatment for metastatic castration resistant prostate cancer is a complex and challenging journey for patients and their families. This comprehensive guide explores the various stages of this disease, from its initial progression to the latest treatment approaches and emerging therapies. We’ll delve into the hormonal changes, symptoms, and treatment options, examining the efficacy and side effects of different regimens.
The importance of personalized medicine, patient factors, quality of life considerations, and future directions will also be discussed.
Understanding the progression of prostate cancer from localized disease to metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer is crucial. This journey often involves hormonal shifts, leading to a range of symptoms that can significantly impact patients’ quality of life. Fortunately, there are various treatment options available, including systemic therapies, targeted therapies, and emerging immunotherapies. We’ll explore these options, highlighting their efficacy and potential side effects.
Ultimately, the goal is to empower patients and their families with the knowledge and resources needed to navigate this challenging disease.
Overview of Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer (mCRPC)
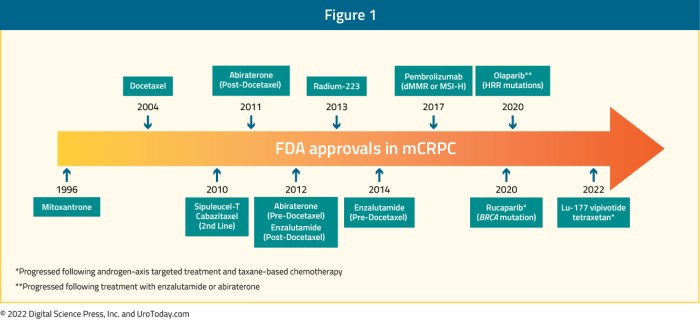
Prostate cancer, when it spreads beyond the prostate gland to other parts of the body, presents a significant challenge. This advanced stage, known as metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC), represents a particularly difficult phase of the disease. Understanding its progression, hormonal influences, and symptoms is crucial for effective patient management.Metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer is a stage of prostate cancer characterized by the cancer’s resistance to hormonal therapies (often initially used to treat prostate cancer) and its spread to distant sites within the body.
This stage signifies a significant shift in the disease’s behavior, demanding a multifaceted approach to treatment and management.
Progression from Localized Prostate Cancer to mCRPC
Prostate cancer typically progresses through several stages. Initially, it may be localized within the prostate gland, treatable with surgery or radiation therapy. If left untreated or if the cancer cells exhibit aggressive characteristics, it can spread locally to nearby tissues. Hormonal therapy is often employed to control the growth of prostate cancer cells by altering the hormonal environment.
However, over time, the cancer cells can adapt and develop resistance to these hormonal therapies, leading to the emergence of mCRPC. This resistance signifies a more aggressive form of the disease, demanding more complex treatment strategies.
Hormonal Changes Associated with mCRPC
The hormonal landscape significantly alters as prostate cancer progresses to mCRPC. Initially, hormonal therapies, such as androgen deprivation therapy (ADT), aim to lower the levels of testosterone, a hormone that fuels prostate cancer growth. However, in mCRPC, cancer cells develop mechanisms to either bypass the effects of ADT or to find alternative growth signals, potentially even stimulating growth in the absence of testosterone.
This resistance to hormonal manipulation underscores the complexity of managing mCRPC.
Symptoms and Signs of mCRPC
The symptoms of mCRPC can vary depending on the specific sites of metastasis. Common symptoms include bone pain (often a prominent feature), fatigue, loss of appetite, weight loss, and general weakness. Additionally, symptoms related to the affected organs can arise. For instance, if the cancer spreads to the lungs, breathing difficulties might become apparent. If the cancer spreads to the spine, neurological symptoms like numbness or weakness in the limbs could manifest.
Dealing with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) can be tough, especially when standard hormone therapies start to lose their effectiveness. This often leads to a situation where the cancer continues to progress, and unfortunately, finding new treatment options becomes crucial. Understanding what happens when hormone treatment for prostate cancer stops working, as detailed in this article what happens when hormone treatment for prostate cancer stops working , is vital for navigating the complexities of mCRPC.
This knowledge empowers patients and their families to proactively discuss treatment options with their doctors, ensuring the best possible care plan moving forward.
Recognizing these symptoms and their potential connections to mCRPC is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment.
Stages of mCRPC
| Stage | Symptoms | Treatment Options | Prognosis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Early mCRPC | Bone pain, fatigue, back pain, decreased appetite, weight loss. | Hormonal therapies, chemotherapy, targeted therapies, radiation therapy. | Potentially responsive to treatment, with a median survival time that can vary depending on individual factors. Some patients may experience prolonged periods of stable disease or even remission. |
| Intermediate mCRPC | Progressive bone pain, neurological symptoms, fatigue, cachexia, organ dysfunction. | Combination therapies (e.g., hormonal therapy + chemotherapy), targeted therapies, immunotherapy. | Treatment response can be variable. Median survival time is typically shorter than in early mCRPC. |
| Late mCRPC | Severe bone pain, neurological deficits, multiple organ dysfunction, cachexia, and significant fatigue. | Palliative care, symptom management, experimental therapies. | Prognosis is often poor, with a shorter life expectancy. The primary focus shifts to symptom relief and quality of life. |
Current Treatment Approaches for mCRPC
Navigating the complexities of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) requires a multi-pronged approach. While a cure remains elusive, various treatment strategies aim to extend survival, improve quality of life, and manage symptoms effectively. This involves a nuanced understanding of the disease progression and a personalized strategy tailored to individual patient needs.
Systemic Treatment Options
Current systemic treatments for mCRPC encompass a range of approaches, each with its own efficacy profile and potential side effects. These therapies often target specific molecular pathways involved in cancer growth and spread. Key options include hormonal therapies, chemotherapy, targeted therapies, and immunotherapy. Understanding the strengths and limitations of each treatment is crucial for informed decision-making.
Androgen Deprivation Therapy (ADT)
Androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) remains a cornerstone of mCRPC treatment. ADT works by reducing the amount of androgens, hormones that fuel prostate cancer growth. While effective in the early stages of mCRPC, its efficacy diminishes over time as the cancer adapts and becomes resistant to these hormonal manipulations. Maintaining effective ADT strategies, or exploring alternative approaches, is vital as resistance emerges.
Personalized Medicine
Personalized medicine plays an increasingly critical role in mCRPC management. The approach recognizes that individual patients respond differently to treatments based on genetic profiles, tumor characteristics, and other factors. Genetic testing and biomarker analysis can identify patients who may benefit most from specific therapies, potentially optimizing treatment outcomes and minimizing adverse effects.
Targeted Therapies Comparison
| Drug | Mechanism | Efficacy | Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enzalutamide | Blocks the androgen receptor, preventing the activation of pathways driving prostate cancer growth. | Demonstrates improved overall survival and progression-free survival compared to placebo or control arms in clinical trials. | Common side effects include fatigue, hot flashes, muscle pain, and decreased appetite. More serious side effects, though less common, include liver damage and neurological issues. |
| Abiraterone | Inhibits the production of androgens, reducing the fuel for prostate cancer growth. | Studies show improved survival outcomes when combined with ADT compared to ADT alone. | Potential side effects include fatigue, nausea, vomiting, and liver damage. Other possible complications include skin reactions and changes in blood pressure. |
| Darolutamide | Androgen receptor inhibitor, similar to enzalutamide, but potentially with different side effect profiles. | Clinical trials have shown promising efficacy in prolonging survival and delaying disease progression in patients with mCRPC. | Common side effects include fatigue, nausea, vomiting, and muscle pain. Less common, but potentially serious, side effects include liver damage and neurological issues. |
Potential Treatment Strategies
- Combination Therapies: Combining different systemic therapies, such as combining ADT with targeted therapies or chemotherapy, can often enhance treatment efficacy and delay disease progression.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy agents like docetaxel can be used in combination with other therapies or as a single agent in patients whose cancer has become resistant to other treatment options. Efficacy and side effects vary based on the specific chemotherapy agent and patient characteristics.
- Immunotherapy: Research is ongoing into the potential of immunotherapy agents to target immune responses against prostate cancer cells, particularly in the context of mCRPC. Initial studies are promising but more clinical trials are needed.
- Radiation Therapy: In some cases, radiation therapy may be used to target specific sites of bone metastases, reducing pain and preventing further skeletal complications.
- Supportive Care: Managing symptoms, including bone pain, fatigue, and other complications, is crucial to maintaining patient well-being and quality of life. Supportive care should be integrated into the overall treatment plan.
Emerging Therapies and Research
The fight against metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) is a relentless pursuit, demanding innovative approaches. Emerging therapies, including immunotherapies and novel targeted therapies, are offering hope for improved outcomes and enhanced quality of life for patients. Understanding these advancements is crucial for navigating the complexities of mCRPC treatment.Recent research suggests promising avenues for treatment, focusing on exploiting vulnerabilities within the cancer cells and bolstering the body’s immune response.
Clinical trials are actively exploring these new strategies, and early results are often encouraging, though long-term efficacy and safety profiles remain to be fully established.
Navigating treatment options for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) can be daunting. While there’s a lot of research into new therapies, understanding the potential side effects and long-term implications is crucial. Interestingly, some studies are exploring potential links between digestive issues like celiac disease and prostate cancer, which might help us better understand the underlying mechanisms of the disease.
For a deeper dive into celiac disease facts and statistics, check out this resource: celiac disease facts and statistics. Regardless of the connection, the need for targeted and effective treatment for mCRPC remains a critical area of research.
Immunotherapies for mCRPC
Immunotherapy aims to harness the body’s immune system to identify and destroy cancer cells. In mCRPC, this approach seeks to stimulate the immune response against tumor cells that have evaded detection by other treatments. This can be achieved by checkpoint inhibitors, which block proteins that normally suppress immune responses, or by cancer vaccines, which train the immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells.
Novel Targeted Therapies
Beyond immunotherapies, novel targeted therapies are emerging that exploit specific molecular pathways involved in mCRPC growth and progression. These therapies, often developed based on genetic analysis, target specific genetic mutations or proteins that drive the cancer’s growth, offering more precise and potentially less toxic treatment options. This precision medicine approach aims to maximize efficacy while minimizing side effects.
Dealing with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer is tough, but there are treatments available. While researching different options, I stumbled upon information about how similar therapies like those used for asthma, like Symbicort, Dulera, Advair, and Breo, might offer new avenues of treatment. Learning about these inhalers and their use in treating asthma through this resource symbicort dulera advair and breo to treat asthma gave me a fresh perspective on potential approaches to this challenging cancer.
Ultimately, more research is needed to understand how these therapies might apply to metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer.
Clinical Trials and Research
Numerous clinical trials are underway, exploring various combinations of existing and emerging therapies, and investigating the efficacy of novel agents. These trials are essential for advancing our understanding of mCRPC and for developing new treatment strategies. Patients should discuss participation in clinical trials with their oncologists to determine if they are eligible.
Genetic Testing and Personalized Therapy
Genetic testing plays a crucial role in identifying patients who may benefit from specific therapies. Certain genetic alterations, such as mutations in specific genes or proteins, can indicate a patient’s likelihood of responding to particular treatments. This knowledge allows for a more personalized approach, selecting treatments tailored to the individual genetic profile of the cancer.
Emerging mCRPC Treatments: A Comparative Overview
| Treatment Type | Mechanism | Potential Benefits | Potential Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors | Block proteins that suppress immune responses, allowing the immune system to attack cancer cells. | Potentially enhanced immune response against tumor cells, reduced cancer growth. | Potential for severe immune-related side effects, not effective for all patients. |
| Targeted Therapy (e.g., PARP inhibitors) | Specifically target molecular pathways involved in cancer growth, often based on genetic mutations. | Precise targeting of cancer cells, potentially fewer side effects compared to traditional chemotherapy. | Limited efficacy in patients without specific genetic mutations, potential drug resistance. |
| Combination Therapies | Combining various treatments (e.g., chemotherapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy) to enhance efficacy. | Potentially higher response rates, more comprehensive treatment strategy. | Increased risk of side effects due to the combination of multiple treatments, complexity in administration. |
Patient Factors and Considerations: Treatment For Metastatic Castration Resistant Prostate Cancer
Navigating metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) is a deeply personal journey. Beyond the medical treatment, understanding how individual patient factors shape the course of care is crucial. Factors like age, overall health, and pre-existing conditions significantly influence treatment choices and outcomes. This understanding fosters informed decision-making, both for the patient and their healthcare team.Patient factors, including age, general health, and comorbidities, are paramount in determining the most appropriate and effective treatment strategy for mCRPC.
Consider a 70-year-old patient with significant cardiovascular issues versus a 50-year-old with no major health concerns. The older patient might require a more conservative approach, potentially prioritizing quality of life over aggressive treatment options that could negatively impact existing health conditions.
Impact of Age and Overall Health, Treatment for metastatic castration resistant prostate cancer
Age and overall health status directly affect treatment tolerance and potential side effects. Older patients may be more susceptible to adverse reactions to certain medications or therapies. Consequently, treatment plans often prioritize minimizing side effects while maximizing effectiveness. For example, a younger patient might tolerate a more intensive regimen, while an older patient might benefit from a less aggressive, but equally effective, approach.
Careful consideration of the patient’s functional capacity, including daily activities and mobility, is also critical.
Comorbidities and Their Influence
Existing health conditions, or comorbidities, can significantly impact treatment options. Conditions like heart disease, kidney problems, or diabetes require careful consideration during treatment selection. For instance, a patient with chronic kidney disease might be ineligible for certain chemotherapeutic agents that can further strain kidney function. Treatment decisions must carefully weigh the potential benefits of treatment against the risks associated with existing health problems.
Shared Decision-Making
Shared decision-making is paramount in the mCRPC journey. It’s a collaborative process where patients actively participate in choosing their treatment plan. This involves discussing treatment options, potential side effects, and expected outcomes. By actively engaging in this process, patients can make informed decisions aligned with their values and preferences. Healthcare providers must provide comprehensive information in a clear and understandable manner to empower patients to actively participate in their care.
Psychological and Emotional Impact
The diagnosis and treatment of mCRPC have profound psychological and emotional implications for patients and their families. The uncertainty surrounding the disease’s progression, the potential for side effects, and the emotional toll of the illness can significantly impact mental well-being. Support from family, friends, and healthcare professionals is crucial in navigating these emotional challenges.
Available Support Systems
Navigating mCRPC requires a robust support network. Recognizing the emotional and practical challenges can significantly improve outcomes. This includes providing patients and families with access to resources that offer guidance, emotional support, and practical assistance. A multidisciplinary approach involving medical professionals, support groups, and community resources can help patients cope with the disease’s physical and emotional burdens.
Support Resources Table
| Resource Type | Description | Contact Information | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cancer Support Groups | Offer peer-to-peer support and shared experiences. | Local cancer centers, online forums | Emotional support, practical advice, and a sense of community. |
| Support Groups for Families | Provide guidance and resources for family members dealing with the emotional and practical challenges of mCRPC. | Local cancer centers, online forums | Shared experiences, support for caregivers, and stress reduction. |
| Mental Health Professionals | Offer counseling, therapy, and support to address emotional and psychological needs. | Local mental health clinics, online therapy platforms | Improved coping mechanisms, stress management, and emotional well-being. |
| Patient Navigators | Provide guidance and support throughout the healthcare journey. | Cancer centers and hospitals | Coordination of care, assistance with insurance and financial concerns, and access to resources. |
Quality of Life and Palliative Care
Living with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) can significantly impact a patient’s quality of life. The disease’s progression, coupled with the side effects of treatments, can lead to physical discomfort, emotional distress, and a profound shift in daily routines. Understanding and addressing these challenges is crucial for ensuring patients’ well-being throughout their journey.Palliative care plays a vital role in managing the symptoms and improving the quality of life of patients with mCRPC.
It focuses on providing relief from the physical, emotional, and spiritual burdens of the disease, and it’s crucial to understand that palliative care is not a sign of giving up hope, but rather a way to enhance the overall experience.
Impact on Quality of Life
mCRPC can affect various aspects of a patient’s quality of life, including physical function, emotional well-being, and social interactions. Bone pain, fatigue, and other physical symptoms can significantly reduce mobility and independence. The emotional toll of a life-threatening illness, coupled with uncertainty about the future, can lead to anxiety, depression, and isolation. The burden on family members and caregivers is also considerable.
The impact on daily activities, such as work, hobbies, and social engagements, is substantial, impacting the individual’s sense of self-worth and fulfillment.
Importance of Palliative Care
Palliative care provides comprehensive support to mCRPC patients, addressing their physical, emotional, and spiritual needs. It aims to improve the quality of life for patients and their families by managing symptoms, providing emotional support, and coordinating care with other healthcare providers. Early integration of palliative care can help patients maintain a good quality of life even as the disease progresses.
By addressing physical discomfort, emotional distress, and practical issues, palliative care helps patients feel more empowered and in control of their experience.
Managing Pain and Symptoms
Effective pain management is crucial for mCRPC patients. A multi-faceted approach, incorporating medication, non-pharmacological techniques, and psychological support, is often needed. This includes:
- Pharmacological interventions: Opioids, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and other pain medications can effectively manage pain. Regular monitoring and adjustment of medication dosages are essential to optimize pain relief while minimizing side effects. The healthcare team will carefully balance the need for pain relief with the potential for side effects.
- Non-pharmacological strategies: Techniques like physical therapy, relaxation exercises, and massage can complement medication to manage pain and improve function. These approaches can also address other symptoms like fatigue and sleep disturbances.
- Symptom management: Beyond pain, mCRPC can cause a range of symptoms, including nausea, vomiting, constipation, and swelling. A holistic approach that addresses these symptoms through medication, dietary adjustments, and lifestyle modifications is crucial.
Role of Hospice Care
Hospice care provides specialized support for individuals in the later stages of mCRPC, focusing on comfort and quality of life. It offers a range of services, including pain and symptom management, emotional support, and spiritual counseling. Hospice care recognizes that the focus shifts from curing the disease to providing comfort and dignity during the final stages of life.
The goal is to ensure patients experience a peaceful and dignified end-of-life experience.
Emotional Support
“Providing emotional support is just as important as managing physical symptoms. Acknowledging the emotional distress and fear associated with a life-limiting illness is vital to help patients cope with the emotional burden of mCRPC.”
The emotional toll of mCRPC can be profound. Patients and families may experience grief, anxiety, fear, and a sense of loss. Emotional support from healthcare professionals, support groups, and family members is essential to help patients and their loved ones navigate these challenges. This support can help patients maintain a sense of hope, dignity, and well-being. Creating a supportive environment where patients feel heard, understood, and valued is paramount.
Future Directions
The journey to conquering metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) is fraught with challenges, but also brimming with potential. Ongoing research promises exciting advancements in treatment strategies, offering hope for improved outcomes and a better quality of life for patients. We’ll delve into potential future directions, highlighting key challenges and opportunities, and the crucial role of preventative measures in reducing the disease’s incidence.
Potential Future Directions in mCRPC Research and Treatment
The landscape of mCRPC treatment is constantly evolving, with researchers exploring novel therapeutic approaches beyond current standards of care. These include targeted therapies that specifically attack cancer cells, immunotherapies to bolster the body’s own defenses, and innovative combination therapies. Scientists are also examining the use of precision medicine, tailoring treatment plans based on a patient’s unique genetic profile and tumor characteristics.
This personalized approach promises more effective treatments and fewer side effects.
Key Challenges and Opportunities in mCRPC Treatment
One significant hurdle is the inherent heterogeneity of mCRPC. Different patients respond differently to treatment, and tumors exhibit varying genetic and molecular characteristics. Understanding and addressing this heterogeneity is crucial for developing more effective and personalized therapies. Another challenge lies in overcoming drug resistance, a common phenomenon in cancer treatment. Researchers are exploring strategies to circumvent this resistance, potentially by combining therapies or targeting different pathways within the cancer cells.
The opportunities lie in developing more effective therapies, improving patient outcomes, and reducing the side effects associated with current treatments.
Role of Prevention Strategies in Reducing the Incidence of mCRPC
While curative treatment for mCRPC remains elusive, preventive strategies could play a significant role in reducing the disease’s incidence. These strategies may include early detection and intervention, focusing on lifestyle modifications, and possibly targeting specific genetic risk factors. For example, lifestyle interventions like maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, and following a balanced diet have been linked to a reduced risk of various cancers, including prostate cancer.
However, more research is needed to definitively identify and implement effective preventative measures.
Areas Where More Research Is Needed
Further research is critical to address the gaps in our understanding of mCRPC. This includes investigating the complex molecular mechanisms driving mCRPC development and progression, exploring the potential of new therapeutic targets, and refining methods for early detection and risk stratification. A deeper understanding of the specific genetic and epigenetic alterations that contribute to mCRPC resistance is crucial for developing more effective treatments.
The long-term effects of various treatment strategies also warrant further investigation.
Summary Table of Predictions for Future mCRPC Treatments
| Prediction | Rationale | Supporting Evidence | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Targeted therapies, personalized to each patient’s genetic profile, will become the standard of care. | Personalized approaches tailor treatment to specific molecular characteristics, maximizing efficacy and minimizing side effects. | Ongoing clinical trials demonstrate promising results in targeted therapy applications for mCRPC. | Improved patient outcomes, reduced treatment-related toxicity, and enhanced quality of life. |
| Immunotherapies will play a more significant role in mCRPC treatment, potentially boosting the body’s immune response against cancer cells. | The immune system can be harnessed to fight cancer, and clinical trials show encouraging signs of success. | Preclinical studies and early clinical trials suggest potential for immunotherapeutic agents to target mCRPC. | Increased response rates, prolonged survival, and reduced reliance on conventional cytotoxic therapies. |
| Combination therapies, combining multiple agents with different mechanisms of action, will emerge as a potent strategy to overcome drug resistance. | Combating multiple pathways involved in mCRPC progression may overcome resistance and enhance treatment effectiveness. | Synergistic effects of combined therapies have been observed in other cancers and are being investigated in mCRPC trials. | Improved treatment response, increased remission rates, and enhanced survival. |
| Prevention strategies, including lifestyle modifications and early detection programs, will become increasingly important in reducing the incidence of mCRPC. | Proactive measures can significantly reduce the risk of developing mCRPC, preventing its onset altogether. | Observational studies demonstrate a correlation between lifestyle factors and prostate cancer risk. | Reduction in the overall burden of mCRPC, potentially reducing healthcare costs and improving public health. |
Conclusion
In conclusion, treatment for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer presents a multifaceted challenge requiring a personalized approach. From understanding the disease’s progression and current treatment strategies to exploring emerging therapies and the crucial role of patient factors and support systems, this guide provides a comprehensive overview. Ultimately, a collaborative effort between patients, healthcare providers, and support networks is vital in optimizing treatment outcomes and improving the quality of life for those affected by this disease.
The future of treatment hinges on continued research and the development of innovative therapies. This discussion emphasizes the importance of compassion, empathy, and a proactive approach to patient care.