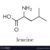
Yeast infection before period can be a frustrating experience, disrupting your routine and causing discomfort. Understanding the link between hormonal fluctuations and yeast infections, as well as recognizing the symptoms, is key to managing this issue effectively. This comprehensive guide explores the various aspects of yeast infections occurring before your period, including potential causes, effective treatments, and preventive measures.
This article will delve into the specifics of yeast infections appearing just before your period. We’ll examine the possible causes, the symptoms to look out for, and the best strategies to manage the discomfort. It’s important to remember that this is not a comprehensive medical guide; always consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
Introduction to Yeast Infections Before Periods

Yeast infections, also known as candidiasis, are common vaginal infections caused by an overgrowth of yeast, most oftenCandida albicans*. These infections can manifest with a range of symptoms, impacting a woman’s comfort and daily life. Understanding the link between hormonal fluctuations and yeast infections can be helpful in managing these occurrences.The symptoms of yeast infections typically include itching, burning, and a thick, white discharge that resembles cottage cheese.
Some women may experience pain during urination or sexual intercourse. The timing of yeast infections can vary, but they are frequently observed in the days leading up to or during menstruation.
Timeframe of Yeast Infections and Menstrual Cycles
Yeast infections can occur at any time during a woman’s menstrual cycle. However, there is a noticeable correlation between the increase in yeast infections and the pre-menstrual phase. Hormonal changes associated with the menstrual cycle can influence the vaginal environment, potentially creating an environment conducive to yeast overgrowth.
Possible Links Between Hormonal Fluctuations and Yeast Infections
Hormonal fluctuations throughout the menstrual cycle significantly impact the vaginal pH balance. As estrogen levels decrease in the luteal phase (the second half of the menstrual cycle), the vaginal pH rises. This shift can create an environment where yeast thrives. Furthermore, fluctuations in progesterone levels during the menstrual cycle can also affect the vaginal ecosystem, potentially influencing the susceptibility to yeast infections.
Factors That Increase the Risk of Yeast Infections
Several factors can contribute to the development of yeast infections. These include:
- Weakened immune system:
- Antibiotics:
- Tight clothing:
- Unhygienic practices:
Conditions like diabetes, stress, or taking certain medications can suppress the immune system, making a woman more vulnerable to yeast infections.
Antibiotics can disrupt the normal vaginal flora, allowing yeast to overgrow. This is a common side effect and should be considered when using antibiotics.
Wearing tight clothing in the genital area can trap heat and moisture, fostering a humid environment favorable to yeast growth. This can increase the risk of yeast infections, especially in hot and humid climates.
Poor hygiene practices, such as not cleaning the genital area properly or using scented feminine products, can increase the risk of yeast infections.
Comparison of Yeast Infections Before Periods with Other Vaginal Infections
| Characteristic | Yeast Infection (Before Period) | Bacterial Vaginosis | Trichomoniasis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Discharge | Thick, white, clumpy (cottage cheese-like) | Thin, grayish-white, or yellowish; often with a fishy odor | Thin, greenish-yellow or gray; often with a strong odor |
| Itching/Burning | Common, often intense | Less common or mild | Common, often intense |
| Pain | May occur during urination or intercourse | May occur during urination or intercourse | May occur during urination or intercourse |
| Odor | Typically odorless, or slightly yeasty | Fishy odor | Strong odor |
| Treatment | Over-the-counter antifungal medications or prescription drugs | Prescription antibiotics | Prescription antibiotics |
Symptoms and Diagnosis: Yeast Infection Before Period
Understanding the symptoms of a yeast infection, especially before your period, is crucial for timely treatment. Often, these symptoms can mimic pre-menstrual syndrome (PMS) symptoms, making accurate diagnosis challenging. This section will help you differentiate between the two and identify potential signs of a yeast infection.
Key Symptoms of Yeast Infections Before Periods
Yeast infections, like other vaginal infections, can manifest with noticeable symptoms. These symptoms, while sometimes subtle, can be more prominent before menstruation. Identifying these signs is key to seeking prompt medical attention.
- Vaginal itching and burning: This is a common and often intensely uncomfortable symptom. Itching may worsen before your period as hormonal changes can increase vaginal secretions, potentially creating a breeding ground for yeast.
- Thick, white, clumpy discharge: This discharge, often described as cottage cheese-like, is a telltale sign of a yeast infection. The consistency and appearance of the discharge can vary, and it’s essential to pay attention to any unusual changes.
- Redness and swelling of the vulva: Inflammation of the vulva, the external genital area, is another common symptom. This may be accompanied by soreness and tenderness, particularly when touching the area.
- Pain during urination: Discomfort or pain when urinating (dysuria) can occur with a yeast infection. This is often due to irritation and inflammation in the vaginal area.
Symptoms That Can Mimic Pre-Menstrual Symptoms
Many pre-menstrual symptoms overlap with the symptoms of a yeast infection. This overlap can make distinguishing between the two challenging. Recognizing these shared symptoms is crucial for accurate self-assessment.
Ugh, yeast infections before your period are the worst! It’s like your body is playing a cruel joke. Understanding how hyperkalemia is diagnosed, a condition related to electrolyte imbalance, might offer some insights into the root causes of these frustrating infections. Often, hyperkalemia is diagnosed through blood tests, which measure the potassium levels in your blood. The good news is that yeast infections before your period are usually easily treated with over-the-counter medication.
Hopefully, this helps you feel better, quicker! how hyperkalemia is diagnosed can offer a deeper look into the process.
- Bloating and abdominal cramps: These are common PMS symptoms, but they can also be associated with vaginal infections. The severity and duration of these symptoms may differ between PMS and yeast infections.
- Mood swings and irritability: Hormonal fluctuations before menstruation can significantly impact mood, causing irritability, anxiety, or depression. Similarly, discomfort from a yeast infection can also contribute to emotional distress.
- Fatigue and low energy: These are frequently reported pre-menstrual symptoms and may also accompany a yeast infection due to the discomfort and inflammation it causes.
- Backache and breast tenderness: These are common pre-menstrual symptoms that might also accompany a yeast infection due to the body’s response to inflammation.
Distinguishing Yeast Infections from Pre-Menstrual Symptoms
Differentiating between pre-menstrual symptoms and yeast infections requires careful observation and consideration of additional factors.
- Symptom location: PMS symptoms often affect the entire body, while yeast infections are typically localized to the vaginal area and surrounding tissues. Pay attention to the specific areas where you feel discomfort.
- Symptom intensity: The severity of symptoms varies between PMS and yeast infections. While both can cause discomfort, a yeast infection may manifest with more intense localized itching, burning, and discharge.
- Symptom duration: PMS symptoms typically begin a few days before your period and usually subside within a day or two after menstruation begins. Yeast infections, if left untreated, can persist longer, potentially worsening if not managed properly.
Diagnosis Methods
Accurate diagnosis of a yeast infection involves a combination of self-assessment and professional evaluation.
- Self-assessment: Carefully monitoring your symptoms, noting their location, intensity, and duration, can provide valuable information for your healthcare provider. Tracking your menstrual cycle can also help.
- Physical examination: A healthcare professional can visually inspect the vaginal area and assess the discharge. They may also take a sample for laboratory analysis to confirm the diagnosis.
- Laboratory tests: A sample of vaginal discharge can be tested to identify the presence of yeast or other microorganisms. This is crucial for confirming the diagnosis and determining the most effective treatment approach.
Potential Causes
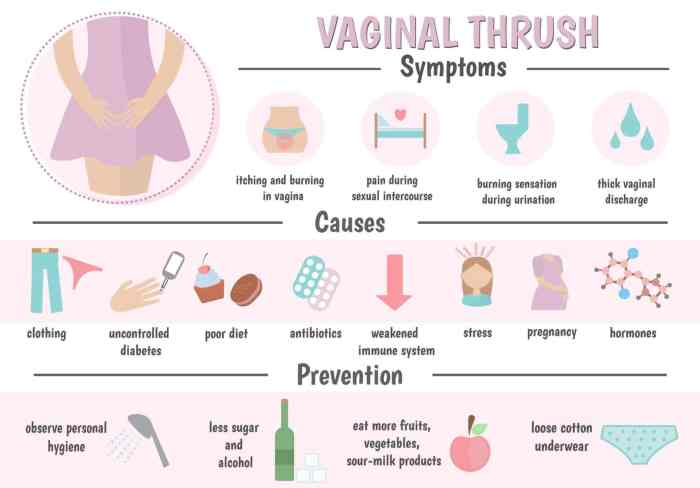
Yeast infections before your period can be frustrating and uncomfortable. Understanding the possible reasons behind them can help you take proactive steps to prevent future occurrences. Several factors contribute to the delicate balance of your vaginal environment, and changes in this balance can lead to yeast overgrowth.Hormonal fluctuations during the menstrual cycle play a significant role in the development of yeast infections.
The shifts in estrogen and progesterone levels can alter the pH of the vagina, making it more conducive to the growth of yeast. This is why yeast infections are sometimes more prevalent around the time of menstruation. Additionally, stress impacts the body’s immune response, potentially weakening your defenses against yeast overgrowth.
Hormonal Fluctuations
The fluctuating levels of hormones, estrogen, and progesterone during the menstrual cycle directly influence the vaginal environment. Estrogen tends to thicken the vaginal lining and increase glycogen production. Glycogen is a type of sugar that yeast feed on. When estrogen levels decrease, the vaginal pH shifts, potentially creating an environment more favorable for yeast to proliferate. Similarly, changes in progesterone levels can affect the vaginal flora, disrupting the balance between beneficial bacteria and yeast.
Stress and Immune Response
Stress significantly impacts the body’s immune system. When you’re stressed, your body releases stress hormones like cortisol, which can suppress the immune response. A weakened immune system makes you more susceptible to infections, including yeast infections. Chronic stress can weaken your immune system over time, increasing the risk of recurring yeast infections.
Hygiene Practices
Maintaining proper hygiene plays a crucial role in preventing yeast infections. Excessive use of harsh soaps or douches can disrupt the natural balance of vaginal flora, making you more prone to yeast overgrowth. Douching, in particular, can significantly alter the pH and introduce harmful chemicals, further disturbing the delicate equilibrium. It’s important to maintain a clean but gentle hygiene routine.
Impact of Diet
A balanced diet can significantly influence your overall health, including your vaginal health. A diet high in refined sugars can contribute to yeast overgrowth. Sugar provides a readily available food source for yeast, allowing them to multiply rapidly. Incorporating a balanced diet that includes fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can support a healthy vaginal environment.
Table of Potential Causes
| Potential Cause | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Hormonal Fluctuations | Changes in estrogen and progesterone levels during the menstrual cycle can alter vaginal pH, creating a more favorable environment for yeast overgrowth. |
| Stress | Stress hormones can suppress the immune system, making you more vulnerable to infections, including yeast infections. |
| Hygiene Practices | Excessive use of harsh soaps or douches can disrupt the natural balance of vaginal flora, increasing the risk of yeast overgrowth. |
| Diet | A diet high in refined sugars provides a readily available food source for yeast, promoting their rapid multiplication. |
Treatment and Prevention
Dealing with a yeast infection before your period can be frustrating, but effective treatment and proactive prevention strategies can significantly reduce discomfort and recurrence. Understanding the various treatment options and preventive measures empowers you to take control of your health and well-being.Yeast infections are often treatable with over-the-counter medications, but consulting a healthcare professional is crucial for accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plans, especially if symptoms persist or worsen.
Common Treatments for Yeast Infections
Over-the-counter antifungal medications, often in the form of creams or suppositories, are commonly used to treat yeast infections. These medications work by targeting the growth of the yeast Candida albicans, the primary culprit behind most vaginal yeast infections. The active ingredients, such as clotrimazole, miconazole, or butoconazole, disrupt the yeast’s cellular processes, effectively reducing the infection. It’s essential to follow the prescribed dosage and duration of treatment to ensure the infection is fully eradicated.
Consistency is key for successful treatment.
Ugh, yeast infections before your period are the worst! They’re super common, and the itching and discomfort can be seriously disruptive. Luckily, there are natural remedies like tea tree oil for yeast infection that might help. Tea tree oil for yeast infection can be a potential option, but it’s crucial to use it correctly and be mindful of any potential side effects.
Still, knowing about natural remedies like this can be really helpful in managing yeast infections before your period.
Preventive Measures to Reduce the Risk of Yeast Infections Before Periods
Maintaining good hygiene practices and understanding potential triggers can significantly reduce the risk of yeast infections before your period.
- Maintaining good hygiene: Regular, gentle cleansing of the genital area with mild soap and water is crucial. Avoid harsh soaps, douching, and scented products, as these can disrupt the natural vaginal pH balance, increasing the risk of infection. Using a cotton underwear is recommended, as they allow for better air circulation and reduce moisture build-up in the genital area.
- Avoiding tight-fitting clothing: Tight clothing can trap heat and moisture, creating an ideal environment for yeast overgrowth. Opt for breathable fabrics and loose-fitting garments to promote better airflow.
- Maintaining a healthy diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and probiotics can help support a healthy vaginal microbiome, which helps prevent yeast infections.
- Managing stress: Stress can weaken the immune system, potentially increasing the susceptibility to yeast infections. Stress-reducing techniques like yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature can be helpful.
- Avoiding excessive use of antibiotics: Antibiotics can disrupt the natural vaginal flora, increasing the risk of yeast infections. Only take antibiotics when prescribed by a healthcare professional and follow the prescribed dosage diligently.
Effectiveness of Different Treatment Methods
The effectiveness of various treatment methods for yeast infections can vary. Over-the-counter antifungal medications are generally effective for mild to moderate cases when used as directed. However, if symptoms persist or worsen, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and potentially a stronger course of treatment.
Importance of Maintaining Good Hygiene Practices
Maintaining proper hygiene practices is fundamental to preventing yeast infections. Gentle cleansing with mild soap and water, avoiding harsh chemicals, and ensuring proper ventilation are crucial in maintaining a healthy vaginal environment. These practices help maintain the natural balance of vaginal flora, reducing the risk of yeast overgrowth.
Comparison of Treatment Options
| Treatment Option | Active Ingredient | Dosage Form | Effectiveness | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clotrimazole | Clotrimazole | Cream, Suppository | Generally effective for mild to moderate cases | Possible local irritation |
| Miconazole | Miconazole | Cream, Suppository | Generally effective for mild to moderate cases | Possible local irritation |
| Butoconazole | Butoconazole | Cream | Generally effective for mild to moderate cases | Possible local irritation |
| Fluconazole (oral) | Fluconazole | Tablet | Highly effective for a wider range of cases, often a single dose | Possible headache, nausea, or abdominal pain |
When to Seek Medical Attention
While yeast infections are often manageable at home, there are situations where medical attention is crucial. Ignoring certain symptoms or persistent issues can lead to complications or mask more serious underlying conditions. Understanding when to seek professional help is key to ensuring your health and well-being.
Ugh, yeast infections before your period are the worst! It’s like your body is playing a weird game of hide-and-seek right before your monthly visitor arrives. But, have you ever considered how high cholesterol might be affecting your body in other ways? For example, did you know high cholesterol can sometimes manifest in unusual ways, like affecting your eyes?
Learn more about the potential signs and symptoms of high cholesterol impacting your vision at high cholesterol and the eyes signs and symptoms. Regardless of the cause, though, dealing with that pesky yeast infection is a top priority! So, let’s just get this over with and get back to feeling normal.
Situations Requiring Medical Evaluation
Yeast infections, though common, can sometimes indicate a more complex health issue. Failure to address certain symptoms can lead to worsening conditions or complications. This section details situations demanding prompt medical attention.
Symptoms Warranting Immediate Medical Evaluation
Certain symptoms, regardless of the presence of a yeast infection, necessitate immediate medical evaluation. These symptoms could be indicative of other conditions, or may signal a more severe infection. It’s essential to seek prompt medical care if you experience any of the following:
- Severe pain or burning that significantly interferes with daily activities.
- Signs of a systemic infection, such as fever, chills, or body aches.
- Presence of unusual discharge, such as green, yellow, or gray discharge, or a foul odor.
- Pain during urination, or difficulty urinating.
- Pain in the lower abdomen or pelvic area that is persistent or severe.
- Swelling or redness in the genital area that is extensive or spreading.
- Bleeding or spotting not associated with menstruation.
- Visible sores or blisters in the genital area.
- Symptoms that don’t improve or worsen despite using over-the-counter treatments for several days.
Persistent or Worsening Symptoms, Yeast infection before period
If your yeast infection symptoms persist or worsen despite treatment, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional. This could indicate an underlying issue or a less responsive infection. Ignoring these persistent symptoms can lead to complications or mask a more serious underlying problem.
- Symptoms that do not improve after a week of treatment with over-the-counter medication.
- Recurring yeast infections within a short period, even after treatment.
- Symptoms that return soon after completing treatment.
- Symptoms that significantly impact your quality of life.
Importance of Professional Diagnosis and Treatment
A healthcare professional can accurately diagnose the cause of your symptoms and provide appropriate treatment. A proper diagnosis is crucial for effective management and prevention of potential complications. Self-treating persistent or worsening symptoms can be harmful. A healthcare provider can differentiate between a yeast infection and other conditions with similar symptoms.
- A medical professional can perform a physical examination and potentially conduct additional tests to determine the exact cause of the infection.
- They can prescribe appropriate medication tailored to your specific needs, considering any underlying health conditions.
- They can provide guidance on preventive measures and lifestyle changes that can help prevent future infections.
- They can rule out other potential causes for similar symptoms.
Table: Situations Requiring Immediate Medical Consultation
This table summarizes situations requiring immediate medical consultation for yeast infections.
| Situation | Description |
|---|---|
| Severe Pain or Burning | Pain significantly impacting daily life. |
| Systemic Infection Signs | Fever, chills, body aches. |
| Unusual Discharge | Green, yellow, gray discharge, foul odor. |
| Urination Problems | Pain during urination, difficulty urinating. |
| Pelvic/Abdominal Pain | Persistent or severe pain in the lower abdomen or pelvic area. |
| Extensive Swelling/Redness | Extensive swelling or redness in the genital area. |
| Abnormal Bleeding/Spotting | Bleeding or spotting not related to menstruation. |
| Visible Sores/Blisters | Visible sores or blisters in the genital area. |
| Treatment Failure | Symptoms persist or worsen despite treatment. |
Impact on Daily Life
Dealing with a yeast infection before your period can significantly impact your daily life, affecting both your physical comfort and emotional well-being. The itching, burning, and discomfort can disrupt your routine and cause stress. Understanding how these infections can affect your day-to-day life and how to manage them is crucial for maintaining a sense of normalcy.Yeast infections, particularly when occurring pre-menstruation, can manifest with symptoms that range from mild to severe.
This can lead to various challenges in navigating everyday activities, and the emotional distress can be substantial. Knowing how to manage discomfort and maintain a healthy lifestyle during an infection is essential for maintaining a sense of normalcy and well-being.
Impact on Physical Activities
The physical symptoms of a yeast infection, such as itching and burning, can make it difficult to engage in certain activities. Simple tasks like wearing tight clothing or participating in physical activities can exacerbate discomfort. For example, strenuous exercise might increase irritation and worsen symptoms. This can limit participation in sports, workouts, or other activities that require physical exertion.
Wearing loose-fitting clothing and avoiding tight-fitting undergarments can be beneficial during an infection.
Emotional and Psychological Impact
Yeast infections, especially those occurring before menstruation, can have a significant emotional and psychological impact. The discomfort and embarrassment associated with the symptoms can lead to feelings of anxiety, frustration, and even self-consciousness. This can affect self-esteem and overall well-being. For some, the emotional impact can be significant, affecting their confidence and social interactions.
Strategies for Managing Discomfort
Effective management of yeast infection symptoms is crucial for minimizing disruption to daily life. Over-the-counter remedies and prescribed medications can help alleviate itching and burning. Keeping the affected area clean and dry can also help. Maintaining good hygiene, such as using gentle cleansers and avoiding harsh soaps or scented products, is vital. Applying cool compresses to the affected area can provide relief from discomfort.
Maintaining Normalcy During an Infection
Maintaining a sense of normalcy during a yeast infection is important for mental well-being. Prioritizing self-care activities, such as getting enough rest and eating a healthy diet, can help manage symptoms and maintain a positive outlook. Avoiding stressful situations and engaging in relaxing activities, like taking a warm bath or listening to music, can help alleviate stress and discomfort.
Remembering that the infection is temporary and manageable is crucial for maintaining a sense of normalcy.
Coping Mechanisms
Coping mechanisms for managing a yeast infection can vary from person to person. Some individuals find comfort in relaxation techniques like meditation or deep breathing exercises. Others might find support in talking to friends, family, or a healthcare professional. Keeping a journal or using a relaxation app can help track symptoms and manage stress. For example, some people find that maintaining a regular sleep schedule and incorporating stress-reducing activities into their daily routine can significantly ease the emotional toll of the infection.
It is important to find coping mechanisms that work best for individual needs.
Final Conclusion
In conclusion, yeast infections before your period can be a real pain, but understanding the potential causes and symptoms can empower you to take control of the situation. By maintaining good hygiene, recognizing potential triggers, and knowing when to seek medical help, you can effectively manage this issue and maintain a comfortable routine. Remember, knowledge is power, and this guide provides a foundation for informed decision-making regarding your health.